Regional anesthesia – Valley Anesthesia – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
How may vertebrae are there?
answer
33
question
What are the high points of the spinal canal?
answer
C3 & L3
question
What are the low points of the spinal canal?
answer
T6 & S2
question
Where does the SC extend from?
answer
The foramen magnum to lumbar level 1 in adults & 3 in the newborn
question
The SC terminates at the _____ _____ & the _____ ____ extends down & anchors in the lower sacral region.
answer
conus medullaris filum terminale
question
There are ____ pairs of spinal nerves.
answer
31
question
What is the nerve group in the lower dural sac?
answer
The cauda equina (horses tail)
question
What ligament runs from the sacrum to C7?
answer
The supraspinous ligament
question
What ligament runs the full length of the spinal column?
answer
The interspinous ligament
question
Which ligament occurs in short segment between spinous processes?
answer
The ligamentum flavum
question
The _____ _____ is the space that surrounds the spinal meninges.
answer
epidural space
question
The epidural space extends from the ____ ____ to the _____ _____.
answer
foramen magnum to the sacral hiatus
question
Which ligament binds the epidural space posteriorly?
answer
The ligamentum flavum
question
At what level is the epidural space the widest?
answer
L2
question
At what level is the epidural space the narrowest?
answer
C5
question
Where does the dura mater extend from?
answer
The foramen magnum to S2-3 vertebrae
question
Where does the arachnoid end?
answer
S2
question
What space lies between the arachnoid & pia mater?
answer
The subarachnoid space
question
The epidural space is a potential space that is bound by the ____ & _____ ____.
answer
dura ligamentum flavum
question
Where is the blood supply to the SC & nerve roots derived from?
answer
A single anterior spinal artery & paired posterior spinal arteries
question
Where is the principle site of action for neuraxial blockade?
answer
The nerve root
question
Most important factors in determining distribution of LAs for spinal anesthesia
answer
Density Dosage & volume injected Position of the patient during & immediately after injection..other factors are height, spine, needle angle, site of injection, dose, vol, baracity density, sg
question
Uptake of LA is greatest where the concentration of the LA is the ______.
answer
greatest
question
What determines the level of a block?
answer
Position
question
How do all subarachnoid blocks work?
answer
By diffusion down a concentration gradient
question
What does the rate of elimination determine?
answer
The duration of spinal anesthesia
question
How are LAs eliminated?
answer
By vascular absorption via subarachnoid & epidural blood vessels
question
The more the LA is bound to lipids, the less chance there is for ____ ____.
answer
vascular absorption
question
What will decrease the rate of elimination of LAs?
answer
Decreases in SC blood flow Vasoconstriction
question
What is the predominant action of sympathetic blockade due to?
answer
Venodilation
question
What does venodilation result in?
answer
Reduced venous return, SV, CO, & BP
question
What can occur is sympathetic outflow from T1-T4 is blocked by a LA?
answer
Unopposed vagal stimulation will produce bradycardia (Bainbridge reflex)
question
What is bradycardia associated w/?
answer
Blockade of the cardioaccelerator fibers & decreased venous return
question
What occurs w/ the decrease in venous return & corresponding reduction in right atrial filling?
answer
The frequency of action potentials from stretch receptors to the RA & great veins is diminished -> a reflex decrease in HR
question
What is the best means for treating hypotension during spinal analgesia?
answer
Give IV fluids if not normovolemic Give ephedrine if normovolemic
question
Why should glucose solutions be avoided in the treatment of hypovolemia?
answer
Glucose acts as a diuretic & can worsen the situation (hypotension)
question
What is the best drug of choice for symptomatic bradycardia & why?
answer
A mixed alpha & beta agonist (ephedrine) It increases the HR & peripheral vascular resistance
question
What occurs w/ a high block (C2-C3)?
answer
Phrenic nerve paralysis & loss of accessory muscle of ventilation -> hypoxia
question
What ventilatory changes occur w/ a high spinal?
answer
Decreased FRC d/t paralysis of abdominal muscles Apnea (d/t hypoperfusion of the respiratory centers in the medulla 2˚ to severe hypotension)
question
At what level of blockade do patients start to feel dyspneic?
answer
T2-T4
question
What is the advantage of spinal over epidural anesthesia?
answer
The ability to control the spread of the anesthetic by controlling the specific gravity of the solution & the position of the patient.
question
How can trauma to the dura be minimized in the sitting position?
answer
Using a pencil point needle (separates the dura) If using a cut-bevel, needle will need to face either left/right to separate (rather than tear) the dura
question
How can trauma to the dura be minimized in the lateral position?
answer
Using a pencil point needle (separates the dura) If using a cut-bevel needle, the needle must face up or down
question
How long should ticlodipine (ticlid) be stopped prior to neuraxial anesthesia?
answer
14 days
question
How long should clopidogrel (Plavix) be stopped prior to neuraxial anesthesia?
answer
7 days
question
How long should LMWH (enoxaparin [lovenox]) be delayed postop to decrease the risk of a spinal hematoma?
answer
24 hrs
question
If postop LMWH will be used, epidural catheters should be removed _____ ____ prior to the 1st dose.
answer
2 hrs.
question
T7 dermatome
answer
Inferior border of scapula (lower tip)
question
L4 dermatome
answer
Iliac crest (superior)
question
L1 dermatome
answer
Inguinal ligament
question
Absolute contraindications to spinal anesthesia
answer
Infection at injection site Shock/severe hypovolemia Increased ICP Gross abnormality of blood clotting mechanism Patient refusal Severe AS/MS
question
Relative contraindications to spinal anesthesia
answer
Major surgical procedure above umbilicus Deformity of the spinal column Chronic HA/backache Sepsis Mobitz I or II 3˚ heart block w/o pacer
question
Describe the spread of LAs
answer
Spreads to the nerves of the cauda equina & laterally to the nerve rootlets & nerve roots Can also diffuse into the SC
question
List the structures penetrated by the needle for a subarachnoid block (midline)
answer
Skin SC tissue Supraspinous ligament Interspinous ligament Ligamentum flavum Epidural space Dura mater Arachnoid mater
question
What structures are bypassed with a lateral approach to a subarachnoid block?
answer
The supraspinous & interspinous ligaments
question
What symptoms should be identified as signs of central hypoxia until proven otherwise?
answer
N/V
question
What is the most common complication of neuraxial anesthesia?
answer
Backache
question
What is the 2nd most common complication of neuraxial anesthesia?
answer
Postdural puncture HA (PDPH) - except in OB (#1)
question
Describe the PDPH
answer
Bifrontal & occipital (involves head, neck & shoulders) Aggravated by upright position, coughing, or straining
question
S/S of PDPH
answer
Nausea, loss of appetite, photophobia, ∆s in auditory acuity, tinnitus, depression, bed-ridden
question
What causes a PDPH?
answer
A decrease in the amount of CSF in the subarachnoid space causing the medulla & brainstem to drop into the foramen magnum.
question
What is an additional complication to a decrease in CSF caused by PDPH?
answer
Cranial nerve palsy->decreased blood supply to the nerves
question
How is a PDPH treated?
answer
With a blood patch: 10-30 cc injected into the epidural space until patient can feel pressure in their back
question
Elbow
answer
Extend: Radial Flex: Musculocutaneous
question
Forearm
answer
Supinate: Radial Pronate: Medial
question
Wrist
answer
Extend: Radial Flex: Medial and ulnar
question
Fingers
answer
Extend: Radial Adduct: Ulnar Abduct: Medial Flex lateral 3: medial Flex and oppose to thumb: ulnar
question
What are the preganglionic and postganglionic neurotransmitters for the somatic nervous system, the PNS, and SNS?
answer
Somatic: preganglionic-Ach PNS: preganglionic & postganglionic-Ach SNS: preganglionic-Ach, postganglionic-NE
question
In regards to the SNS, where do preganglionic B fibers originate?
answer
In the intermediolateral cell column segments T1-L2 or L3
question
In regards to the SNS, where do preganglionic B fibers exit the spinal cord?
answer
With the ventral ramus.
question
In regards to the SNS, once the preganglionic B fibers exit the spinal cord with the ventral ramus they synapse. Where do they synapse?
answer
Synapse in the lateral chain ganglia along the ventrolateral surface of the vertebral bodies or pass thru to synapse in other (collateral) sympathetic ganglia.
question
What type of neuron leave the ganglia and travel to segmental nerves & target organs?
answer
Postgagnlionic neurons (unmyelinated C fibers).
question
Describe the lateral chain ganglia?
answer
Paravertebral ganglia T1-L2 on the anterolateral surface of the vertebral bodies.
question
What are the collateral ganglia?
answer
Cardiac, celiac, superior % inferior mesenteric ganglia.
question
What do the collateral ganglia accommodate?
answer
Preganglionic fibers which do not synapse in lateral chain, but continue in visceral ramus->splanchnic nerves which end in collateral ganglia.
question
What are the superior cervical ganglion?
answer
C1-C4
question
What are the middle cervical ganglion?
answer
C5-C6
question
What are the inferior cervical ganglion?
answer
C7 & C8
question
What are the target organs of the superior cervical ganglions (C1-C4)?
answer
Iris & ciliary body Lacrimal & salivary glands Parotid gland Heart
question
What are the target organs of the middle cervical ganglions (C5-C6) & the stellate ganglions?
answer
Heart All preganglionic fibers arise below the stellate, blockade at this level affects all sympathetics above this level.
question
Describe the lumbo-sacral lateral chain
answer
Receives all presynaptic input enters from L1 & L2. These ganglia are not fused but the coccygeal ganglia meet at the midline
question
What forms the stellate ganglion?
answer
Inferior cervical ganglion fuses w/ T1.
question
What are the target organs for the celiac ganglion?
answer
Stomach, small bowel, adrenal medulla
question
Where does the cardiac plexus receive its sympathetic input from?
answer
T1-T4
question
What are the target organs of the superior mesenteric ganglion?
answer
Large & small bowel
question
What are the target organs of the inferior mesenteric ganglion?
answer
Lower colon & rectum
question
What are the target organs of the hypogastric ganglion?
answer
Urogenital organs
question
What ganglions are supplied by the greater, lesser, & least splanchnic nerves?
answer
Greater & lesser: celiac plexus Least: inferior mesenteric & hypogastric ganglia
question
Blocking what ganglion will knock out all the sympathetics, why, and what can it result in?
answer
Stellate ganglion. All preganglionic fibers arise below the stellate ganglion. Could result in Horner's syndrome
question
Blocking what plexus is indicated in treatment of intraabdominal malignancies & chronic pancreatitis; diagnostic (local or therapeutic (neurolytic block)?
answer
Celiac plexus
question
Blocking what ganglion is indicated in painful conditions of the lower extremities and pelvic viscera and vascular insufficiency in the legs?
answer
Lumbar sympathetic ganglion.
question
Blocking what plexus and ganglion is indicated in tx of painful conditions of the pelvis and perineum?
answer
Superior hypogastric plexus & ganglion impar
question
Describe the cervical lateral chain.
answer
Located in the neck. All presynaptic input enters from T1 w/ minor contributions from T2 & T3. Cervical lateral chain ganglia are fused.
question
Where do all sympathetics to the head & neck come from?
answer
T1 or below
question
Where is the cervical sympathetic chain located?
answer
Lies on the anterolateral surface of the vertebral bodies.
question
Where does the cervical sympathetic chain receive its input from?
answer
T1 or below
question
Blocking what ganglion is indicated in treatment & diagnosis of pain syndromes, vascular insufficiency, hyperhidrosis, and dysrhythmias?
answer
Stellate
question
What are the S/S of Horner's syndrome?
answer
Ptosis (drooping of eyelid), flushing, miosis (pupillary constriction), anhidrosis (lack of sweating).
question
Describe the cardiac plexus
answer
Superficial & deep divisions. Both organized around the aortic arch.
question
Where do the celiac ganglion (collateral ganglion) receive its input?
answer
From the greater & lesser splanchnic nerves.
question
What does sympathetically mediated pain involve (CRPS)?
answer
An initiating event-crush, stretch, axotomy, ischemia, etc... to a peripheral nerve.
question
What does CRPS stand for?
answer
Complex regional pain syndrome.
question
What occurs with sympathetically mediated pain?
answer
There is a sensitization of peripheral (C-fibers) & central (dorsal horn laminae 1& 2).
question
What does the sensitization of peripheral (C-fibers) & central (dorsal horn laminae 1& 2) involve?
answer
↑ spontaneous neuronal activity d/t ectopic pacemakers (probably dysfunctional Na channels) ↑ response to stimuli ↓ stimulus threshold (less stimulation required to cause nerves to fire).
question
What does C fiber sensitization lead to?
answer
↑ adrenergic receptors ↑ sensitivity to stimuli (↑ action potential per stimulus) ↑ "cross talk"
question
What is "cross talk"?
answer
Phenomenon where neurons carrying normal sensory info cross over & are interpreted as high intensity pain & accounts for allodynia
question
Describe the dorsal horn changes that occur w/ sympathetically mediated pain.
answer
A-beta fibers form abnormal connections in shallow laminae (1 & 2)->normal sensory input interpreted as high intensity noxious stimuli. ↑ gene expression for receptors for pain related neurotransmitters (substance P). ↓ opioid binding sites.
question
Describe the wind-up theory.
answer
Involves repetitive noxious stimuli (c-fibers)->prolonged discharge of dorsal horn cells-> progressive ↑ in APs per stimulus->long term potentiation (LTP).
question
What occurs with LTP?
answer
↑ in receptive field of nociceptive neurons d/t formation of more dendrite connections in the dorsal horn. Dropout of inhibitory neurons.
question
What are NMDA receptors important for?
answer
In triggering wide dynamic range (WDR) neurons that are responsible for generalization of specific nociceptive info.
question
What are the NMDA agonists and what releases them?
answer
Aspartate, glutamate, etc-released by c-fiber stimulation.
question
What are the NMDA antagonists, what are they useful for?
answer
Ketamine, dextromethorphan, methadone, PCP Useful in chronic pain syndrome
question
In regards to the lumbo-sacral lateral chain, where do most sympathetic fibers to the lower ext pass thru, and what would blockade at this level cause?
answer
Pass thru L2/L3. Causes near complete sympathectomy of the lower ext.
question
In regards to the cardiac plexus, where does sympathetic input arise from?
answer
Cervical ganglia.
question
In regards to the cardiac plexus, where does parasympathetic input arise from?
answer
Vagus & recurrent laryngeal nerves.
question
Describe "cross talk".
answer
Abnormal connections by demyelinated (loss of myelin d/t some sort of neurologic phenomenon) neurons called ephapses.
question
How does the body send signals over long distances?
answer
Chemical messengers, electrical or a combination of the two. Peripheral nerves are constructed for electrical transmission that leads to a chemical messenger activation.
question
Describe the cell body (soma).
answer
Contains the nucleus, located mainly in the CNS.
question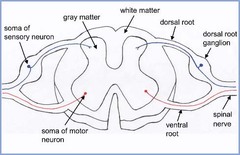
Where are the cell bodies of sensory neurons located?

