Phys Dys: Chapter 1 "OT & Physical Disabilities" – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
O.T.P.F. - definition
answer
Occupational Therapy Practice Framework: outlines the territory of OT in the realm of physical disability.
question
O.T.P.F.
answer
"Supporting health and participation in life through engagement in occupation"
question
Preoccupations - vs - Occupations
answer
Preoccupations: hot packs, massage, functional exercises Occupations: client does the occupation (dressing, eating) 1. RAMP 2. Requires planning
question
OT practice
answer
Overlaps with other areas of practice (speech, PT)
question
OT - Domain of Concerns
answer
Areas of Occupation Client Factors Performance Skills Performance Patterns Context & Environment Activity Demands
question
Areas of Occupation
answer
1. ADL's (Activities of Daily Living) 2. IADL's (Instrumental Activities of Daily Living) 3. Rest and Sleep 4. Education 5. Work 6. Play 7. Leisure 8. Social Participation
question
Client Factors
answer
1. Values, beliefs and spirituality 2. Body Functions 3. body Structures
question
Performance Skills
answer
1. Motor & Praxis skills 2. Sensory - Perceptual Skills 3. Emotional Regulation Skills 4. Cognitive Skills
question
Performance Patterns
answer
1. Habits 2. Routines 3. Roles 4. Rituals
question
Context & Environment
answer
1. Cultural 2. Personal 3. Physical 4. Social 5. Temporal 6. Virtual
question
Activity Demands
answer
1. Objects used & their properties 2. Space demands 3. Social demands 4. Sequencing & Timing 5. Required actions 6. Required body functions 7. Required body structures
question
Theories, Models and Frames of Reference
answer
Provide a starting point for information gathering, treatment planning and treatment implementation.
question
Model of Human Occupation
answer
M.O.H.O. - a systems model
question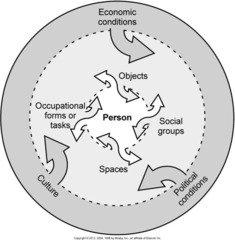
M.O.H.O. = Basic Tenet

answer
1. Humans have intrinsic motivation to explore, interact with and master their environment (regardless of age or cognitive state). 2. Individual cannot be separated from the environment; they interact with one another (intertwined) 3. A Holistic Model - vs - Reductionist Model
question
A Holistic Model
answer
Looks at the person as a whole.
question
A Reductionist Model
answer
Looks intensely at one part (i.e. muscular function).
question
3 Subsystems of Human Occupation
answer
1. Volition (motivation) 2. Habituation 3. Performance Capacity and the Lived Body
question
Volition
answer
aka: motivation 1. Personal Causation 2. Values 3. Interests
question
Personal Causation
answer
1. Sense of competence (the persons beliefs about personal effectiveness. 2. Locus of Control (Internal & External)
question
Values
answer
1. What is meaningful and important. 2. Motivate behavior
question
Interests
answer
1. What is satisfying and interesting (attraction) 2. Energized, alive and ready to try new things.
question
Habituation - definition
answer
Refers to activities that have been performed enough times to become routine and customary.
question
Habituation
answer
1. Habits 2. Internalized Roles; role change or transition
question
Habits
answer
1. Automatic routines or patterns of activity that a person seems to perform almost by reflex, without much conscious awareness. 2. Conserves energy & free up cortical space.
question
Internalized roles
answer
1. Common roles that are personalized by the individual. 2. Consist of many different habits, routines and skills (homemaker, student)
question
Role change or transition
answer
1. Occurs as life moves forward and the person grows. 2. Roles contract, expand, modified, abandoned, replaced.
question
Performance Capacity
answer
1. Ability to participate in activities 2. Subjective beliefs about capabilities 3. "the ability for doing things"
question
Lived Body (Kielhofner)
answer
1. "the experience of being and knowing the world through a particular body". 2. Perception of activities changes when body is disabled.
question
M.O.H.O. - Guidelines for OT Intervention (Tenets)
answer
1. Client change is the focus of therapy. 2. Only clients can accomplish their own change. 3. For Occupations to be therapeutic, activity must be actual - vs - contrived. 4. Activities must be relevant, meaningful and appropriate in order to be therapeutic. 5. Therapeutic change involves alterations in the individual, the environment and their relationships. 6. The OT Practitioner guides and supports change.
question
Client change is the focus of therapy
answer
The client must take what is presented/learned during the therapy and implement their own change.
question
Only clients can accomplish their own change.
answer
Client must be actively involved in the therapy process; treatment is not done to an individual.
question
Occupations must be actual - vs - contrived for the activity to be therapeutic.
answer
Maximal gain from treatment occurs during appropriate, meaningful, relevant activities; "real" to the pt.
