KJZ First Aid For The USMLE Step 2 CK: Infectious Disease – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Classic symptoms of pneumonia
answer
Sudden onset, fever, productive cough (purulent yellow-green sputum or hemoptysis), dyspnea, night sweats, pleuritic
question
Atypical symptoms of pneumonia
answer
Gradual onset, dry cough, headaches, myalgias, sore throat
question
Pts who may have minimal or atypical signs of pneumonia on PE
answer
Elderly, COPD, diabetes, immunocompromised
question
PE of pneumonia
answer
? or bronchial breath sounds, rales wheezing, dullness to percussion, egophony, tactile fremitus
question
Common causes of pneumonia: children (6 wks - 18 yrs)
answer
Viruses (RSV), Mycoplasma, Chlamydia pneumoniae, Streptococcus pneumoniae
question
Common causes of pneumonia: adults (18 - 40 yrs)
answer
Mycoplasma, C. pneumoniae, S. pneumoniae
question
Common causes of pneumonia: Adults (40 - 65 yrs)
answer
S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, Anaerobes, Viruses, Mycoplasma
question
Common causes of pneumonia: Elderly (66+)
answer
S. pneumoniae, Viruses, Anaerobes, H. influenze, Gram + rods
question
Atypical causes of pneumonia
answer
Mycoplama, Legionella, Chlamydia
question
Nosocomial (hospital acquired) causes of pneumonia
answer
Gram - rods (GNRs), Staphlococcus, anaerobes
question
Causes of pneumonia in Immunocompromised
answer
Staphylococcus, Gram + rods, Fungi, Viruses, Pneumocystis jiroveci (w/ HIV), Mycobacteria
question
Causes of aspiration pneumonia
answer
Anaerobes
question
Causes of pneumonia in Alcoholics/IV drug users
answer
S. pneumonia, Klebsiella, Staphylococcus
question
Causes of pneumonia in Cystic Fibrosis (CF)
answer
Pseudomonas, Burkholderia, S. aureus, Mycobacteria
question
Causes of pneumonia in COPD
answer
H. influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, S. pneumoniae
question
Causes of Postviral pneumonia
answer
Staphlyoccocus, H. influenzae
question
Causes of pneumonia in Neonate
answer
Group B Streptococci (GBS), E. coli
question
Causes of recurrent pneumonia
answer
Obstruction, Bronchogenic carcinoma, Lymphoma, Wegener's granulomatosis, immunodeficiency, unusual organisms (e.g. Nocardia, Coxiella burnetii, Aspergillus, Pseudomonas)
question
Workup for pneumonia
answer
Physical exam, CXR, CBC, sputum Gram stain ; cx, nasopharygeal aspirate, blood cx, ABG
question
Test for Legionella pneumonia
answer
Urine Legionlla antigen test (detects only serogroup 1), sputum staining w/ direct fluorescent antibody (DFA), Cx
question
Test for Chlamydia pneumoniae
answer
Serologic testing, Cx, PCR
question
Test for Mycoplasma pneumonia
answer
Usu clinical, Serum cold agglutinins ; serum Mycoplasma antigen may also be sued
question
Test for Streptococcus pneumonia
answer
Urine pneumococcal antigen test, Culture
question
Test for Viral pneumonia
answer
Nasopharyngeal aspirate, Rapid tests for pathogens (influenza, RSV), DFA, Viral culture
question
What makes an adequate sputum Gram stain
answer
Many PMNs (;25 cells/hpf), few epithelial cells (;25 cells/hpf)
question
Criteria that risk stratifies pts with pneumonia
answer
PORT criteria (pneumonia severity index), based on age, comorbidity, ; presentation (Do not apply to AIDS pts)
question
When is in-hospital tx w/ IV antibiotics recommended for pts?
answer
;65 yrs of age, Comorbitidities (alcoholism, COPD, DM, malnutrition), Immunosuppression, Unstable vitals or signs of respiratory failure, AMS, and/or multilobar involvement
question
Coverage to add for pts with obstructive dz (CF or bronchictasis)
answer
Pseudomonal, Staphylococcal, anaerobic coverage
question
Likely pathogens ; tx for pt w/ OP community-acquired pneumonia, ?65 yo, otherwise healthy
answer
Suspected Pathogens: S. pneuoniae, Mycoplama pneumonia, C. pneumoniae, H. influenze, viral Empiric coverage: Macrolide (azithromycin), doxycycline, or fluoroquinolone
question
Likely pathogens ; tx for pt ;65 yo or w/ comorbidity (COPD, heart failure, renal failure, DM, liver dz, EtOH abuse)
answer
Suspected Pathogens: S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, aerobic GNRs (E. coli, Enterobacter, Klebsiella), S. aureus, Legionella, viruses Empiric coverage: Macrolide or fluoroquinolone; consider adding a second-generation cephalosporin or ?-lactam to the macrolide.