answer
In the dorsal root ganglia (DRG).
question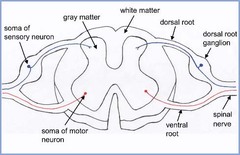
Where are the cell bodies of motor neurons located

answer
In the ventral horn.
question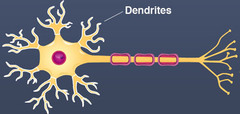
What are dendrites, where are they located, and what are their functions?

answer
Multiple branches close to cell body allow local cell to cell communication.
question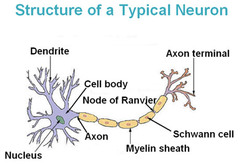
Where is the axon located and what are their functions?

answer
Extends from the cell body, impulse transmission over long distance, defines receptive field.
question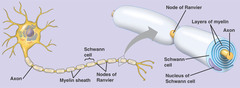
Describe Schwann cells

answer
Envelopes every axon, produces myelin. May produce myelin sheaths around larger axons (>1 micron)
question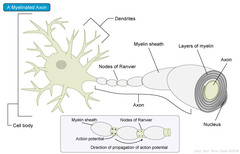
Describe the myelin sheath

answer
Supporting cells wrap layers of their own PM around the axon forming an insulating layer. Each supporting cell surrounds about 1 mm of axon-many cells required to cover whole axon.
question
How does myelination affect capacitance?
answer
Decreases capacitance (decreases the loss of electrical signal).
question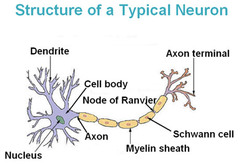
Describe the nodes of Ranvier

answer
Interruptions in the myelin sheath.
question
What are the functions of the nodes of Ranvier?
answer
Allows axolemma to be exposed to the extracellular matrix-specifically the Na channel (the axonal membrane is uninsulated & therefore capable of generating electrical activity). Allows for more rapid electrical conduction. Largery axons transmit impulses at a faster rate (less Na channels to open).
question
Describe how nerve impulses travel along unmyelinated axons.
answer
Travel as a uniform wave of depolarization d/t conformational changes in ion channels.
question
Describe how nerve impulses travel along myelinated axons.
answer
The Na channels act like booster stations for the propagation of a passively conducted electrical current. This is a more rapid and efficient system.
question
Describe peripheral nerves
answer
Mixed type w/ afferent & efferent fibers, a single nerve is both myelinated & unmyelinated.
question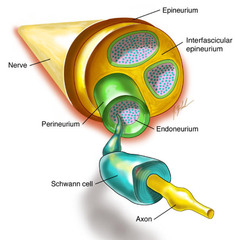
Describe the anatomy of a nerve.

answer
Three layers: Endoneurium Perineurium Epineurium
question
Describe the endoneurium
answer
Surrounds each individual axon, non-neuronal glial cell.
question
Describe the perineurium
answer
Contains the nerve fibers in fascicles, semipermeable, acts as a major barrier to diffusion of LAs (tight junctioned).
question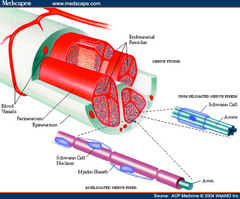
Describe the epineurium

