spinal and epidural anesthesia – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
there are no absolute indications for spinal or epidural anesthesia. There are clinical situations where patient preference, physiology, or the surgical procedure makes a block the technique of choice. things epdiural anesthesia have been shown to do are?
answer
1. blunt the "stress response" to surgery 2. decrease intraoperative blood loss. 3. lower the incidence of postoperative thromboemolic events. 4. possibly decrease morbidity in high-risk patients. avoid airway manipulation. 5. serve as a useful method to extend analgesia into the postoperative period.
question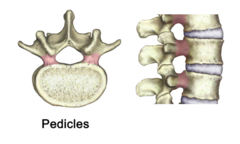
Pedicles, where is it

answer
there are 2 pedicles project posteriorly
question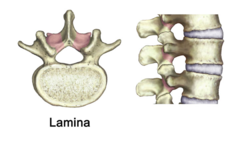
Lamina, what does it bridge

answer
2 lamina that connect the pedicles together forming the vertebral canal
question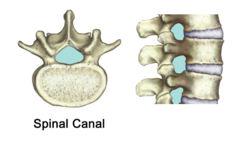
Spinal canal, what (3) things does it contain?

answer
vertebral canal contains the spinal cord, spinal nerves, and epidural space to the sides
question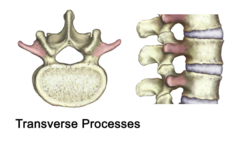
Transverse Processes

answer
The laminae give rise to the TRANSVERSE PROCESSES, which project LATERALLY, and the SPINOUS PROCESS, which projects POSTERIORLY.
question
The spine consits of? #verabrae, cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacrac, coccygeal?
answer
33 vertabrae 7 cervicle 12 thoracic 5 lumbar 5 fused sacral 5 fused coccygeal
question
cervical & lumbar convex?
answer
anteriorly (<
question
thoracic & sacral convex?
answer
Posteriorly >)
question
Supine: High points/ Low points?
answer
high points= C5 and L5 Low points = T5 and S2
question
the _____th sacral verebra is not fused giving rise to the sacral hiatus. what is this ?
answer
this opening into the sacral canal is the caudal termination of the epidural space
question
sacral cornu
answer
bony prominneces on either side of the hiatus, is a caudal landmark.
question
landmark, spinous process of C7
answer
most prominent, back of the neck
question
landmark, spinous process of T7
answer
inferior angle of the scapula
question
landmark, spinous process of T12
answer
12 rib attachement
question
landmark, spinous process of L5
answer
line between the iliac creasts crosses the L5 or L4-L5 interspace
question
how many pairs of spinal nerves?
answer
31 pairs of spinal nerves, each with a ventral and dorsal root
question
how many cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal nerves?
answer
8 cervical-----------------------PNS 12 throacic-----------Sympathetic 5 lumbar--------------Sympathetic 5 sacral---------------Sympathetic 1 coccygeal nerve------------PNS
question
cervical nerves transverse ___________ to corresponding vertebra
answer
cephalad (up)
question
Throacic and lumbar nerves traverse _________ to the vertabra
answer
caudad (down)
question
efferent motor fibers are located
answer
anteriror nerve roots of the anteriror and lateral horns of the spinal cord gray matter
question
afferent sensory fibers are located?
answer
dorsal nerve roots from the cell bodies inthe dorsal root ganglia
question
the cauda equina "horses tail" starts in the ______ for adults and ________ in neonates. what significance is this?
answer
L1= adults L3=neonates beyond these points is the termination of the spinal cord. would want to go in the L4-L5 spinal to avoid permanent damage.
question
dermatome is?
answer
a semental area of skin innervated by one spinal nerve root.
question
Dermatones significance: clavicle-c4 little finger-c6 nipple line-t4 umnbilicus-t10 popliteal fossa-s2
answer
-Clavicle= difficulty breathing -"little finger"= WARNING SIGN! all cardioaccelerator fibers are blocked T1-T4, may need to give ephidrine. -nipple line= some cardioaccelerator blockade -umbilicus= some sympathetics to LE -Popliteal fossa= pop fossa blocks
question
C3 dermatone
answer
difficutly breathing, they can still inervate the diaphram but they do not sensate breathing, putting hand on chest can help this.
question
dermatomes for surgery -upper addominal -intestinal, gyn, pelvice, and renal surgery -turp, vaginal delivery -knee, lower leg -foot surgery -hemorrhoidectomy
answer
- upper abd = T4-T5 Nipple -intestn....=T6-T8 (xiphoid) -turp.....= T10 (umbilicus) -knee = L1 (inquinal ligament) - foot = L2-L3 (knee and below) -hemorrhoi....... = S2-S5 (perineal)
question
most difficult nerve root to block?
answer
S1 outer side of foot, there is no lumbar sympathetic block
question
how many dorsal roots need to be interrupted to produce complete denervation of a dermatome?
answer
three (3)
question
Ligaments
answer
vertebral bodies are stabilized by several ligaments -supraspinous -interspinous -ligament flavum -longitudinal ligaments
question
supraspinous ligament, extends from _______ to ________. where is it thickest?
answer
strong fibrous cord, connects the spinous processes from the sacrum to C7. we know this is the lateral portion. it is thickest and broadest int he lumbar region
question
interspinous ligament. characteristics?
answer
is a think membrane, connecting the spinous processes as well. it is also thickest in the lumbar region
question
ligamentum flavum. characteristics, location
answer
"yellow ligament", connects adjacent laminae (the middle of the vertabrea, but not the spinous process it begins in the roots of the articular processes extending posteriorly/medially to where the laminae join to form the spinous process.
question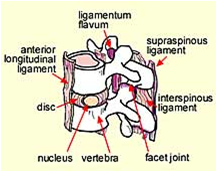
spinal ligaments (picture)

