HSP – Chapter 8 – Perceiving Motion – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Survival in the Environment Movement Perception
answer
Predators use movement of prey as a primary means of location in hunting.
question
Attentional Capture Movement Perception
answer
Motion attracts attention to the moving object. If prey remains motionless, it is less likely to be noticed.
question
Akinetopsia Movement Perception
answer
Blindness to motion. - Difficulties in pouring tea. - Difficulties in social interactions. - Sudden appearances of objects potentially life-threatening.
question
Functions of Movement Perception
answer
- Motion helps us understand gestures and activities. - Motion perception is essential for navigating in the environment. - Motion attracts attention. Movement helps perceptual organization. - Helps disambiguate the "inverse projection problem".
question
Real Motion
answer
An object is physically moving.
question
Apparent Movement Illusory Motion
answer
Stationary stimuli are presented in slightly different locations. Basis of movement in movies and TV.
question
Induced Motion
answer
Movement of one object results in the perception of movement in another object.
question
Motion Aftereffect
answer
View a moving stimulus for 30 to 60 seconds causes a stationary stimulus to appear to move. Movement appears to occur in the opposite direction from the original movement. The waterfall illusion is an example of this.
question
Larsen et. al Comparison of Apparent and Real Motion
answer
Participant is scanned by an fMRI while viewing three different displays. - Control condition - two dots in different positions are flashed simultaneously. - Real motion - A small dot is moved back-and-forth. - Apparent motion - dots are flashed so they appear to move. Results: - Control condition - each dot activated a separate area of visual cortex. - Apparent and real motion - activate visual cortex representing the space between the dots, both sets of stimuli were similar. The perception of motion in both cases is related to the same brain mechanism.
question
An object moves, and the observer is stationary.
answer
Movement creates an image that moves on the observer's retina. Motion perception is more than a stimulus crossing the retina.
question
An object moves, and the observer follows the object with his or her eyes.
answer
Movement is tracked so that the image is stationary on the retina. Motion perception is more than a stimulus crossing the retina.
question
An observer moves through a stationary environment.
answer
Image of environment moves across the retina but environment is perceived as stationary Motion perception is more than a stimulus crossing the retina.
question
Fovea
answer
Focus
question
Retina (peripheral)
answer
Non-focus
question
Ecological Approach - J.J. Gibson Motion Perception: Information in the Environment
answer
Information is directly available in the environment for perception. Look as an object moves past.
question
Optic Array
answer
Whole picture. Structure created by surfaces, textures, and contours. Change as the observer moves through the environment. Accounts for self movement and environmental movement.
question
Local Disturbance in the Optic Array
answer
Objects relative to background such that it is covered and uncovered. When anything changes in optic array. Perceiving motion.
question
Global Optic Flow
answer
Information for movement that occurs when all elements in a scene move. Indicates that it is the observer that is moving and not the scene. Overall movement of optic array.
question
Follow a Moving Object Motion Perception: Information in the Environment
answer
- As Maria follows Jeremy with her eyes. - Though Jeremy's image is stationary on the retina, there is local disturbance in the optic array. - Jeremy still covers and uncovers parts of the array.
question
Look Around the Room Motion Perception: Information in the Environment
answer
As Maria scans the room: everything moves at once. Global optic flow.
question
Reichardt Detectors Motion Perception: Information in the Environment
answer
Neurons that fire to movement in one direction. Inhibition and excitation changes can code it movement. Can only explain detection of image moving across retina situation.
question
Corollary Dishcharge
answer
Signals from the retinal and the eye muscles.
question
Image Displacement Signal (IDS) Corollary Discharge Theory Motion Perception: Retina Eye Information
answer
Movement of image stimulating receptors across the retina. Movement perception depends on these three signals.
question
Motor Signal (MS) Corollary Discharge Theory Motion Perception: Retina Eye Information
answer
Signal sent to eyes to move eye muscles.
question
Corollary Discharge Signal (CDS)
answer
Split from the motor signal.
question
Comparator
answer
The corollary discharge signal and the sensory movement signal meet at the __________ to determine whether movement will be perceived. A structure hypothesized by the corollary discharge theory of movement perception.
question
Corollary discharge signal (CDS) OR image displacement signal (IDS). Corollary Discharge Theory Motion Perception: Retina Eye Information
answer
Movement is perceived when comparator receives input from
question
Movement is not perceived when comparator receives input from: Corollary Discharge Theory Motion Perception: Retina Eye Information
answer
Both corollary discharge and image displacement signals at the same time.
question
Behavioral Evidence for Corollary Discharge Theory Demonstrations
answer
Eliminating the IDS with an afterimage. Seeing motion by pushing on the eyelid.
question
Physiological Evidence for Corollary Discharge Theory
answer
Damage to the MST in humans leads to perception of movement of stationary environment with movement of eyes; Experienced vertigo. Yes = IDS, but due to damage; no = CDS
question
Real-Movement Neurons Physiological Evidence for Corollary Discharge Theory
answer
Found in monkeys that respond only when a stimulus moves and do not respond when eyes moved.
question
Neurons on the striate cortex Motion Perception in the Brain
answer
Respond to movement of ends of objects.
question
Middle Temporal sensitive to motion Motion Perception in the Brain
answer
Evidence for this has been found in the MT cortex of monkeys.
question
Firing and Coherence Experiment by Newsome et. al Motion Perception in the Brain *KNOW THIS STUDY!!*
answer
Coherence to indicate the degree to which the dots move in the same direction; coherence of movement of dot patterns was varied. Monkeys were taught to judge direction of dot movement and measurements were taken from MT neurons. Results: Showed that as coherence of dot movement increased: the firing of MT neurons increases, and the judgment of movement accuracy increases.
question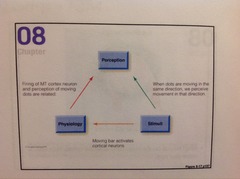
Lesioning Experiment by Newsome & Paré Motion Perception in the Brain