answer
Sheath covering the entire nerve, contains nutrient blood vessels.
question
Describe A-fibers.
answer
All myelinated. Alpha, beta, gamma, delta.
question
What are the functions of a-fibers (alpha, beta, gamma, delta)?
answer
Motor, tactile, proprioception, muscle tone, touch.
question
What are the functions of small A delta fibers?
answer
Pain and temperature.
question
Describe B fibers
answer
Myelinated, preganglionic autonomic
question
Describe C fibers (sC, dC)
answer
Unmyelinated, postganglionic autonomic
question
What are the functions of C fibers (sC, dC)?
answer
Pain and temperature.
question
Describe the phospholipid bilayer.
answer
Impermeable to ions, electrical capacitance (acts as a capacitor plate)
question
Describe depolarization & action potential of a nerve.
answer
Must hit threshold (point at which the cell will become fully depolarized) Once threshold reached, Na channels open rapidly, the cell becomes positive (depolarized).
question
Describe repolarization & action potential if a nerve.
answer
Na channel closes, K channels open (inside of cell is negative).
question
Describe the resting phase
answer
Na & K channels are closed but K channels leak (100x more leaky than Na channels) Na K ATPase restores ionic gradients.
question
What is the Nernst potential
answer
The electrical potential across a cell membrane that exactly opposes the net diffusion of a particular ion through the membrane following its concentration gradient.
question
Describe the hyperpolarization phase (refractory period)
answer
The membrane potential becomes transiently more negative than the normal resting potential. Refractory period makes the axon unidirectional.
question
Describe membrane threshold
answer
That point in the process of depolarization when continued stimulation leads to complete action potential.
question
Describe impulse firing threshold
answer
Point where the balance of ionic currents reverses from ATP requiring polarization to gradient dependent depolarization.
question
What is normal resting potential of a neuron?
answer
-60 mV
question
What are the 2 means of propagation?
answer
Passive spread & active spread
question
Where does passive propagation occur?
answer
In the dendrites & cell body-different kinds of Na channels depending on nerve cell type.
question
What are the different kinds of Na channels involved in passive propagation?
answer
Ligand gated, gap junctions, temperature gated, mechano gated. Very few voltage gated.
question
What is passive propagation responsible for?
answer
Sensory function, cell-to-cell communication & impulse modulation.
question
Describe active propagation.
answer
Occurs in the axon. Myelinated-node to node (more rapid & efficient). Nonmyelinated- continuous wave.
question
In regards to active propagation, describe what occurs.
answer
Once an action propagation is initiated in 1 region of a neuron, the depolarization "wave" will spread out sequentially to the rest of the neuron.
question
Potential complications of any regional anesthetic technique include: a. Infection b. Bleeding c. block failure d. all of these are correct e. Nerve damage
answer
d. all of these are correct
question
Addition of NaHCO3 to local anesthetics accomplishes all of the following except: a. Speeding the onset of local anesthetic block b. Intensifying local anesthetic block by ion trapping c. Causing more of the local anesthetic to be in its unionized form d. Decreasing the pH of local anesthetic rendering it more water soluble e. Acidifying the axonal cytoplasm
answer
d. Decreasing the pH of local anesthetic rendering it more water soluble
question
Propagation of an impulse wave down an axon occurs due to: a. Activation of the sodium / potassium ATPase pump b. Ionic diffusion c. Two of these are correct d. Electrical conduction e. Closure of voltage gated sodium channels
answer
c. Two of these are correct
question
Which sequence correctly lists injection sites in order from most rapid systemic absorption to least rapid? a. Epidural > subarachnoid > brachial plexus > subcutaneous > intercostal b. Intercostal > subarachnoid > brachial plexus > epidural > subcutaneous c. Intercostal > epidural > brachial plexus > subarachnoid > subcutaneous d. Brachial plexus > subcutaneous > subarachnoid > intercostal > epidural e. Subcutaneous > Intercostal > epidural > brachial plexus > subarachnoid
answer
c. Intercostal > epidural > brachial plexus > subarachnoid > subcutaneous
question
The injection of local anesthetic into which site would provide the highest venous plasma level? a. Subarachnoid b. Caudal c. Subcutaneous d. Brachial plexus e. Lumbar epidural
answer
b. Caudal
question
Which LA results in cardiotoxicity: fast in, slow out leads to reentrant dysrhythmias?
answer
Bupivicaine
question
Which LA results in a poor differential block?
answer
Etidocaine
question
Which LA has prolonged metabolism in the fetus?
answer
Mepivicaine
question
Which LA metabolizes to O-toluidine in the liver, potentially causing methemoglobinemia?
answer
Prilocaine
question
Which LA has a S isomer leads to less cardiotoxicity and is an intrinsic vasoconstrictor?
answer
Ropivicaine
question
Which LA may render bupivacaine and epidural narcotics ineffective?
answer
Chloroprocaine
question
Which LA is used as a topical anesthetic, rapid onset, and medium to long duration?
answer
Tetracaine
question
Which LA is used for IVRA, epidural, peripheral nerve block, topically on mucous membranes, and IV to blunt airway reflexes?
answer
Lidocaine
question
What local anesthetic is an amide? a. Procaine b. Chlorprocaine c. Cocaine d. Bupivacaine e. Teracaine
answer
d. Bupivacaine
question
Addition of epinephrine to local anesthetic solutions has which of the following effects? a. Slows absorption b. Lowers the pH c. All of these are correct d. Causes more profound motor block e. Direct antinociceptive effects at the spinal cord level
answer
c. All of these are correct
question
Describe tonic block.
answer
Closed channel inhibition
question
Describe phasic block
answer
The anesthetic binds when channels are stimulated or open.
question
The maximum recommended dose for plain bupivacaine given in the epidural space is approximately ____ mg/kg. a. 5 b. 1 c. 10 d. 2 e. 7
answer
d. 2
question
Changes in fluid and electrolye disposition in response to surgical stress include: a. Sodium and water loss b. Increased functional extracellular fluid (intravascular volume) c. Potassium excretion d. Diuresis from increased ADH e. Hypoglycemia
answer
c. Potassium excretion
question
In the sympathetic division of the Autonomic Nervous System, the main neurotransmitter for the postganglionic axon is? a. glutamine b. acetylcholcholine c. dopamine d. norepinephrine. e. epinephrine
answer
d. norepinephrine. NE is the main neurotransmitter for the sympathetic division of the ANS. NE is also a catecholamine released from the adrenal medulla effector organ when stimulated to cause vasoconstriction in the periphery.
question
Describe the resting phase
answer
Na & K channels closed, K channels leaking
question
Describe the refractory phase
answer
Slow voltage gated Na channels closed and inactivated.
question
Describe the repolarization phase
answer
Na channels are inactivated K channels open
question
Describe the depolarization phase
answer
Na channels open
question
A more profound depth of conduction blockade may be attained by adding Na+ bicarb to the local anesthetic, for all of the following reasons EXCEPT a. Decrease in intracellular pH occurs from CO2 diffusion across the cell membrane b. Direct depressant effects of CO2 on nerves c. The bicarbonate ion diffuses into the cytoplasm, contributing to ion trapping. d. By raising the pH, you increase the non-ionized form of the local anesthetic outside the axolemma e. CO2 lowers the intracellular pH and traps the ionized form of the local anesthetic in the cytoplasm
answer
c. The bicarbonate ion diffuses into the cytoplasm, contributing to ion trapping.
question
The pKa of a local anesthetic is correlated with which characteristic of local anesthetics? a. Duration of action b. Potency c. color d. pH e. Latency of conduction blockade (onset time)
answer
e. Latency of conduction blockade (onset time)
question
What is the primary result of increased cortisol
answer
Gluconeogenesis, lipolysis, protein catabolism
question
What is the primary result of increased catabolic hormones?
answer
Negative nitrogen balance
question
What is the primary result of increased ADH?
answer
Free H20 retention
question
What is the primary result of Virchow's triad?
answer
Increased DVT risk
question
What is the primary result of severe anxiety?
answer
Increased catecholamines, increased overall stress response
question
Hyperglycemia in response to surgical stress may be caused by all of the following except: a. Glycogenolysis from increased epinephrine and glucagon b. Increased secretion of atrial natriuretic peptide c. Gluconeogenesis from increased epinephrine, glucagon, and Cortisol d. All of the choices are correct e. Insulin resistance
answer
b. Increased secretion of atrial natriuretic peptide
question
Factors contributing to the resting membrane potential include: a. 2 of these 3 choices are correct b. All of these choices are correct c. Potassium ion leakage d. Sodium / potassium ATPase pump e. Sodium channels
answer
a. 2 of these 3 choices are correct
question
Which of the following amide local anesthetics has the lowest pKa? a. Bupivacaine b. Lidocaine c. Ropivacaine d. Mepivacaine e. Tetracaine
answer
d. Mepivacaine
question
The Nernst potential is: a. The electrical potential at which enough Na+ channels open to propagate an impulse b. The minimal voltage required to stimulate an axon c. The ionic concentration gradient across a capacitance membrane d. The electrical potential across a cell membrane that exactly opposes the net diffusion of a particular ion through the membrane following its concentration gradient e. All of the choices are correct
answer
d. The electrical potential across a cell membrane that exactly opposes the net diffusion of a particular ion through the membrane following its concentration gradient
question
Which ionic fluctuation is primarily responsible for early depolarization? a. Potassium Efflux b. Sodium Efflux c. Potassium Influx d. Sodium Influx e. Calcium influx
answer
a. Potassium Efflux
question
Which of the following local anesthetics can cause methemoglobinemia? a. Chirocaine b. Benzocaine c. Ropivacaine d. Mepivacaine e. Bupivacaine
answer
b. Benzocaine
question
All of the following cross the plasma membrane easily except a. Carbon dioxide b. Bicarbonate ion c. Local anesthetics at pH > pKa d. Hydrophobic drugs e. Unprotonated local anesthetics
answer
b. Bicarbonate ion
question
What is the MOA of LAs?
answer
Bind to receptors on Na channels, inhibit the flux of Na ions & prevent membrane depolarization. Work by blockade of the excitation conduction process in the nerves.
question
Describe use dependent inhibition (AKA-phasic inhibition).
answer
The channel opens & the LA binds More depolarization leads to more rapid response
question
Describe LAs
answer
All lipid soluble to some degree, weak bases
question
What form does the LA have to be in to penetrate the cell?
answer
Must penetrate the cell in unionized state to bind from the cytoplasmic side of the Na receptor.
question
Describe the structure of the more potent LAs.
answer
Higher lipid solubility Greater hydrophobicity (ionized form less soluble) Covalent dipolar bond linking the aromatic moiety to the tertiary amine group
question
What is the effect of higher lipid solubility?
answer
Allow for more rapid transfer across the membrane. Higher concentration in the bilayer.
question
What is the effect of greater hydrophobicity?
answer
Blocks the resting or closed Na channels
question
Describe the ester & ether bond, linear amide bond, and cyclic amide bond.
answer
Ester & ether bonded are more potent. Linear amide bonded less potent. Cyclic amide bonded least potent.
question
What are the determinants of potency?
answer
Dependent more on the inhibition of Na currents alone. Some LAs also block K current (these are less potent). CO2 potentiates the conduction blockade.
question
What is the effect of the potentiated conduction blockade of CO2?
answer
Raises the threshold for impulse firing. Acidifies the cytoplasm & ↑ the cationic form of the LA
question
What does the onset, depth, and duration of the block depend on?
answer
Amount How rapidly it arrives How rapidly it's removed from the site
question
What agents diffuse more rapidly?
answer
More hydrophobic, neutral & unprotonated (unionized) agents.
question
What greatly enhances the uptake of LAs?
answer
CO2
question
Describe the depot effect of the myelin sheath.
answer
Highly lipophilic agents go to the myelin (acts as a depot, gives prolonged block).
question
What does uptake (speed of onset) depend on?
answer
pKa of the LA: low pKa=more rapid onset (more hydrophobic, less ionized) pH of the various compartments: LAs won't work at sites of infection (more acidic)
question
What does duration depend on?
answer
Protein binding strength, pKa & partition coefficient
question
What would occur if insufficient length of the nerve is blocked?
answer
The impulse conduction will be slowed down, but complete conduction block will not occur.
question
What fibers are most sensitive to blockade?
answer
Pain & temperature fibers-smallest myelinated A & nonmyelinated C fibers. Light touch & hair vibration-larger myelinated A fibers.
question
What fibers are the most difficult to block?
answer
Large A fibers that are responsible for proprioception & motor function.
question
Describe the distal block and proximal block in regards to differential blockade among fibers.
answer
Mantle bundles (proximal) 1st to be anesthetized-early block. Core bundles (distal) last to be anesthetized-delayed block.
question
What are the effects of Mu1 opioid receptors?
answer
Analgesia (supraspinal, spinal); euphoria; low abuse potential; mitosis, bradycardia, hypothermia, urinary retention.
question
What are the effects of Mu2 opioid receptors?
answer
Analgesia (spinal); respiratory depression; physical dependence; marked constipation.
question
What are the effects of kappa opioid receptors?
answer
Analgesia (supraspinal, spinal); dysphoria; sedation; low abuse potential; mitosis; diuresis
question
What are the effects of delta opioid receptors?
answer
Analgesia (supraspinal, spinal); respiratory depression; physical dependence; marked constipation; urinary retention.
question
What are the Mu1 & Mu2 agonists?
answer
Endorphins, morphine, synthetic opioids
question
What are the kappa agonists?
answer
Dynorphins
question
What are the delta agonists?
answer
Enkephalins
question
What are the Mu1, Mu2, kappa, and delta antagonists?
answer
Nalaxone, naltrexone, nalmefene.
question
Where does resting or tonic inhibition occur?
answer
In a closed channel
question
Describe ionization of LAs.
answer
Ionization of a weak base occurs when the pH is pKa
question
Describe how the length of the nerve determines the amount of LA needed to block it.
answer
In smaller nerves, the same diffusion of LA blocks 3 nodes of Ranvier, where on the larger nerve it only blocks one.
question
Critical density is ____ ____ to conduction velocity & nerve size as conduction velocity increases & more LA is required to block conduction.
answer
Directly proportional
question
In regards to phasic inhibition describe charged LAs vs uncharged LAs.
answer
Charged LAs are more effective at inhibiting the Na channels Uncharged LAs penetrate lipid bilayer easier
question
In regards to phasic inhibition describe LAs & inactivated Na channels.
answer
During stimulation Na channels in the inactivated state bind LAs more tightly which stabilizes the channel the inactive state.
question
Describe LAs & open & activated Na channels.
answer
Open & activated channels react most rapidly w/ LAs but bind less tightly.
question
What drug characteristics are more potent in producing a tonic block?
answer
Hydrophobic & neutral drugs.
question
What drug characteristics have a weaker tonic block?
answer
Very polar & charged LAs.
question
What determines how rapidly the LA arrives?
answer
pKa, pH, & hydrophobicity
question
What determines how rapidly the LA is removed from the site?
answer
pKa & protein binding
question
What opioid receptors have low abuse potential?
answer
Mu1 and Kappa
question
Which opioid receptors provide spinal and supraspinal analgesia?
answer
Mu1, kappa & delta
question
Which opioid receptors are associated w/ respiratory depression?
answer
Mu2 and delta
question
Which opioid receptors are associated w/ marked constipation?
answer
Mu2 and delta
question
Which opioid receptors are associated w/ urinary retention?
answer
Mu1 and delta
question
Which opioid receptors are associated w/ mitosis?
answer
Mu1 and Kappa
question
What occurs w/ the anticipatory response (cognitive anticipation of stress or trauma)?
answer
Limbic system influences (via amygdala): Brainstem (locus coeruleus)-> ↑d catecholamines Prefrontal cortex signals the hypothalamus to ↑ secretion of CRH-> ↑ pituitary secretion of ACTH.
question
What factors are involved in the sequential physiology of pain (processes involved in pain).
answer
Induction/transduction Inflammation Granulation & healing Conduction/transmission Modulation Perception
question
Describe induction/transduction in regards to sequential physiology of pain.
answer
Conversion of physical stimulus to nociceptive action potential via peripheral sensory neurons.
question
Describe inflammation in regards to sequential physiology of pain.
answer
Leukocyte adhesion, diapedesis, mediator release Complement, kinin, & coagulation activation Arachidonic acid metabolites
question
Describe conduction/transmission in regards to sequential physiology of pain.
answer
Nociceptive impulses are carried to CNS
question
Describe the nociceptive response to stress.
answer
Arrival (in CNS) of nociceptive signals from PNS: Pain impulses (c-fiber) ascend (via lateral spinothalamic tract) to thalamus triggers: ↑ hypothalamus release of CRH->release of pituitary hormones. Hypothalamic signals to locus coeruleus-> ↑ production & release of NE.
question
Describe the inflammatory response to stress.
answer
Tissue damage incites immediate production & release of inflammatory mediators: Initiation of plasma defense systems: kinin, complement, coagulation Leukocyte adhesion, diapedisis, & release of chemotactic factors & inflammatory mediators Production & release of arachidonic acid metabolites.
question
Describe the endocrine response to stress.
answer
↑ catabolic hormones ∆ in anabolic hormones
question
Describe what occurs w/ carbohydrate metabolism d/t the stress response.
answer
Hyperglycemia, glucose intolerance, insulin resistance d/t ↑d glycogenolysis & gluconeogenesis ↓d insulin secretion & responsiveness
question
Describe what occurs w/ protein metabolism d/t the stress response.
answer
Muscle protein catabolism, ↑d synthesis of acute-phase proteins
question
Describe what occurs w/ fat metabolism d/t the stress response.
answer
↑d lipolysis & oxidation
question
Describe what occurs w/ fluid & e-lyte flux d/t the stress response.
answer
H20 & Na retention, K excretion, ↓d functional ECF
question
Describe when & why hypercoagulability occurs d/t the stress response.
answer
Throughout the peri-operative period-Virchow's Triad
question
How does pain and anxiety affect the surgical stress response?
answer
Compounds it.
question
What are the adverse effects of post-op pain on the pulmonary system?
answer
Atelectasis, V/Q mismatch, arterial hypoxemia, hypercapnia, pneumonia
question
What are the adverse effects of post-op pain on the CV system?
answer
HTN, tachycardia, myocardial ischemia, dysrhythmias
question
What are the adverse effects of post-op pain on the endocrine system?
answer
Hyperglycemia, Na & H20 retention, protein catabolism, K wasting
question
What are the adverse effects of post-op pain on the coagulation system?
answer
↑d platelet adhesiveness, ↓d fibrinolysis, hypercoagulability, DVT
question
What are the adverse effects of post-op pain on the GI/GU system?
answer
Ileus (d/t ↑d sympathetic output), urinary retention
question
How do spinals & epidural affect the response to surgical stress?
answer
Blunts peri-op stress hormones Blunts metabolic response
question
How do spinals & epidural affect the fluid e-lyte shifts d/t surgical stress?
answer
Complex relationship-↓ GFR; blunts stress hormones that cause Na & H20 retention & K excretion
question
How do spinals & epidural affect thermoregulation d/t surgical stress?
answer
Vasodilation predisposes to hypothermia
question
How do spinals & epidural affect platelet aggregation d/t surgical stress?
answer
Platelets-blunts ↑d aggregation (direct effects of LAs-inhibit ADP induced aggregation)
question
How do spinals & epidural affect factor VIII activity d/t surgical stress?
answer
Inhibits increased activity.
question
How do spinals & epidural affect fibrinolytic activity d/t surgical stress?
answer
Inhibits post-op inhibition
question
How do spinals & epidural affect plasminogen activity d/t surgical stress?
answer
Activity increased
question
How do spinals & epidural affect inhibition of leukocyte adhesion d/t surgical stress?
answer
Preservation of endothelial structure ↓ the inflammatory phase.
question
Describe immunocompetence
answer
Degree of post-op immunodepression is correlated w/ the amount of surgical trauma rather than type of anesthetic (exception-thermoregulation) Minimal effects
question
What is the primary stress hormone?
answer
Cortisol
question
What are the inflammatory mediators?
answer
Interleukins (IL) & tumor necrosis factor (TNF)
question
What does the Virchow triad include?
answer
1) Hypercoaguability 2) Endothelial damage 3) Venous stasis
question
What are the catabolic hormones that are released by the endocrine system?
answer
ACTH, cortisol, ADH, GH, catecholamines, renin, angiotensin II, aldosterone, glucagon, IL-1, IL-6
question
What are the anabolic hormone changes caused by the stress response?
answer
insulin ↓s, testosterone ↑s
question
What factors are involved in glyogenolysis?
answer
Epi, glucagon
question
What factors are involved in gluconeogenesis?
answer
Cortisol, glucagon, GH, epi, free fatty acids
question
What causes the ↑d synthesis of acute-phase proteins?
answer
↑d cortisol, epi, glucagon, IL-1, IL-6, TNF.
question
What causes ↑d lipolysis & oxidation?
answer
↑d catecholamines, cortisol, glucagon, GH
question
What causes H20 & Na retention, K excretion, ↓d functional ECF known as 3rd spacing & intracellular shift?
answer
↑d catecholamines, aldosterone, ADH, cortisol, angiotensin II, prostaglandins
question
What is Virchow's Triad and what is involved?
answer
Risk of thromboembolism & DVT Fibrinolysis- ↑d intra-op, ↓d post-op ↑d platelet aggregation
question
What are the stress hormones that are blunted by spinals and epidurals?
answer
Cortisol, RAAS, epi/NE, GH
question
What metabolic responses are blunted by spinals and epidurals?
answer
Hyperglycemia, ketosis
question
What causes shivering?
answer
Not necessarily d/t hypothermia: Protective reaction to cold environment (vasodilated pt) LA S.E.
question
What is the locus coeruleus
answer
A nucleus in the brainstem involved w/ physiologic responses to stree & panic.
question
With the anticipatory response to stress, how doe the prefrontal cortex signal the hypothalamus?
answer
Via the thalamus.
question
What is ↓d functional ECF known as?
answer
3rd spacing & intracellular shift
question
What innervates the kidneys?
answer
T10-L1
question
In regards to perception, where is nociceptive info processed?
answer
In the cerebral cortex prefrontal gyrus/cingulate gyrus.
question
In regards to modulation, where do interneurons modulate ascending impulses?
answer
In the substantial gelatinosa/periaqueductal grey matter.
question
In regards to modulation how does descending modulation occur?
answer
Via the corticospinal tract
question
Describe Amino Esters
answer
No i before the caine (only one i) Cocaine, procaine, chloroprocaine, tetracaine
question
Describe the amino amides
answer
All have i before caine (have two i's) Lidocaine, bupivicaine, mepivicaine, prilocaine, etidocaine, ropivicaine
question
Describe the chemical stability of esters and amides?
answer
Esters=unstable in solution (mix when used) Amides=extremely stable
question
Describe the site of action for esters & amides
answer
Na channels for both
question
Describe biodegradation of esters & amides
answer
Esters=break down in high temps, hydrolyzed by plasma cholinesterase to PABA Amides=enzymatic degradation in the liver
question
Describe the allergic potential of esters and amides
answer
Esters=PABA-para-amino benzoic acid causes allergic reactions Amides=very rare allergic reactions
question
Describe anesthetic potency of LAs
answer
Lipid solubility-varies w/ aromatic groups & pKa & pH of solution. Vasodilation of tissue redistribution The higher the octonal/buffer partition coefficient the more potent the LA
question
Describe latency of conduction blockade of LAs
answer
Correlated to the local pH, pKa & MW of the LA. Uncharged base forms diffuse more rapidly than charged cationic forms. pKa of LAs are higher than the surrounding pH-> ↑ ionized form. B(unionized) + H+ BH +
question
When pH ____pKa ionization is minimized.
answer
When pH > pKa ionization is minimized
question
What pH are most LAs stored at and why?
answer
5 or 6. ↑s the ionized form & improves stability for storage. Addition of epi ↓s the pH to 3 or 4
question
What are the effects of increasing the bathing solutions pH?
answer
Reduces the onset of duration, but risks precipitation of the LA.
question
What is the onset time clinically influenced by?
answer
Dose, concentration (chloroprocaine 3%)
question
What agents have a faster onset and why?
answer
Lido and mepivicaine, have a low pKa
question
What agents have a delayed onset and why?
answer
Procaine, chloroprocaine, tetracaine, have high pKas
question
What does the DOA correlate with?
answer
Degree of protein binding, peripheral vascular effects
question
Describe how the degree of protein binding affects the DOA
answer
The stronger the protein binding to the Na channels & other cytoplasmic or membrane proteins the longer the DOA.
question
Describe how the peripheral vascular effects affect the DOA
answer
The more vasodilation, the shorter the DOA. Prolong the effect by the addition of epi.
question
Epi has a more profound effect on which type of LAs?
answer
More profound if the drug is a vasodilator (tetracaine), & less profound if its a vasoconstrictor (ropivicaine)
question
What factors influence anesthetic activity?
answer
Needle has to be in right place (has to bathe the nerves you are aiming for) Dosage Site of injection/type of block Vasoconstrictors Carbonation (CO2) & pH adjustment (NaHCO#3) Mixtures of LAs Pregnancy
question
What are the effects of increases the dosage of LAs?
answer
More profound depth of block, prolongation of satisfactory anesthesia, ↓ in onset, more SE & risk of complications.
question
How can the dosage of LAs be increased?
answer
Administer a larger volume->more rapid absorption, more S.E. More concentrated solution (risky if BV entered) Mostly vasodilators at clinical dosage
question
What dosage of epi can be added to decrease the rate of vascular absorption?
answer
5 mcg/ml-epi 1:200000=5 mcg/cc
question
What are the effects of adding epi to LAs?
answer
↓ the rate of vascular absorption, more profound motor block, direct antinociceptive properties in the spinal cord, ↓s the pH to 3-4-> to formation of cationic forms of the LAs.
question
What are the effects of adding epi to bupivicaine, prilocain, and etidicaine?
answer
No effect
question
How does the site of injection/type of block influence anesthetic activity?
answer
Duration is dependent on location (intrathecal, SQ, brachial plexus block). Areas where LAs are more rapidly cleared have a shorter DOA. Central blocks have more rapid clearance than peripheral blocks.
question
Describe how pregnancy influences anesthetic activity.
answer
The spread & depth of spinal & epidural anesthesia are enhanced during pregnancy Venous dilation ↓s the capacitance of the epidural & subarachnoid spaces Hormonal factors-progesterone levels elevated
question
What is vascular absorption dependent on?
answer
Injection site, dosage/volume, addition of a vasoconstrictor
question
The degree of addition of a vasoconstrictor is ____ ____ to the intrinsic vasodilatory effects of the LA.
answer
Directly proportional
question
What agent has intrinsic vasoconstrictor effects?
answer
Ropivicaine
question
How does injection site affect absorption?
answer
Highest venous plasma levels to lowest. Intercostal>paracervical>caudal>lumbar epidural>brachial plexus>subarachnoid>subcutaneous
question
Describe the two-three compartment model.
answer
Alpha phase-uptake by rapid equilibration of tissue Beta phase-distribution of slowly equilibrating tissues, biotransformation & excretion
question
Describe biotransformation & excretion of amino esters
answer
Plasma cholinesterases hydrolyze the esters making PABA Excreted by kidney
question
Describe biotransformation & excretion of amino amides
answer
Metabolized mainly by the liver. Rate is inversely r/t protein binding-hepatic extraction ratio. Excreted by the kidney (pH dependent)
question
What patient characteristic could influence the disposition of LAs?
answer
Patient age
question
What is elimination of LAs influenced by?
answer
Individual patients hepatic, renal, & cardiac status.
question
What are the S/S and causes of CNS toxicity in the initial phase?
answer
Tinnitus, lightheadedness, confusion, circumoral numbness. High blood flow areas.
question
What are the S/S and causes of CNS toxicity in the excitation phase?
answer
Shivering, muscular twitching & tremors, tonic-clonic seizures. Inhibition of inhibitory pathways in the cerebral cortex.
question
What are the S/S and causes of CNS toxicity in the depression phase?
answer
Unconsciousness, CNS depression, respiratory arrest. Inhibition of inhibitory and facilitatory pathways.
question
What causes CV toxicity?
answer
Alter electrical acitivity Alter muscular activity
question
How does altered electrical activity cause CV toxicity?
answer
Exacerbated by hypoxia, acidosis, hypercapnia: Bupivicaine (fast in, slow out)-depresses rapid phase of AP->unidirectional blockade->reentrant dysrhythmias
question
How does altered muscular activity cause CV toxicity?
answer
Dose related negative isotropy, exacerbated by hypercapnia, acidosis, & hypoxia, r/t binding Na & Ca channels.
question
What are the S/S of CV toxicity in the initial phase?
answer
HTN, tachycardia during CNS excitation
question
What are the S/S of CV toxicity in the intermediate phase?
answer
Myocardial depression, ↓d CO, mild-moderate hypotension
question
What are the S/S of CV toxicity in the terminal phase?
answer
Peripheral vasodilation, profound hypotension, SB, conduction defects, ventricular dysrhythmias, circulatory collapse.
question
What factors enhance CV toxicity?
answer
Specific agents (bupivicaine CV/CNS toxicity highest), pregnancy (higher toxicity w/ bupivicaine), acidosis, hypoxia.
question
What LA causes local tissue toxicity, what are the S/S of local tissue toxicity & why?
answer
Chloroprocaine, muscle damage, back pain. Due to preservatives: bisulfate, EDTA.
question
Besides prilocaine, what other LAs can produce methemoglobinemia?
answer
Cetacaine, benzocaine, lido
question
What causes the allergic reactions associated w/ LAs?
answer
PABA in esters, methylparaben in multi dose amides
question
What is cocaine and what is it used for?
answer
An ester, used topically for anesthesia & vasoconstriction (awake nasal intubation).
question
Why is procaine rarely used?
answer
Short duration, slow
question
Describe chloroprocaine
answer
Rapid onset low toxicity, used for fast onset epidurals, renders bupivicaine ineffective, muscle spasm w/ high doses.
question
What is tetracaine used for?
answer
Long duration spinals, epi prolongs spinal block
question
Describe lidocaine
answer
Widely used, good for everything, cauda equina syndrome/TNS seen w/ 5 % spinals.
question
Describe mepivicaine
answer
Similar to lidocaine, less toxic (less vasodilation), not effective topically, metabolism very slow in fetus & newborns.
question
Describe prilocaine
answer
Least toxic, useful in IVRA (bier block), methemoglobinemia.
question
Describe bupivicaine
answer
Used for everything but topical and IVRA, differential blockade, cardiac toxicity.
question
Describe etidocaine
answer
Rapid onset long duration, dense muscle block
question
Describe robivicaine
answer
S-isomer, similar to bupivicaine, less CV toxic
question
What is the disadvantage of cocaine?
answer
High toxicity, addictive potential
question
What is the disadvantage of chloroprocaine?
answer
May render bupivicaine & epidural ineffective, toxicity d/t pH, bisulfate, & EDTA
question
What is a disadvantage of tetracaine?
answer
Motor block outlast sensory
question
The spinal canal runs from the ____ _____ to the _____ _____.
answer
Foramen magnum sacral hiatus
question
Where does the spinal cord begin?
answer
At the medulla oblongata
question
Where does the spinal cord end?

