OCC Nursing Challenge Exam: Med Admin – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
medication rights. 8- 10 rights
answer
right: drug, patient, dose, route, time, reason, assessment data, documentation, response, education, refuse
question
Three Checks
answer
Label should be read: 1. when the nurse reaches for the unit dose package 2. after retrieval from the drawer and compared with the MAR immediately before pouring from a multi dose container 3. Before giving it to the patient or when replacing the container in the drawer or shelf
question
oral meds
answer
Intended for absorption in stomach and small intestines. Drug action has slower onset and more prolonged, but less potent, effect.
question
enteric coated meds
answer
impede absorption in the stomach and absorbed in small intestines. Good for meds that call stomach upset. Do not chew or crush.
question
SR
answer
sustained release Do not chew or crush.
question
XL
answer
extended release Do not chew or crush.
question
CR or CRT
answer
controlled release Do not chew or crush.
question
SA
answer
sustained action Do not chew or crush.
question
LA
answer
long acting Do not chew or crush.
question
Liquid meds admin with syringe
answer
place syringe between pt's gums and cheek and give slowly.
question
admin of drugs that can damage teeth enamel or discolor teeth
answer
mix well with H2O/some form of liquid and have patient take med via a straw and encourage pt to drink water after med admin.
question
admin of drug that pr finds distasteful
answer
crush if appropriate and add to food or drink. If med cannot be crush allow pt to suck on piece of ice for a few minutes before taking med.
question
Oily meds
answer
store in fridge--cold oil is less aromatic
question
parenteral
answer
admin of drug outside of intestines or alimentary tract
question
Intradermal injection
answer
5 to 15 degrees. Admin in dermis, just below epidermis. Longest absorption time. Used for sensitivity test due to long absorption time. TB, allergen, and lovely anesthetics. 1/4" to 1/2", 25- or 27- gauge needle. Forearm or back under the scapula.
question
Subcutaneous injections
answer
Admin in adipose tissue. 90 - 45 degrees. Admin here is slow, sustained rate of absorption. Insulin and heparin. Sites: lateral upper arm- slower absorption then ABD, ABD-most rapid absorption (costal margarine to iliac crest), anterior aspects of thigh-slower then arms, upper back, upper central or dorsogluteal area- slowest absorption. Use a 25- to 40-gauge needle. 3/8" (90 degrees)to 1" (45 degrees) Usually around 1 ml given.
question
Intramuscular injections
answer
Faster onset and action. ABTs, hormones, vaccines. Sites: ventrogluteal site, vastus lateralis, and deltoid muscle. Meds in aqueous solutions or biological agents should be admin with 20- to 25- gauge. Meds in oil based solutions should be admin with 17- to 25- gauge. Generally 1-4 ml can be admin. 72 to 90 degrees. Always use z-track technique with admin.
question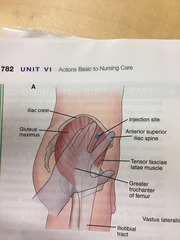
ventrogluteal site

answer
Intramuscular site. Place palm over greater trochanter with fingers facing patients head. Place index finger on anterosuperior iliac spine and extend middle finger dorsally. Forming a triangle to injection is given in the triangle. 1 1/2" needle.
question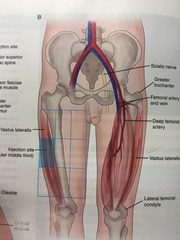
Vastus lateralis site

answer
Intramuscular site. Divide thighs into thirds horizontally and vertically and admin injection in the outer middle third. 5/8" to 1" needle
question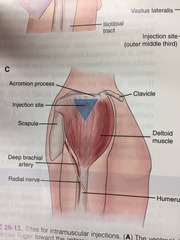
Deltoid muscle

answer
Intramuscular injection. Only 1ml can be given at this site. Not developed enough in infants under 1 to absorb meds correctly. Damage to radial nerve and artery are a risk. Locate by palpating the lower edge of the acrimonious process and a triangle is formed at the midpoint in line with the Scilla or the lateral aspect of the arm. Should definitely give hepatitis b here because it induces adequate levels of antibodies. Adults: 5/8" to 1 1/2". Child: 5/8" to 1 1/4" needle.
question
Intravenous route.
answer
Most dangerous route. Immediate onset and action. PCA pumps. Aseptic technique.
question
Med admin via intravenous solutions
answer
Patient receives it slowly and over a long period of time. Monitor for adverse reactions at least every hour.
question
Ned admin via intravenous bolts or push
answer
Sing or injection of a concentrated solution into IV line. Admin drug slowly over at least 1 minute.
question
Ned admin via intermittent IV infusion
answer
Drug mixed with small amount of IV solution such as 50-100ml and admin over short period of time. Usually with IV pump
question
Topical application
answer
Direct action at a particular site.
question
Skin application
answer
Also called an inunction. Drug absorbed through sebaceous glands. Clean skin thoroughly then apply med.
question
Transdermal
answer
Patches or discs. Hormones, narcotic analgesics, cardiac meds, nicotine. Do not apply estrogen transdermal to breast skin. Slow onset of action. Maintain consistent serum drug levels.