question
Likely pathogens ; tx for pt w/ Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization
answer
Suspected Pathogens: S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, anaerobes, aerobic GNRs, Legionella, Chlamydia Empiric coverage: Extended spectrum cepalosporin, ?-lactam/?-lacatamase inhibitor, or fluoroquinoloe; add a macrolide if atypical organisms are suspected
question
Likely pathogens ; tx for pt w/ Community-acquired pneumonia requiring ICU care
answer
Suspected Pathogens: S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, anaerobes, aerobic GNRs, Mycoplasma, Legionella, Pseudomonas Empiric coverage: Fluoroquinolone or extended-spectrum cephalosporin or ?-lacatam/?-lactamase inhibitor + macrolide
question
Likely pathogens ; tx for pt w/ Institution-/hospital-acquired pneumonia (pts hospitalized ;48 hrs or in a long-term care facility ;14 days)
answer
Suspected Pathogens: GNRs (including Pseudomonas ; Acinetobacter), S. aureus, Legionella, mixed flora Empiric coverage: Extended-spectrum cephalosporin or ?-lactam w/ antipseudomonal activity or carbapenem. Consider adding an aminoglycoside or a fluoroquinolone for coverage of resistant organisms (Pseudomonas) until lab sensitivites identify the best single agent.
question
Likely pathogens ; tx for pt who is critically ill or worsening over 24-48 hrs on initial antibiotic therapy
answer
Suspected Pathogens: MRSA Empiric coverage: Add vancomycin or linezolid; borader gram- coverage
question
Cause of tuberculosis
answer
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
question
Organ systems infected by TB
answer
Pulmonary most common, Can infect almost any including lungs, CNS, GU tract, bone, and GI tract
question
Risk factors for active TB (reactivation)
answer
Immunosuppresion (HIV), Alcoholism, Preexisting lung dz, diabetes, Advancing ages
question
Risk factors for TB exposure
answer
Homelessness, Crowded living conditions (prison), Immigration/travel from developing nations, Working in an allied health profession, Interacting with known TB contacts
question
History/PE of pt w/ TB
answer
Cough, Hemoptysis, dyspnea, Weight loss, Fatigue, Night sweats, Fever (TB = common cause of fever of unknown origin), Cachexia, Hypoxia, Tachycardia, Lymphadenopathy, Abnormal lung exam, Prolonged (;3 wk) sx duration
question
Type of pt who presents with atypical signs/sx ; has higher rates of extrapulmonary TB
answer
HIV
question
Tests to diagnose active TB
answer
1. Mycobacterial culture of sputum = gold standard, takes weeks 2. Acid-fast stain = rapid, but lacks sensitivity
question
CXR findings in TB
answer
Cavitary infiltrate in upper lobe, HIV pts or those with 1° TB may show lower lobe infiltrates w/ or w/o cavitation, Multiple fine nodular densities distributed throughout both lungs = miliary TB
question
Miliary TB
answer
Hematologic or lymphatic dissemination of TB
question
What to do if AFB stain is - but there is a high degree of clinical suspicion
answer
Bronchoscopy w/ bronchoalveolar lavage or bx (HIV pts have high rate of - sputum stains = -AFB smear accompanied by a + cx)
question
Drugs for TB
answer
"RIPE" Rifampin, INH, Pyrazinamide, Ethambutol
question
Test to diagnose Latent TB infection (LTBI, AKA previous exposure)
answer
+ PPD test, But immunocompromised individuals w/ LTBI may not mount a +LTBI (anergy) = interferon-? release assay, All cases of LTBI should be evaluated with CXR to r/o active dz
question
Tx of Active TB
answer
All cases should be reported to local ; state health departments, Respiratory isolation should be instituted, Tx with 4 drug regimen (rifampin, INH, pyrazinamide, ethambutol) x 2 mos, followed by rifampin ; INH x 4 mos,
question
SE of INH
answer
Peripheral neuritis (Administer vit B6 (pyridoxine)), Hepatitis
question
Tx of LTBI
answer
+ PPD but no s/s of active dz = INH x 9 mos, Alternatively INH x 6 mos or Rifampin x 4 mos
question
SE of Rifampin
answer
Turns body fluids orange
question
SE of Ethambutol
answer
Optic neuritis
question
Size of induration that indicates a + PPD test
answer
? 5 mm: HIV or risk factors, close TB contacts, CXR evidence of TB; ? 10 mm: Indigent/homeless, residents of developing nations, IV drug use, chronic illness, reidents of health ; correctional institutions, health care workers; ? 15 mm: everyone else, including those with no known risk factors
question
PPD test with - reaction with - control
answer
Anergy from immunosuppression, old age, or malnutrition; Does not rule out TB
question
How a PPD test is performed
answer
Injected intradermally on volar surface forearm, Diameter of induration measured at 48-72 hours, BCG vaccinnation usu = +PPD
question
Causes of acute pharyngitis
answer
Viral (90% in adults): Rhinovirus, coronavirus, adenovirus, HSV, EBV, CMV, influenza, Coxsackievirus, acute HIV infection; Bacterial: Group A streptococci (GAS), Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Corynebacterium diptheriae, M. pneumoniae; Impt to identify group A ?-hemolytic Streptococcus pyogenes
question
History/PE of typical streptoccocal pharyngitis
answer
Fever, sore throat, pharyngeal erythema, tonsillar exudate, cervical lymphdenopathy, soft palate petechiae, HA, vomiting, scarlatiniform rash (= scarlet fever)
question
History/PE of atypical streptoccocal pharyngitis
answer
Coryza, hoarseness, rhinorrhea, cough, conjunctivitis, anterior stomatitis, ulcerative lesions, GI sx,
question
Centor Criteria
answer
Used to ID streptococcal pharyngitis, need 3/4: 1. fever, 2. tonsillar exudate, 3. tender anterior cervical LAD, 4. lack of cough
question
How to dx step throat
answer
Clinical evaluation, Rapid GAS antigen detection (w/ 3/4 Centor Criteria, sensitivity ;90%), Throat cx
question
How to tx step throat
answer
PCN x 10 days; Alternative options = cephalosporins, amoxicillins, azithromycin, Symptomatic relief w/ fluids, rest, antyipyretics, ; salt-H2O gargles
question
Nonsuppurative complications of strep throat
answer
Acute rheumatic fever, Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis
question
Suppurative complications of acute pharyngitis