answer
supra,inter,flavum, then longtidunal is anterior
question
what insertion technique is least likely to result in accidnetal menigeal puncture? at what level is the ligamentum flavum the thickest?
answer
midliine insertion of an epidural needle. at L2-3 the ligamentum flavum is thickest in the midline (3-5mm) and farthest from the spinal memninges in the midline, which is what we want to aviod.
question
epidural space
answer
surrounds the spinal meninges, extends from the foramen magnum to the base of the skull to the sacral hiatus (S5) the epi space is composed of a series of dicontinous compartments, which become cointous when fluid or air is injected into them it is bound anteriorly by the posterior longitudinal ligament laterally by the pedicles and the intervertebral foramina posteriorly by the ligamentum flavum and the anteriror surgace of the lamina
question
where is the epidural space widest
answer
posteriorly and varies witht he verebral level. C5= 1-1.5mm T6= 2.5-3mm L2= 5-6mm (widest)
question
average distance to epidura space -adult -obese adult -thin adult
answer
adult= 4-6cm obese adult= up to 8cm thin adult= 3cm
question
contents of the epidural space
answer
nerve roots fat areolar tissue lymphatics arteries extensive venous plexus of batson, "valveless veins" this can be easily threaded into
question
Meninges
answer
the spinal cord is protected by both the bony vertebral column and the three connective tissue of the meninges. dura mater arachnoid mater pia mater
question
dura mater? / what space lies below this?
answer
the outermost membrane, and is a tough fibroelstic tube of fibers which run longtiudinally. below this is the "subdural" space drug intended for either the epidural space or subarachnoid space may be accidentally injected into this space, and this would be a failed block.
question
arachnoid mater? / what space lies below this?
answer
avascular membrane that serves as the principal physiologic barrier for drugs moving between the "epidural space and the subarachnoid space." puncturing this one runs into the subarachnoid space (spinal drug area). this space between the arachnoid mater and pia mater contains CSF. spinal nerve roots and rootlets run in the subarachnoid space, and it is continous to the brain ventricles.
question
pia mater
answer
delicate, highly vascular membrane that clings to the spinal cord and brain. BLOOD VESSELS supplying the spinal cord are in this space. aids in lateral support of spinal cord by laterally projecting denticulat lagaments to the dura
question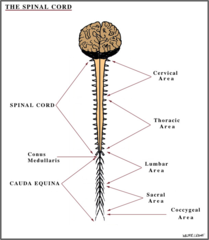
Spinal cord picture, ends at _______neonates and ________ in adults

