SCC Cole Lec 3 Exam Lymphatic System – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
immune system
answer
a system that protects the body from foreign substances and pathogenic organisms by producing the immune response. split into the innate and acquired(adaptive) responses.
question
adaptive immunity
answer
immunity, resistance to a specific pathogen. Also called acquired immunity
question
lysozyme
answer
one of many antimicrobial proteins found in saliva and sweat and tears that destroys the cell walls of certain bacteria
question
phagocytosis
answer
process in which phagocytes engulf and digest microorganisms and cellular debris
question
humoral response
answer
The branch of acquired immunity that involves the activation of B cells and that leads to the production of antibodies, which defend against bacteria and viruses in body fluids.
question
neutrophils
answer
A type of white blood cell that engulfs invading microbes and contributes to the nonspecific defenses of the body against disease.
question
macrophages

answer
A type of WBC that destroy bacteria, cancer cells, and other foreign matter by phagocytosis
question
dendritic cells
answer
Type of WBC in with many protrusions that presents an MHC II-antigen complex after engulfing microbe to attract helper T-cells
question
natural killer cells
answer
Non-phagocytic WBCs that circulate in the blood. NK cells are important in innate immunity to viruses, bacteria, and cancerous cells.
question
interferons
answer
nonspecific antiviral proteins secreted by T cells
question
complement system
answer
A group of antimicrobial proteins that bind non-specifically to the surface proteins of foreign cells (such as bacteria), causing lysis (bursting) - part of the innate immunity.
question
inflammatory response
answer
nonspecific defense reaction to tissue damage caused by injury or infection
question
mast cells
answer
a vertebrate body cell that produces histamine and other molecules that trigger the inflammatory response
question
cytokines
answer
chemicals released by T helper cells that stimulate B cells to proliferate and differentiate into effector cells and memory B cells
question
lymphocytes
answer
the two types of white blood cells that are part of the body's immune system: B lymphocytes form in the bone marrow and release antibodies that fight bacterial infections; T lymphocytes form in the thymus and other lymphatic tissue and attack cancer cells, viruses, and foreign substances.
question
thymus

answer
a ductless glandular organ at the base of the neck that produces lymphocytes and aids in producing immunity
question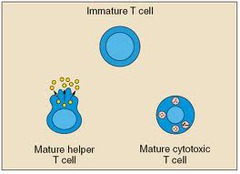
T cells

answer
lymphocyte cells that coordinates the immune system and attacks many infected cells as part of acquired immunity
question
B cells
answer
lymphocyte cells manufactured in the bone marrow that create antibodies for isolating and destroying invading bacteria and viruses
question
antigen
answer
any substance (as a toxin or enzyme) that stimulates the production of antibodies
question
immunoglobulin
answer
synonym for antibodies (IgM)
question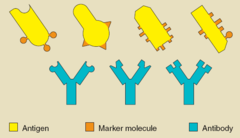
antibody

answer
any of a large variety of proteins normally present in the body or produced in response to an antigen which it neutralizes, thus producing an immune response
question
MHC molecule
answer
A combination of antigen fragments from within the cell and normal cell surface proteins that are presented outside the cell so that infected cells can be recognized by T cells
question
antigen presentation
answer
The process by which an MHC molecule binds to a fragment of an intracellular protein antigen and carries it to the cell surface, where it is displayed and can be recognized by a T cell
question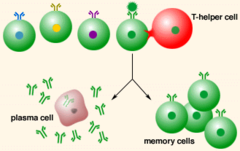
clonal selection