answer
Cervical lymphadenitis, Mastoiditis, sinusitis, Otitis media, Retropharyngeal or peritonsillar abscess, and rarely Lemierre's syndrome (thrombophlebitis of jugular vein) d/t Fusobacterium
question
Dx & tx of peritonsillar abscess
answer
Sx: odynophagia, trismus ("lockjaw"), muffled voice, unilateral tonsillar enlargement, erythema, w/ uvula & soft palate deviated away from affected side; Dx: localize abscess via intraoral US or CT, culture abscess fluid; Tx: antibiotics & surgical drainage
question
Causes of acute sinusitis (sx <1 mo)
answer
MC associated w/ viruses S. pneumonia, H. influenzae, & M. catarrhalis; bacterial causes are rare and are characterized by sx lasting <1 week
question
Causes of chronic sinusitis (sx > 3 mo)
answer
Represents a chronic inflammatory process, often d/t obstruction of sinus drainage & ongoing low-grade anaerobic infections; In diabetic pts, mucormycosis should be considered
question
MC affected sinuses
answer
Maxillary
question
History/PE of sinusitis
answer
Presents w/ fever, facial pain/pressure, HA, nasal congestion, & discharge; Exam = tenderness, erythema, & swelling over affected area; Bacterial = high fever, leukocytosis, & purulent nasal discharge
question
How to dx sinusitis
answer
Clinical dx - cx & X-ray not required but may guide management of chronic cases; Transillumination shows opacification of sinuses; CT is test for sinus imaging, but only if sx persist after tx; MRI is useful for differentiating soft tissue from mucus; Bacterial cx by sinus tap = gold standard but not routinely performed b/c of discomfort
question
Potential complications of sinusitis
answer
Meningitis, Frontal bone osteomyelitis, Cavernous sinus thrombosis, Abscess formation
question
Tx for viral/self-limited aute sinusitis
answer
Symptomatic therapy (decongestants, antihistamines, pain relief)
question
Tx for acute bacterial sinusitis (usu <7 days)
answer
Amoxicillin/clavulanate 500 mg PO TID x 10 days, Alternatively: clarithromycin, azithromycin, TMP-SMX, fluoroquinolone, or 2nd gen cephalosporin x 10 days
question
Tx for chronic sinusitis (4-12 wks)
answer
Adjuvant tx w/ intranasal corticosteroids, decongestants, & antihistamines; ABs like acute dz (amox/clavulanate 500 mg PO TID) but longer course (3-6 weeks); Surgical intervention possibly
question
Pts you would see w/ coccidiodomycosis
answer
HIV+, Filipino, AA, or pregnant pt from the SW US presenting with respiratory infection
question
History/PE of coccidiomycosis
answer
Presents like acute or subacute pneumonia or flulike illness, may involve extrapulmonary sites including bone, CNS, and skin; FEVER, anorexia, HA, chest pain, COUGH, dyspnea, arthralgias, & NIGHT SWEATS; Disseminated infection can present w/ meningitis, bone lesions, and soft tissue abscesses
question
How to dx a coccidiomycosis infection
answer
BAL w/ fungal cx of sputum, wound exudate, or other affected tissue; ID Coccidioides immitis spherules on H&E; Serology: antibodies: precipitin (IgM): 2 wks-2 mos; complement fixation (IgG) ? at 1-3 mos; titers > 1:16 ? disseminated infection
question
CXR findings in coccidiomycosis
answer
Normal or may show infiltrates, nodules, cavity, mediastinal or hilar adenopathy or pleural effusion
question
Location Coccidiomycosis is endemic to
answer
SW US (San Joaquin Valley, CA)
question
Incubation period of Coccidiomycosis
answer
1-4 wks after exposure
question
Tx for acute Coccidiomycosis
answer
Consider IV Amp B for severe or protracted 1° pulm infection & disseminated dz; PO fluconazole or itraconazole may be used for mild infection or continuation tx when pt stable
question
Tx for chronic Coccidiomycosis
answer
No tx for asymptomatic chronic pulm nodules or cavities; Progressive cavitary or symptomatic dz usu requires surgery + long-term azole tx for 8-12 mos
question
Antigenic drift
answer
Small, gradual ?s in surface proteins through pt mutations; allow virus to escape immune recognition
question
Antigenic shift
answer
Acute, major ? in influenza A subtype (significant genetic reassortment) circulating among humas; leads to pandemics
question
Who should get inactivated vaccine for the flu
answer
>50 yo, children 6 mo - 19 yo, pts any age w/ chronic medical problems (DM, heart dz, renal failure, HIV), pregnant women, Nursing home residents, & contacts of high-risk groups (e.g. health care workers)
question
US typical influenza season
answer
Nov - Mar
question
Influenza
answer
Highly contagious orthomyxovirus transmitted by droplet nuclei; 3 types: A,B,C; Subtypes of A are classified by glycoproteins (hemagglutinin & neuraminidase, eg H5N1)
question
History/PE of Influenza
answer
Abrupt onset of fevers, myalgias, chills, cough, coryza, weakness; Elderly may have atypical presentations characterized only by confusion
question
Dx of Influenza
answer
Often see leukopenia; Nasopharyngeal swab rapid influenza test available; Definitive dx can be made w/ DFA test or viral cx
question
Tx of Influenza
answer
Symptomatic: analgesics & cough medicine; Antivirals (oseltamivir or zanamivir) should be used w/in 2 days of onset, may shorten course by 1-2 days
question
Who can get live attenuated, nasally delivered, vaccine for the flu
answer
Healthy ppl 2-49 yo who are not pregnant or severely immunocompromised
question
Complications of influenza
answer
Severe 1° viral pneumonia, 2° bacterail pneumonia, sinusitis, bronchitis, & exacerbation of COPD & asthma; Reye's syndrome or fatty liver encephalopathy, is associated w/ ASA use in children w/ viral infections
question
Risk factors for meningitis
answer
Recent ear infection, Sinusitis, Immunodeficiencies, Recent neurosurgical procedures, ; sick contacts
question
History/PE of Meningitis
answer
FEVER, malaise, HA, NECK STIFFNESS, PHOTOPHOBIA, AMS, N/V, seizures, or signs of meningeal irritation (+ Kernig's & Brudzinski's signs)
question
How to dx meningitis
answer
Obtain blood cx, LP for CSF Gram stain ; cx (glucose, protein, WBC, RBC, opening pressure), Viral PCRs (HSV), Cryptococcal antigen (for HIV pts), CT or MRI to r/o other dx.
