Neurology H&P – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Common neurologic conditions
answer
-migraine -epilepsy -MS -stroke -TBI -spinal cord injury
question
Conditions with younger onset
answer
-epilepsy -Huntington -MS
question
Conditions with older onset
answer
-Alzheimer's -Parkinson's -brain tumors -stroke
question
Neurological symptoms (CC)
answer
-Confusion: memory impairment, getting lost, difficulty understanding or producing spoken or written language, problems with numbers, faulty judgment, personality change, or combinations thereof -Dizziness: vertigo (the illusion of movement of oneself or the environment),imbalance (unsteadiness due to extrapyramidal, vestibular, cerebellar, or sensory deficits), or presyncope (light-headedness resulting from cerebral hypoperfusion). -Weakness: muscle weakness or fatigue -Shaking: tremor, chorea (rhythmic motions), athetosis, myoclonus (mild shaking), tonic-clonic seizure (whole body) or fasciculation -Numbness: hypesthesia(decreased sensitivity), hyperesthesia (increased sensitivity), or paresthesia ("pins and needles" sensation). -Blurred vision: diplopia -Spells: fainting, pre-syncope, or syncope (and what happened during that time)
question
Neuro HPI points
answer
-Quality of symptoms: hyperalgesia, hyperesthesia, allodynia (neuropathic pain); severity -location: want to localize lesion -time course: especially with headaches -precipitating, exacerbating, alleviating factors: travel, viral infection, med change -associated symptoms: N/V, loss of bladder or bowel (seizures), diplopia, stiff neck, fever, LOC, photophobia, phonophobia
question
Precipitating factors (PMH)
answer
-Illnesses: HTN, DM, cancer, AIDS -Surgeries -Obstetrical history: pregnancy (hypertension and proteinuria -> preeclampsia) -Medications -Immunizations: polio, meningitis, tetanus, rabies, Guillan-Barre -Diet: Folate in pregnancy (spina bifida), B1 vitamin deficiency in alcohols (Wernicke's), encephalitis, B12 deficiency (paresthesia and loss of vibrations), DM problem with B12 absorption (pernicious anemia, botulism) -Tobacco, alcohol, and drugs: lung cancer metastatic to brain, alcohol withdrawal -Social history-education, occupation, sexual history, travel
question
ROS points
answer
-General -Immune: HIV -Heme: thrombocytosis, thrombocytopenia, polyctemia, Warfarin -Endocrine: hyperthyroid can lead to atrial fibrillation -Skin: neurofibromatosis, meningitis -Neck, eyes, ears, nose and throat
question
Physical exam
answer
-Vitals: BP (regular, irregular, atrial fib, orthostatic hypotension), Pulse, Respiratory rate, temperature, skin -Head (trauma), Eyes, Ears, Neck (passive flexion) -Cardiovascular: look for increased HR -Abdomen: association with back pain (aortic aneurysm) -Extremities and back: perform reflex and ROM -Rectal and Pelvic: check for urinary incontinence and sphincter tone
question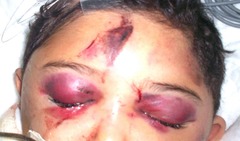
Racoon Eyes

answer
-Consistent with basilar skull fracture -Might see CSF drainage (rhinorrhea or otorrhea)
question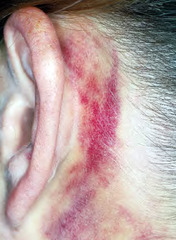
Battle sign

answer
-Trauma to temporal bone
question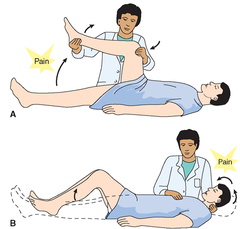
Kernig sign/Brudzinski sign

answer
-Positive in meningitis
question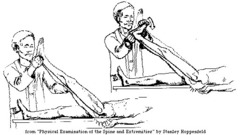
Lumbosacral nerve root irritation