question
Eye drops.
answer
Instillation for local effects. Pupil dilation or construction. Treat an infection, control IOP in patients with glaucoma.
question
Eye Ointment instillation
answer
Used for local infection or irritation. Placed on exposed lower conjunctival sac after cleansing eyelids and eyelashes. About 1/2". Inner to outer then close eyes and move eyes whilst closed. Do n it rub. May blurt vision temporarily.
question
Ear instillation.
answer
Instilled in auditory canal for local affect. Soften wax, relieve pain, local anesthetic, destroy insect or organisms lodge in there. Adults: pull up and back. School sheds Kids: straight back. Kids 3 and under: down and back.
question
Nasal instillation
answer
Treat allergies, sinus infections, nasal congestion. Have patient blow nose before instilling nasal drops.
question
Rectal instillations
answer
Do not give if had recent rectal or prostate surgery. Antipyretic, laxatives, softeners. Patients who have thrombocytopenic or neutropenic should not receive or cardiac arrhythmias.
question
Piggyback delivery system

answer
Requires intermittent or additive solution to be place higher then the primary solution container via an extension hook. Port on primary IV has a back check valve that automatically stops the primary and allows the piggyback or secondary to flow. Check manufacturers recommendations for use.
question
metric system/international system
answer
The decimal measuring system based on the meter, liter, and gram as units of length, capacity, and weight or mass.
question
1 kilgram equals how many grams
answer
1000 grams WEIGHT
question
1 gram equals how many milligrams
answer
1000 milligrams WEIGHT
question
1 milligram equals how many micrograms
answer
1000 micrograms WEIGHT
question
1 liter equals how many milliliters or cubic centimeters
answer
1000 milliliters or cubic centimeters VOLUME`
question
pediatric med calculations
answer
based on weight. Recommended dosage is usually expressed as the amount to be given over 25 hour period. (mg/kg/day) or single does (mg/kg/dose) Weigh child and convert to kilograms.Then multiple weight in kg by prescribed dose. Example: 2mg/5kg/day. Child weighs 10 pounds. 10/2.2= 4.55 then 4.55 x 5 =22.7mg/day
question
apothecary
answer
a health professional trained in the art of preparing and dispensing drugs
question
The nurse is preparing supplies for a TB screening. The nurse should choose which of the following syringes and needles? A. 10ml syringe; 3", 18 gauge B. 1ml syringe, 1/2", 26 gauge C.5 ml syringe, 2", 20 gauge D. Insuline syringe, 1", 16 gauge
answer
B. 1ml syringe, 1/2", 26 gauge
question
A nurse needs to admin a subQ injection to a client. For which of the following clients can she admin the subQ at a 90 degree angle? A. infant client B. obese client C. thin client D children
answer
B. obese client
question
A client is ordered a shot IM. The nurse chose the ventrogluteal site based on which reason? A. the area is free of major vessels and fat B. the site is in close proximity to the sciatic nerve C. there is high possibility of injecting into subQ fat D. the site lies close to the radial nerve
answer
A. the area is free of major vessels and fat
question
What is the common maximum volume of a subQ shot? A. 0.05ml B. 3ml C. 1ml D. 0.01ml
answer
C. 1ml
question
A nurse needs to use a moisturizer for an older clients. Why is the onset of the med action atypical in older clients? A. decreased appetite B. decreased body temp C. diminished mobility D. diminished subQ fat
answer
D. diminished subQ fat reasoning:results in quicker absorption
question
A nurse brings a client meds and finds that the client is not in their room. What should the nurse do? A. return meds to cart or med room B. leave meds at pt's bedside C. inform physician about the pt's absence D. inform headdress about the pt's absence
answer
A. return meds to cart or med room
question
A nurse is admin'ing meds through a med lock. How often should the nurse flush the med lock to maintain patency? A.every 8-12 hours B. every 72-96 hours C. every 1 to 2 hours D. every 36 to 48 hours
answer
A.every 8-12 hours
question
A nurse needs to admin in sho to a toodler. Which of the following sites is most suitable? A. vastus lateralis site B. deltoid site C. ventrogluteal site D. dorsegluteal site
answer
A. vastus lateralis site
question
drug chemical name
answer
identifies the meds atomic and molecular structure
question
generic name
answer
identifies the drugs active ingredient and is assigned by manufacturers when first developing the drug
question
official med name
answer
the name by which the drug is identified in the official publications--often the generic name
question
trade name
answer
also called the brand name or proprietary name, is selected by pharmaceutical company that sells drug and is protected by trademark.
question
med absorption
answer
process by which a drug is transferred from its site of entry to the blood stream. Influenced by route, lipid solubility, pH, blood flow, local conditions at site of admin, and drug dosage.
question
med that has a more lipid soluble can be absorbed more readily and pass more easily through cell membranes
answer
...
question
acidic drugs are absorbed best in stomach
answer
...
question
meds that are basic pH remain ionized of insoluble in an acid environment. Absorbed in small intestines
answer
...
question
impaired circulation can inhibit or make for slower drug absorption
answer
...