answer
The process by which an antigen selectively binds to and activates only those lymphocytes bearing receptors specific for the antigen. the selected lymphocytes proliferate and differentiate into a clone of effector cells and a clone of memory cells specific for the stimulating antigen.
question
effector cells
answer
the activated T or B cells that actually carry out the body's responses to antigen stimulus in that moment
question
memory cells
answer
B lymphocytes that do not become plasma cells(effector cell) but remain dormant until reactivated by the same antigen.
question
primary immune response
answer
the initial immune response to an antigen, which appears after a lag of several days from the proliferation and differentiation of lymphocytes
question
secondary immune response
answer
The adaptive(acquired) immune response provoked by a second exposure to an antigen. It differs from the primary response by starting sooner and building more quickly.
question
humoral immune response
answer
an immune response (chiefly against bacterial invasion) that is mediated by B cells whose major job is to create antibodies
question
cell-mediated immune response
answer
The branch of acquired immunity that involves the activation of cytotoxic T cells, which defend against infected cells.
question
helper T cell
answer
T cell with CD4 receptor that recognizes MHCII-antigens on the surface of a virus-infected cell and secretes cytokines that stimulate B cells and cytotoxic T cells to differentiate and proliferate
question
antigen-presenting cell
answer
Specialized Cells(B cells, macrophages, and dendritic) that possess MHC II. They are able to digest infected cells and display bits of ingested antigen on their surface in order to activate T cells.
question
cytotoxic T cells
answer
T cells that can kill other cells. These cells are important in host defense against viruses and other pathogens, because they recognize and kill the infected cells.
question
plasma cells
answer
Cells that develop from B cells and produce antibodies. Also called effector cells.
question
active immunity
answer
a form of acquired immunity in which the body produces its own antibodies against disease-causing antigens
question
passive immunity
answer
an non-permanent form of acquired immunity in which antibodies against a disease are acquired naturally (as through the placenta to an unborn child) or artificially (as by injection of antiserum)
question
Lymph
answer
Fluid in lymphatic capillaries and vessels, usually clear and colorless.
question
15, immunity,cells,lipids
answer
Three main functions of lymph: 1) reabsorbs __% of blood filtered by blood and capillaries. 2) Provides _________ & protection from foreign ______ and matter in the body. 3) Absorbs dietary ____ in small intestine and transports to blood.
question
lymph capillaries
answer
provides unique one way structure where ends of endothelial cells overlap an permit interstitial fluid in, but not out.
question
Lymphatic vessels (COLLECTING)
answer
Histology similar to veins, yet has thinner walls and more valves
question
Lymph Nodes,reticular
answer
Identify this structure: In line filters that cleanse the lypmh as is passes through. ________ fibers act as filters and delay microbe debris.
question
Macophages,reticular cells
answer
What are the primary cells that remove 99% of impurities in lymph nodes? _____________ &______________
question
Lymphoid Nodules,macro,follicular
answer
Identify:Nodule in cortex of lymph nodes __________ has a germinal center. B cells, _____phages, and ________dendritic cells are found
question
Spleen
answer
Large filtration organ, recycles old blood cells and Iron.
question
spleen
answer
the largest lymphatic organ in the body; serves as a blood reservoir, disintegrates old red blood cells, and produces lymphocytes and plasmids
question
Thymus Gland
answer
Source of maturation of T Cells (lymphocytes become T Cells)
question
Pharyngeal Tonsils
answer
These tonsils are a collection of lymphatic tissue found in the nasopharynx to combat microorganisms entering the body through the nose.(innate immunity)
question
Palatine Tonsils
answer
collections of lymph tissue in the oropharynx (innate immunity)
question
Lingual Tonsils
answer
a mass of lymphoid tissue, which covers the base of the tongue posterior to the oral cavity properb(innate immunity)
question
Thoracic Duct
answer
Primary venous return of lymph to the blood supply of the body
question
Right Lymphatic Duct
answer
large lymphatic vessel in the chest that receives lymph from the upper right part of the body
question
Natural Killer,immune,defense
answer
NK _________ _______ cells, are a part of _________ surveillance. They are a part of the innate________ system.
question
Natural Killer Cells,bacteria,infected,cancer
answer
Identify: 2% of these free roaming lymphocytes (specialized) patrol the body lookinig to find and destroy;__________, transplanted cells,viral-_________ cells and _________ cells
question
Natural Killer Cells,Perforin,granzymes,apoptosis
answer
Identify: These Innate cells bind target cells and release _________, that forms holes in membrane. Protein-digesting enymes (__________) enter cell, break down enzymes and trigger _____________ (programmed cell death)
question
T Lymphocytes
answer
These lymphocytes mature in the thymus gland and provide cell mediated immunity.
question
B Lymphocytes
answer
These lymphocytes mature in bone marrow and provide antibody-mediated immunity
question
Macrophages,phagocytic,matter,antigen
answer
These cells develop from monocytes, they are _____________. They are large, highly ___________ cells that destroy foreign matter and dead tissue ______. They are also ______ presenting cells
question
Antigen Presenting
answer
B cells, macrophages, dendritic cells are all ___________ __________ cells.
question
Antigen Presenting Cells
answer
either by phagocytosis or endocytosis, these cells break down foreign matter and display it on their surface with MHC-II molecules
question
Dendritic Cells,lymphatic
answer
APC's that engulf foreign matter by endocytosis:_________ Located in epidermis (langerhans),mucous memranes and ________ organs.
question
Reticular Cells,thymus,hormones,T
answer
Identify:These cells act as APC's in the thymus. They form the blood-______ barrier that isolates lymphocytes from blood-borne antigens. They produce __________ that promote development and actions of _____ cells.
question
Innate Immune Response, non, non,wide
answer
Identify this immune response:__________ Present at birth and is _____ specific and ___ adaptive Provides protection against a ________ range of pathogens
question
Adaptive immunity,one,self,pathogen
answer
Identify this immune response: Is specific and is directed only at ______ (quantity) pathogen. Involves distinguishing between ________ and non-self. An initial exposure to a specific __________ will create a memory
question
skin,lysozymes,stomach
answer
The first line of defense for Innate Immunity includes External Barriers: __________,mucous membrans, secretions (tears, saliva,vaginal secretions), _____________ (enzymes that can break down cell walls), and __________ acid
question
macrophages,immune,system,fever
answer
The second line of defense for Innate Imunity includes: Leukocytes & ____________, ____________ Surveillance, Complement __________ (collection of proteins),Inflammatory Response,and _________
question
neutrophils,phagocytosis,toxic,bacteria
answer
as part of the innate 2nd line of defense, ____________ a type of leukocyte protect the body via ____________. Neutrophil lysosomes trigger the respiratory burst, a cloud of highly ____________ oxidizing agents that form a killing zone that kills many __________ and the neutrophil
question
eosinophils, phagocytosis,kill,allergens
answer
As a part of the innate second line of defense ____________ a type of leukocyte protect the body via,______________, plus release toxic chemicals that ___________ pathogens. KEY in affect against _________ and parasites
question
Neutrophils
answer