question
Causes of Meningitis in newborns (0-6 mos)
answer
GBS, E. coli/GNRs, Listeria
question
Causes of Meningitis in Children (6 mos- 6 yrs)
answer
S. pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis, H. influenzae type b, Enteroviruses
question
Causes of Meningitis in 6-60 yo
answer
N. meningitidis, Enteroviruses, S. pneumoniae, HSV
question
Causes of Meningitis in 60+ yo
answer
S. pneumoniae, GNRs, Listeria, N. meningitidis
question
Causes of Meningitis in HIV pts
answer
Cryptococcus, CMV, HSV, VZV, TB, toxoplasmosis (brain abscess), ; JC virus (PML)
question
Normal CSF Profile (RBCs, WBCs, Glucose, Protein, Opening pressure, Appearance, ?-globulin)
answer
;10 RBCs, ; 5 WBCs, ~2/3 serum Glucose, 15-45 Protein, 10-20 Opening pressure, Clear Appearance, 3-12 ?-globulin
question
CSF Profile in Bacterial meningitis (RBCs, WBCs, Glucose, Protein, Opening pressure, Appearance, ?-globulin)
answer
? RBCs, ? (;1000 PMNs) WBCs, ? Glucose, ? Protein, ? Opening pressure, Cloudy Appearance, ? or ? ?-globulin
question
CSF Profile in Viral meningitis (RBCs, WBCs, Glucose, Protein, Opening pressure, Appearance, ?-globulin)
answer
? RBCs, ? (monos/lymphs) WBCs, ? Glucose, ? or ? Protein, ? or ? Opening pressure, Most often clear Appearance, ? or ? ?-globulin
question
CSF Profile in Aseptic meningitis (RBCs, WBCs, Glucose, Protein, Opening pressure, Appearance, ?-globulin)
answer
? RBCs, ? WBCs, ? Glucose, ? or ? Protein, ? Opening pressure, Clear Appearance, ? ?-globulin
question
CSF Profile in SAH (RBCs, WBCs, Glucose, Protein, Opening pressure, Appearance, ?-globulin)
answer
?? RBCs, ? WBCs, ? Glucose, ? Protein, ? or ? Opening pressure, Yellow/red Appearance, ? or ? ?-globulin
question
CSF Profile in Guillain-Barre (RBCs, WBCs, Glucose, Protein, Opening pressure, Appearance, ?-globulin)
answer
? RBCs, ? WBCs, ? or ? Glucose, ?? Protein, ? Opening pressure, Clear or Yellow (high protein) Appearance, ? ?-globulin
question
CSF Profile in MS (RBCs, WBCs, Glucose, Protein, Opening pressure, Appearance, ?-globulin)
answer
? RBCs, ? or ? WBCs, ? Glucose, ? Protein, ? Opening pressure, Clear Appearance, ?? ?-globulin
question
CSF Profile in Pseudotumor Cerebri (RBCs, WBCs, Glucose, Protein, Opening pressure, Appearance, ?-globulin)
answer
? RBCs, ? WBCs, ? Glucose, ? Protein, ??? Opening pressure, Clear Appearance, ? ?-globulin
question
Tx for viral meningitis
answer
Supportive care, Close f/u
question
Tx for close contacts of pts with meningococcal meningitis
answer
Rifampin, ciprofloxacin, or ceftriaxone prophylaxis
question
Drug to be given 15-20 min before antibiotics to tx bacterial meningitis (esp S. pneumoniae)
answer
Dexamethasone
question
Empiric tx of bacterial meningitis in pts ;1 mo
answer
Ampicillin + cefotaxime or gentamicin (GBS, E.coli/GNRs, Listeria)
question
Empiric tx of bacterial meningitis in pts 1-3 mos
answer
Vancomycin IV + ceftriaxone or cefotaxime (Pneumococci, meningococci, H. influenzae)
question
Empiric tx of bacterial meningitis in pts 3 mos - adulthood
answer
Vancomycin IV + ceftriaxone or cefotaxime (Pneumococci, meningococci)
question
Empiric tx of bacterial meningitis in pts ;60 yrs/alcholism/chronic illness
answer
Ampicillin + Vancomycin IV + ceftriaxone or cefotaxime (Pneumococci, gram - bacilli, Listeria, meningococci)
question
Complications of meningitis
answer
Cerebral edema, Subdural effusions, Ventriculitis/hydrocephalus, Seizures, Hyponatremia, Subdural empyema, Other (Cranial nerve palsies, sensorineural hearing loss, coma, death)
question
Dx ; tx cerebral edema d/t meningitis
answer
Visible on CT/MRI, Presents w/ loss of oculocephalic reflex, Tx with IV mannitol
question
Dx ; tx Subdural effusions d/t meningitis
answer
May see on CT, occurs in 50% infants w/ H. influenzae meningitis, no tx necessary
question
Dx ; tx ventriculitis/hydrocephalus d/t meningitis
answer
Worsening clinical pic w/ improved CSF findings, Requires ventriculostomy ; possible IV antibiotics
question
Tx seizures d/t meningitis
answer
Tx w/ benzodiazepines ; phenytoin
question
Tx hyponatremia d/t meningitis
answer
Administer fluids ; monitor sodium concentration
question
Dx ; tx Subdural Empyema d/t meningitis
answer
Presents w/ intractable seizures, Requires surgical evacuation
question
Causes of Encephalitis
answer
MCC: HSV ; Arboviruses; Rarer etilogies: CMV, toxoplamosis, West Nile virus, VZV, Borrelia, Rickettsia, Legionella, enterovirus, Mycoplasma, ; cerebral malaria; (Children ; the elderly are the most vulnerable)
