Peds2 Pediatric Anesthesia & Pain Management – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion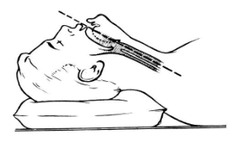
In the sniffing position the neck & head are

answer
Neck: flexed Head: extended
question
What age group would it be best to place a blanket roll under the shoulders in order to align the 3 axis for proper sniffing position
answer
Less than 2 years [PALS] (maybe up to 5) (large occiput causes babies to otherwise be overly sniffed)
question
What age group would it be best to place a blanket roll under the neck as they are already aligned to the 3 axis of proper sniffing position (under neck to simply keep head from rolling side-to-side)
answer
Children 6-11
question
What age groups would it be best to place a blanket roll or pillow under the head in order to align the 3 axis for proper sniffing position
answer
Teenagers and adults
question
Sodde's Law of Anesthesia
answer
"The laryngoscope light stays on until the blade is down the patient's throat" (keep 2 laryngoscopes available in case failure)
question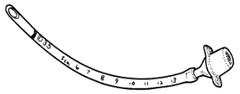
How would you place an ET tube with a single vocal cord distance marker near the end?

answer
Line at the vocal cords (just barely hidden by vocal cords)
question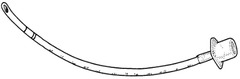
How would you place an ET tube with two vocal cord distance marker lines near the end?

answer
Vocal cords between the two sets of lines
question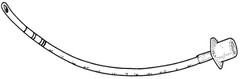
How would you place an ET tube with three vocal cord distance marker lines near the end?

answer
Vocal cords at the second set of lines
question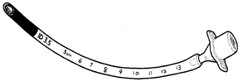
How would you place an ET tube that was all black at the end?

answer
All of the black goes past the vocal cords with the cords at the line between black ; not black
question
*!* How long is the average newborn trachea from vocal cords to carina ; compare to adult
answer
Neonate: 5 cm Adult: 8-13 cm (If you look at neonatal ETT you'll notice it is 2.5 cm from vocal cord line marker to end. This is 1/2 total trachea length)
question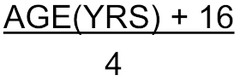
*!* ETT internal diameter formula for peds older than 2 yrs (up to ~12 yrs old?)
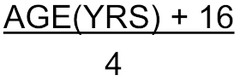
answer
(a 5 yr old takes a 5 50% of the time)
question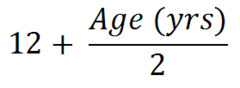
*!* Depth of ETT insertion (at the teeth) formula for peds
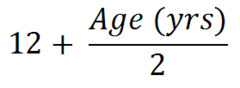
answer
(Use the vocal cord marker, then note the line marker at teeth is a better method)
question
*!* ETT insertion (at the gums) formula for premature

answer
(# kg + 6) = # cm
question
When to use cuffed vs uncuffed ETT for peds
answer
A low pressure, high volume cuff "generally" indicated for children older than 8-10. Otherwise uncuffed for younger.
question
What is very important in regards to children with cervical spine abnomoralities?
answer
Don't cause a C-spine injury! Control the C-spine -hold at the neck when moving pt (not head) -don't try to make the neck fit the laryngoscope rather modify the technique to the anatomy of the neck (hold true for all pts)
question
Anesthesia considerations for Down's syndrome (x4)
answer
-Macroglossia (large tongue) -C-spine instability (atlantoaxial subluxation in ~20%) -Congenital subglottic stenosis (web below vocal cords causes stenosis) -Congenital AV canal defects
question
What is an AV canal defect?
answer
Atrio-ventricular septal defect (ASD, VSD, or both)
question
Term for undersized jaw
answer
Micrognathia
question
The most common anatomical cause of a difficult intubation
answer
Micrognathia (undersized jaw/chin)
question
Fetal origination of the mandible
answer
1st branchial arch
question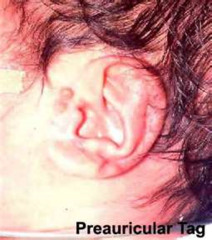
Anesthesia concern for preauricular skin tags or abnormally developed external ears