answer
neonate= L3 Adults= L1 but extends to L3 in 10% of the population
question
CSF brain/spinal cord volumes? total volume made per day? where does most of it lie?
answer
is an ultrafiltrate of blood plasma Brain volume: 100-150ml Spinal volume: 25-35ml total of 350-500cc mader per day most lies in the cauda equina, below L1 in adults, L3 in children.
question
where is CSF formed
answer
choroid plexus of the lateral ventricles third vetricle (via foramen and monroe) fourth ventricle, aqueduct of sylvias brain and spinal cord via luska and foramen of magendie
question
where is CSF reabsorbed
answer
arachnoid villi
question
what big differences are there in the concentration of CSF and serum
answer
Protien: 28csf/7000serum both osmos are 289
question
spinal cord blood supply
answer
arterial blood -1 anterior spinal artery provides 75% of blood -2 posterior spinal arter provide ofther 25% of blood there are also 3 small segmental spinal arteries that are barely contributing
question
artery of adamkeiwicz
answer
is largest feeder artery to spinal cord, and supplies the anteriror spinal artery in the lumbar area, this would primaryly effect motor function if blocked.
question
spinal anesthesia
answer
the major cause of loss of sensation and muscle relaxation during spinal anestheis is the action of local anestheics on the spinal nerve root, dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord. SAB sub arachnoid block
question
zones of differential blockade related to spinal anesthesia
answer
SNS--->SENSORY----->MOTOR are blocked in that order. preganglionic sympathetic nervous system fibers (B-fibers) are located more proximally within the spinal nerve roots and the anesthetize first, then sensory (C-fibers) and finally motor fibers (A-delta and the A-gamma, A-beta, A-alpa)
question
why does the duration of action of ester local anesthetics as well as of amides placed in the subarachnoid space depen on vascular absorption of the drug?
answer
because csf does not contain significant amounts of cholinesterase enzymes.
question
the level of sympathetic nervous system block extends ________ spinal segments __________ to the level of sensory anestheisa and the levl of motor blcok averages ___________ segments _____ sensory anesthesia
answer
two cephalad (up) two segements belows
question
Baricity
answer
specific gravity of loval anesthetic relative to CSF, will influence spread.
question
hyperbaric solution
answer
heavier than csf, add glucose will increase specific gravity
question
isobaric solution
answer
same specific gravity as csf, dilut the LA solution with equal parts of csf
question
hypobaric solution
answer
add distilled water, lowers the specific gravity of the LA solution below that of csf
question
what should always be available during spinal anesthesia
answer
airway resuscitation equipment monitor: ekg, bp,sao2,oxygen via FM applied sterile glove>spinal tray>spinal drugs
question
epidural needles are typically __________gauge? spinal needles are typically ________ gauge?
answer
epi= 16-19 gauge spinal- 22-29 gauge
question
what is traversed from outside to inside while inserting a spinal needle using the midline technique
answer
skin> subQ tissue> supraspinous ligament> interspinous ligament> ligamentum flavum> epidural space> dura mater "pop"> subarachnoid space is entered until CSF is obtained.
question
spinal vs epidural dosing
answer
spinal probably 1-1.5cc of LA epidural: could be up to 10cc sometimes
question
epdiural anesthesia test does
answer
adminstered through the catheter to rule out catheter tip entry in the intravenous epidral veirn or intrathecal space (subdural,subarachnoid) before incrementally giving the entrie drug dose. -3ml of LA solution (1.5% lidocaine with 5mcg/ml of epinephrine. (1:200,000) -LA will produce evidence of spinal anesthesia with accidnetal intrathecal injection -Epi dose will increase heart rate 30bts/min, in <30 seconds lasting 30 seconds.
question
positive epidural test would be?
answer
increase heart rate 30bts/min, in <30 seconds lasting 30 seconds.
question
baricity and patient positioning with -Hyperbaric -hypobaric -isobaric