question
History/PE of Encephalitis
answer
Altered consciousness, HA, fever, ; seizures; lethargy, confusion, coma, ; focal neurologic deficits (CN deficitis, accentuated DTRs) may also be present
question
DDx for encephalitis
answer
Abscess or malignancy, toxic-metabolic encephalopathy, subdural hematoma, SAH
question
Dx encephalitis
answer
CSF shows lymphocytic pleocytosis ; ? protein, RBCs w/o trauma suggests HSV encephalitis, glucose ? in TB, fungal, bacterial, ; amebic infections; CSF Gram stain (bacteria), acid-fast (mycobacteria), India ink (Cryptococcus), wet prep (free-living amebae), ; Giemsa (trypanosomes); PCR (highly sens/spec) for HSV, CMV, EBV, VZV, ; enterovirus
question
MRI findings in HSV encephalitis
answer
Contrast-enhancing lesion in temporal lobe (HSV)
question
Tx for encephalitis
answer
HSV (associated w/ high morbidity): IV acyclovir; CMV: IV ganciclovir +/- foscarnet, Rocky Mt spoted fever, Lyme dz, ehrlichiosis: doxycycline
question
Classic clinical triad found in 50% cases of brain abscess
answer
Headache, Fever, Focal neurologic deficit
question
Major ddx of brain mass when fever is absent
answer
1° ; metastatic brain tumors
question
Focal, supurative infection of brain parenchyma, usu w/ "ring enhancing" appearance d/t fibrous capsule
answer
Brain abscess
question
MC infective organisms in brain abscess
answer
Streptococci, Staphylococci, Anaerobes; Multiple organisms often implicated (80-90% cases are polymicrobial)
question
Nonbacterial causes of abscess
answer
Toxoplasma, Aspergillus, Candida; Zygomycosis in immunocompromised host; Neurocysticercosis in relevant epidemiologic settings
question
Modes of transition in brain abscess
answer
Direct spread, Direct inoculation, hematogenous spread
question
Direct spread in brain abscess formation
answer
Paranasal sinusitis (10% cases, frequently affects young males, often d/t Strep milleri), Otitis media or mastoiditis (33%), or dental infection (2%)
question
Direct inoculation in brain abscess formation
answer
Affects pt w/ h/o head trauma or neurosurgical procedures
question
Hematogenous spread
answer
25% of cases; Often shows MCA distribution w/ multiple abscesses, Poorly encapsulated, Located at gray-white junction
question
History/PE in brain abscess
answer
Early sx: HA (MC sx, dull, constant, refractory to tx), drowsiness, inattention, confusion, seizures; Late: signs of ?ICP ; then focal neurologic deficit (CN III ; VI)
question
Dx brain abscess
answer
CT scan shows ring-enhancing lesion; MRI higher sensitivity for early abscesses ; posterior fossa lesions; CSF analysis not needed, may cause herniation syndrome; Lab values may show peripheral leukocytosis, ?ESR, ?CRP
question
Tx brain abscess
answer
Initiate borad-spec IV antibiotics ; surgical drainage; Third-generation cephalosporin + metronidazole +/- vancomycin; IV therapy for 6-8 wks followed by 2-3 wks PO; Dexamethasone for severe cases to ? cerebral edema; IV mannitol to ?ICP
question
Commonly tested AIDS-defining illnesses
answer
Oropharyngeal/esophageal candidiasis; CMV retinitis; Kaposi's sarcoma; CNS lymphoma, toxoplasmosis, or PM:; PJP or recurrent bacterial pneumonia; Disseminated mycobacterial or funal infection; Invasive cervical cancer
question
HIV
answer
Retrovirus, Targets and destroys CD4+ T lymphocytes
question
CD4+ count
answer
Indicates degree of immunosuppression; guides tx and prophylaxis & helps determine prognosis
question
Viral load
answer
May predict the RATE of HIV dz progression; provides indications for tx & gauges response to antireroviral tx
question
History/PE of HV infection
answer
Acute: often ASYMPTOMATIC, may have MONONUCLEOSIS-LIKE or FLULIKE sx (fever, LAD, maculopapular rash, pharyngitis, diarrhea, N/V, weight loss, HA) Later: night sweatrs, weight loss, thrush, recurent infections, opportunistic infections
question
Tests to dx HIV
answer
ELISA test (high sens, mod spec) detects anti-HIV ABs in bloodstream (can take ? 6 mos to appear); Western blot (low sens, high spec) = confirmatory; Rapid HIV tests
question
Baseline evaluation tests for HIV+ pt
answer
HIV RNA PCR (viral load), CD4+ cell count, CXR, PPD skin testing, Pap smear, VDRL/RPR, & serologies for CMV, hepatitis, toxoplasmosis, & VZV
question
Mutation that confers resistance to HIV infection
answer
CCR5
question
Drug to avoid in pregnant HIV+ pts
answer
Efavirenz
question
Tx for pregnant HIV+ pts not on an antiretroviral tx at time of delivery
answer
