Nursing Anatomy & Physiology – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
RED MARROW support and movement: the musculoskeletal system
answer
bone marrow found at the end of the long bones, also manufactures red and white blood cells
question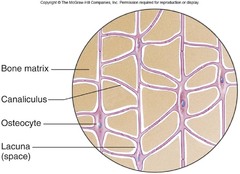
OSTEOCYTES support and movement: the musculoskeletal system

answer
They are bone cells that produce a hard, calcium rich extracellular matrix, and are embedded in a matrix of collagen and minerals and form the skeleton of an organism
question
SKELETON support and movement: the musculoskeletal system

answer
the hard structure (bones and cartilages) that provides a framework for the body, as well as attachment sites for muscle. Over 200 bones.
question
AXIAL SKELETON support and movement: the musculoskeletal system
answer
pertaining to the central part of the body, the head and trunk
question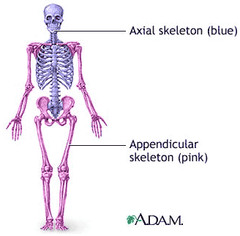
APPENDICULAR SYSTEM support and movement: the musculoskeletal system

answer
composed of 126 bones in the human body. The word appendicular is the adjective of the noun appendage, which itself means a part that is joined to something larger. Functionally it is involved in locomotion (Lower limbs) of the axial skeleton and manipulation of objects in the environment (Upper limbs).
question
JOINTS support and movement: the musculoskeletal system
answer
is the location at which two or more bones make contact. They are constructed to allow movement and provide mechanical support, and are classified structurally and functionally.
question
ligaments support and movement: the musculoskeletal system
answer
fibrous tissue that connects bone to bone, to provide stability to joints
question
tendon support and movement: the musculoskeletal system
answer
the strong connective tissue cords that attach skeletal muscles to bones
question
cartilage support and movement: the musculoskeletal system
answer
strong connective tissue that supports the body and is softer and more flexible than bone
question
osteoarthritis support and movement: the musculoskeletal system
answer
Inflammation of the bone and joint
question
rheumatoid arthritis support and movement: the musculoskeletal system
answer
A chronic systemic disease characterized by inflammation of the joints, stiffness, pain, and swelling that results in crippling deformities
question
osteoporosis support and movement: the musculoskeletal system
answer
a condition in which the body's bones become weak and break easily
question
cardiac muscle support and movement: the musculoskeletal system
answer
muscle tissue found only in the heart
question
smooth muscle support and movement: the musculoskeletal system
answer
involuntary muscle found in internal organs, muscle that forms the walls of the intestine, stomach, blood vessels, and other internal organs. has individual nucleus cells and no strations
question
skeletal muscle support and movement: the musculoskeletal system
answer
Vouluntary, striated muscle that moves bones, works in pairs and is attatched to bones by tendons
question
flexor support and movement: the musculoskeletal system
answer
a muscle that bends a part of the body, such as an arm or a leg
question
extensor support and movement: the musculoskeletal system
answer
A muscle that causes extension.
question
kidney
answer
organ that removes urea, excess water, and other waste products from the blood and passes them to the ureter
question
nephron
answer
blood-filtering unit in the renal cortex of the kidney
question
glomerulus
answer
little ball-shaped cluster of capillaries located at the top of each nephron
question
bowman's capsule
answer
cup-shaped strucutre of the nephron of a kidney which encloses the glomerulus and which filtration takes place.
question
proximal convoluted tubule
answer
first section of the renal tubule that the blood flows through; reabsorption of water, ions, and all organic nutrients
question
loop of Henle
answer
section of the nephron tubule that conserves water and minimizes the volume of urine
question
distal convoluted tubule
answer
The portion of the nephron between the loop of Henle and the collecting duct system.
question
urine
answer
a fluid produced by the kidneys that contains water, urea and other waste materials
question
ureter
answer
either of a pair of thick-walled tubes that carry urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder
question
urinary bladder
answer
a membranous sac for temporary retention of urine
question
urethra
answer
duct through which urine is discharged in most mammals and which serves as the male genital duct
question
sweat glands
answer
glands of the skin that secrete small amounts of water to the skins surface
question
liver
answer
Large organ just above the stomach that produces bile
question
gamete
answer
sex cell, a haploid reproductive cell that unites with another haploid reproductive cell to form a zygote
question
sperm
answer
the male reproductive cell
question
egg
answer
animal reproductive body consisting of an ovum or embryo together with nutritive and protective envelopes
question
testosterone
answer
a potent androgenic male sex hormone produced chiefly by the testes
question
van deferens
answer
During ejaculation carries the sperm from the testes to the urethra.