answer
-Back pain: straight leg test which tests nerve roots -; pain will be reproduced in the popliteal area
question
Neurologic physical exam (all)
answer
-Mental Status Exam (MSE) -Cranial Nerves I-XII -Motor Function -Sensory Function -Coordination (Cerebellar Function) -Reflexes (Deep Tendon and Superficial Reflexes) -Stance and Gait
question
Mental status exam
answer
-Level of consciousness: awake, alert (visual or verbal cues), oriented (self, space, time situation); measure with Glascow coma scale -Cognitive function
question
Mental status exam components
answer
-Attention: focus on a stimuli at exclusion of others -(repeat 5-7 digits back) -Concentration: sustained attention (serial 7s) -Insight and judgment (differences between orange and apple) -Fund of knowledge (name of President, current events) -Affect (external and internal mood, facial expression, posture, talkativeness) -Immediate recall: (objects or numbers) - three objects -Recent recall: (same list 3-5 minutes later) -Remote recall: (major historic events) -Apraxia: Inability to perform previously learned tasks despite intact motor and sensory function
question
CN I test
answer
-ability to recognize common odors
question
CN II test
answer
-visual acuity (with corrective lenses): far vision (snellen chart) and near vision (using Rosenbaum pocket screener or reading newsprint) -visual fields: assessment of peripheral vision -fundoscopic exam: *optic disc color (creamy yellow): a very white disc suggests atrophy of the optic nerve *optic disc clarity (flat and sharp): increased intracranial pressure causes the optic disc to elevate ("papilledema") and increased intraocular pressure (glaucoma) causes the optic disc to depress ("cupping")
question
CN III Testing
answer
-motor: EOMs (also CN IV, VI) and levator palpebrae muscle -parasympathetic branch (PSNS constricts pupil, SNS dilates pupil): *ambient pupil size (normal lighting) *direct and consensual (opposite eye) pupillary constriction to light *near-far accommodation (pupils constrict when looking near and dilate when looking far)
question
CN IV Testing
answer
-Motor: EOMs (also CN III and VI)
question
CN VI Testing
answer
-Motor: EOMs (also CN III and IV)
question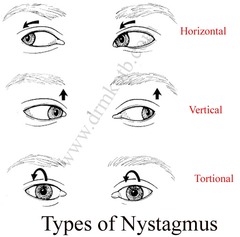
Nystagmus

answer
-check in EOMs -usually horizontal, but can be vertical -Horizontal nystagmus: peripheral/ear -Vertical nystagmus: suspicious of neurologic pathology -could be normal finding -alcohol, vertigo, head trauma, MS, dilantin SE (seizure medication)
question
CN V Testing
answer
-motor: muscles of mastication (temporalis, masseter, bulk) -sensory: *sensation in 3 divisions (ophthalmic, maxillary, mandibular) of Trigeminal nerve -; cotton wisp to all 3 areas *corneal touch reflex -; cotton wisp to eye
question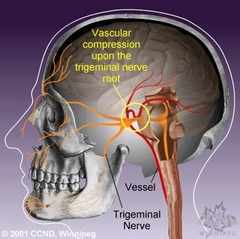
Trigeminal neuralgia

answer
-usually compression upon the trigeminal nerve root
question
CN VII Testing
answer
-motor: facial symmetry and movements (smile, puff cheeks, raise eyebrows), close eyelids tightly against resistance, labial speech sounds (b,p,m) -sensory: sweet and salty taste on anterior 2/3 of tongue
question
CN VIII Testing
answer
-Vestibular divison (semicircular canal/vestibular nerve): stand on one leg and keep balance -Cochlear division (hearing): assess auditory acuity (whisper or watch tick), Rinne test (using 512 Hz tuning fork), Weber test (using 512 Hz tuning fork)
question
CN IX Testing
answer
-sensory: gag response (also CN X), sour/bitter taste on posterior 1/3 tongue -motor: movement of soft palate upon phonation (say "ah"), swallowing function (swallow cup of water - also CN X)
question
CN X Testing
answer
-sensory: gag response (also (CN IX) -motor: movement of soft palate upon phonation (say "ah"), swallowing function (swallow cup of water - also CN IX)
question
CN XI Testing
answer
-motor: trapezius and SCM strength against resistance
question
CN XII Testing
answer
-motor: tongue midline position, movement and strength, atrophy or fasciculations of tongue, lingual speech sounds (l,t,d,n)
question
Bulk motor testing
answer
-atrophy: from muscle or nerve damage -dystrophy: hereditary cause, abnormal muscle fibers
question
Tone motor testing
answer
-tone = resistance of a muscle to passive movement at a joint -decreased tone: flaccidity (muscle, lower motor neuron, or cerebellar disease) -increased tone: *rigidity (increase constant over ROM): basal ganglia disease *spasticity (increase velocity dependent and not constant): corticospinal tracts affected
question
Muscle strength testing
answer
-Compare strength side to side, involving single muscle or groups of muscles -Grading: 5/5 Movement against gravity ; full resistance 4/5 Movement against gravity ; some resistance 3/5 Movement against gravity only 2/5 Movement if gravity is eliminated 1/5 Slight contractility (flicker) but no movement 0/5 No movement at all
question
Upper extremity muscle strength testing