Which leukocyte creates a toxic cloud as a part of the innate immune system?
question
Eosinophils
answer
Which leukocyte releases toxic chemicals effective against allergens and parasites? (think EEEOOWW parasites)
question
Basophils,heparin
answer
As a part of the innate second line of defense, ___________ secrete histamine (vasodilator) and ________ (anticoagulant) that AID other leukocytes
question
monocytes,macrophages,freely,fixed
answer
As a part of the innate second line of defense, ____________ leave blood and become ____________ that employ phagocytosis (and thus becoming apc's in acquired immunity). They wander ___________ Or they can be __________ and wait
question
non self,bind,perforin,membrane,enzymes
answer
INNATE SECOND LINE OF DEFENSE Immunological Surveillance or (Self vs_______ ___________) About 2% of lymphocytes are NK cells that patrol the body looking to find and destroy:bacteria,transplanted cells, viral infected cells & cancer cells. NK cells _______ to target cell, release _________ which creates holes in the cell _________. Granzymes enter cell,break down _______ and trigger apoptosis
question
Complement
answer
INNATE SECOND LINE OF DEFENSE _________ system, is a group of proteins which plays an important rule in innate immunity and later on, acquired immunity.
question
inflammation,antigens,opsonization,cytolysis
answer
COMPLEMENT SYSTEM: (innate second line of defense) Mechanisms of pathogen destruction; 1) Stimulates __________ 2) Clears _________ from blood 3) ____________ (encourages phagocytosis) 4) _______________ (cell breakdown)
question
Inflammatory response
answer
Innate second line of defense: A defensive response to harmful stimuli, like damaged cells that helps remove the injurious stimuli and initiate the healing process.
question
Fever
answer
Innate second line of defense: AKA Pyrexia An abnormal increase in body temp due to the hypothalamus raising the set point for body temp.
question
Adaptive Immunity
answer
The third line of defense for innate immunity:
question
Acute
answer
____________ inflammation is a rapid response that only lasts few days and has three stages
question
vasodilation,phagocytes,tissue,bystander
answer
Acute inflammation includes three stages: 1) __________ which allows more blood to flow to the damaged area which helps remove toxins and debris (Increased permeability of the blood vessels allows increased filtration of fluids and permits entrance of defensive proteins to site of injury, produces swelling or edema) 2) Movement of ___________ from the blood into the Interstitial Fluid 3) ____________ repair *Inflammation must be actively terminated when no longer in need to prevent unnecessary ________ damage to tissues. Failure to do so results in chronic inflammation and cellular destruction
question
Chronic
answer
This type of _____________ inflammation lasts months or years, characterizedby simultaneous healing and destruction of the tissue. Often a progressive shift in the type of cells present at the site of inflammation.
question
inflammation,diseases,ischemic
answer
Chronic ___________ also causes inflammatory disorders such as allergic reactions, and myopathies (both of which are referred to as immune ________). Non-immune diseases associated with chronic inflammation are: cancer, atherosclerosis and ________ heart disease
question
heat, redness,swelling,pain
answer
The four main characteristics of acute inflammation are: ___________,___________,__________,_________
question
mast,histamine, tissue,histamine
answer
The events in acute inflammation include: _______ cells which release chemicals that dilate blood vessels at the wound site _________ which increases the blood flow to the areas and the leakage of fluid and proteins from the blood into the _______ space. Thus the quick release of ________ produces the redess and swelling associated with inflammation
question
margination,diapedesis,neutrophils
answer
The events in acute inflammation include: ___________ loose adhesion to a vessel wall, Neutrophils loosely adhere to wall edges. __________ is when ____________ crawl through clefts out of the capillary or vessel towards an injury.
question
prostaglandins
answer
The events in acute inflammation include: release of __________________ which are lipids released by damaged cells and intensify the effects of histamine and cytokines.
question
neutrophils,phagocytes
answer
The events in acute inflammation include: __________ releasing signalling molecules (cytokines) to attract more ______ through chemotaxis
question
macrophages,cells,neutrophils,stimulating,leukocytes
answer
The events in acute inflammation include: _________ which engulf and destroy pathogens and casualties, for example tissue __________ and spent __________. Macrophages also secrete colony-_______ factors, that trigger increase production of more ___________ (reinforcements)
question
chemotaxis,pus,cells,debris
answer
The events in acute inflammation include: ____________ the movement of cells toward chemical signals from damaged cells. The remaining subsance in swelling is ___ which is formed from dead_____, tissue_________ and fluid
question
Cytokine
answer
a small protein hormone, secreted by lymphocytes and antigen-presenting cells, that helps regulate cellular activities during innate or adaptive immune responses
question
itis
answer
words that end in the suffix _ _ _ _ means inflammation of that particular tissue
question
naturally,antibodies
answer
_____________ acquired immunity The body develops immunity by being exposed to an antigen, or receiving ___________ from another through a natural process (IE:nursing)
question
artificially,develops,artificially
answer
_________ acquired immunity: the body _________ immunity by being exposed to an antigen or receiving antibodies __________ such as through an injection
question
Active,natural,responds,memory
answer
____________ immunity The body develops immunity by ______ exposure to an antigen and _______ by making its OWN antibodies and producing __________ cells.
question
passive,not,receiving,short
answer
__________ immunity Antibodies from another person or animal etc enter the body. Since the body is ___ making it's own antibodies or producing memory cells but rather is ________ premade antibodies passively, this immunity is _______ lived
question
artificial, active
answer
Immunity example: Vaccine creates ___________ __________ immunity
question
artificial,passive
answer
Immunity example: Gamma Globulin shot is __________ _______ immunity
question
natural, active
answer
Immunity example: Infectious agent caused by sickness is ____________ _________ immunity
question
natural, passive
answer
Immunity example: Mom's antibodies tranferred to baby by crossing placents or in breast milk. is _______ __________ immunity
question
Specificity
answer
Identify: The property of antibodies and other antigen-binding molecules for selective interaction with only one or a few types of molecule or cell.
question
B,lymphatic,same
answer
Memory as a property of immunity: During clonal selection, memory _________ cells are also created in the germinal centers of _________ nodules. They form plasma cells within hours and mount a very rapid secondary response that prevents symptoms in future exposure to the ______ antigens.(meaning, they are specific)
question
antibody,mark,mechanisms, antibodies
answer
Humoral (__________-mediated) IMMUNITY *Antibodies tag or _______ the pathogen for destuction by other ________ * Indirect attack by ___________ instead of immune cells directly
question
mediated,cells,inside
answer
Cellular (cell-___________)IMMUNITY *lymphocytes directly attack and destroy foreign cells or diseased host _____ where pathogen is ________ human cells
question
Antigens
answer
(Ag), any MOLECULE that MAY trigger an immune response, usually proteins or large polysaccharides. epitopes are key in the making of an antigen. Ag can have multiple ________ determinants (epitopes), each one capable of producing an immune response.
question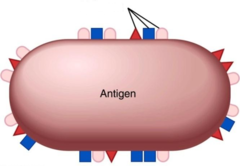
epitope,antibodies

