HPD Exam 2 (Cardio, breast, abd, peripheral vascular, male/female genitalia) – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What is the number one risk factor for breast cancer?
answer
Age
question
HPV Vaccination
answer
Males age 11-12 thru 21 y/o. HPV responsible for genital warts, anal cancer, penile cancer, HPV in women
question
Know different types of breast masses (4 types)
answer
Fibroadenoma -smooth, rubbery, round, mobile, nontender Cyst - soft to firm, round, mobile, tender Fibrocystic changes - nodular, ropelike Cancer - irregular, firm, mobile OR fixed to surrounding tissue
question
What are the recommendations for breast self exam?
answer
USPSTF recommends against self breast examination
question
Know the tail of Spence
answer
female breast is divided into 4 quadrants based on horizontal and vertical line passing thru the nipple; 5th area above upper outer quadrant is tail of spence
question
What are the different shapes, sizes, types of speculum?
answer
Plastic or metal, small, med, or large Pedersen is flat and narrow Graves is wider and curved
question
Which speculum is used for sexually active women that are nonparous?
answer
Medium pedersen is most comfortable
question
Which speculum is used for small introitus (virgen or elderly)?
answer
Narrow bladed Pedersen
question
Which speculum is used for parous women or women with vaginal prolapses?
answer
Graves speculum
question
What are the symptoms of STI? Which STI lacks symptoms?
answer
-Chlamydia: often asymptomatic or subtle in females; white penile discharge -Gonorrhea: yellow penile discharge; rash -Syphilis: penile ulcers(chancre) -Herpes: genital ulcers; cold sores
question
Inguinal hernias
answer
-Inspect both sides of groin to compare; -Palpate anterior inferior margin of scrotum, more upward toward external ring, invaginating scrotal skin behind peripubic fat; Follow spermaticord up toward inginal ligament, hook laterally to internal interior ring, ask pt to cough, palpate for mass as it moves against tip of index finger
question
Scrotal Hernia
answer
will be mass into scrotum (large, painful, or pulsatile)
question
Femoral hernia
answer
place fingers on anterior thigh in region of femoral canal, ask pt to cough or strain, note swelling/tenderness
question
Breast self exam advice
answer
BSE is best timed 5-7 days after menses, when hormonal stimulation of breast tissue is low
question
How to perform female breast exam? (proper techniques)
answer
-Systemic up-and-down search pattern, varying palpation pressure and a circular motion with the fingerpads; Best time to check 5-7 days after menstrual period -Inspection: fully expose chest looking for skin changes, symmetry, contours, retraction. -4 views to use (arm at side - skin, size and symmetry, contour, nipple; arms overhead - bringing out dimpling or retraction; hands on hips; leaning forward) PALPATION - patient should be supine, palpate from clavicle to bra line, mid-sternum to posterior axillary line and then the tail of spence. Pads of hands, vertical strip pattern, take your time (3min/breast), small concentric circles applying light, medium, and deep pressure at each point. Lateral examination, patient places same side hand over head. BREAST TISSUE - consistency varies, notably at lower ridge, irregular but symmetry, note NODULES location, size, shape, consistency, circumscribed, tenderness, mobility. NIPPLE - palpate & compress areola, note discharge (color, consistency, quantity of discharge).
question
Male breast exam
answer
Inspection - nipple and areola Palpation - areola and breast tissue for nodules, not in fatty deposition or normal disc or enlarged > 2 cm Examine in sitting position (preferred) or supine Repeat left and right. Abnormal is > 2 cm matted together, fixed, firm/hard
question
Mammography recommendations (USPSTF)
answer
50-74 y/os biennially (every 2 years); 75 y/os, insufficient evidence to recommend
question
Mammography recommendations (American Cancer Society)
answer
40-45 y/o-optional annual screening; 45-54 y/o-annual screening; >/= 55 y/o-biennial screening; continue screening if good health and life expectancy is >/= 10 y/o's
question
Mammography recommendations (American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists)
answer
;/= 40 y/o-annually
question
USPSTF Recommendations for Chlamydia screening
answer
young women under 24 y/o
question
USPSTF Grade A Recommendation for screening for HIV
answer
Screen 15-65 y/o and pregnant women
question
American Cancer Society Recommendation for Testicular Cancer
answer
Recommend this should be a part of the general physical exam; No recommendation for self exam
question
Assessing possible peritonitis
answer
Positive cough test, guarding, rigidity, rebound tenderness, and percussion tenderness. Start with one finger then hand -Rovsings sign!