answer
L1-2 conus medullaris->cauda equina
question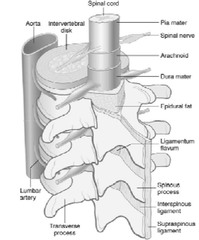
What is the primary site for neuraxial anesthesia?

answer
The lumbar vertebral column
question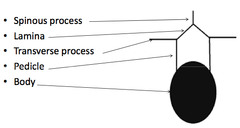
Describe the bony anatomy of the vertebrae

answer
Anterior-vertebral body, disc Posterior-ring containing the spinal cord-body, fascicles, laminae
question
What attaches to laminae superiorly & inferiorly?
answer
Ligamentum flavum
question
What is found in the epidural space?
answer
Epidural fat, blood vessels (epidural veins), nerve roots (spinal nerves)
question
Describe the dura mater
answer
Outer most layer covering the spinal cord
question
What is the dura mater attached to?
answer
Attached superiorly to the foramen magnum
question
Where does the dura mater end?
answer
Inferiorly it ends at the S1-S2 vertebra
question
What covers spinal nerves?
answer
Dura mater
question
Where do the spinal nerves exit?
answer
Via the intervertebral foramina (in pedicles)
question
Where do spinal nerves enter?
answer
The paravertebral space
question
The meninges consist of 3 layers, name them.
answer
Dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
question
The sympathetic are part of the _______ system.
answer
thoracolumbar system
question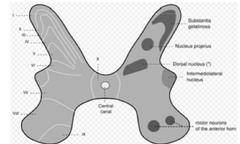
Describe the thoracolumbar system

answer
Sympathetic nerve fibers run thru the intermediolateral cell column of T1-L2 & consist of preganglionic beta fibers.
question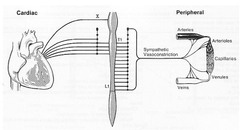
What vertebral levels are the cardiac accelerators?

answer
T1-T4 (T5)
question
Efferents at every level contribute to ____ ____->sympathectomy causes _______ in proportion to the ______ of ______ blocked.
answer
vasomotor tone vasodilation # of dermatomes blocked
question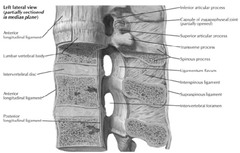
What are the 4 major structural ligaments of the spinal column?

answer
Posterior to anterior Supraspinous ligament Interspinous ligament Ligamentum flavum Posterior longitudinal ligament
question
What does spinal cord consist of?
answer
An outer white matter & middle gray matter
question
What does the gray matter consist of
answer
Shaped like a butterfly Consists of anterior, lateral, & dorsal horns
question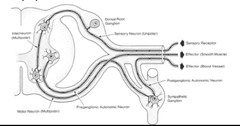
Sympathetics exit via ____ ____ then enter the ____ _____ ____.