answer
-hyperbaric solution flow to dependent regioins of the spinal column -hypobaric solutions tend to float in the CSF -gravity has no effec on the distribution of isobaric solutions.
question
adrenergic agonists typically prolong duration of LA for lidocain and mepivacaine but have no effect on?
answer
bupivacaine and etidocaine
question
potency of local anesthetics is related to ?
answer
their lipid solubility
question
the duration of local anesthetic is affected by?
answer
the amount of protient binding
question
the onset of action of local anesthics is related to?
answer
the amount of local anesthic available in the base form
question
3 important factors in setting of sab/block height
answer
-braicity of LA -Postion of the patient during and just after adminstration of LA -Dose of anesthitic injected
question
order of blockade for spinal anesthesia
answer
autonmic> temperature>pain>touch>pressure>motor>vibration>proprioception>
question
what levels of the spinal cord constitute the diaphram drive
answer
C3,C4,C5 make and keeps the brain alive
question
sympathetic cardioaccelterator fibers are located?
answer
T1,T2,T3,T4 this also decreases sensativity to stretch receptors
question
Possible indication for spinal/epi
answer
-full stomach -anatomic distortions of upper airway -certain types of operations, pregnancy, turps sometimes (dilutional hyponatremia)
question
absolut contraindications to spinals/epi
answer
1.infections at the site of injection 2. dermatologic condition (psoriasis) 3. speticemia or baceremia 4. shock or severe hypovolmeia 5.preexisting disease involving the spinal cord 6. increased ICP 7. major abnormality of blood clotting mechanicsms 8.patient refusal, phychiatric unsuited 9.lack of skill in or experience with placing regional blocks 10. the surgeo cannot predicatably perform operation in time. 11. uncertainty about the duration of the operation, "ex-lap or whipple"
question
would you perform spinal on someone with aortic stenosis
answer
probably not, this is a relative contraindication based on cardiac diseass, that if sensory levels of T6 or above were affected there could be issues.
question
complications of spinal/epi?
answer
1. backache 11% spinal 30% epidurals 2.post dural punctur headache (up to 50% of patient after menigeal puncure by epidural) 3.systemic toxicity 4.epdiral hematoma, (late complication) 5.infection/abcess 6. total spinal (coughing can raise level of spinal)
question
coughing can do what when adminstering a spinal?
answer
it can actually raise the level of LA and block
question
total spinal
answer
Hypotension - treat as detailed above, volume, pressors. Remember that nausea may be the first sign of hypotension. Repeated doses of vasopressors and large volumes of fluid may be necessary. Bradycardia - give atropine. If this is not effective give ephedrine or epinephrine. Increasing anxiety - reassure. Numbness or weakness of the arms and hands, indicating that the block has reached the cervico-thoracic junction. Difficulty breathing - as the intercostal nerves are blocked the patient may state that they can't take a deep breath. As the phrenic nerves (C3,4,5) which supply the diaphragm become blocked, the patient will initially be unable to talk louder than a whisper and will then stop breathing.
question
treatment of post subdural headache
answer
Treatment Supine Fluids Analgesic/caffeine Epidural blood patch
question
spinal advantages
answer
Less time/skill/equipment to perform More rapid onset Better quality/denser sensory and motor block Less pain during surgery
question
epidural advantages
answer
Less risk of PDPH Less hypotension if no epi added Can prolong/ extend block via an indwelling catheter Epidural catheters aid with post-op pain Epidural often used to supplement general anesthesia for large abdominal surgeries
question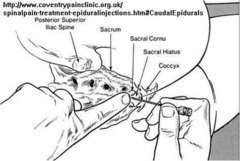
indication for caudal block

answer
Surgery below the umbilicus Hernia repair Lower limb surgery Skin grafting GU procedures Procedures on the anus and rectum Orthopedic surgery on the pelvic girdle Pediatric GU/hernia surgery