Intrapartum Zidovudine (AZT); Infant should receive AZT for 6 wks after birth
question
When to initiate antiretroviral tx for HIV+ pt
answer
1. Symptomatic pts (have AIDS-defining illness) regardless of CD4+ count or viral load; 2. Asymptomatic pts w/ CD4+ count < 350; 3. Pregnant pts; 4. Pts w/ specific HIV-related conditions (e.g., HIV-associated nephropathy)
question
Initial HIV+ antiretroviral regimen
answer
Most importantly use multiple meds (usu ?3) to achieve durable response & limit resistance; Some combo of 2 nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (RTIs) plus either 1 non-nucleoside RTI (NNRTI) or 1 protease inhibitor
question
Goal of HIV+ therapy
answer
viral suppression (<50 copies), which occurs more rapidly than immune reconstitution
question
Only live vaccine that should be given to HIV pts
answer
MMR (Do not give oral polio vaccine to HIV+ pts or their contacts!)
question
AIDS pathogens
answer
"The Major Pathogens Concerning Complete T-Cell Collapse" Toxoplasma gondii, Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare, Pneumocystis jiroveci, Candida albicans, Cryptococcus neoformans, Tuberculosis, CMV, Cryptosporidium parvum
question
Indication & tx for PJP prophylaxis
answer
CD4+ 200 for ? 3 mos
question
Indication & tx for MAC prophylaxis
answer
CD4+100 for >6 mos
question
Indication & tx for Toxoplasma gondii prophylaxis
answer
CD4+< 100 & + IgG serologies; Tx: double-strength TMP-SMX
question
Indication & tx for M. tuberculosis prophylaxis
answer
PPD > 5 mm or "high risk;" Tx: Sensitive: INH x 9 mos (+ pyridoxine) or rifampin +/- pyrazinamide x 2 mos; (Include pyridoxine w/ INH-containing regimens)
question
Indication & tx for Candida prophylaxis
answer
Multiple recurrences; Tx esophagitis w/ Fluconazole, oral w/ Nystatin swish & swallow
question
Indication & tx for HSV prophylaxis
answer
Multiple recurrences; Tx: Acyclovir, famciclovir, or valcyclovir
question
Indication & tx for S. pneumoniae prophylaxis
answer
All HIV+ pts, give every 5 yrs or when CD4+ <200; Tx: pneumovax
question
Indication & tx for Influenza prophylaxis
answer
All HIV+ pts; Tx: influenza vaccine annually
question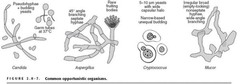
Describe appearance of common opportunistic infections

answer
Candida: Pseudohyphae + budding yeasts, germ tubes @ 37°C; Aspergillus: 45° angle branching septate hyphae, rare fruiting bodies; Cryptococcus: 5-10 µm yeasts w/ wide capsular halo, narrow-based unequal budding; Mucor: irregular broad (empty looking) nonseptate hyphae, wide-angle branching
question
Risk factors for Oropharyngeal candidiasis (thrush)
answer
Xerostomia, antibiotic use, denture use, immunocompromised states (HIV, leukemias, lymphomas, ca, DM, corticosteroid inhaler use, immunosuppressive tx)
question
Hx/PE of oropharyngeal candidiasis
answer
Soft white plaquest that can be rubbed off; Erythematous base & possible mucosal burning; Odynophagia if candidal esophagitis; DDx: oral hairy leukoplakia (lateral borders tongue, not easily rubbed off)
question
Dx oropharyngeal candidiasis
answer
Usu clinical; KOH or gram stain shows budding yeast and/or pseudohyphae
question
Tx oropharyngeal candidiasis
answer
Thrush: Local therapy (Nystatin suspension or clotrimazole tabs, PO azole like fluconazole); Candidal esophagitis w/ PO azole
question
Risk factors for Cryptococcal meningitis
answer
AIDS, exposure to PIGEON DROPPINGS
question
Hx/PE of Cryptococcal meningitis, DDx
answer
HA, fever, impaired mentation, ABSENT MENINGISMUS, DDx: toxoplamosis, lymphoma, TB meningitis, AIDS dementia complex, PML, HSV encephalitis, other fungal dz
question
Dx Cryptococcal meningitis
answer
LP (?CSF glucose, ?protein, ?leukocyte count w/ monocytic predominance, ?? opening pressure); + CSF cryptococcal antigen test; INDIA INK STAIN; fungal cx
question
Tx Cryptococcal meningitis
answer
IV Amphotericin B + flucystosine x 2 wks, Then give fluconazole 400 mg x 8 wks; Lifelong maintenance tx w/ fluconazole 200 mg QD or until CD4+ > 200 for > 6 mos; ? opening pressure may require serial LPs or VP shunt for management
question
Highly sensitive & specific test for Cryptococcal meningitis
answer
CSF antigen test
question
Risk factors for Histoplasmosis
answer
AIDS, spelunking, exposure to bird & bat excrement, Esp in OHIO & MISSISSIPPI RIVER VALLEYS
question
History/PE of Histoplasmosis
answer
1° exposure: asymptomatic or flulike; Presentation ranges from ø sx to fulminant dz w/ pulmonary or extrapulmonary manifestations; Fever, weight loss, hepatosplenomegaly, LAD, nonproductive cough, pancytopenia = disseminated infection (most often w/in 14 days)