question
ovaries
answer
In animals, the female gonad, which produces egg cells.
question
oocyte
answer
Immature egg cell
question
ovum
answer
the female reproductive cell, female sex cell
question
zygote
answer
the fertilized egg; it enters a 2-week period of rapid cell division and develops into an embryo
question
monoploid
answer
of a cell or organism having a single set of chromosomes
question
diploid
answer
a cell that contains both sets of homologous chromosomes
question
ovulation
answer
process in which an egg is released from the ovary
question
fallopian tubes
answer
tubes which carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus and which provides the place where fertilization occurs
question
uterus
answer
organ of the female reproductive system in which a fertilized egg can develop
question
endometrium
answer
the mucous membrane that lines the inner wall of the uterus
question
menstruation
answer
the shedding of the uterine lining
question
penis
answer
the male organ that transfers sperm to a female and that carries urine out of the body.
question
scrotum
answer
external sac that contains the testes
question
testes
answer
organ that produces sperm
question
placenta
answer
a membrane that becomes the link between the developing embryo or fetus and the mother
question
fetus
answer
the developing human organism from 9 weeks after conception to birth
question
umbilical cord
answer
membranous duct connecting the fetus with the placenta
question
cornea
answer
the clear tissue that covers the front of the eye
question
iris
answer
muscular diaphragm that controls the size of the pupil
question
pupil
answer
the adjustable opening in the center of the eye through which light enters
question
retina
answer
the light-sensitive inner surface of the eye, containing the receptor rods and cones plus layers of neurons that begin the processing of visual information
question
rod cells
answer
work best in dim light and enable you to see black, white, and shades of gray
question
cone cells
answer
work best in bright light and enable you to see colors
question
optic nerve
answer
the nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
question
outer ear
answer
the part of the ear visible externally
question
tympanic membrane
answer
the membrane in the ear that vibrates to sound
question
middle ear
answer
the chamber between the eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, and stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea's oval window
question
malleus
answer
the ossicle attached to the eardrum, The first bone in the series of bones or ossicles of the middle ear. It is also called the hammer.
question
incus
answer
the ossicle between the malleus and the stapes, one of the three bones of the middle ear shaped like anvil
question
stapes
answer
The final bone in the series of small bones or ossicles of the middle ear. It is also called the stirrup.
question
eustachian tube
answer
A narrow tube between the middle ear and the throat that serves to equalize pressure on both sides of the eardrum
question
inner ear
answer
the innermost part of the ear, containing the cochlea, semicircular canals, and vestibular sacs
question
cochlea
answer
a coiled, bony, fluid-filled tube in the inner ear through which sound waves trigger nerve impulses
question
mechanical
answer
digestion Part of digestion that uses movement and muscles to break down food
question
chemical
answer
digestion the digestion process in which enzymes are used to break foods into their smaller chemical buiding blocks
question
hydrolysis
answer
A chemical process that lyses, or splits, molecules by the addition of water; an essential process in digestion.
question
enzymes
answer
molecules, usually proteins or nucleic acids, that act as catalysts in biochemical reactions
question
anus
answer
A muscular opening at the end of the rectum through which waste material is eliminated from the body
question
alimentary
answer
canal Also known as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract of the digestive tract, the alimentary canal is the long muscular "tube" that includes the mouth esophagus, somatch, small intesitne, and large intestine.
question
accessory
answer
organs In the GI tract, organs that play a role in digestion but not directly part of the alimentary canal. These include the liver, the gallbladder, the pancreas, adn the salivary glands.
