Psychology Exam 1 – Flashcards with Answers
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What is Science
answer
the method of seeking knowledge using observable experiments
question
What is Psychology
answer
the study of the way people think and act..
question
Hindsight Bias
answer
believing that an answer would have been easy to find previously, because it seems easy to find after the answer is revealed.
question
Hindsight Bias Ex. *rather tha reliabe statistics, our beliefs and actions are usually affected by what comes to mind easily*
answer
WREAT and ETRYN
question
Confirmation Bias
answer
people seek evidence that supports their beliefs, and ignore/downplay evidence that goes against them.
question
Confirmation Bias Ex. *Intuition can contradict itself*
answer
-Opposites attract -Birds of a feather flock together
question
Self-Serving Bias
answer
The tendency for people to take personal credit for success but blame failure on external factors
question
Self-Serving Bias Ex.
answer
-Taking the credit for positive events(Making an A on a quiz and blaming your intelligence) -Blame external factors for negative events.(Making a F on a quiz and blaming it on the teacher for disliking you)
question
Nature
answer
Biologically innate
question
Nurture
answer
Shaped by environment
question
What is the current view on the nature/nurture debate?
answer
"Both Nature and Nurture dynamically interact in human psychological development"
question
What historical practices or beliefs about psychology is Frued associated with?
answer
Freud popularizerd the idea of unconscious -Mental processes below conscious awareness **Correct about unconscious processes **Incorrect about what those were -Psychoanalysis
question
Psychoanalysis
answer
a system of psychological theory and therapy that aims to treat mental disorders by investigating the interaction of conscious and unconscious elements in the mind and bringing repressed fears and conflicts into the conscious mind by techniques such as dream interpretation and free association.
question
What is behaviorism? *Important behaviorists John B. Watson B.F Skinner*
answer
-Said psychology should focus on behavior **The mind is too complicated/subjective -the theory that human and animal behavior can be explained in terms of conditioning, without appeal to thoughts or feelings, and that psychological disorders are best treated by altering behavior patterns.
question
Levels of Analysis
answer
-Biological -Individual -Social -Cultural
question
Biological Analysis- Focus
answer
-The brain systems -Neurochemistry -Genetics
question
Individual Analysis- Focus
answer
-Individual differences -Perception and cognition -Behavior
question
Individual Analysis-What is studied?
answer
-Personality, gender, developmental age groups, self-concept -Thinking, decision-making, language, memory, seeing, hearing -Observable actions, responses, physical movements.
question
Biological Analysis- What is studied?
answer
-Neuroanatomy, animal research, brain imaging -Neurotransmitters and hormones, animal studies, drug studies -Gene Mechanisms, heritability, twin and adoption studies
question
Social Analysis-Focus
answer
-Interpersonal behavior -Social cognition
question
Social Analysis- What is Studied
answer
-Groups, relationships, persuasion, influence, workplace -Attitudes, stereotypes, perceptions
question
Cultural Analysis- Focus
answer
Thoughts, actions, behaviors-in different societies and cultural groups
question
Cultural Analysis- What is Studied?
answer
Norms, beliefs, values, symbols, ethnicity.
question
Cognitive Psychologists
answer
study cognition, perception, and action. They investigate processes such as thinking, perceiving, problem solving, decision making, using language, and learning.
question
Clinical Psychologists
answer
interested inboxed the factors that cause psychological disorders and methods best used to treat them
question
Social Psychologists
answer
focus on how people are affected by the presence of others and how they form impressions of others.
question
Developmental Psychologists
answer
study how people change across the life span, from infancy through old age.
question
Goals of science
answer
-Description -Prediction -Control -Explanation
question
The Scientific Method
answer
Step 1: Form a Hypothesis Step 2: Conduct a Literature Review Step 3: Design and Conduct a Study Step 4: Analyzethe Data Step 5: Report Results
question
What makes a scientific theory "good"
answer
-Simple -Falsifiable( meaning there is an experimental result that would prove it wrong. -Generates testable hypotheses
question
Operational Definitions
answer
An agreed-upon definition for an abstract concept. -It describes(tells what counts) -It measures(tells how much)
question
Operational Definition: Aggression
answer
-The number of times someone attempts to, or succeeds in, physically assaulting. -Verbally insulting or irritating, an object, person or animal.
