Mcas Biology: Anatomy And Physiology Test Questions – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
skeletal system
answer
system which creates new blood cells, protects vital organs, allows for movement, and stores calcium
question
muscular system
answer
system which is responsible for moving bones and for moving materials inside the body (in your digestive system, also your heart!)
question
digestive system
answer
system responsible for breaking food into small molecules that can be taken in by cells
question
circulatory system
answer
system which is the transport (of gases, wastes, nutrients, etc) and delivery system of the body
question
respiratory system
answer
system responsible for taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide using the lungs (alveoli!)
question
excretory system
answer
the organ system, including the kidneys and bladder, that removes waste materials from the blood
question
nervous system
answer
system that consists of brain, spinal cord, and nerves and regulates the body's responses to internal and external stimuli
question
endocrine system
answer
collection of glands that secrete hormones into the blood which regulate growth, development, and homeostasis
question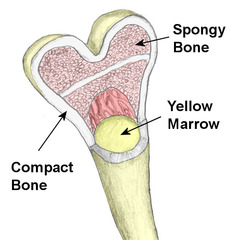
bone marrow

answer
a soft tissue inside the bone that produces blood cells
question
tendons
answer
structures which connect skeletal muscles to bones
question
ligaments
answer
structures that connect bone to bone at joints
question
cartilage
answer
a connective tissue that cushions the ends of bones and keeps them from rubbing together
question
smooth muscle
answer
Muscle tissue found in the walls of hollow organs, e.g., blood vessels, the digestive tract, etc. Smooth muscle is non-striated, and involuntary
question
skeletal muscle
answer
Voluntary, striated muscle that is attached to and moves bones
question
cardiac muscle
answer
Striated, involuntary muscle found only in the heart
question
mechanical digestion
answer
the physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces; occurs in mouth and stomach
question
chemical digestion
answer
the digestion process in which enzymes are used to break foods into their smaller chemical buiding blocks
question
esophagus
answer
a muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach
question
peristalsis
answer
wavelike contractions that move food throught the digestive system
question
stomach
answer
churns the food; HCl and pepsin work to chemically digest proteins
question
small intestine
answer
organ that completes the chemical digestion of food and absorbs the nutrients
question
villi
answer
finger-like projections lining the small intestine that absorb the nutrients and diffuse them into the blood
question
large intestine
answer
organ that absorbs water from undigested material
question
salivary glands
answer
produce saliva, which contains the enzyme amylase
question
Liver
answer
makes the bile; also removes toxins from the blood
question
gall bladder
answer
stores the bile
question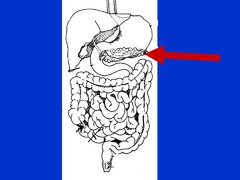
pancreas

answer
gland that makes digestive enzymes that break down carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins
question
bile
answer
chemical which breaks fats down into smaller globules
question
proteases
answer
enzymes produced by the pancreas to break down protein
question
lipases
answer
enzymes produced by the pancreas to break down lipids (fats)
question
sucrase
answer
enzyme produced by small intestine to break down the disaccharide sucrose
question
lactase
answer
enzyme produced by the small intestine to break down the disaccharide lactose
question
amylase
answer
enzyme produced by salivary glands and pancreas which breaks starch into sugar
question
heart
answer
pumps the blood
question
atria
answer
upper chambers of the heart that receive the blood
question
ventricles
answer
lower chambers of the heart that pump the blood out of the heart
question
valves
answer
ensure that blood flows in one direction only
question
pulmonary
answer
word meaning lungs
question
cardio
answer
word meaning heart
question
artery
answer
blood vessel with thick walls that carries blood AWAY from the heart; most carry oxygen rich blood
question
veins
answer
blood vessel containing valves that carries blood back to the heart; mostly carry oxygen poor blood
question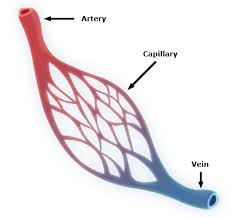
capillaries

answer
tiny, thin walled vessels that allow molecules to be exchanged
question
plasma
answer
liquid part of the blood that carries nutrients, hormones, etc.
question
red blood cells
answer
type of blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen
question
white blood cells
answer
type of blood cells responsibel for fighting germs
question
platelets
answer
cell part that help clot blood
question
pharynx
answer
passageway for food and air; the throat
question
nasal passage
answer
warns, moistens, and filters incoming air
question
hemoglobin
answer
iron-rich protein in red blood cells that oxygen binds to
question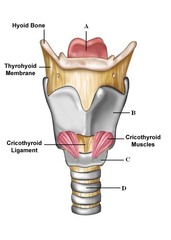
larynx

answer
passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea; contains the vocal chords
question
epiglottis
answer
flap of cartilage that covers the trachea so food is pushed into the esophagus
question
trachea

answer
tube leading down to the lungs
question
cilia
answer
hair-like structures in the trachea that sweep out particles
question
mucus
answer
sticky substance that helps trap germs
question
bronchi

answer
large branches off the trachea that lead to the lungs
question
bronchioles
answer
smaller branches off the bronchi
question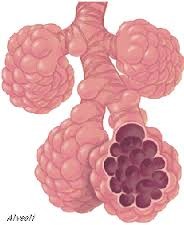
alveoli

answer
air sacs at the ends of the bronchioles where carbon dioxide and oxygen are exchanged
question
diaphragm
answer
large muscle involved in allowing the lungs to expand and contract
question
carbon dioxide
answer
gas produced by cellular respiration that is collected by the blood and released from the lungs
question
oxygen
answer
gas brought into lungs and delivered to body cells by red blood cells
question
excretion
answer
getting rid of waste, i.e. carbon dioxide, urea, toxins
question
kidney
answer
organ that filters urea out of the blood
question
urea
answer
nitrogen rich waste product produced by cells breaking down proteins
question
urine
answer
liquid waste composed of water, urea, and salts
question
ureter

answer
tube carring urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder
question
urinary bladder
answer
temporarily stores the urine until it can be released from the body
question
urethra
answer
tube leading from urinary bladder to outside the body
question
nephron
answer
tiny filtering unit of the kidney
question
filtration in nephron
answer
removal of water, salt, urea, and glucose from the blood
question
absorption in nephron
answer
return of glucose to the blood, as well as the correct amount of water and salt to maintain homeostasis
question
secretion in nephron
answer
removal of urea, water, and salts
question
homeostasis
answer
steady, internal state
question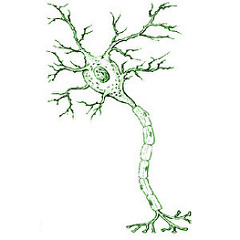
neuron

answer
a nerve cell
question
dendrites
answer
branching extensions of neuron that receives messages from neighboring neurons
question
axon
answer
long fiber that carries impulses away from the cell body of a neuron
question
synapse
answer
the gap between neurons
question
neurotransmitter
answer
a chemical that is released by a neuron for the purpose of carrying information across the gaps (synapses) between neurons
question
sensory neurons
answer
neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
question
interneurons
answer
neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally; connect sensory and motor neurons
question
motor neurons
answer
neurons that carry information from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands
question
glands
answer
organs that secrete hormones into the bloodstream