answer
Normal monkeys can detect motion with coherence of 1 or 2%. Monkeys with lesions in MT cortex cannot detect motion until the coherence is 10-20% Further evidence linking the firing of MT neurons to the perception of the direction of motion.
question
Microstimulation Experiment Movshon & Newsome Motion Perception in the Brain
answer
Electrically stimulate neurons in the MT cortex. - Monkey was trained to indicate direction of fields of moving dots. - - Neurons in MT cortex that respond to specific direction were activated. - Experimenter used micrositmulation to activate different direction sensitive neurons. - Monkey shifted judgment to the artificially stimulated direction. *Direction perception matched stimulated MT cells not the actual direction of the stimuli.*
question
Complex Cortical Cells Motion from a Single Neuron's POV
answer
Respond preferentially to an oriented bar moving in a specific direction.
question
MT and MST Cortex
answer
Respond to motion.
question
Response of a single directionally selective neuron
answer
Does not provide sufficient information to indicate the direction of movement.
question
Aperture Problem
answer
Observation of a small portion of a larger stimulus leads to misleading information about direction of movement. Activity of a single complex cell does not provide accurate information about direction of movement.
question
Biological Motion Perceptual Organization
answer
Movement of person or other living organism.
question
Point-Like Walker Stimulus
answer
Biological motion made by placing lights on the joints of a person.
question
Structure-from-Motion
answer
Takes place with point light walkers.
question
Neurological studies show biological motion is
answer
Processed by STS and FFA.
question
Solving the aperture problem
answer
MT pools responses of many V1 neurons (transform info.)
question
Grossman et. al Motion and the Human Body
answer
- Participants viewed point-light stimulus for activities. - Task was to determine whether motion was biological or scrambled. - Noise was added to dots so they can only achieve a 71% accuracy. - Transcranial magnetic stimulation applied to STS caused a decrease in ability to detect biological motion.
question
Implied Motion
answer
Still pictures that depict an action that involves motion.
question
Representational Momentum
answer
Observers show that the implied motion is carried out in the observer's mind.
question
Stimulus used by Freyd

answer
Frozen pictures remembered in the anticipated state.
question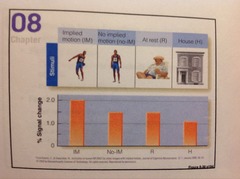
Kourtzi & Kanwisher

answer
fMRI response was measured in the MT and MST to pictures with: Implied motion, no-implied motion, at rest, houses. Results: Showed areas of brain responsible for motion fire in response to pictures of implied motion.
question
Event Event Perception
answer
A segment of time at a particular location with a beginning and an end.
question
Event Boundary Event Perception
answer
The point where one event ends and another begins.
question
Connection between events to motion perception
answer
Events almost always involve motion. Changes in the nature of motion are often associated with event boundaries.
question
the MT neuron fired more rapidly.
answer
Newsome, Britten, and Movshon found that as the coherence between the dots' direction of movement increased
question
the "time-forward" condition.
answer
Freyd (1983) presented two pictures sequentially that implied motion, such as a person jumping off a low wall. In the "same" condition, the second picture was identical to the first; in the "time-forward" condition, the second picture was the jumper closer to the ground; and in the "time-backward condition, the jumper was further from the ground. The observer's task was to respond whether or not the two pictures were the "same" or "different." The response time was longest for
question
similar when viewing apparent motion and real motion.
answer
Larsen et al. (2006) showed that the activation of brain areas is
question
person when the point-light walker is moving.
answer
A "point-light walker" wears lights on different body locations. When viewed in a dark room, an observer would perceive a(n)
question
decreased the person's ability to perceive biological motion.
answer
Presenting transcranial magnetic stimulation to the area of the STS in humans
question
apparent movement
answer
Our ability to perceive movement when reading "message boards" used in advertising, is based on
question
movement, because there is a CDS, but not an IDS.
answer
Percy is injected with a drug that paralyzes his eye muscles. When he is instructed to try to move his eye when looking a stationary scene, he perceives
question
the comparator receives the corollary discharge signal alone or image displacement signal alone.
answer
According to Corollary Discharge Theory, movement is perceived when
question
being motionless reduces both the attention-attracting effect of motion, and the chance that the cat will see the mouse against the background.
answer
A mouse "freezes" when it sees a cat nearby. This assists the mouse's survival because
question
a stimulus; the eye
answer
Real-motion neurons found in the monkey cortex fire when _____ moves, but do not fire when _____ moves.