answer
spinal nerves lateral sympathetic chain
question
Why nerve fibers are involved in sympathetically mediated pain?
answer
Afferents (sensory)
question
How do the afferent nerves affect the SNS?
answer
Activated by stretching, ischemia, & inflammation
question
What is the only parasympathetic nerve that innervates the heart?
answer
Vagus
question
What parasympathetic nerves are affected by epidural blockade?
answer
Only sacral S2-4
question
What parasympathetic nerves are not affected by epidural blockade?
answer
Cranial nerves (vagus, oculomotor, facial, glossopharyngeal, & accessory)
question
Spinal or epidural above _______ leads to increased risk of trauma to spinal cord.
answer
L1-L2 Must go below
question
Why is it safer to place a spinal or epidural below L1-2?
answer
Cauda equina nerves freely float in CSF = not easily traumatized
question
Why is the lumbar epidural the most commonly performed block?
answer
Easiest approach d/t near horizontal spinous processes, ligamentum flavum thick in comparison to thoracic, bigger interspaces
question
What disease process causes difficulty in regards to a lumbar epidural?
answer
Osteoarthritis
question
What is the most common injection site in a lumbar epidural and why?
answer
L3-4 Larger interspaces
question
How do spinal nerves that come off the spinal cord innervate the body?
answer
In a dermatomal fashion
question
What do dermatomes correspond with?
answer
The level at which the nerves exit the spinal cord, they don't correspond w/ peripheral nerves
question
In regards to dermatomes blocking what level leads to hand numbness?
answer
C6, 7, 8
question
In regards to dermatomes what level affects below the clavicle?
answer
T1
question
In regards to dermatomes what level affects the nipple line?
answer
T4
question
In regards to dermatomes what level affects the xiphoid process?
answer
T6
question
In regards to dermatomes what level affects the umbilical level?
answer
T10
question
In regards to dermatomes what level affects the ilio-inguinal level?
answer
L1
question
In regards to dermatomes what level affects the pubic rectal area?
answer
S2-4
question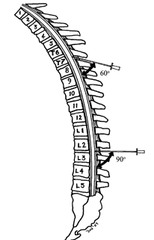
At what level do spinous process meet their maximal angulation?

answer
T7 (60˚ angle)
question
Where is the site of action of epidurals & why is this important?
answer
Peripheral cord Spinal nerve roots, the LA has to cross all 3 layers of meninges = slower onset than spinals
question
What layer of meninges acts as a major barrier to diffusion in epidurals and what is its effects?
answer
Arachnoid-epidurals set up slower than spinals
question
What is the mechanism of epidural blockade?
answer
Spread of local in the epidural space (bidirectional spread) Crosses meninges
question
Describe a differential blockade w/ epidurals.
answer
Lower concentrations block sympathetic & sensory fibers while leaving proprioception & motor intact.
question
What are CV effects dependent on?
answer
Dose & level obtained
question
At what level would adrenal afferents be knocked out and what is the effects?
answer
T6-L1; increased vagal tone->blunts HR response
question
What factors cause a decrease in arterial pressure?
answer
↓ peripheral resistance ↓ CO d/t ↓d venous return & T1-T5 blocked-> ↓d HR & contractility ↓ in central venous pressure d/t venodilation
question
What is the major factor causing a decrease in arterial pressure and why?
answer
↓ CO d/t venodilation causing ↓ venous return Also blocks T1-5
question
How does arterial vasodilation & ↓ BP affect limb blood flow?
answer
Limb BF below the block is improved Limb BF above the block is reduced
question
At what level are CV effects of neuraxial blockade at maximal level?
answer
T1 (after T1 will result in profound bradycardia)
question
Arterial vasodilation but local compensation: Only ____-____% ↓ total vascular resistance. Mean arterial pressure only ↓ ___-____% even w/ high block provided CO maintained.
answer
15-18% 15-18%
question
Venodilation may be maximal May be ____ ____ w/ changes in posture. What do pooling effects lead to?
answer
venous pooling ↓ preload & CO
question
What is CO determined by? May be normal if ______ & _____ ____ _____ ____.
answer
Preload May be normal if normovolemia, & legs above heart level.
question
What happens to the HR w/ a T1-T4 block?
answer
Decreases
question
What happens to HR if RA pressure is decreased?
answer
Decreases (usually ↓ 10-15% unless T1 block or ↓↓ RA pressure)
question
What is the key to preventing a decrease in HR?
answer
Volume loading
question
If a patient c/o nausea what could be the cause and how should it be treated?
answer
↓ BP-ephedrine
question
Describe how neuraxial blockade can effect the respiratory system.
answer
Rare. Can block the phrenic nerve if C3C4 blockade ("high spinal"). Chest wall heaviness common - Intercostal muscles segmentally innervated - Lack of sensation (proprioception).
question
Describe how neuraxial blockade can effect the GI system.
answer
Unopposed vagal tone-> ↑ in GI motility ↓ incidence of colonic anastomotic dehiscence d/t improved BF
question
What are the indications for epidural blockade?
answer
Surgical anesthesia, relief of acute & chronic pain
question
What procedures are associated w/ acute pain and would be relieved w/ epidurals?
answer
OB, post-op pain, fractured ribs, etc...
question
Epidurals block ____ & _____ at the level of the nerve root.
answer
Afferents & efferents
question
How should an epidural be placed in order to minimize SE & maximize therapeutic effects?
answer
Should be placed at the center of the dermatome providing the maximal stimulation. Epidurals provide segmental analgesia->spreads from a central area where they are placed then cephalic & caudal.
question
What are the advantages of epidurals in OB?
answer
Sympathectomy early ↑ing UBF (if BP maintained) Motor blockade can be minimized Continuous dosing Lower body only 2nd stage labor (S2-4) needs deeper block (need larger volume) Easy to convert for c-section Advantage in certain OB complications ↓ the BP on pre-eclamptic pts
question
What are the absolute contraindications for epidurals?
answer
Hypovolemia, ↑d ICP, infection at site, septicemia, hypocoagulation states, patient refusal (assault), critical AS
question
Why is it contraindicated to perform an epidural on a pt w/ critical stenosis?
answer
Restrict the ability of the ♥ to ↑ CO as compensation for hypotension d/t the sympathectomy induced by neuraxial anesthesia. In these circumstances, the hypotension can become refractory to tx.
question
What are the relative contraindications for epidurals?
answer
Severe AS (need a-line) Chiari malformation & cerebral aneurysms (risk occurs w/ wet tap) Degenerative spine ds w/ neurologic findings (sciatica, foot drop, etc) Unstable neurologic ds Spine pathology (prior sx, severe scoliosis)
question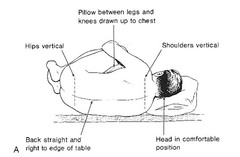
What is the most common approach for epidurals?

answer
Lumbar midline approach-pt in upright or lateral position.
question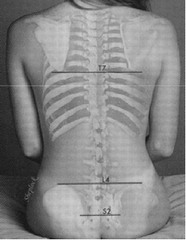
____ _____ is at L4 spinous process.

answer
Iliac crest
question
What level is the best place for epidurals?
answer
L3-4
question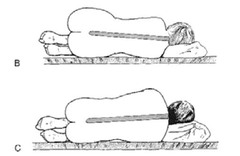
What factors need to be considered in regards to lateral positioning in men & women, especially w/ spinals?

answer
Women have larger hips->will cause hyperbaric LA to travel more cephalad Men have broader shoulders->higher chance of inadequate spinal
question
What techniques are used in neuraxial anesthesia?
answer
Paramedian lumbar & thoracic approach Midline thoracic approach Cervical approach Caudal approach
question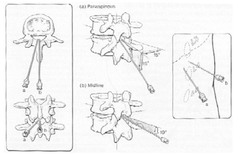
Describe the paramedian approach

answer
Bypasses the supraspinous & interspinous ligaments->resistance can be boggy until ligamentum flavum is engaged.
question
What are the 2 risks involved w/ epidurals and how can it be prevented?
answer
Accidental intrathecal or intravascular injections. Test dose
question
What drugs and dosages are used w/ epidural test doses?
answer
1.5% lido w/ epi 1:200,000 3cc = 45mg lido + 15 µg epi Allow enuf time (sensory check)
question
Why should each dose of an epidural be treated as a test dose?
answer
Catheters can migrate intrathecally after a negative test dose->need to aspirate & don't give big doses as a bolus = high spinal
question
What level should be blocked for labor analgesia?
answer
L2-L4
question
What level should be blocked for hip/knee surgery?
answer
L2-L4
question
What level should be blocked for laparotomy under GA?
answer
T8-T10
question
What level should be blocked for a thoracotomy or fractured ribs?
answer
At relevant interspace usually T5-T7
question
What is the MOA of duramorph?
answer
↓ substance P mediated transmission from A-delta & C fibers by ↓ing presynaptic Ca influx & hyperpolarizing the 2nd order ascending nerve by ↑ing K conductance->suppresses expansion of nociceptive field of 2nd order neuron-> ↓s c-fos expression.
question
What is the DOA of duramorph?
answer
Long-24˚
question
What are the disadvantages of duramorph?
answer
Slow onset-1.5-3˚ Can cause delayed respiratory depression up to 12˚
question
What are the differences between duramorph & lipid soluble opioids?
answer
Duramorph spread more = > risk for CNS SE
question
What are the advantages of lipid soluble opioids?
answer
Quick onset, low risk of respiratory depression (less dermatomal spread)
question
What are the disadvantages of lipid soluble opioids?
answer
Short DOA, must be injected near the site of action (d/t less dermatomal spread), rapid systemic absorption
question
What are the S.E. of neuraxial opioids?
answer
Respiratory depression (may be delayed 8-12˚), N&V, pruritis, urinary retention, ↓ GI motility (less than w/ IV)
question
Why does urinary retention occur w/ neuraxial opioids?
answer
Due to inhibition of sacral parasympathetics
question
Describe why pruritis occurs w/ neuraxial opioids and how its treated.
answer
Mu receptor, peripheral histamine release Antihistamines have limited efficacy, narcotic agonist/antagonist best-naloxone
question
How does addition of epi affect neuraxial blockade?
answer
Vasoconstriction-> ↓d uptake of LAs, prolongs block, ↓d spinal cord BF, intensifies motor block, direct α-2 mediated antinociceptive effects on 1˚ afferents & descending pathways.
question
How does addition of phenyephrine affect neuraxial blockade?
answer
Vasoconstrictor->prolonged block, ↓d uptake May ↑ risk of TNS
question
Describe effects of adjuvant clonidine & neuraxial blockade
answer
Inhibit A-delta & C fiber afferents by ↑d K conductance Rapid systemic absorption->peripheral inhibition of norepi release
question
Describe effects of adjuvant neostigmine & neuraxial blockade
answer
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor-> ↑ Ach, stimulates receptors in substantia gelatinosa
question
What is a disadvantage of neostigmine?
answer
High incidence of nausea
question
Describe effects of adjuvant ketamine & neuraxial blockade?
answer
Non-competitive NMDA atagonist-> ↓s central sensitization "wind up"
question
Describe effects of adjuvant ketorolac & neuraxial blockade?
answer
COX inhibitor (NSAID)->under investigation, may enhance opioid & clonidine analgesia
question
What patients cannot be sedated prior to epidural blockade?
answer
OB pts
question
Between ephedrine & phenylephrine which is a better choice in treatment of hypotension & why?
answer
Ephedrine best (↑ preload & CO) Phenylephrine (↑ afterload)
question
Why is atropine a poor choice in the treatment of hypotension?
answer
↑ HR & MVO2
question
What factors affect the spread of LAs in the epidural space?
answer
Rapidity of dose (>), volume injected (>), placement of catheter, position, unique epidural anatomy (prior sx, spinal stenosis, pregnancy, ht)
question
Describe the difference in subarachnoid block vs epidural block.
answer
Dura & arachnoid intentially punctured, smaller needle gauge, pencil point needles (less risk of PDPH), introducer needles used.
question
Why are introducer needles used w/ subarachnoid blocks?
answer
Due to smaller needle gauge (25-27 ga), prevents skin "coring" & provides rigidity.
question
Where are spinals performed?
answer
Below L2-3->spinals above L2-3 carry the additional risk of direct trauma to the cord (iatrogenic syringomyelia) or the posterior spinal artery.
question
With a subarachnoid block where is the drug deposited?
answer
Into the CSF
question
How are spinals performed?
answer
Single shot
question
With a subarachnoid block what determines the level?
answer
Baricity & positioning
question
Describe onset of the subarachnoid block
answer
Rapid->LA doesn't have to diffuse across dura & arachnoid->rapid sympathectomy
question
What are the advantages of a subarachnoid block?
answer
Lower dose of LA needed, slower absorption of LA Both decrease risk of systemic toxicity
question
Where do subarachnoid blocks work?
answer
Directly on nerve roots & spinal cord (Virchow-Robin spaces)
question
What factors affect the distribution of subarachnoid anesthetics?
answer
Relative baricity of LA, position, volume inj, level where spinal was placed, rapidity of inj
question
How does the rapidity of the injection affect the aubarachnoid block?
answer
Provides good mixing w/ the CSF->causes turbulence
question
____ is duration. ____ determines the level.
answer
Dose is duration Positioning determines the level
question
Compare epidural vs spinal blockade
answer
Covering the nerves-onset Location of action Differential blockad-more difficult w/ spinals Dermatomal spread Density differences
question
What dermatome level is necessary for upper abdominal surgery w/ a spinal?
answer
T4-T5 (nipple)
question
What dermatome level is necessary for intercostal sx (including appy, gynecologic pelvic sx, & ureter & renal pelvic sx) w/ a spinal?
answer
T6-T8 (xiphoid)
question
What dermatome level is necessary for a TURP, obstetric vaginal delivery, & hip sx w/ a spinal?
answer
T10 (umbilical)
question
What dermatome level is necessary for TURP, if no bladder distention; thigh sx; lower limb amputations w/ a spinal?
answer
L1 (inguinal ligament)
question
What dermatome level is necessary for foot surgery w/ a spinal?
answer
L2-L3 (knee & below)
question
What dermatome level is necessary for perineal surgery, hemorrhoidectomy, anal dilation w/ a spinal?
answer
S2-S5 (perineal)
question
When a spinal is done & the pt is laid completely flat where does the LA usually spread & why?
answer
T4, it's a little above the bottom of the thoracic kyphosis (most dependent portion of the thoracic spine)
question
How is the epidural space identified?
answer
With loss of resistance
question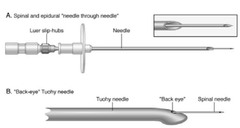
How is a combined spinal-epidural performed?