question
DDx of Histoplasmosis
answer
Atypical bacterial pneumonias, blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, TB, sarcoidosis, pneumoconiosis, & lymphoma
question
Dx Histoplasmosis
answer
CXR: diffuse nodular densities, focal infiltrate, cavity (= chronic), or hilar lymphadenopathy; Urine & serum POLYSACCHARIDE ANTIGEN TEST = most sensitive; Cx diagnostic; Yeast form seen w/ SILVER STAIN on bx or BAL
question
Tx of Histoplasmosis
answer
Mild pulmonary dz or stable nodules: supportively in immunocompromised host; Chronic cavitary lesions: itraconazole for > 1 yr; Severe acute pulmonary dz or disseminated: Amphotericin B x 3-10 days followed by itraconazole x 12 wks or longer, maintenance tx w/ daily itraconazole
question
Risk factors for P. jiroveci pneumonia
answer
Impaired cellular immunity, AIDS
question
History/PE of P. jiroveci pneumonia
answer
DYPSNEA ON EXERTION, NONPRODUCTIVE COUGH, tachypnea, weight loss, fatigue, and IMPAIRED OXYGENATION
question
HIV pt w/ nonproductive cough & dyspnea
answer
Suspect P. jiroveci pneumonia
question
DDx of P. jiroveci pneumonia
answer
TB, histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis (PJB can present as disseminated dz or local dz in other organ systems)
question
Dx of P. jiroveci pneumonia
answer
Sputum cytology or bronch specimen w/ silver stain & immunofluorescence; ABG to check PaO2; CXR may show diffuse, BL interstitial infiltrates w/ ground-glass appearance, any presentation possible
question
Tx of P. jiroveci pneumonia
answer
HIGH-DOSE TMP-SMX x 21 days; Clindamycin & primaquine for pts w/ sulfa allergy; Prednisone taper for pts w/ hypoxemia (PaO2 35)
question
Transmission of CMV
answer
Sexual contact, Via breast milk, Respiratory droplets in nursery or day care facilities, Blood tranfusions
question
Percent of adults in US infected with CMV
answer
70%
question
Risk factors for CMV reactivation
answer
first 100 days s/p tissue or bone marrow transplant; HIV+ w/ CD4+ 10,000
question
History/PE of CMV
answer
May resemble EBV mononucleosis; manifests w/ CMV retinitis, GI & hepatobiliary invlovement (bloddy diarrhea, AIDS cholangiopathy), CMV pneumonitis, or CNS involvement (polyradiculopathy, transverse myelitis, subacute encephalitis)
question
CMV retinitis
answer
High rate retinal detachment ("pizza pie" retinopathy), presents w/ floaters & visual field ?s (CD4+ < 50)
question
CMV pneumonitis
answer
Cough, fever, sparse sputum production; High mortality rate; Pts w/ hematologic malignancies/transplant pts > AIDS
question
Dx CMV infection
answer
Virus isolation, cx, tissue examination, serum PCR
question
Tx CMV infection
answer
Ganciclovir or foscarnet; Tx underlying dz if pt is immunocompromised
question
Lady Windermere syndrome
answer
1° form of MAC infection, Occurs in apparently health non-smokers
question
2° pulmonary form of MAC
answer
affects pts w/ preexisting pulmonary dz such as COPD, TB, or CF
question
History/PE of Mycobacterium avium Complex (MAC)
answer
Disseminated infection occurs in AIDS pts w/ CD4+ <50, associated w/ fever, eakness, weight loss in pts who are not on HAART or chemoprophylaxis for MAC; Hepatosplenomegaly & LAD are occasionally seen; Adrenal insufficiency is possible if infiltrates adrenals
question
Dx MAC
answer
Obtain mycobacterial blood cx (+ in 2-3 wks); Labs show anemia, hypoalbuminemia, ? serum alk phos & LDH; Bx of bone marrow, intestine or liver reveals foamy macrophages w/ acid fast bacilli
question
Tx MAC
answer
Clarithromycin & ethambutol +/- rifabutin & HAART; Continue for >12 mos & until CD4+ >100 for >6 mos
question
Prevention for MAC
answer
Weekly azithromycin for those w/ CD4+ <50 or AIDS defining opportunistic infection
question
Risk factors for Toxoplasmosis
answer
Ingesting raw or undercooked meat; Changing cat liver; Exposure highest in France
question
History/PE of Toxoplasmosis
answer
1° infection asymptomatic; Reactivated in immunosuppressed, may present in specific organs (brain, lung, eye > heart, skin, GI tract, liver); Encephalitis common in seropositive AIDS pts (fever, HA, AMS, seizures, focal neurologic deficits)
question
Dx Toxoplasmosis
answer
Serology, PCR; With CNS involvement obtain CT (multiple isodense or hypodense, ring-enhancing mass lesions) or MRI (more sensitive for predilection for basal ganglia)
question
Tx of Toxoplasmosis
answer