answer
Potentially difficult intubation (possible sign of congenital disorder)
question
What to expect when attempting to intubate a micrognathic patient (x2) ; what improves these problems
answer
-Tongue ; soft tissue will not be easily displaced during laryngoscopy as it is not pulled forward in the normal developmental fasion. -Mouth unable to open as easily or widely These tend to improve with age.
question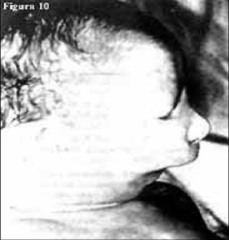
A very rare disease characterized by the complete absence of the mandible and other structures derived from the first branchial arch.

answer
Bilateral 1st arch syndrome
question
2 similar but less severe (; more common) conditions to bilateral 1st arch syndrome
answer
-Treacher Collins syndrome -Pierre Robin syndrome
question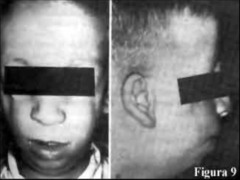
Syndrome characterized by underdeveloped cheek ; jaw, down slanting eyes, ; ear deformities

answer
Treacher Collins Syndrome
question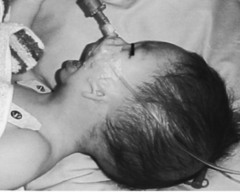
Syndrome characterized by hemicraniofacial ; vertebral defects related to the abnomal development of the 1st ; 2nd branchial arches

answer
Goldenhar's Syndrome
question
Goldenhar's Syndrome major systems affected (x5)
answer
-Facial ; airway defects -Vertebral defects -Congenital heart disease -Pulmonary defects -Renal defects
question
Airway issues with Goldenhar's syndrome (x5)
answer
-Retrognathia (recessed jaw) -Micrognathia (underdeveloped jaw) -Mandibular hypoplasia (undersized jaw) -Palatal defects -Vertebral anomalies
question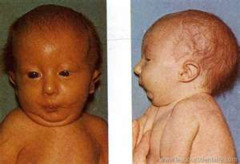
Airway-related characteristics of Pierre-robin syndrome (x4)