answer
Epidural space identified, subarachnoid block then performed by inserting a spinal needle thru the Touhy/modified Touhy, epidural catheter is then inserted via the Touhy
question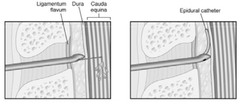
What are the advantages of a combined spinal-epidural?

answer
Offers the advantages of rapid onset & dense block of a spinal & the flexibility of redosing via an epidural catheter.
question
After the subarachnoid block is performed, the epidural must be threaded & secured expeditiously so the pt may be positioned to allow proper spread of the subarachnoid LA, what would occur if the pt remained seated too long?
answer
A saddle block would result
question
When dosing the epidural after spinal block, the epidural exerts a ____ ___ on the epidural space, this will push the spinal level _____ than expected for simple epidural dosing.

answer
mass effect higher
question
When dosing an epidural after a dural puncture, some local will leak thru the puncture site, what does this result in?

answer
Some degree of subarachnoid block.
question
Describe the complications associated w/ neuraxial anesthesia
answer
Systemic toxicity (less w/ spinals), accidental IV dosing (rare w/ spinals-very placement w/ asp of CSF)
question
What are the S/S of a high spinal?
answer
High level of sensory & motor blockade, C3-5 paralysis (respiratory arrest), hypotension & apnea.
question
How are high spinals treated?
answer
ABCs - epi early
question
Describe the subdural/epiarachnoid space
answer
Potential space between the dura & arachnoid
question
What occurs w/ an accidental subdural/epiarachnoid blockade?
answer
Unusual presentation-patchy block, high level block, hypotension, respiratory depression, unilateral/bilateral
question
How is an accidental subdural/epiarachnoid blockade treated?
answer
Supportive
question
When does high epidural blockade occur?
answer
With large volumes
question
How is a high epidural blockade treated?
answer
Supportive, usually resolves w/in 30 minutes
question
How is a high epidural blockade prevented?
answer
Incremental dosing
question
What are the symptoms of a dural puncture?
answer
HA (positional in nature) can be severe-occiput distribution, CN involvement
question
What can a dural puncture cause?
answer
Subdural hematoma or ICH
question
How is a dural puncture treated?
answer
Conservative-IV fluids, rest, caffeine, epidural blood patch
question
What is the success rate of the epidural blood patch?
answer
90-95% provides immediate relief
question
When should the blood patch be performed?
answer
Sooner the better, no coagulopathy
question
How does the blood patch work?
answer
Mass effect in epidural space-> ↑ in ICP, blood clots cause a temporary seal
question
How is the blood patch performed?
answer
Strict sterile technique, same as epidural, draw 20cc of blood from the pt, inject w/o causing pain (nl pressure)
question
What are the common complaints of pts while receiving blood patches?
answer
Low grade fever, back spasm, radiculopathy, sore back.
question
What are the common discharge orders after a blood patch?
answer
No lifting for 2 wks, no heavy exercise, tylenol/motrin for pain, heating pad & massage to lumbar musculature, notify MD if radiculopathy, high fever or return of pain
question
What are the causes of neurologic damage?
answer
Trauma, anterior spinal artery thrombosis, adhesive arachnoiditis, spinal cord compression, injection of a neurolytic agent (accidental, drug toxicity)
question
What should raise a red flag w/ trauma in regard to neurologic damage?
answer
Parasthesias
question
Describe anterior spinal artery thrombosis.
answer
Rare but catastrophic, rapid, painless permanent paraplegia
question
How is adhesive arachnoiditis caused and what are the S/S?
answer
Injection of wrong drug (preservatives, betadine, other into CSF) Chronic pain Paraplegia possible
question
What causes spinal cord compression, how is it diagnosed & treated?
answer
Epidural hematoma/abscess MRI Immediate decompression laminectomy
question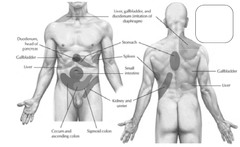
Organotomes spinal level for stomach and site of referred pain.