question
Goal of Descriptive Research
answer
Description
question
Goal of Correlational Research
answer
Prediction
question
Goal of Experimental Research
answer
Control and Explanation
question
Descriptive Research (case study)
answer
involves observing behavior to describe that behavior objectively and systematically.
question
Correctional Research
answer
When one thing happens, another thing happens too
question
Experimental Research
answer
purposeful manipulation of a variable
question
What challenges must psychological researchers deal with when using observation or self-report to conduct research?
answer
-Desirable Responses -Reactivity/Hawthorne Effect -Observer Bias -Coding -Experimenter Expectancy Effect
question
observer bias
answer
This flaw consists of systematic errors in observation that occur because of an observers expectations.
question
experimenter expectancy effect
answer
actual change in behavior of the people or nonhuman animals being observed that is due to the expectations of the observer.
question
Third Variable Problem
answer
-something else could be affecting BOTH variables. -researcher cannot directly manipulate variables
question
Problem of Directionality
answer
-either variable could affect the other -researchers find a relationship between two variables, but they cannot determine which variable may have caused the changes in the other variable
question
Psychopathology
answer
sickness or disorder of the mind
question
Causes of mental disorder
answer
-Genetics -Brain function -Situations/Environment Socioeconomic status, culture, learned thoughts/beliefs
question
Etiology
answer
factors that contribute to the development of a disorder
question
Treatments for psychological disorders
answer
-Medication -Therapy
question
Psychodynamic therapy
answer
-Focuses on finding unconscious influences on behavior (insight) -Has both supporters and critics
question
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
answer
-Focuses on changing maladaptive thoughts and behaviors -Most widely used evidence-based therapy -Effective for a large number of psychological disorders
question
Other treatments
answer
-Trepanning -Frontal Lobotomy -Phototherapy -Electroconvulsive Therapy -Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
question
What are the parts of the nervous system?
answer
-Central Nervous System **Brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, midbrain) **Spinal Cord -Peripheral Nervous System
question
Parts of the Brain
answer
-Neurons -Glial cells -Blood Vessels
question
Parts of the Neuron
answer
-Dendrites -Terminal Buttons -Axon -Nucleus -Cell Body
question
Main function of the neuron
answer
Receives and sends electrochemical signals i.e. ions
question
What causes a neuron to fire
answer
Once the threshold is reached (the electrochemical signal travels down the axon to the terminals.)
question
What happens to a neuron during an action potential?
answer
The electrical charge inside the neuron starts out slightly negative (resting membrane potential, -70 millivolts) As a neuron fires, it allows more positive ions inside the cell( depolarization). It then returns to its slightly negative resting state.
question
Neurotransmitter
answer
Chemical substances that transmit signals from one neuron to another.
question
Frontal Lobe (Outer "crust" of the brain)
answer
regions of the cerebral cortex-at the front of the brain-important for movement and higher-level psychological processes associated with the prefrontal cortex.
question
Parietal Lobe
answer
regions of the cerebral cortex-in front of the occipital lobes and behind the frontal lobes-important for the sense of touch and for attention to the environment.
question
Temporal
answer
regions of the cerebral cortex-below the parietal lobes and in front of the occipital lobes-important for processing auditory information, for memory, and for object and for object and face perception
question
Occipital Lobe
answer
Regions of the cerebral cortex-at the back of the brain-important for vision
question
Prefrontal Cortex
answer
the frontmost portion of the frontal lobes, especially prominent in humans; important for attention, working memory, decision making, appropriate social behavior, personality.
question
Primary Motor Cortex
answer
includes neurons that project directly to the spinal cord to move the body's muscles. Its responsibilities are split down the middle of the body, like those of the sensory areas. (left hemisphere controls right arm, right hemisphere controls left arm.)
question
Primary Auditory Cortex
answer
the brain region responsible for hearing.
question
Primary Visual Cortex
answer
the major destination for visual information
question
Primary Somatosensory Cortex
answer
a strip in the front part of the lobe, running from the top of the brain down the sides. The primary somatosensory cortex groups nearby sensations.
