Hematology – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Hemoglobin
answer
This molecule transports oxygen from the capillary beds of the lungs to the body tissues
question
Oxygen saturation
answer
The ratio of oxygen bound to hemoglobin Measured with a pulse oximeter
question
2,3 DPG
answer
This enzyme stimulates oxygen release from hemoglobin when blood pH is low (hypoxic/acidotic).
question
Carboxyhemaglobin
answer
Hemoglobin disorder in which hgb has a higher affinity for carbon monoxide than for oxygen. The Oxygen-Hemoglobin curve shifts left, patient is hypoxemic, and blood appears bright red.
question
Methemoglobin
answer
Hemoglobin disorder in which the iron molecule of hgb is oxidized into Fe+3, causing a left shift in the Oxygen-Hemoglobin curve. Blood becomes brown colored.
question
Erythropoiesis
answer
The production and formation of red blood cells
question
Reticulocyte
answer
The stage of red blood cell development just prior to maturation
question
Metarubricyte
answer
A red blood cell more immature than a reticulocyte
question
Rubriblast
answer
The most immature stage of red blood cell development
question
Leukocytosis
answer
Medical term for an increase in white blood cells
question
Leukopenia
answer
Medical term for a decreased number of white blood cells
question
Neutrophil
answer
Granulocyte that functions in phagocytosis, secretion of mediators of inflammation, antibacterial properties, and microbiocidal action
question
Eosinophil
answer
Granulocyte that functions in phagocytosis, parasiticidal action, and allergy reactions
question
Basophil
answer
Granulocyte that functions in inflammation and parasiticidal action, and release histamines
question
Circulating pool
answer
Consists of freely moving neutrophils, this is the pool sampled from when blood is drawn
question
Marginal pool
answer
Consists of neutrophils that are "stuck" to the walls of small vessels Neutrophils from this pool will be sampled more often in a stressed animal
question
Heterophil
answer
Neutrophils in other species that are elongated and have red staining granules
question
Band neutrophil
answer
Immature neutrophil that is slightly darker staining and with a horseshoe shaped, symmetrical nucleus with rounded ends
question
Left shift
answer
An increase in band neutrophils in the peripheral blood, resulting from an increased demand for neutrophils due to infection.
question
Barr body
answer
Represents a remnant of the X chromosome and indicates the animal is female Small protrusion on the nucleus of a neutrophil
question
Lymphocyte
answer
An agranulocytic leukocyte that normally makes up a quarter of the white blood cell count but increases in the presence of infection Only leukocyte that recirculates
question
B cell
answer
A type of lymphocyte that produces antibodies
question
T cell
answer
A type of lymphocyte that produces lymphokines, the mediates of cellular immunity
question
Lymphoblast
answer
An immature lymphocyte that should never be seen in the circulating blood -- usually indicates cancer is present in the patient.
question
Monocyte
answer
An agranulocytic leukocyte that performs phagocytosis to fight infection The largest leukocyte, has a very irregular nucleus and sometimes contains vacuoles
question
Macrophage
answer
Monocyte that migrates from the blood to tissue spaces
question
Macrocytosis
answer
Increased number of larger than normal cells, indicative of immature cells present in the blood likely resulting from regenerative anemia.
question
Microcytosis
answer
Increased numbers of smaller than normal red blood cells, indicative of the presence of spherocytes May occur in IMHA
question
Normocytic
answer
Refers to normal sized (mature) erythrocytes Term used to describe a normal MCV value (66-77 fL)
question
Anisocytosis
answer
A general presence of variation in cell size
question
Normochromic
answer
Term used to describe a normal MCHC value Cells stain pink with an area of central pallor
question
Polychromasia
answer
Medical term used to describe cells with a bluish tint because of remaining organelles in the cytoplasm
question
Hypochromasia
answer
Lack or decrease in staining intensity because of a decrease in cellular hemoglobin Term for a low MCHC value
question
Poikilocytosis
answer
A general presence of variation in cell shape Common in pigs
question
Acanthocytes
answer
Cells with irregularly shaped margins/projections from the cell wall Commonly seen with liver disease, hemangiosarcoma, poor technique
question
Schistocytes
answer
Fragmented red blood cells Clots in the vessels result in RBCs getting damaged and fragmented as they pass through Seen with DIC, vascular neoplasia, and bad heartworm disease
question
Echinocytes
answer
Also called burr cells, these red blood cells have regular spine-like projections from all surfaces of the cell, appear fuzzy Commonly seen in renal disease and lymphosarcoma
question
Crenation
answer
Term used to describe misshapen red blood cells, often due to poor technique
question
Target cell
answer
Also called a Mexican Hat cell, the membrane folds over and becomes distorted Commonly seen in liver disease
question
Spherocytes
answer
Small, dense, and dark staining cells that lack central pallor Suggestive of IMHA, toxins, and infectious disorders May be seen in mismatched blood transfusions Hallmark sign of hemolysis in a dog
question
Rouleaux
answer
A clump of red blood cells that appear to be stacked like a roll of coins Is a normal finding in horses and cats Should not be seen in dogs
question
Agglutination
answer
Clumped RBCs, typically seen with immune diseases such as IMHA and may be seen in mismatched blood transfusions
question
Basophilic stippling
answer
A type of RBC inclusion in which small, blue staining granules are visualized, giving the cell a speckled egg appearance Granules are residual RNA Indicative of lead toxicity in dogs
question
Equine
answer
This species does not release reticulocytes in response to anemias
question
CBC
answer
This diagnostic blood test includes red and white blood cell counts, platelet counts, PCV, differential blood smear, and hemoglobin measurement
question
Buffy coat
answer
This portion of the PCV is composed of white blood cells and platelets
question
PCV
answer
Also called the hematocrit, this measurement is the percentage of erythrocytes compared to the total sample volume in the tube
question
MCV
answer
Erythrocyte index that describes the average RBC size, measured in fentoliters
question
MCHC
answer
Erythrocyte index that indicates the average concentration of hemoglobin in the RBC, measured in grams per deciliter
question
MCH
answer
Erythrocyte index that indicates the amount of hemoglobin per average RBC by weight, measured in picograms
question
Megakaryocyte
answer
Large, giant cell with a big nucleus, is the precursor to platelets
question
Hemostasis
answer
Medical term for the function of platelets
question
Thrombocytopenia
answer
Medical term for a deficiency of platelets
question
Thrombocytosis
answer
Medical term for an abundance of platelets
question
Neutrophilia
answer
Medical term for an abundance of neutrophils
question
Neutropenia
answer
Medial term for a deficiency of neutrophils
question
Eosinophilia
answer
Medical term for an abundance of eosinophils
question
Eosinopenia
answer
Medical term for a deficiency of eosinophils
question
Lymphocytosis
answer
Medical term for an abundance of lymphocytes
question
Lymphocytopenia
answer
Medical term for a deficiency of lymphocytes
question
Monocytosis
answer
Medical term for an abundance of monocytes
question
Monocytopenia
answer
Medical term for a deficiency of monocytes
question
Regenerative left shift
answer
Total white blood cell count is elevated due to neutrophilia and the number of band neutrophils is equal to or less than the number of mature neutrophils Indicates proper bone marrow response
question
Degenerative left shift
answer
Total white blood cell count may be normal or low, and the number of band neutrophils exceeds the number of mature neutrophils Indicates bone marrow cannot meet the demand for production and is usually a poor prognosis
question
Stress leukogram
answer
An unusual leukogram that shows... Moderate leukocytosis Mature neutrophilia Lymphopenia and eosinopenia No left shift
question
Exercise response
answer
An unusual leukogram that shows... Leukocytosis Mild neutrophilia with no left shift Lymphocytosis
question
Reactive lymphocyte
answer
Lymphocytes that have been stimulated to produce antibodies or lymphokines Appear to have increased cytoplasm, increased basophilia
question
Hypersegmentation
answer
A type of neutrophil toxicity in which the nucleus has 5 or more lobes May be due to normal aging changes, Cushing's disease, or chronic inflammation Indicates neutrophils are working too hard for too long
question
Pelger-Huet Anomaly
answer
WBC disorder in which neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils are not segmented properly, but function normally Mimics a left shift
question
Chediak-Higashi syndrome
answer
WBC disorder in which granules are abnormally large in granulocytes Cells do not function properly, leading to an increased susceptibility to infection
question
Inflammatory leukogram
answer
An unusual leukogram that shows... Leukocytosis Neutrophilia Lymphocytopenia Degenerative left shift
question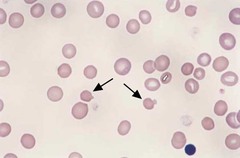
Heinz body