answer
T5-9 Epigastric or LEFT hypochondrium
question
Organotomes spinal level for duodenum and site of referred pain.
answer
T5-8 Epigastric or RIGHT hypochondrium
question
Organotomes spinal level for jejunum and site of referred pain.
answer
T6-10 Periumbilical
question
Organotomes spinal level for ileum and site of referred pain.
answer
T7-10 Periumbilical
question
Organotomes spinal level for cecum and site of referred pain.
answer
T10-11 Periumbilical or RLQ
question
Organotomes spinal level for appendix and site of referred pain.
answer
T10-11 Periumbilical, then to right iliac fossa
question
Organotomes spinal level for ascending colon and site of referred pain.
answer
T10-12 Periumbilical or right lumbar
question
Organotomes spinal level for sigmoid colon and site of referred pain.
answer
L1-2 LLQ
question
Organotomes spinal level for spleen and site of referred pain.
answer
T6-8 Left hypochondrium
question
Organotomes spinal level for liver & gallbladder and site of referred pain.
answer
T6-T9 Epigastric-later to right hypochondrium
question
Organotomes spinal level for pancreas and site of referred pain.
answer
T7-9 Inferior epigastrium
question
Organotomes spinal level for kidney and site of referred pain.
answer
T10-L1 Small of back, flank
question
Organotomes spinal level for ureter and site of referred pain.
answer
T11-L1 Loin to groin
question
Concerning the addition of epinephrine to a neuraxial block which statement is INCORRECT: a. increases systemic uptake of local anesthetics b. intensifies motor block c. decreases spinal cord blood flow d. direct alpha-2 antinociceptive effects on primary afferents and decending pathways e. decreases pH of local anesthetic solution
answer
a. increases systemic uptake of local anesthetics
question
The Superior Laryngeal Nerve (SLN) and Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve (RLN) are branches of which cranial nerve? Choose one answer. a. IX-Glossopharyngeal nerve b. VIII-Vestibulocochlear nerve (aka auditory-vestibular nerve) c. X-Vagus nerve d. IV-Trochlear nerve e. phrenic nerve
answer
c. X-Vagus nerve
question
T/F Hyperbaric solutions sink to the dependent portions of the subarachnoid space.
answer
True
question
T/F A paravertebral block is performed at the level of the spinal nerve root.
answer
True
question
Which statement is incorrect in regards to the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII)? a. None of these answers are correct b. Supplies taste and sensation to anterior tongue c. Passes through the sublingual salivary gland d. Supplies motor function to muscles of facial expression e. Exits the skull via the stylomastoid foramen
answer
c. Passes through the sublingual salivary gland
question
T/F The substantia gelantinosa contains a high concentration of opioid receptors.
answer
True
question
For an intercostal nerve block, what needle insertion approach has a greater risk for pneumothorax? a. paravertebral b. lateral c. Inferior-vertebral d. Superior-lateral e. anterior midline
answer
b. lateral
question
Which of the following is NOT a side effect of neuraxial opioids? Choose one answer. a. respiratory depression b. puritis c. nausea and vomiting d. increased GI motility e. urinary retention
answer
d. increased GI motility
question
A combined spinal-epidural is performed in the sitting position. If too much time elapses between injection of the hyperbaric marcaine into the subarachnoid space and positioning the patient supine, the likely result is: Choose one answer. a. astigmatism b. a Saddle Block c. Dural puncture headache d. a Bier Block e. Cauda Equina Syndrome
answer
b. a Saddle Block
question
Why is the presence of a cerebral aneurysm a relative contraindication for placement of an epidural catheter? a. Patients with aneurysms have high ICPs which would contraindicate an epidural b. Patients with aneurysms have coagulopathies c. Aneurysms cause a decrease in afterload and if the epidural accidentally went intrathecal, the patient would receive a high spinal d. This is an unstable neurologic state e. An accidental dural puncture would cause a rapid decrease in ICP thereby increasing the transmural pressure gradient across the aneurysm increasing risk of rupture
answer
e. An accidental dural puncture would cause a rapid decrease in ICP thereby increasing the transmural pressure gradient across the aneurysm increasing risk of rupture
question
Oculocardiac reflex can lead to which of the following: Choose one answer. a. asystole b. dysrhythmias c. All of these are correct d. None of these answers are correct e. bradycardia
answer
c. All of these are correct
question
Which statement about lipid soluble neuraxial opioids is INCORRECT: Choose one answer. a. produce quick onset of action b. have short duration of action c. high risk for respiratory depression d. rapid systemic absorption e. limited dermatomal spread
answer
c. high risk for respiratory depression
question
The spinal cord ends at the following level: Choose one answer. a. L4-S2 b. T10-T11 c. L1-L2 d. S2-S4 e. T10-T12
answer
c. L1-L2
question
T/F Paravertebral and intercostal blocks provide relief from somatic pain.
answer
True
question
Preoperative management of an epidural block includes all of the following EXCEPT: a. Be prepared for any disaster b. Discuss and obtain consent c. Position & sedate if applicable d. Monitor the patients e. All of the above must be considered
answer
e. All of the above must be considered
question
Which of the following is not found in the epidural space? Choose one answer. a. Nerve roots b. Blood vessels c. Fat d. all of these are found in the epidural space e. Cerebrospinal fluid
answer
e. Cerebrospinal fluid
question
The meninges are composed of 3 layers. Which of the following is in the correct order starting with the outermost layer? Choose one answer. a. Arachnoid mater, dura mater, pia mater b. Dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater c. Dura mater, pia mater, arachnoid mater d. Pia mater, arachnoid mater, dura mater e. Whatsa mater, aintgonna mater, tow mater
answer
b. Dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
question
T/F The addition of phenylephrine to neuraxial blockade may increase the risk of TNS?
answer
True
question
Which of the following is not a complication or side effect of a Cervical Plexus block? Choose one answer. a. Hoarseness b. Hemidiaphramatic paralysis c. All of the above are potential side effects or complications of cervical plexus block d. Total Spinal e. Seizures
answer
c. All of the above are potential side effects or complications of cervical block
question
T/F The substantia gelatinosa (lamina II) receives input from A-delta and C-fibers?
answer
True
question
Which of the following is an advantage of a periorbital block versus a retrobulbar block. Choose one answer. a. Less failure rate b. Less expensive c. Less complications d. None of these answers are correct e. Less volume of local anesthetic is needed
answer
c. Less complications
question
Which of the following borders the epidural space posteriorly? Choose one answer. a. The posterior longitudinal ligament b. The dura mater c. The supraspinous ligament d. The subarachnoid space e. The ligamentum flavum
answer
e. The ligamentum flavum
question
Which of the following is a major diffusion barrier for epidurals? Choose one answer. a. The pia mater b. The arachnoid mater c. The subdural space d. cerebrospinal fluid e. The dura mater
answer
b. The arachnoid mater
question
Which of the following dermatome levels is improperly matched? Choose one answer. a. T6 : Xyphoid Process b. T4 : Nipple Line c. T1 : Below clavicle d. L1 : Umbilical Level e. L3 anterior knee
answer
d. L1 : Umbilical Level
question
T/F Preganglionic sympathetic nerves enter the lateral chain upon leaving the spinal cord?
answer
True
question
Which landmark would be located for a superior laryngeal nerve block? Choose one answer. a. The hyoid bone b. The mastoid process c. The cricothyroid membrane d. The junction of the sternum and clavicle
answer
a. The hyoid bone
question
Which of the following is not a contraindication for an epidural? Choose one answer. a. The patient has a platelet count of 93,000 b. The patient has road rash over their entire back c. The patient's ICP is 5 mmHg d. The patient refused the epidural e. Last dose of plavix 4 days ago
answer
c. The patient's ICP is 5 mmHg
question
After performing a combined spinal-epidural, extra caution is needed when dosing the epidural catheter because of which factors? Choose one answer. a. The compression of the subarachnoid space by the local anesthetic in the epidural space can raise the neuraxial level quickly. b. A small amount of medication leaking through the dural puncture from the epidural to the subarachnoid space. c. None of these answers are correct d. 2 of these answers are correct e. Mass effect from the volume of local anesthetic in the subarachnoid space causes greater spread of the epidural medication.
answer
a. The compression of the subarachnoid space by the local anesthetic in the epidural space can raise the neuraxial level quickly.
question
The epidural space extends from ____ ____ ____ to _____ ____.
answer
base of skull to sacrococcygeal membrane
question
In adults, ___-____ mL of LA per segment to be blocked.
answer
1-2 mL (i.e. want a T4 sensory level from an L4-5 injection site - 12 segments to reach T4 (12 x 1-2 mL/segment = 12-24 mL)
question
What LAs have a fast onset & short durations?
answer
Chloroprocaine & prilocaine
question
What LAs have an intermediate onset?
answer
Lidocaine & mepivicaine
question
What LAs have a slow onset & long duration?
answer
Bupivicaine & ropivicaine
question
What are the 2 mechanisms of epidurally-produced conduction block?
answer
The LA acts directly at the nerve roots & dorsal ganglia beyond the dura after diffusing thru the intervertebral foramen The LA acts on the dorsal & ventral rootlets & SC after diffusing across the dura & arachnoid The LA also diffuses thru the CSF & into the SC
question
For intrathecal (spinal) or epidural anesthesia, LAs act on ___ ___, ____ ___, & the _____ _____.
answer
nerve roots nerve rootlets spinal cord
question
List in order which nerves are blocked following epidural administration of a LA.
answer
B fibers (preganglionic sympathetic efferents) C & A-delta fibers (pain, tempurature, & touch afferents-postganglionic sympathetic neurons) A-gamma A-beta A-alpha
question
Explain the differential nerve blockade
answer
Small-diameter nerve fibers are found close to the nerve root surface (shortens the diffusion path of LAs) The diffusion path to the large-diameter fibers is longer (situated deep to the nerve bundle)
question
What fibers see the greatest concentration of LAs 1st?
answer
B fibers then C fibers
question
What family of fibers receives a lesser concentration of LAs & what is the importance of this?
answer
A They are VERY sensitive
question
List the nerve fibers in order of sensitivity.
answer
Large myelinated > smaller myelinated > unmyelinated (large myelinated fibers require less LA to be blocked)
question
List in order the structures the needle passes through for an epidural block.
answer
Skin SC tissue Supraspinous ligament Interspinous ligament Ligamentum flavum Epidural space
question
Distance from skin to epidural space in an average adult.
answer
4-6 cm
question
Distance from skin to epidural space in an obese individual.
answer
Up to 8 cm
question
Distance from skin to epidural space in a thin person.
answer
3 cm
question
What is the most sensitive indicator of initial onset of sensory block?
answer
Alcohol swab to assess loss of temperature sensation
question
What is the most ACCURATE assessment of overall sensory block?
answer
The pinprick
question
What factors affect sensory block?
answer
Site of injection & nerve root size
question
What are the most common complications of epidural blockade?
answer
Penetration of a blood vessel Intravascular catheterization
question
Why is a test dose performed after satisfactory placement of the epidural catheter?
answer
It detects subarachnoid & intravascular injection
question
How far is the epidural catheter threaded into the epidural space?
answer
4 cm
question
Advantages of spinal vs. epidural anesthesia
answer
Takes less time to perform Rapid onset Sensory & motor block quality is better Pain during sx is less
question
Advantages of epidural vs. spinal anesthesia
answer
Less risk of PDPH Less hypotension Can prolong block w/ catheter Catheter can be used for postop pain management
question
Anatomy of the caudal epidural block
answer
Sacrum: triangular bone consisting of 5 fused sacral vertebrae
question
What membrane is penetrated during a caudal epidural?
answer
The sacrococcygeal membrane
question
What is the most common postop complaint w/ a caudal epidural?
answer
Pain at the injection site
question
What is the 2nd most common postop complaint w/ a caudal epidural?
answer
Urinary retention
question
Dosages for caudal epidural block in adults
answer
S5-L2 15-20 mL S5-T10 25 mL
question
Dosages for caudal epidural block in children
answer
0.5-1.0 mL/kg of 0.125% to 0.25% bupivicaine Chloroprocaine 1 mL/kg as bolus; o.3 mL/kg until desired level is met (kids calm down & pinch test)
question
Cervical plexus
answer
C1-C5
question
Phrenic nerve
answer
C3-C5 w/ C4 making major contribution
question
Brachial plexus
answer
C5-C8, T1
question
Advantages of the axillary block
answer
Provides anesthesia for sx on forearm & wrist Fewer complications than supraclavicular block Safest & most reliable for the patient
question
Limitations of the Axillary block
answer
Not for shoulder or upper arm sx Musculocutaneous nerve lies outside sheath & must be blocked separately
question
Complications of the axillary block
answer
Intravascular injection Increased risk of hematoma in patients w/ elevated bleeding times
question
Volume of lidocaine, etidocaine, & bupivicaine for an axillary block.
answer
30-40 mL
question
Which nerve is most superior in the brachial bundle?
answer
Median
question
Which nerve is most inferior in the brachial bundle?
answer
Radial
question
Which nerve is most medial in the brachial bundle?
answer
Ulnar
question
Sensory distribution of the ulnar nerve
answer
Both surfaces of the medial 1-1/2 fingers (ring & pinky)
question
Sensory distribution of the radial nerve
answer
Dorsal surface of the lateral 3-1/2 fingers (1st, middle, ring)
question
Sensory distribution of the median nerve
answer
Palmar surface of the later 3-1/2 fingers (1st, middle, ring)
question
What is the femoral nerve & 3-in-1 block provide?
answer
Anesthesia for the anterior thigh, knee, & small part of the medial foot
question
What are you watching for w/ the nerve stimulator when performing a femoral nerve block?
answer
Quadricep twitch or patellar snap
question
How much LA is injected for a femoral nerve block?
answer
30 mL
question
What nerves are blocked w/ the 3-in-1 block?
answer
The femoral, obturator, & lateral femoral cutaneous nerves
question
Complications of a femoral nerve block
answer
Intravascular injection -> LA toxicity
question
Where does the sciatic nerve originate?
answer
From the lumbosacral trunk
question
What is the sciatic nerve composed of?
answer
The nerve roots L4-5 & S1-3
question
What does the sciatic nerve supply?
answer
Sensory fibers to the posterior hip capsule & knee
question
What does the sciatic nerve provide?
answer
Motor activity to the hamstrings & to all the lower extremity muscles distal to the knee.
question
The sciatic nerve provides all sensory innervation to the lower extemity distal to the knee, except for the ______ aspect, which is covered by the _____ nerve.
answer
anteromedial saphenous
question
How much LA is injected for a sciatic nerve block?
answer
20 mL
question
Where does the femoral nerve lie in relation to the femoral artery (pulse)?
answer
Lateral Medial -> lateral (VAN) Vein - Artery - Nerve
question
What response do you look for when performing a sciatic nerve block w/ a nerve stimulator?
answer
A motor response in the distal ankle, foot, or toes
question
What are the most frequent complication of the sciatic nerve block?
answer
Partial block d/t the branching of the sciatic nerve Intraneural injection
question
What are the 2 major nerves supplying the leg?
answer
The femoral and the sciatic nerves
question
Just below (distal to) the knee, the femoral nerve continues as the ____ ____.
answer
saphenous nerve.
question
In the proximity of the knee, the sciatic nerve bifurcates into the ____ ____ ____ & the ____ _____.
answer
common peroneal nerve tibial nerve
question
What does the common peroneal nerve bifurcate into?
answer
The superficial peroneal never & the deep peroneal nerve
question
What does the tibial nerve give rise to?
answer
The sural nerve
question
What does the ankle block consist of ?
answer
Anesthetizing 5 nerves: Posterior tibial (L4-5, S1-3) Sural (branch of the tibial nerve) Saphenous (branch of the femoral nerve) Deep peroneal (L4-5, S1-2) Superficial peroneal (L4-5, S1-2)
question
Which nerve of the ankle is the most difficult to block?
answer
Posterior tibial
question
Which nerve of the ankle is the most superficial (easier to block)?
answer
All the nerves that begin w/ S (saphenous, superficial peroneal, & sural) & the deep peroneal
question
Which nerve of the ankle is the deepest?
answer
Posterior tibial
question
Describe the tibial nerve
answer
Largest division of the sciatic trunk w/ fiber from L4-S3
question
What does the tibial nerve supply?

answer
Sensation to skin of heel & medial side of the sole of the foot
question
What does the superficial peroneal nerve supply?

answer
Sensation to dorsum of foot & adjacent sides of the 1st -5th toes
question
What is the largest sensory branch of the femoral nerve?
answer
The saphenous nerve (L3-L4)
question
What does the saphenous nerve supply?

answer
Skin on the medial side of the legs, ankle, & onto the foot
question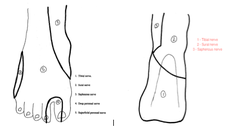
What does the sural nerve supply?

answer
Sensation to posterior lateral aspect of lower calf & lateral side of foot & 5th toe
question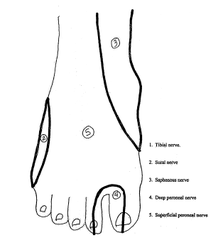
Where does the deep peroneal nerve enter the ankle?

answer
Between the flexor hallicus longus & the extensor digitorium longus tendons
question
What does the deep peroneal nerve innervate?
answer
Toe extensors
question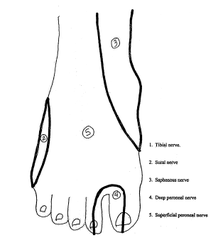
What does the deep peroneal nerve supply?

answer
Sensation to the medial half of the dorsal foot, 1st & 2nd digits
question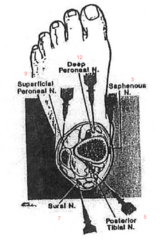
Describe the location of the 5 nerves of the ankle in relation to a clock.