question
Cerebellum
answer
important for proper motor function. (motor learning and motor memory)
question
Brainstem
answer
an extension of the spinal cord , it houses structure that control functions associated with survival such as heart rate , breathing, swallowing, vomiting, urination, and orgasm.
question
Corpus Callosum
answer
connects the left and right hemispheres ; sends signals from one to the other .
question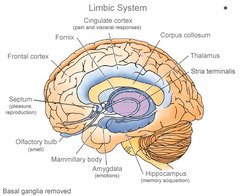
Lymbic Systems and its functions

answer
involved in emotion, memory, ; motivation. -(Thalamus relays all sensory information except smell) -Hypothalamus : master regulatory structure - - - internal organs, body temperature, body rhythms, blood pressure, blood glucose levels. (controls hormones in the body through the pitiuary gland. four f's. -Hippocampus: Memory function. (damage= anterograde amnesia) the olfactory bulb has direct links to the hippocampus and amygdala . -amygdala : fear, emotional memory [generalized anxiety disorder] a diffuse state of anxiety not associated with any specific object or event. ( frequent amygdala activation)
question
What does the Basal Ganglia do ?
answer
functions in planning/producing movement [ Parkinson's/ Huntington's disease involve damage to this area] - some can benefit. NUCLEUS ACCUMBENS . : reward, motivation. -wanting vs. liking
question
What are the main excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters in the brain?
answer
-Glutamate = excitory -GABA = inhibitory
question
What is epigenetics?
answer
change in gene expression, due to an organism's experiences. ( common experiences also directly impact the brain).
question
What does it mean that "neurons that fire together, wire together", and how does that affect behavior?
answer
a connection is strengthened when the neurons fire together. ; Builds skill, better learning. [negative consequence : stereotype]
question
What is neurogenesis, and how is it affected by one's environment/behavior?
answer
is the growth of new neurons in the brain. -- affected by things like: stressful experience , social hierarchy, exercise increase neurogenesis.
question
Can a person's interpretation of an event affect brain activity? What did Antonio Rangel's famous wine-tasting study show?
answer
yes; placebo effect and stress. -participants drank wine in a fMRI scanner ; when wine was said to be more expensive, pleasure areas become more active -- even with same wine.
question
How do drugs work in the brain?
answer
psychoactive drug - impacts the mind drugs and toxins alter neurotransmitters
question
What does it mean for a drug to be an agonist or an antagonist?
answer
*agonists: enhance the actions of neurotransmitters *antagonists: inhibit the actions of neurotransmitters
question
What are the short-term effects of each of the main categories of drugs, and what primary neurotransmitter does each type of drug work on?
answer
*Opiates : short term effects: pain relief & Euphoria. TARGET : endorphins & Dopamine *hallucinogens: short term effects: alter mood, cognition, perception, extreme hallucinations, distortion of time TARGET: Serotonin *Stimulants: short term effects: increase behavioral and mental activity TARGET: dopamine, norepinephrine, GABA *Depressants: short term effects: decrease behavioral and mental activity. TARGET: GABA
question
Why do people become addicted to drugs, and what types of things can change addictive behavior?
answer
it makes them feel good ; dopamine activity in the limbic system -change in environment
question
What is transduction?
answer
conversion of physical stimuli into an electrical signal
question
How are signals from the outside world received in vision, hearing, smell, and taste?
answer
sense perception
question
How is data interpreted and what are the Gestalt principles of vision? How does pitch affect the basilar membrane?
answer
- - Gestalt principles are proximity, similarity, continuity, and closure. - base recognize the high pitch -apex recognize the low pitch
question
What is the "McGurk Effect" and what does it show? What types of senses within the body are not typically represented within the "5 senses"?
answer
perceptual phenomenon that demonstrates an interaction between hearing and vision in speech perception. The illusion occurs when the auditory component of one sound is paired with the visual component of another sound, leading to the perception of a third sound.
question
MDMA
answer
produces an energizing effect similar to that of that of stimulants but it also causes slight hallucinations.