answer
Name this RBC inclusion
question
Howell-Jolly body
answer
Name this RBC inclusion
question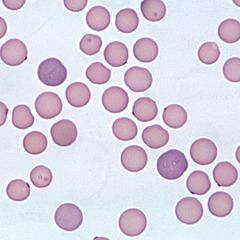
Mycoplasma felis

answer
Name this blood parasite
question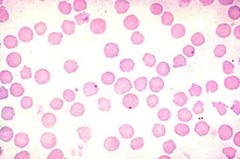
Anaplasma marginale

answer
Name this blood parasite
question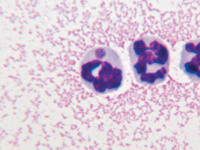
Anaplasma phagocytophilium

answer
Name this blood parasite
question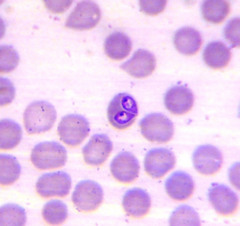
Babesia

answer
Name this blood parasite
question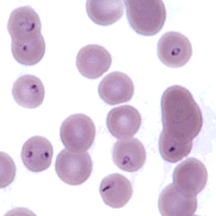
Cytauxzoon felis

answer
Name this blood parasite
question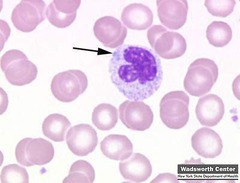
Dohle body

answer
The abnormality on this cell is an indication of a toxic neutrophil (Small blue dot on upper left quadrant of cell)