question
surface
answer
area The ability to transport oxygen, food, and waste across cell membrane depends on, the amount of exposed surface of a substance
question
salivary
answer
glands three pairs of exocrine glands in the mouth that secrete saliva; the parotid, submandibular (submaxillary), and sublingual glands
question
amylase
answer
enzyme in saliva that breaks the chemical bonds in starches
question
pharynx
answer
muscular tube at the end of the gastrovascular cavity, or throat, that connects the mouth with the rest of the digestive tract and serves as a passageway for air and food
question
esophagus
answer
muscular tube that moves food from the pharynx to the stomach
question
epiglottis
answer
The flap of tissue that seals off the windpipe and prevents food from entering.
question
stomach
answer
large muscular sac (organ) that continues the mechanical and chemical digestion of food
question
peristalsis
answer
involuntary waves of muscle contraction that keep food moving along in one direction through the digestive system
question
gastric
answer
juice A digestive liquid added to food in the stomach to chemically break down protein.
question
protease
answer
Enzyme that breaks down proteins
question
chyme
answer
a semiliquid mass of partially digested food that passes from the stomach into the small intestine
question
small
answer
intestine digestive organ in which most chemical digestion takes place
question
pyloric
answer
sphincter circular muscle that controls the movement of chyme from the stomach to the small intestines
question
liver
answer
large organ just above the stomach that produces bile and functions in metabolism of protein and carbohydrate and fat; synthesizes substances involved in the clotting of the blood
question
bile
answer
a mixture of salts and phospholipids that aids in the breakdown of fat,, a digestive juice secreted by the liver and stored in the gallbladder
question
gallbladder
answer
a muscular sac attached to the liver that secretes bile and stores it until needed for digestion
question
pancreas
answer
located partially behind the stomach in the abdomen, and it functions as both an endocrine and exocrine gland. It produces digestive enzymes as well as insulin and glucagon
question
villi
answer
Small fingerlike projections on the walls of the small intestines that increase surface area
question
large
answer
intestine colon; organ that removes water from the undigested materials that pass through it
question
rectum
answer
The last part of the digestive tract, through which stools are eliminated
question
egestion
answer
Removal of undigested waste
question
atrium
answer
upper chamber of the heart that receives and holds blood that is about to enter the ventricle
question
ventricle
answer
a chamber of the heart that receives blood from an atrium and pumps it to the arteries
question
atrioventricular
answer
valve either of two heart valves through which blood flows from the atria to the ventricles
question
pulmonary
answer
artery carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs
question
deoxygenated
answer
blood blood that contains little oxygen (blue)
question
oxygenated
answer
blood blood that carries an abundant amount of oxygen
question
pulmonary
answer
vein carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart
question
systole
answer
the contraction of the chambers of the heart (especially the ventricles) to drive blood into the aorta and pulmonary artery
question
diastole
answer
relaxation period, the widening of the chambers of the heart between two contractions when the chambers fill with blood
question
pulmonary
answer
circulation circulation of blood between the heart and the lungs
question
systematic
answer
circulation flow of blood from the heart through the body back to the heart
question
coronary
answer
circulation the flow of blood to and from the tissues of the heart
question
blood
answer
The thick red fluid that flows through the body's blood vessels and transports important substances throughout the body.
question
plasma
answer
liquid portion of blood made up of water, dissolved salts, proteins, and other substances
question
hemoglobin
answer
iron-containing protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen for delivery to cells
question
white
answer
blood cells neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, lymphocytes and monocytes, cells that help the body fight diseases and infections
question
platelets
answer
cell fragments that play an important part in forming blood clots
question
lymph
answer
capillaries Tiniest lymphatic vessels, Drains away fluid so that it does not accumulate in the tissues of our body.
question
lymph
answer
nodes bean-shaped organs varying in size found throughout the body; filter microorganisms and foreign materials from lymphocytes
question
ateries
answer
carry blood from the heart to all parts of the body
question
veins
answer
blood vessels that carry blood back to the heart
question
capillaries
answer
tiny, thin-walled blood vessels that allow the exchange of gases and nutrients between the blood and the cells of the body
question
lymph
answer
the clear fluid that bathes each cell and transfers needed substances and wastes back and forth between the blood and the cells
question
pharynx
answer
throat; passageway for food to the esophagus and air to the larynx
question
larynx
answer
voice box; passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea; contains vocal cords
question
bronchi
answer
The passages that branch from the trachea and direct air into the lungs
question
bronchioles
answer
small subdivisions of the bronchi that are dead ends with tiny air sacks called alveoli at the end
question
alveoli
answer
tiny sacs of lung tissue specialized for the movement of gases between air and blood
question
diaphragm
answer
Large, flat muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity that helps with breathing
question
aerobic
answer
respiration Respiration that requires oxygen, sequentially releasing energy and storing it in ATP
question
anaerobic
answer
respiration Respiration in the absence of oxygen. This produces lactic acid.
