Human Disease chapter 3 and 4 PTT 140 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Describe the grades of cancers.
answer
Grades-microscope examination of the tumor to determine the degree of differentiation. More differentiated, the more it looks like tissue of origin. Good prognosis. Undifferentiating or anaplastic not resembling the tissue of origin, poor prognosis and highly malignant .
question
Describe the stages of cancers
answer
determines the extent of spread of the neoplasm by clinical examination, xrays, and biopsy. I= no lymph node spread; good prognosis , II- small % of nodes nearby: fair survival; mod survival, IV= aggressive invasive, metastases; poor survival rate.
question
Stages
answer
I = well differentiated resemble normal, II moderately differentiated, III poorly differentiated, IV= undifferentiated difficult to recognize tissue of origin
question
Grades
answer
I= no lymph node spread; good prognosis , II- small % of nodes nearby: fair survival; III distant nodes involved; mod survival, IV= aggressive invasive, metastases; poor survival rate.
question
TMN
answer
Another staging system. T= Tumor size and extent of primary, N= Nodes- number of lymph nodes involved, M= Metatasis to other sites.
question
Describe the signs and symptoms of cancer.
answer
Pain, Obstruction, Hemorrhage, Anemia, Pathologic Fx, Infection, cachexia.
question
Pain
answer
Late symptom. Cancer cell growing to destruction normal tissue and placing pressure on nerve endings, causing inflammation leading to pain.
question
Obstruction
answer
- can occur from a growing tumnor that compresses or pushes into the organ ex. Bronchus of the lung and intestine.
question
Anemia
answer
might be the result or hemorrhage or RBC loss as a result of cancer treatment
question
Pathologic Fracture
answer
- weakness in bone tumor may be a sign primary or secondary cancer.
question
Infection
answer
Tumor ulceration allow entry of microorganisms, chemotherapy and radition causes a decrease production of WBC.
question
Cachexia
answer
- condition of general illness from malnutrition seen terminally ill pt. evidence from rapidly growing tumor and treatment modalities with poor nutritional intake. - Ca cell take all of the nutrition from the good like a bully, that is why person atrophy.
question
What are some of the causes of cancer and how are they treated
answer
1. Chemical Carcinogens 2. Hormones, 3. Radiation, 4.Viruses, 5.Genetic predisposition, 6.smoking and tobacco,7. Diet, 8.Alcohol.
question
Chemical Carcinogens
answer
abound in our environment, frequency of exposure and potency (inhaled, ingested). Sometime, they do not cause a problem by themselves, but enhance cancer development.
question
Hormones

answer
can stimulate or treat cancers
question
Radiation
answer
UV, Xray exposure: basal and squamous cell, Melanomas, leukemia.
question
Viruses

answer
Hep B - liver Cancer, Herpes Simplex: and Cervical Cancer
question
Genetic Predisposition
answer
run in the family, colon and breast cancer.
question
Smoking and Tobacco

answer
smokers are 10 to 20 x likely to get lung cancer . bladder, pancreas, throat and mouth.
question
Diet and alcohol
answer
increase risk for many cancers alc- mouth,throat, and esophagus. diet- colon
question
Sexual bahavior
answer
increase the risk if cervical cancer.
question
cancer is treated with...
answer
Surgery, Chemotherapy, Radiation, and Hormones
question
surgery

answer
lung, stomach, colon, skin, breast, uterus, ovaries
question
Chemotherapy
answer
alone or in combination with surgery and radiation therapy
question
Radiation
answer
esp for tumors not surgically accessible, or as adjunct post-op X 6 wks
question
Hormones
answer
usually palliative for metastatic tumors
question
How can you tell from the name if a cancer is benign or malignant?
answer
Suffix indicates benign or malignant -oma = benign -carcinoma = malignant epithelial & glandular tissue: skin, breast, liver -sarcoma = malignant connective tissue: bone, muscle, fat, cartilage; faster spread & growth via circulation
question
Give examples of the exceptions of the oma suffix rule.
answer
Exceptions = lymphoma- lymph or bloodforming organs,- glioma- starts in brain or spine, melanoma- skin, glioblastoma- Brain, leukemia-WBC
question
Brain Death Irreversible