answer
a localized region on the surface of an antigen that is chemically recognized by antibodies; also called antigenic determinant._________ (Sites where ___________ bind) * multiple specific of these can trigger multiple immune responses
question
Antigens
answer
Examples of __________ includes: Protein-coat molecules (viruses) Capsule and cell wall parts (bateria) Macromolecules on surface cells, protozoans and parasitic worms Molecules on surface of foreign blood cells or tissue cells Bacterial toxins or bee venom dissolved in body fluids
question
foreign,organic,structurally,large
answer
Antigen Recognition: Not all substances are antigenic. Molecules tend to be antigenic if they are: *__________ not ourselves *________ (I.E. Glass is not ourselves) *_________ complex *________ (High molecular weight
question
Major Histocompatibility Complex,two,self, non
answer
MHC means? How many types of these are there?_________ These are key in ________ vs _______ self
question
MHC-1
answer
These pick up antigens from inside the cell, migrating to the surface of the cell and displaying them
question
self
answer
MHC-1 are _________ antigens, they pick up endogenous (inside cell) antigens and present epitopes of them. MHC-1 gives a read out of what proteins are inside the cell
question
phagocytosis,fragments,epitope
answer
development of Antigen Presenting Cells: ______________ of antigen(Ag) Enzymatic break down of antigen (Ag) into molecular __________ Display of __________ fragments on it's MHC-II proteins *APC's usually move to nearest lymph node to display their epitope for T cells
question
two (II)
answer
Class _____ (number) MHC proteins only on APC's dendritic cells, macrophages, b lymphocytes, reticular cells
question
monomer, antigens
answer
Antibodies(Ab) or Immunoglobins (Ig) * Have a _________ made of four polypeptides *Antibodies bind to specific ___________
question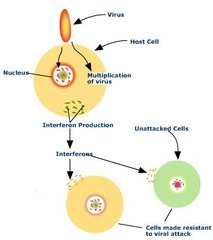
proteins,bind,antiviral,cell