question
lactic
answer
acid when a muscle continues to burn sugar but doesn't have enough oxygen to do it properly and becomes sore
question
neuron
answer
nerve cell that is specialized to conduct nerve impulses
question
sodium
answer
maintains cell fluids; helps nerves communicate, Na
question
potassium
answer
helps build protein; maintains fluids; helps nerves communicate; helps muscles contract, K
question
impulse
answer
the electrical discharge that travels along a nerve fiber
question
dendrite
answer
extension of the cell body of a neuron that carries impulses from the environment or from other neurons toward the cell body
question
cell
answer
body largest part of a typical neuron; contains the nucleus and much of the cytoplasm
question
axon
answer
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands.
question
axon
answer
terminal The endpoint of a neuron where neurotransmitters are stored.
question
neurotransmitter
answer
chemical used by a neuron to transmit an impulse across a synapse to another cell
question
synapse
answer
location at which a neuron can transfer an impulse to another cell
question
sensory
answer
neuron picks up stimuli from the internal or external environment and converts each stimulus into a nerve impulse
question
interneuron
answer
a nerve cell that relays messages between nerve cells, especially in the brain and spinal cord
question
motor
answer
neuron nerve cell that carries messages away from the central nervous system towards the muscles and glands; efferent neuron
question
nerve
answer
any bundle of nerve fibers running to various organs and tissues of the body
question
CNS
answer
Central Nervous System, the portion of the vertebrate nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord
question
PNS
answer
Peripheral Nervous System, the sensory and motor neurons that connect the CNS to the rest of the body
question
somatic
answer
a division of the nervous system that controls voluntary muscle movements
question
autonomic
answer
This nervous system provides involuntary control over smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands.
question
reflex
answer
arc Sensory receptor, sensory neuron, motor neuron, and effector that are involved in a quick response to a stimulus.
question
spinal
answer
cord a major part of the central nervous system which conducts sensory and motor nerve impulses to and from the brain
question
brain
answer
The part of the central nervous system that is located in the skull and controls most functions in the body
question
cerebrum
answer
anterior portion of the brain consisting of two hemispheres, large part of the brain that controls the senses and thinking
question
cerebellum
answer
the "little brain" attached to the rear of the brainstem; it helps coordinate voluntary movement and balance
question
brain
answer
stem the part of the brain continuous with the spinal cord and comprising the medulla oblongata and pons and midbrain and parts of the hypothalamus
question
medulla
answer
part of the brain nearest the spinal cord which controls breathing, heart rate and blood pressure
question
homeostasis
answer
process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment
question
hormones
answer
chemical messengers, mostly those manufactured by the endocrine glands that are produced in one tissue and affect another
question
negative
answer
feedback mechanism homeostatic control mechanism that reduces the output of the stimulus
question
positive
answer
feedback mechanism homeostatic control mechanism that increases the stimulus to push the variable farther from its originial value
question
pituitary
answer
gland the endocrine system's most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, the pituitary regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands
question
thyroid
answer
gland Two lobes joined by a central mass in the throat, inferior to the larynx, produces two major hormones., produces hormones that regulate metabolism, body heat, and bone growth
question
parathyroid
answer
gland behing the thyroid gland, acts to maintain homeostasis of calcium levels in blood
question
adrenal
answer
gland On the kidneys, fight or flight hormone, regulates water balance, blood pressure, and joint articulation, hormones: adrenaline, steroids (cortisone)
question
Isles
answer
of langerhans controls storage of sugar in the liver and blood level of sugar, insulin and glucagan, in the pancreas
question
testes
answer
In the scrotum, testosterone, the male gonads, which produce sperm and secrete male sex hormones.
question
ovaries
answer
female gonads, estrogen and progesterone, pelvic region, female secondary sex characteristics, menstrual cycle.