answer
No response to stimuli No reflexes No respirations or effort to breathe No brain activity evident on EEG Flat line EEG Irreversible for death
question
Compare and contrast benign vs malignant tumors.
answer
Benign-"tumor" Malignant-"Ca"
question
Benign-"tumor"
answer
Slow growth, local Symmetrical Encapsulated -won't spread Similar to original Similar to normal cells Non-recurrent Good prognosis -if not in brain, SC, gland, passageway(obstruct
question
Malignant-"Ca"
answer
Fast, metastasizes Invasive, crab-like Cells break away Different from original Atypical, immature Frequent recurrence Poor prognosis
question
What are some of the carcinogens that promote DNA cell changes that lead to cancers?
answer
cancer causing agent. virus, chemicals and radiation.
question
Cancer Diagnosis
answer
*C*hange in *bowel or bladder* habits *A* *sore* that does not *heal* *U*nusual *bleeding or discharge* *T*hickening or *lump in breast* or elsewhere *I*ndigestion or *difficulty swallowing* *O*bvious change in a *wart or mole* *N*agging *cough or hoarseness*
question
Development of Malignant Cancers
answer
1.Normal cell growth & differentiation stops 2.Mutation - genetic alteration of DNA 3.Precipitated by virus, chemicals, radiation, other carcinogens 4.Continued exposure to carcinogens causes cell abnormality & dysfunction 5.Immune system may prevent or reverse 6.Rapid growth to establish a site & thrive 7.Pre-cancerous if not yet firmly established 8.Deprive normal cells of nutrients
question
Describe the first steps in the inflammation process in cell and tissue healing.
answer
1.Body's response to cell or tissue injury 2.Must precede cell or tissue repair 3.Triggered by any trauma; physical injury, micro-organism invasion, ischemia, burn...
question
Describe the second steps in the inflammation process in cell and tissue healing.
answer
1. Mast cells release histamine when tissue is injured or irritated. 2.RUBOR redness, COLOR heat results, TUMOR-edema due to dilation DOLOR - pain: pressure on nerve endings. 3.Guarding creates loss of function.
question
Describe the third steps in the inflammation process in cell and tissue healing.
answer
1.Phagocytosis by neutrophils creates pus formation 2.Macrophages enter & clean up dead cells 3.If >7-10 days lymphocytes respond & form antibodies to destroy invader Becomes chronic if >2 weeks 4.Collagen & calcium deposits wall off invader = granuloma, may be permanent
question
antigen
answer
all cell have a protein or saccharide marker on the their surface that identify them.
question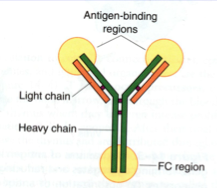
antibodies

answer
made by the lymphocytes to indentify and link to forgiein antigen and then remember the invader if returns
question
antibodies also
answer
also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large Y-shape protein produced by plasma cells that is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as bacteria and viruses.
question
Compare primary intention healing of wounds.
answer
Clean surgical incision + approxim. Small am't exudate. Little granulation tissue. Smallest scar. Shrinks in size in months or years.
question
Compare secondary intention healing of wounds.
answer
Large or dirty wound. Cannot be approx. must fill in. Large am't exudate. A lot of granulation tissue. Large scar. May need graft if epithelium cannot bridge the gap.
question
What factors help cells and tissues to heal? Positive
answer
Good blood supply to provide O2 and nutrients. Clean wound area - debridement. Good nutrition with protein, Vit A & C. Immobilization. No complications (infection).
question
What factors help cells and tissues to heal? Negative-detrimental
answer
Impaired circulation. Dead tissue & debris present. Large wound. Poor nutrition, dehydration. Infection, esp virulent organism. Excessive mobility - tears, bleeding. Radiation exposure - cell mitosis impaired. Steroid therapy.
question
mitosis

answer
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle process by which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus.
question
Describe potential complications that can occur during healing of wounds.
answer
Wound dehiscence, Adhesions, Infection, Keloid, and Soft tissue contractures.
question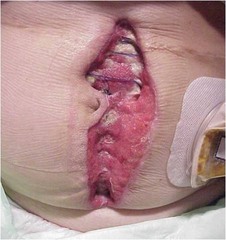
Wound dehiscence

answer
due to poor scar
question
Adhesions
answer
fibrous bands scar cling to nearby surface of organs
question
Infection
answer
esp resistant micro-organisms
question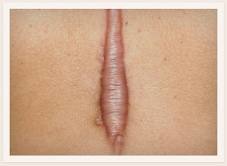
Keloid

answer
not cosmetic, but harmless
question
soft tissue contractures
answer
due to wound and scar contraction over time
question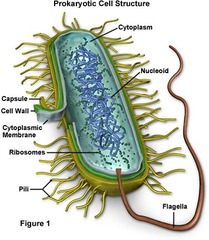
the characteristics of bacteria

answer
Normal flora on skin, orifices, intestines. ex: Staph, Strep, E.Coli, Pseudomonas, Salmonella. Doesn't require living tissue to survive. *Short incubation time (hours)*. Multiply very rapidly. Form characteristic pus. *Need antibiotic treatment*
question
the characteristics of Viruses

answer
Smallest micro-organisms. Invade living host cell nucleus to survive. Take over the cell and reproduce by replicating its DNA. Tendency to MUTATE . Incubation of *days, weeks, months, years*. Often has LATENT effect. *Antibiotocs do not kill it -immunizations create antibodies*. Produce a serous exudate. *Flu, colds, herpes, mononucleosis, AIDS, measles, small pox, mumps*.
question
What are the signs/symptoms of infection?
answer
- fever, tachycardia, fatigue, malaise Leukocytosis - increase in WBC #. Septicemia may develop if not controlled. Culture from involved tissue will identify organism.
question
10. How can you prevent infections?
answer
Universal precautions. Minimize direct/indirect exposure. Use disinfectants for objects & antiseptics for skin. Good nutrition.
question
What is the medical treatment for bacterial infections?
answer
antibiotics Broad-spectrum vs narrow-spectrum. Follow directions for taking with food, fluids, or fasting. Take in evenly-spaced intervals. Complete full course of meds. Avoid unnecessary use. May cause drug resistance.
question
What important steps must be followed while taking this medication? Why?
answer
Complete full course of meds. Avoid unnecessary use because it May cause drug resistance.
question
Give examples of infections that can be prevented by immunizations.

answer
-immunizations create antibodies Flu, colds, mononucleosis, measles, small pox, mumps