answer
Deep peroneal at 12 o'clock Saphenous at 3 o'clock Posterior tibial at 5 o'clock Sural nerve at 7 o'clock Superficial peroneal at 9 o'clock
question
Complications of the cervical plexus block
answer
Phrenic nerve block (hiccups) Horner's syndrome Hoarseness (RLN block) Accidental subarachnoid/epidural injection
question
Horner's syndrome
answer
Ptosis, miosis, facial & arm flushing, anhydrosis, nasal congestion (on same side of face as the block)
question
How much LA is used at each level of the cervical plexus block?
answer
3-5 mL
question
Advantages of the interscalene block
answer
Appropriate for shoulder sx Risk of pneumo is small Landmarks are easy to identify in obese pts
question
Problems associated w/ the interscalene block
answer
Parasthesias are elicited Ulner nerve frequently blocked
question
Complications associated w/ the interscalene block
answer
Unintentional epidural/spinal anesthesia Vertebral artery puncture Unilateral phrenic nerve block
question
Dosages of lidocaine, mepivicaine, etidocaine, bupivicaine for interscalene block
answer
20-40 mL
question
Advantages of the supraclavicular block
answer
Brachial plexus most compact here (3 trunks) Quick onset
question
Limitations & problems of the supraclavicular block
answer
Need parasthesias Difficult to perform/teach Pneumo is a risk
question
Contraindications to a supraclavicular block
answer
Severe respiratory ds Bilateral upper extremity block (avoid bilateral phrenic nerve block, avoid pneumo)
question
Dosages of mepivicaine, etidocaine, & bupivicaine for a supraclavicular block
answer
40 mL
question
Advantages of the infraclavicular block
answer
Nerves missed w/ axillary approach are blocked Musculocutaneous nerve blocked
question
Limitations of the infraclavicular block
answer
No pulse to assist locating bundle (needle advanced blindly) If injection too far proximal to the clavicle, the musculocutaneous & axillary nerves are missed
question
Motor effects of the radial nerve
answer
Extension at elbow Supination of forearm Extension of wrist & fingers
question
Motor effects of the median nerve
answer
Pronation of the forearm Flexion of wrist Opposition of the middle, forefinger, & thumb Flexion of the lateral 3 fingers
question
Motor effects of the ulnar nerve
answer
Flexion of wrist Adduction of all fingers Flexion & opposition of medial 2 fingers toward thumb
question
Motor effects of the musculocutaneous nerve
answer
Flexion at elbow
question
What is the maximum volume of solution used on each side of the digit?
answer
2 mL on each side total of 4 mL
question
Complications of intercostal nerve blocks
answer
Pneumo, toxicity of LAs, total spinal, nerve injury
question
What should the tourniquet pressure be for a Bier block?
answer
250-300 mmHg (shouldn't feel a pulse)
question
Dose for a Bier block
answer
40-50 mL of 0.5% lidocaine
question
Contraindications to a Bier block
answer
Infection, poor circulation, seizure disorders, heart block
question
Describe the signs of a perineural injection
answer
May produce a brief accentuation of the paresthesia
question
Describe the signs of a intraneural injection
answer
Produces an intense, searing pain that serves as a warning to immediately terminate the injection and reposition the needle.
question
How can surgical anesthesia of the upper extremity & shoulder be obtained?
answer
Following neural blockade of the brachial plexus (C5-T1) or its terminal branches at several sites.
question
What approach is most optimal for procedures on the shoulder, arm, and forearm?
answer
The interscalene approach
question
Injection at the interscalene level tends to produce a block that is most intense at the ___-___ dermatomes and least intense in the ___-___ dermatomes.
answer
C5-C7 C8-T1
question
What is the most optimal approach for procedures from the elbow to the hand?
answer
The axillary approach to the brachial plexus
question
The axillary approach tends to produce the most intense block in the distribution of ____-____ (____-____).
answer
C7-T1 (ulnar nerve)
question
Infraclavicular blocks
answer
Provide good homogeneous anesthesia to the brachial plexus & can be used for procedures involving the hand, forearm, elbow, & upper arm & are quite conducive for placement of an indwelling catheter for postop analgesia.
question
Femoral nerve block
answer
Useful in numerous procedures involving the thigh & knee, such as skin grafting, knee arthroscopy, & patellar surgery, or as an adjunct to procedures distal to the knee that require anesthesia to the medial aspect of the lower leg (saphenous distribution).
question
Sciatic nerve
answer
Useful for many surgical procedures involving the hip, knee, or distal lower extremity
question
Popliteal nerve block
answer
Useful for foot & ankle surgery Can result in complete anesthesia of the limb distal to the knee if a separate saphenous nerve block (terminal nerve of the femoral nerve) is also included.
question
Contraindications to Peripheral Nerve Blocks.
answer
Uncooperative patient Bleeding diathesis Infection Local anesthetic toxicity Peripheral neuropathy
question
What is generally indicative of an intravascular injection?
answer
An abrupt increase in HR >20% over baseline
question
What produces a field block? Give an example of a field block.
answer
A single injection or multiple injections of a relatively large volume of LA in the general location of cutaneous nerves. Superficial cervical plexus block
question
How do intercostal nerves travel?
answer
In a neurovascular bundle on the undersurface of the inferior border of each rib. The nerve maintains an inferior position in the bundle; from superior to inferior the order is vein, artery, & nerve (VAN).
question
Describe the location of the femoral nerve
answer
The femoral nerve is always lateral to the artery; from lateral to medial the order is nerve, artery, vein, empty space, and lymphatics (NAVEL).
question
When a needle makes direct contact with a sensory nerve, a paresthesia is elicited in its area of sensory distribution. With this technique, it is important to ascertain that the needle is making contact with the nerve rather than penetrating it, and that the injection is in ____ to the ____ (_____) rather than within its ____ (_____).
answer
proximity to the nerve (perineural) substance (intraneural).
question
What can the high pressures generated by a direct intraneural injection cause?
answer
Hydrostatic (ischemic) injury to nerve fibers.
question
What is the brachial plexus formed by?
answer
The union of the anterior primary divisions (ventral rami) of the 5th through the 8th cervical nerves & the 1st thoracic nerves
question
The superior trunk of the brachial plexus is predominantly derived from ___-___, the middle trunk from ___, and the inferior trunk from ___-____.
answer
C5-6 C7 C8-T1
question
This interscalene groove lies at the level of the ____ _____.
answer
cricoid cartilage
question
If a nerve stimulator is used, activity of the phrenic nerve suggests the needle is too "_____," whereas stimulation of the trapezius muscle indicates the needle may be too "_____."
answer
anterior posterior
question
What activity should be elicited when performing an interscalene block?
answer
Motor activity of the arm, wrist, or hand, but success has been reported w/ a response noted in the deltoid or pectoralis muscles, w/ subsequent LA injection.
question
What are the potential side effects of an interscalene block?
answer
The phrenic nerve is commonly blocked-> respiratory failure in patients w/ inadequate pulmonary reserve. Horner's syndrome (myosis, ptosis, & anhidrosis), dyspnea, & hoarseness The proximity of the vertebral artery to the injection site increases the risk of an intraarterial injection->seizures
question
Complications of an interscalene block?
answer
Inadvertent epidural, subarachnoid, or subdural injection Pneumothorax
question
Complications of a supraclavicular block
answer
High incidence of pneumothorax (1-6%) Hemothorax Horner's & phrenic nerve block
question
The infraclavicular approach blocks the brachial plexus at the level of the ____.
answer
cords
question
Complications of an infraclavicular block
answer
Pneumothorax, hemothorax, & chylothorax (with a left-sided block) are possible & occur at a higher rate than w/ the supraclavicular approach.
question
In the axilla, the musculocutaneous nerve has already left the sheath and lies within the ____ ____.
answer
coracobrachialis muscle
question
Describe the locations of the median, ulnar, & radial nerves in relations to the axillary artery
answer
The median nerve lies superior to the pulse. The ulnar nerve lies inferior & the radial nerve inferior-posterior to the pulse.
question
What muscles are innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve?
answer
the biceps and brachialis muscles
question
The musculocutaneous nerve supplies sensory input to the lateral aspect of the ___ & ____.
answer
forearm and wrist
question
Indications of an axillary block
answer
Provides an excellent block for procedures distal to the elbow.
question
What muscle does the radial nerve innervate?
answer
The triceps muscle
question
Where do the sensory branches to the lateral side of the thumb lie?
answer
Between the radial artery and the flexor carpi radialis tendon.
question
Complications of radial nerve blockade
answer
Radial artery injection and intraneural injection
question
Describe the location of the median nerve
answer
At the level of the proximal wrist flexion crease, it lies directly behind the palmaris longus tendon in the carpal tunnel.
question
Complications of median nerve blockade
answer
Brachial artery injection or intraneural injection
question
WHere does the ulnar nerve lie in the wrist?
answer
Lateral to the flexor carpi ulnaris tendon & medial to the ulnar artery.
question
Sensory innervation of each finger is provided by ___ small digital nerves that enter each digit at its base in each of the four corners.
answer
four
question
What are the major nerve distributions to the lower extremities?
answer
The lumbar and the lumbosacral plexi
question
The lumbar plexus is derived from the ventral rami of __-__, with some occasional contribution from ____
answer
L1-4 T12
question
The lumbar plexus, primarily from L2 to L4, forms three major nerves that innervate the lower extremity, what are they?
answer
The lateral femoral cutaneous, femoral, and obturator nerves.
question
What do the lateral femoral cutaneous, femoral, & obturator nerves predominantly supply?
answer
Motor & sensory innervation to the anterior portion of the lower extremity & the cutaneous sensory portion of the medial lower leg
question
The lumbosacral plexus is derived from the nerve roots of ___-__ and ___-___ and primarily forms the ____ _____.
answer
L4-5 S1-3 sciatic nerve
question
What does the sciatic nerve supply?
answer
Both motor & sensory innervation to the posterior aspect of the lower extremity & foot
question
What does the sciatic nerve branch into?
answer
The tibial & the common peroneal nerves.
question
What is the easiest and most commonly used lower extremity block, and what is it typically used for?
answer
Ankle block Foot surgery.
question
What are the four major nerves innervate the lower extremities?
answer
The femoral (L2-4), obturator (L2-4), lateral femoral (L1-3), and sciatic nerves (L4-S3).
question
What is the lumbar plexus derived from?
answer
The ventral rami of the lumbar nerve roots.
question
Describe the coarse of the lumbar plexus
answer
The plexus courses via the "psoas compartment" as defined by the fascia of the psoas muscle (which lies anterior to the plexus) & the fascia of the quadratus laborum (which lies posterior to the plexus).
question
Indications of a lumbar plexus (psoas) block
answer
Anesthetizes the lateral femoral cutaneous, femoral, & obturator nerves. Useful for procedures involving the knee, anterior thigh, & hip.
question
Indications of a femoral nerve (3-in-1) block
answer
Provide anesthesia for the anterior thigh, knee, & a small part of the medial foot.
question
What does the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (L2-3) supply?
answer
The cutaneous sensory innervation of the lateral thigh.
question
Indications of a lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
answer
For a skin or muscle biopsy or a harvest site for a skin graft from the lateral thigh, an isolated block of this nerve may be performed.
question
What does an obturator nerve block provide?
answer
An obturator nerve block provides anesthesia to the medial thigh & muscle relaxation of the adductor muscles of the hip.
question
What does the obturator nerve supply?
answer
Sensation to the medial thigh & the hip joint & motor innervation to the adductor muscles of the thigh.
question
Indications of an obturator nerve block
answer
Commonly performed as a compliment to additional blocks performed for knee surgery (eg, femoral and sciatic nerve blocks)
question
What nerve originates from the lumbosacral trunk and is composed of nerve roots L4-5 and S1-3?
answer
The sciatic nerve
question
What does the sciatic nerve supply?
answer
Sensory fibers to the posterior hip capsule Motor activity to the hamstrings & to all the lower extremity muscles distal to the knee. All the sensory innervation to the lower extremity distal to the knee except along the anteromedial aspect
question
What nerve provides sensory innervation to the anteromedial aspect of the knee?
answer
Saphenous nerve.
question
Indications of the sciatic nerve block
answer
Procedures involving the hip, knee, or distal lower extremity
question
Complications of the sciatic nerve block
answer
Partial block due to an injection distal to the branching of the sciatic nerve & intraneural injection
question
What is the upper popliteal fossa bounded by?
answer
Laterally by the biceps femoris tendon & medially by the semitendinosus & semimembranosus tendons.
question
Describe the location of the popliteal artery and vein.
answer
Cephalad to the flexion crease of the knee, the popliteal artery is immediately lateral to the semitendinosus tendon. The popliteal vein is lateral to the artery
question
Describe the location of the tibial & common peroneal nerves
answer
Just lateral to the vein and medial to the biceps tendon, 4-6 cm deep to the skin.
question
What are the 5 nerves that supply sensation to the foot?
answer
Saphenous, deep peroneal, superficial peroneal, posterior tibial, & sural nerve
question
What does the deep peroneal nerve provide?
answer
Sensation to the medial half of the dorsal foot, particularly the 1st & 2nd digits
question
What does the saphenous nerve supply?
answer
Superficial sensation to the anteromedial foot
question
What does the superficial peroneal nerve provide?
answer
Cutaneous sensation to the dorsum of the foot & 5 toes.
question
What does the sural nerve provide?
answer
Sensation to the lateral foot.
question
How is the deep peroneal nerve blocked?
answer
By identifying the groove formed proximally by the extensor hallicus longus tendon & the extensor digitorum longus tendons.
question
Complications of an ankle block?
answer
Hydrostatic damage to small nerves, such as those w/in closed ligamentous spaces, like the tibial nerve.
question
Indications of the superficial cervical plexus block
answer
Performed for unilateral procedures on the neck, such as CEA. Also done as an adjunct to an interscalene block used for shoulder surgery, particularly w/ very anterior incisions.
question
Describe the anatomy of the cervical plexus block
answer
The cervical plexus is formed from the anterior rami of C1-4, which emerge from the platysma muscle posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
question
What does the cervical plexus supply?
answer
Sensation to the jaw, neck, the occiput posteriorly, & areas of the chest & shoulder close to the clavicle.
question
Complications of a cervical plexus block
answer
Rapid systemic absorption and intravascular injection of local anesthetic
question
Indications of an intercostal block
answer
Supplements to GA, for postop analgesia following thoracic & upper abdominal surgery, & for relief of pain associated w/ rib fractures, herpes zoster, & cancer.
question
Where do the intercostal nerves arise from?
answer
The dorsal and ventral rami of the thoracic spinal nerves.
question
Complications of intercostal blocks
answer
Can result in the highest blood levels of LA per volume injected of any block in the body Pneumo
question
Where do the ilioinguinal and iliohypogastric nerves arise primarily from?
answer
L1 but may derive fibers from T12.
question
What does the lateral branch of the iliohypogastric nerve supply?
answer
Sensory to the lateral aspect of the buttock and hip.
question
What does the anterior branch of the iliohypogastric nerve innervate?
answer
The lower abdomen.
question
What does the ilioinguinal nerve supply?
answer
Sensation to the scrotum, penis, & medial thigh in the male, or an equivalent area of the labia & mons pubis in the female.
question
The genitofemoral nerve is derived from ___ & ___.
answer
L1 and L2
question
Innervation of the penis is derived from the ___ ____
answer
pudendal nerve
question
What 2 nerves may additionally provide sensation to the base of the penis via subcutaneous branches?
answer
The genitofemoral and ilioinguinal nerves
question
What signs are characteristic of high spinal and inadvertent cervical epidural anesthesia?
answer
Mental obtundation, apnea, hypotension, and bradycardia
question
Which of the following is a terminal branch of the femoral nerve? A)Saphenous B) Obturator C) Tibial D) Sciatic
answer
A)Saphenous
question
Injury to this nerve eventually causes claw hand. A)Median B) Radial C) Ulnar D) Musculocutaneous
answer
C) Ulnar
question
Which nerve of the ankle is most difficult to block? A) Sural B) Deep peroneal C) Saphenous D) Posterior tibial
answer
D) Posterior tibial
question
What substance decreases the release of substance P in the spinal cord? A) Enkephalin B) Acetylcholine C) Norepinephrine D) Serotonin
answer
A) Enkephalin
question
C fibers synapse in what layers of the dorsal horn? A) Lamina I and IV B) Lamina II and III C) Lamina III and IV D) Lamina IV and V
answer
B) Lamina II and III
question
What spinal cord tract modulates pain? A) Cuneatus B) Gracilis C) Dorsolateral D) Lateral spinothalamic
answer
C) Dorsolateral