answer
-Micrognathia (small lower jaw) -Glossoptosis (tongue tends to ball at back of the mouth & falls toward back of throat) -Breathing problems -Cleft palate may or may not be present
question
Term for when the tongue tends to ball at back of the mouth & falls toward back of throat
answer
Glossoptosis
question
NPO guidelines for Neonate / Pediatrics
answer
Fatty or fried: 8 hrs Light meal: 6 hrs Non-human milk: 6 hrs Infant formula: 6 hrs Breast milk: 4 hrs Clear liquids: 2 hrs (If they are sick they may need more time d/t delayed gastric emptying)
question
Helpful tip for working with pediatrics
answer
Try to give them control (pick flavor, toy, etc.)
question
Neonatal Preop anticholinergic doses (x2)
answer
Glycopyrolate: 0.01 mg/kg Atropine: 0.02 mg/kg
question
How to reduce risk for bradycardia with laryngoscopy of neonate
answer
Give Anticholinergic
question
Concern for laryngoscopy on a neonate
answer
Bradycardia (very developed parasympathetic & little sympathetic)
question
Pediatric midazolam (Versed) dose
answer
0.5 mg/kg PO
question
Which is most common induction method for pediatrics
answer
Inhalation (IV, IM, rectal are possible but only for select & uncommon cases)
question
The "gold standard" monitor for pediatrics
answer
Precordial stethoscope
question
Steps for induction of pediatric pts (x11) (inhalation technique)
answer
-Plan ahead & discuss with all involved -Premedicate -Comfort (parent?, warm, designated talker, min distractions) -Monitors (pulse ox, precordial) -Operator at head, assistant at chest -Mask (not touching face) with 50/50 N?O/O?, increase to 70/30 -Mask to face & Sevoflurane 2% every 3 breaths -Prevent airway obstruction (PEEP if needed) -Place IV -Guarantee airway before paralytics (if using) -Airway (as needed)
question
MAC (%) is greatest for what age
answer
6 months
question
Drinking / Voiding for pediatric patients
answer
Not mandatory
question
Rule of thumb for effect of PRBCs on Hct
answer
1 mL/kg of PRBCs will ? Hct by 1.5%
question
Steriochemistry of Hgb S (sickle) vs normal Hgb
answer
Hgb S: Valine substituted for glutamic acid at position 6 of the ?-chain of hemoglobin
question
Until what age do false negatives occur when testing for sickle cell?
answer
Until 6 months (otherwise false negative d/t presence of fetal hemoglobin)
question
Define Acute chest syndrome
answer
-Sickle cells occlude pulmonary vasculature causing ?PO? which leads to further sickling & more obstuction (a life-threatening emergency)
question
Blood products for sickle-cell patients
answer
Conservative transfusion regimen (don't transfuse if Hgb greater than 10)
question
Precautions for sickle cell patients in the OR (x5)
answer
-Prevent hypoxia -Prevent hypothermia -Adequate hydration -Aseptic technique (prone to infection) -Manage pain (sickling is painful)
question
Most common cause of death in pediatrics
answer
Trauma #1 type is head trauma (greater than the next 5 causes combined)
question
Most common cause of death by disease in pediatrics
answer
Cancer
question
Most common type of cancer in pediatrics
answer
Leukemia
question
Most common type of solid tumor in pediatrics
answer
Brain tumor
question
Risk for intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) among premature newborns (x2)
answer
500-750 grams: 60-70% risk IVH 1000-1500 grams: 10-20% risk IVH
question
Location of brain tumors in pediatrics vs adults
answer
Peds: 2/3 are infratentorial (posterior fossa) Adults: 2/3 are supratentorial
question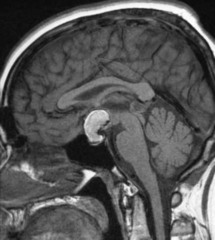
Most common type of supratentorial tumor in pediatric patients

answer
Craniopharyngioma
question
Posterior fossa tumors in peds (x3)
answer
-Astrocytoma (32%) -Medulloblastoma (32%) -Brainstem gliomas (20%)
question
A malformation that can accompany myelomeningocele and other neural tube disorders where the cerebellum and medulla oblongata protrude into the spinal cord
answer
Arnold-Chiari Malformation (ACM)
question
*!* What type of Arnold-Chiari Malformation (ACM) is associated with myelomeningocele

answer
Type 2 (Difficult to distinguish from Dandy-Walker syndrome)
question
Treatment for Arnold-Chiari Malformation (ACM)
answer
Surgery - posterior fossa decompression, cervical laminectomy
question
Caution for Arnold-Chiari Malformation (ACM) (x2)
answer
-BEWARE flexion/extension of the neck may transect the spinal cord -Risk for post-op airway dysfunction (CN10)
question
Malformation caused by cystic expansion of the 4th ventricle (90% occurance of hydrocephalus)
answer
Dandy-Walker Malformation
question
Treatment for Dandy-Walker malformation
answer
Surgery to shunt ventricles ; cyst
question
Condition where the caudal spinal cord attaches to the bottom of the vertebral column
answer
Tethered cord
question
How to calculate a morphine dose for an infant 2-12 months ; why this won't work if less than 2 months
answer
-Using the same mg/kg dose as an adult -Cytochrome P-450 system too immature at birth but reaches adult level at 2 months
question
Pharmacokinetics of morphine for newborn & infant less than 2 months (x3)
answer
-20% protein bound in infant vs 30% in adult -t 1/2 is 2x longer in newborns -BBB immature & more permeable to morphine