answer
Interferons: Small _______ that are released from viral infected cells and ______ to receptors on surface of nearby cells causing them to make __________ proteins that prevent replication, thereby protectecting those cells. Interferons act as cell to ________ signals to stimulate macrophages and NK cells.
question
T,one
answer
Lymphocytes become immunocompetent: ______ lymphocytes are "born" in bone marrow, migrate to the Thymus where they become immunocompetant via development of receptors on their surface that are specific to ________ antigen
question
self,antigens,negative
answer
Lymphocytes become immunocompetent: T Lymphocytes must pass a screening/test after receiving their antigen specific receptors. This ensures that they recognize________ and only attack foreign_____ (only2%) pass. This process is known as ___________ selection (meaning removes those that fail)
question
B
answer
Lymphocytes become immunocompetent ____ cells mature and immunocompetant in the bone marrow
question
naive,antigen,recognition
answer
Immunocompetent B Cells and T Cells that leave the Bone Marrow and Thymus respectively are __________, because they have not yet encountered the _____ to which they are specific. They will circulate until they come across a APC which bears the epitope which will trigger __________
question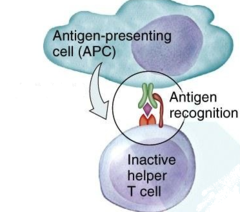
surface,binding