answer
-Palmar pronator drift test -patient asked to extend arms with the palms up and hold them there -test is sensitive for subtle motor strength weakness -abnormal test: weak arm droops downward and pronates
question
Regional muscle testing - C5
answer
-Deltoid (C5): abduction of shoulders against resistance
question
Regional muscle testing - C6
answer
-Wrist extension (C6)
question
Regional muscle testing - C7
answer
-Wrist flexion, finger extension (C7)
question
Regional muscle testing - C8
answer
-Finger flexion (C8)
question
Regional muscle testing - T1
answer
-Interosseous muscles of hand (keep fingers spread apart against resistance) (T1)
question
Regional muscle testing - L4
answer
-Inversion/dorsiflexion of the foot (L4)
question
Regional muscle testing - L5
answer
-Dorsiflex toes (L5)
question
Regional muscle testing - S1
answer
-Evert/plantarflex foot (S1)
question
Regional muscle testing - hips and knees
answer
-Deep knee bend (tests hips and knees)
question
Regional muscle testing - quadriceps/hamstrings
answer
-Quadriceps/Hamstrings (flex ; extend knees against resistance)
question
Regional muscle testing - ankles
answer
-Walk on heels, walk on toes (tests ankle dorsiflexors, ankle plantarflexers)
question
Spinothalamic tract sensory tests
answer
-temperature sensation (hot vs cold) -pain sensation (sharp vs dull object) -crude touch
question
Dorsal column sensory tests
answer
-vibration/position sense -discriminatory sense, fine touch
question
Sensory cortex tests
answer
-stereognosis: patient asked to identify object w/ eyes closed -graphesthesia: patient asked to identify a number drawn in the palm with eyes closed -2 pint discrimination: examiner determines how far apart (in mm) two pointed stimuli must be in order to be perceived by the patient as two separate stimuli
question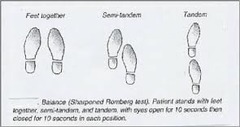
Coordination (cerebellar) testing

answer
-Rhomberg's -finger to nose (point to point) testing -heel-knee-shin: if abnormal leg will shake -rapid alternating movements in UE & LE: tap foot or rotate hand from palm to dorsum
question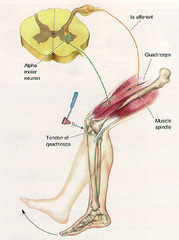
Deep tendon reflexes

answer
-Graded on a scale of 0, 1+, 2+, 3+, or 4+ (2+ is normal) -4+ Hyperactive, with "clonus" (clonus refers to multiple contractions and relaxations of a muscle group occurring in rapid succession after forcefully moving the joint) 3+ Increased, brisk 2+ Expected (normal) 1+ Diminished 0 No response Note: there are various distraction maneuvers that are useful in augmenting DTRs that are difficult to elicit -commonly tested: *biceps, brachioradialis (C5,6) *triceps (C7) *patellar (L3,4) *achilles (S1)
question
Normal vs pathological DTRs
answer
-normal = symmetric -absent or asymmetric = problem at that level of the spinal cord -hyperreflexive = damage to inhibitory UMN (often from stroke)
question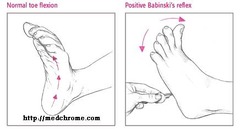
Superficial reflex - Babinski sign

answer
-plantar reflex (Babinski sign) -normal: toes curl downward, negative sign -abnormal: great toe dorsiflexes, other toes fan out, +- flexion withdrawal of ankle, knee, and hip -positive sign suggestive of UMN disease
question
Superficial reflex - upper abdominal
answer
-T8,9,10 -stroke upper abdomen diagonally toward umbilicus -umbilicus normally deviates toward the stroke
question
Superficial reflex - lower abdominal
answer
-T10,11,12 -stroke lower abdomen diagonally toward umbilicus -umbilicus normally deviates toward the stroke
question
Superficial reflex - cremasteric reflex
answer
-L1,2 -scratch the inner thigh -scrotum normally elevates on that side
question
Superficial reflex - anal wink reflex
answer
-S3,4,5 -anal sphincter contracts when perianal area is stroked with stimulus -cauda equina syndrome
question
Gait evaluation
answer
-Romberg's -"Native" gait: normal gait requires proprioception and cerebellar coordination -"Stress" gaits: walk on heels, walk on toes, "tandem" gait (heel-toe walking)