Induction w/ hgih-dose PO pyrimethamine + sulfadiazine & leukovorin x 4-8 wks; Maintenance w/ low-dose same until dz resolved clinically & radiographically; TMP-SMX or pyrimethamine + dapson can be used for prophylaxis in pts w/ CD4+ < 100 and a + toxoplasmosis IgG
question
Two most likely differential diagnoses of ring-enhancing lesions in AIDS pts
answer
Toxoplasmosis CNS lymphoma
question
MC bacterial STD in the US
answer
Chlamydia trachomatis
question
Risk factors for Chlamydia
answer
Unprotected sexual intercourse, New or multiple partners, Frequent douching
question
Common cause of nongonoccocal urethritis in men
answer
Chlamydia infection
question
History/PE of Chlamydia
answer
Often asymptomatic, may present w/ URETHRITIS, MUCOPURULENT CERVICITIS, or PID; women: cervical/adnexal tenderness; men: penile d/c & testicular tenderness; May infect genital tract, urethra, anus, & eye
question
Ddx of Chlamydia
answer
Gonorrhea, Endometriosis, PID, Orchitis, Vaginitis, UTI
question
Lymphogranuloma venereum
answer
CAused by LGV serovars of Chlamydia; 1° form = painless, transient papule or shallow ulcer; 2° form = painful swelling of the inguinal nodes; 3° form = "anogenital syndrome" = anal pruritus w/ d/c, rectal strictures, rectovaginal fistula, & elephantitis
question
Dx of Chlamydia
answer
Usu clinical; Cx = gold standard; Urine tests (PCR or ligase chain reaction) = rapid means of detection, DNA probes & immunofluorescence take 48-72 hrs; Gram stain = PMNs but no bacteria (intracellular)
question
Complications of chlamydia
answer
Arthritis, Neonatal conjunctivitis, Pneumonia, Nongonococcal urethritis/PID (? ectopic pregnancy/infertility), lymphogranuloma venereum
question
Tx of chlamydia
answer
Doxycyclin 100 mg PO BID x 7 days, Or Azithromycin 1 g PO x 1 day; Use Erythromycin in pregnant pts; Tx sexual partners & maintain low threshold to tx for N. gonorrhoeae; LGV serovars require prolonged tx for 21 days
question
Reiter's syndrome
answer
urethritis, conjuncitivits, arthritis; Complication of Chlamydia infection
question
Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome
answer
Perihepatic inflammation ; fibrosis; Complication of Chlamydia infection
question
Gram stain Gonorrhea
answer
Gram -, intracellular diplococcus
question
History/PE of Gonorrhea infection
answer
Females: infect reproductive tract, GREENISH-YELLOW D/C, pelvic or ADNEXAL PAIN, swollen Bartholins glands; Males: limited to urethra, PURULENT URETHRAL D/C, dysuria, ; erythema of urethral meatus
question
Ddx of Gonorrhea
answer
Chlamydia, Endometriosis, Pharyngitis, PID, Vaginitis, UTI, Salpingitis, Tubo-ovarian abscess
question
Dx Gonorrhea
answer
Gram stain ; cx = gold standard; Nucleic acid amplification tests can be sent from penile/vaginal tissue or from urine
question
Sx of disseminated Gonorrhea infection
answer
Monoarticular septic arthritis, Rash, Tenosynovitis
question
Tx for Gonorrhea
answer
Ceftriaxone IM or cefepime PO x 1 dose; Also tx for presumptive chlamydia coinfection (doxycycline x 7 days or macrolide (azithromycin) x 1 dose); Disseminated dz requires IV Ceftriaxone ? 24 hrs
question
Complications of Gonorrhea
answer
Persistent infection w/ pain; Infertility; Tubo-ovarian abscess w/ rupture; Disseminated gonococcal infection
question
The "great imitator"
answer
Syphilis, b/c dermatologic findings resemble those of many other diseases
question
Cause of syphilis
answer
Treponema pallidum, a spirochete
question
History/PE of primary syphilis
answer
(10-90 days after infection): painless ulcer (chancre)
question
History/PE of secondary syphilis
answer
(4-8 wks after chancre): low-grade fever, HA, malaise, LAD, diffuse, symmetric, nonpruritic MACULOPAPULAR RASH ON SOLES ; PALMS, condylomata lata (highly infectious)
question
History/PE of latent syphilis
answer
Early latent: (period from resolution of 1° or 2° syphilis to end of FIRST YEAR of infection): no sx, + serology; Late latent: (period of asymptomatic infection ;1st yr)
question
History/PE of tertiary syphilis
answer
(1-20 yrs after initial infection): GUMMAS, NEUROSYPHILIS, TABES DORSALIS (post column degeneration), meningitis, ARGYLL ROBERTSON PUPIL (constricts w/ accommodation but not reactive to light), CV findings (AORTIC ROOT ANEURYSMS)
question
Dx syphilis
answer
Dark field micorscopy (motile spirochetes), VDRL/RPR (rapid, cheap, sens only 60-75% in 1°), FTA-ABS (sens ; specific, used as 2° dx test), T. pallidum particle agglutination test (TPPA, sens ; spec similar to FTA-ABS but easier to use)