answer
Activation of T cell (Th): Receptor on T cell ______ matches epitope on foreign antigen in MHC II and ONLY on MHC II. Match = _________ of MHC II and APC
question
costimulation
answer
Activation of T cell (Th): Second binding called __________ required for activation (CD4 protein binding is the key)
question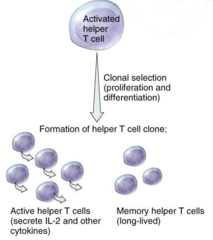
mitosis,clones,memory

answer
Activatin of T cell (Th) After Costimulation (CD4 binding), the Th cell is activated, this triggers repeated ________ which produces ______ of Th cells and __________ Th cells with receptors for the SAME Ag
question
APC's,Specific,presents,Th,costimulation
answer
Activation of B Cells: Immunocompetent B lymphocytes act as __________ Receptor must bind first to it's _________ Ag (NOT shown in picture above), B cell endocytosis and digestion of Ag, which it then __________ on it's surface MHC II. ______ cells then bind and trigger ___________.
question
epitope, B Lymphocytes, Plasma, Memory
answer
Activation of B Cells: After Costimulation, B cells present _______ in MHC II antigen on cell surface. Now SENSITIZED, B cells, become __ _____________. They then clone, differentiating into __________ cells and _____ cells for future Ag response. *** KEY in B Cell recognition is the BINDING of Th which triggers lnterleukins and this COMPLETES activation~***
question
germinal,antibodies
answer
B Cells become Plasma cells which develop mainly in the _______ centers of the lymphatic nodules of the lymph nodes. Plasma cells produce __________ at a rate of 2,000 per second over 4-5 days
question
Attack,CD8
answer
The role of Cytotoxic T Cells or Tc * Carry out _____ on enemy cell *Also known as T8 or _____ cells because they have a surface glycoprotein on cell surface call CD8
question
Helper,Cytotoxic
answer
Th cells aka ______ T cells promote actions of Tc cells aka ______ T Cells and play a key role in humoral and innate defenses
question
CD4
answer
Th cells are also known as _______ cells due to CD4 glycoprotein on cell surface.
question
Cytotoxic T Cells
answer
Memory T Cells are descended from _______ cells. They are APC's which are at the ready for future encounters with specific Ag. (Rapid response)
question
Plasma,Lymphatic
answer
Most B cells become ___ cells that develop mainly in the germinal centers of the ____ nodules.
question
Perforin
answer
one of the proteins released by cytotoxic T cells on contact with their target cells. It forms pores in the target cell membrane that contribute to cell lysis.(contained in granules)
question
Interleukins
answer
Produced by macrophages and lymphocytes in response to pathogen or stimulation by other products of inflammation, enhance the acquired immune response
question
Heavy Chain,complement binding site
answer
Immunoglobulin Molecule (IGm) or Antibody (Ab) Identify A Identify D: (binds Ag-Ab complex to RBC which transports it to phagocytes)
question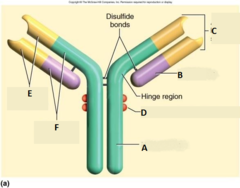
Light Chain, Antigen Binding Site

answer
Immunoglobulin Molecule (IGm) or Antibody(Ab) Identify B: Identify C:
question
Variable Region, Constant Region
answer
Immunoglobulin Molecule (IGm) or Antibody(Ab) Identify E: Identify F:
question
Cell Membrane Binding Sites
answer
Key~ Binding Using the binding Ag-Ab binding system, an antibody (Ag) can tag a microbe on an infected cell attack by OTHER parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it.
question
Neutralization,complement,Agglutination,Precipitation
answer
There are four mechanisms that Antibodies (Ab) use to render antigens (Ag) harmless: 1) __________ masking of active regions on cells 2)_________ Fixation (Ab-Ag) binding complex 3)________ An Ab may have many binding sites thus it clumps antigens allowing for easier phagocytosis 4)________ Ab link Ag molecules (NOT whole cells) together which can be removed via immune clearance
question
Neutralization

answer
Identify:(Mechanism that Ab use to render Ag harmless) Only certain regions of Ag are pathogenic, like the part of a toxin molecule or virus that binds to human cells. Ab can neutralize an Ag by MASKING (Blocking) these regions
question
Complement Fixation,phagocytes,fixation
answer
Identify:(Mechanism that IgM use to render Ag harmless) Antibodies BIND to Ag, on foreign cells forming the Ag-Ab complex. Complement binds Ag-Ab complex to RBC which transports it to __________.(cells for destruction) __________ is the PRIMARY mechanism for destruction of bacteria and mismatched RBC'
question
agglutination,phagocytosis
answer
Identify:__________ (Mechanism that IgM use to roundup Ag for destruction) An Ab may have up to 10 binding sites;thus it can bind to Ag on MORE than one cell(multiple epitope recognition), which encourages ______________.
question
precipitation, molecules,spleen
answer
Identify:(Mechanism that IgM use to render Ag harmless) Antibodies link antigen ____________ (not whole cells) together. This creates a larg Ag-Ab complex, which can be removed by Immune Clearance (RBC transport to liver and spleen for phagocytosis) As RBC's pass through the liver and __________, the macrophages remove and destroy the Ag-Ab complexes. *** This is the PRINCIPAL means of clearing Ag from the blood***
question
Hypersensitivity
answer
allergic or excessive response of the immune system to a drug ,chemical, or allergen
question
Immunodeficiency
answer
immunological disorder in which some part of the body's immune system is inadequate and resistance to infectious diseases is reduced
question
donor, match
answer
The production of Ag in response to exposure to the foreign ABO and Rh blood types: EX: during a blood transfusion, a patients immune system will attack any _________ rbc's that contain Ag that differ from their self-Ag. Therefore Ag transferred must __________.
question
Hemolytic disease
answer
Mom is Rh- Baby is Rh+ Mom produces antibodies against Rh+ and may cause anemia, which can lead to brain damage, in second child