question
Activities must be relevant, meaningful and appropriate in order to be therapeutic.
answer
OT Practitioner must be creative with resources that are available when actual activities are not practical.
question
Therapeutic change involves alterations in the individual, the environment and their relationships.
answer
OT Practitioner modifies task, environment for "just right challenge" for client to learn new ways of doing tasks.
question
The OT Practitioner guides and supports change.
answer
Encourage and support; validate, analyze tasks, give feedback, provide alternatives.
question
Practice Approaches/Frames of Reference
answer
1. Bio-mechanical Approach 2. Sensorimotor and Motor Learning Approach 3. Rehabilitation Approach
question
Bio-mechanical Approach
answer
1. Kinetics (study of motion and forces acting on objects) 2. Physics (study of force, levers, torque) 3. Statics (study of forces acting on objects at rest) 4. ROM, Strength, Endurance, Torque, Force 5. Lever & Joint
question
Bio-mechanical Approach - seeks to ...
answer
1. Evaluate/treat deficits in ROM, strength, task tolerance. 2. Prevent or decrease deformities (fixed or flexible)
question
Bio-mechanical Approach & OT
answer
1. Best used with intact CNS (not stroke) 2. Utilized in ergonomics 3. Utilized in work hardening. 4. Diagnosis of RA, OA/DJD, burns, fx, jt replacement
question
Ergonomics
answer
Evaluation and adaptation of the environment and the individual in the work setting.
question
Work Hardening
answer
Evaluation/treatment aimed at improvements in physical & psycho-social performance skill - return to employment.
question
Sensorimotor Approach
answer
1. Used when CNS is damaged/abnormal, resulting in limited smooth, controlled movements. 2. Utilizes neuro-physiological pathways
question
Neuro-physiological pathways
answer
1. Provide controlled sensory stimulation 2. Normalize muscle tone 3. Elicit reflexes 4. Employ concept of Ontogeny recapitulates Phylogeny
question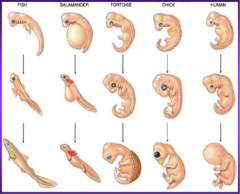
Ontogeny recapitulates Phylogeny

answer
Individual developmental stages from primitive to complex.
question
Motor Learning Approach
answer
1. Newer approach to treatment with focus on practice, client problem solving, reflection and feedback. 2. Relies heavily on context. 3. Integrates the 3 subsystems of MOHO
question
Motor Learning Approach - Pt guidelines
answer
1. Be able to recognize & terminate activity. 2. Be able to repeat tasks. 3. Be able to recognize and correct mistakes.
question
Rehabilitation Approach
answer
1. Focus is on the residual capabilities of the individual 2. Assists with compensatory strategies for purposeful activities that impact quality of life. 3. Role Performance and Performance Skills are of greater focus that the structure/function of the body.
question
The Continuum of Treatment with Physical Disabilities
answer
1. Adjunctive Methods 2. Enabling Activities 3. Purposeful Activities 4. Occupational Performanance & Occupational Roles
question
Adjunctive Methods
answer
1. Used to prepare the patient to engage in activity. 2. Often used in acute stages of illness or injury. 3. First stage of treatment continuum.
question
Adjunctive Methods - examples
answer
1. Exercise 2. Facilitation & Inhibition techniques 3. Positioning 4. Sensory stimulation 5. Selected physical agent modalities (hot/cold packs) 5. Devices (splints & braces)
question
Enabling Activities
answer
1. Used for simulating purposeful (but not necessarily meaningful) activities. 2. Used to train specific sensory, motor, perceptual or cognitive functions necessary for performance skills and occupations. 3. Second stage of treatment continuum.
question
Enabling Activities - examples
answer
1. Sanding boards 2. Stacking cones or blocks 3. Practice boards for clothing fasteners & hardware 4. Driving & work simulators
question
Purposeful Activities
answer
1. Been the core of OT since its inception. 2. Has an inherent or autonomous goal 3. Are relevant and meaningful to the patient. 4. Are used to evaluate, facilitate, restore or maintain a persons ability to function in life roles. 5. Third stage of treatment continuum.
question
Purposeful Activities - examples
answer
1. Hygiene, Dressing, Mobility 2. Arts,Crafts, Games, Sports 3. Work, Education, Communication
question
Purposeful Activities & the OT
answer
The therapist is concerned with evaluating & remediating deficits in performance of skills related to occupation.
question
Occupational Performanance & Occupational Roles
answer
1. Final stage of treatment continuum. 2. Patient resumes/assumes occupational roles in the living environment & in the community. 3. Formal OT intervention is decreased / terminated. 4. OT is concerned with transitioning needs.