question
patient with burns would have poor absorption of an IM at the burn site
answer
...
question
food in stomach can delay absorption in some meds or speed up absorption is some meds
answer
...
question
distribution
answer
occurs after the drug has been absorbed into the bloodstream and the drug is distributed throughout the body. Depends on blood flow to the tissues, meds ability to leave the blood stream, and ability to enter cells.
question
when drug binds to plasma proteins it causes unequal distribution and prevents med from reaching intended site
answer
...
question
drugs readily move across the placenta but not the BBB
answer
....
question
first pass effect
answer
The elimination of drug that occurs before it reaches the systemic circulation and have a considerably higher oral dose than sublingual or parenteral dose. Term that describes drugs metabolizing in the liver before having systemic effects. ORAL meds. Coumadin, lidocaine
question
biotransformation
answer
3rd stage of the Pharmacokinetic process where metabolism of the drug most often occurs in the liver but other tissues may be involved
question
excretion
answer
occurs after med is broken down into an inactive form. kidneys excrete most of meds. lungs are primary excreter for gaseous substances. Through bile of GI tract. Sweat, salivary, and mammary glands.
question
meds to monitro in elderly fro med excretion do to aging
answer
psychotropic, NSAIDs, oral hypoglycemics, anticoagulants, certain broad spectrum ABTs, cardiac meds.
question
therapeutic effect
answer
The desired or intended effect of a particular medication.
question
adverse drug effect/side effect
answer
an undesirable and potentially harmful action caused by the administration of medication. Can develop an iatrogenic disorder. Ex: neutropenia. Some are expected and may be tolerated as part of therapy. EX; morphine-pain management outweighs constipation. Monitor and report as per policy as well as to MedWatch
question
iatrogenic
answer
a disease produced secondary to the treatment of the patient; often it is the result of side effects of the drug therapy chosen by the physician
question
toxic effect
answer
specific group of symptoms related to drug therapy that carry risk for permanent damage or death. Can occur from a cumulative effect. Toxicities named from the system they affect. Ex: hepatoxicity.
question
cumulative effect
answer
occurs when body cannot metabolize one dose of a med before another dose of the same med is administered.
question
allergic reaction
answer
immune response that occurs when the body interprets the drug as foreign and forms antibodies against it. Ranges from minor to serious. S/S: rash, urticaria, fever, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting.
question
anaphylaxis
answer
a severe response to an allergen in which the symptoms develop quickly, and without help, the patient can die within a few minutes. Sudden rest. distress-sudden severe bronchospasm and cardiovascular collapse. Treated with vasopressors, bronchodilators, corticosteroids, O2 therapy, IV fluids, antihistamines
question
idiosyncratic effects/paradoxical effect
answer
any unusual or peculiar responce to a drug that may manifest itself by over response, , under response, or even the opposite of the expected response. R/t patients unique response to meds and thought to be due to genetic enzyme deficiencies.
question
synergistic response
answer
when the effect of two or more combined drugs is greater than the sum of their individual effects Ex: alcohol and barbiturates cause CNS depression but taken together they cause even greater CNS depression
question
BSA
answer
body surface area. Area of external surface of the body. most accurate way to calculate drudges for infants, children and older adults, pt's receiving oncologic meds, with low body weight. Expressed in square meters m2
question
due to differences in men and women fat composition and fluid composition meds have different, weaker, or stronger effects on certain genders.
answer
....
question
christian scientist view on meds
answer
place their faith in spiritual healing, therefore they do not take meds.
question
certain ethnic groups have more genetic variations which affects med therepy
answer
...
question
some ACE inhibitors have been found to be less effective in the african american pop.
answer
...
question
BMR
answer
basal metabolic rate.
question
lowered protein levels in body means less med bounds to plasma leading to a higher concentration of free med in the body. puts pt at risk for adverse effects due to high concentration of med.
answer
....
question
peak level
answer
or highest plasma concentration of the drug should be measure when absorption is complete. Ensures therapeutic levels can be maintained without causing toxicity.`
question
trough level
answer
the point when the drug is at its lowest concentration, indicating the rate of elimination. Ensures therapeutic levels can be maintained without causing toxicity.
question
half life
answer
is the amount of time it takes for 50% of the blood concentration a drug to be eliminated from the body. Ensures therapeutic levels can be maintained without causing toxicity.
question
minimum effective concentration/MEC
answer
Amount of drug required to produce a therapeutic effect.
question
minimum toxic concentration/MTC
answer
level at which toxic effects begin
question
agonist medication
answer
chemical entity extrinsic to endogenously produced substances that acts on a receptor and is capable of producing the maximal effect that can be produced by stimulating that receptor. Full ________ opioids activate the opioid receptors in the brain fully resulting in the full opioid effect. Examples are heroin, oxycodone, methadone, hydrocodone, morphine, opium and others.
question
antagonistic medication
answer
blocks opioids by attaching to the opioid receptors without activating them and cause no opioid effect and block full agonist opioids. Examples are naltrexone and naloxone. Naloxone is sometimes used to reverse a heroin overdose.