question
Right lymphatic duct
answer
drains fluid from right side of head, neck, thorax, and right upper limb into R internal jugular and right subclavian veins
question
Thoracic duct
answer
collects from rest of body and empties into the junction of left internal jugular and left subclavian veins. All filtered thru interspersed LN's
question
Guidelines for Colorectal screening; USPSTF recommendation
answer
Guidelines recommend against screening with fecal occult blood testing following a digital rectal exam until age 75 y/o; USPSTF: screening for persons 50-75 y/o. Several methods DCBE (double contrast barium enema), CT screening
question
Cervical cancer screening guidelines
answer
Start at age 21, do about every 3 years, stop at age 65
question
Classification of Pap smear cytology: Bethesda System
answer
-Epithelial cell abnormalities: precancerous and cancerous lesions such as: squamous cells, including atypical squamous cells (ACS), which may be of undetermined significance (ACS-US); Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LSIL), including mild dysplasia; high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL), including moderate/severe dysplasia with features suspicious for invasion; and invasive squamous cell carcinoma -Grandular cells: including atypical endocervical cells or atypical endometrial cells, specified or not otherwise specified (NOS); atypical endocervical cells or atypical grandular cells, favor neoplasia; endocervical adenocarcinoma in situ; and adenocarcinoma
question
Ovarian Cancer: RFs and Screening
answer
5th leading cause of cancer-related death for women 2/3's of women affected ; 55y/o Most diagnosed late - metastatic disease No effective screening tests 3 symptoms merit attention - Abdominal distention, abdominal bloating, urinary frequency. Problematic due to similar sx's for other dz USPSTF recommend against screening RF = family hx and presence of BRCA1 & BRCA2 gene mutation, first degree relative with breast or ovarian CA, obesity, nulliparity, HRT
question
USPSTF recommendation on STI counseling
answer
Recommends intensive behavioral counseling for all sexually active adolescents and for adults who are at increased risk for STI
question
Where is the pap smear collected from?
answer
Squamocolumnar junction of cervix
question
Dysphagia
answer
difficulty swallowing
question
Odynophagia
answer
painful swallowing
question
Visceral pain
answer
occurs in hollow abdominal organs, or when solid organ capsules stretched, can be difficult to localize. Ischemia also stimulates fibers. Gnawing, burning, cramping, or aching. May cause systemic response-sweating/pallor/nausea/vomiting
question
Parietal pain
answer
originates from parietal peritoneum-peritonitis. Steady, aching, more severe than Visceral, localized over structure, aggravated by movement, coughing. Want to stay still
question
Colorectal cancer
answer
3rd leading cause of death; Lifetime risk 5%
question
Colorectal cancer RFs
answer
age, adenomatous polyps, FHx, chronic inflammatory disease, red meat, tobacco use, excessive EtOH, obesity
question
Referred pain
answer
pain felt in a part of the body other than its actual source
question
Which hepatitis is worse? Why?
answer
Hepatitis C; No immunizations and can lead to liver cancer
question
Addictions
answer
increasingly viewed as chronic relapsing behavioral disorders with substance induced alterations of brain neurotransmitters resulting in tolerance, physical dependence, sensitization, craving, and relapse
question
Urinary tract symptoms
answer
difficulty urinating, frequency, nocturia, urine volume/odor/color, dysuria, leaking or loss, strength or stream, straining, hesitation
question
Lithotomy position
answer
Drape pt appropriately and then assist her into the lithotomy position; Place one heel then another in the stirrups; Ask her to slide all the way down the examining table until her buttocks extends slightly beyond the edge; -Urethra is anterior to vagina which is anterior to rectum
question
Know terms gravida and para; Ex)G2F1L1A1
answer
Gravida=total number of pregnancies; Para=outcomes of pregnancies (full term, premature, abortion, living) Ex) G2F1L1A1=2 pregnancies, 1 full term and living, 1 abortion
question
Testicular Self-Examination (TSE) recommendations (USPSTF and ACS)
answer
USPSTF and American Cancer Society have not recommended routine TSE
question
Male genitalia examination: Best way to palpate
answer
Btwn thumb and fingers, note induration or tenderness
question
What age group of men are at most risk for testicular cancer?
answer
Men 15-34 y/o
question
What organs are in Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ)?
answer
Liver, gallbladder, pylorus of stomach, duodenum, hepatic flexure of colon, and head of pancreas
question
What organs are in Left Upper Quadrant (LUQ)?
answer
Spleen, splenic flexure of colon, stomach, body and tail of pancreas, and transverse colon
question
What organs are in LLQ?
answer
Sigmoid colon, descending colon, left ovary
question
What organs are in RLQ?
answer
Cecum, appendix, ascending colon, right ovary
question
Common or Concerning symptoms: Cardiac
answer
CP, palpitations, SOB, orthopnea(worse when supine), postural nocturnal dyspnea(sudden orthopnea while sleeping), edema, syncope -(always ask pt baseline activity/exercise)
question
Know S1 and S2 sounds; How to palpate?
answer
S1 is btwn diastole and systole (AV valves close); can feel on carotid artery during upstroke S2 is btwn systole and diastole (SL valves close)
question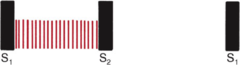
Pansystolic/Holosystolic murmur

answer
Starts with S1 and stops at S2 w/o a gap
question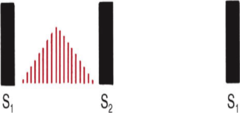
Midsystolic murmur

answer
Begin after S1 and stops before S2, brief gaps are audible btwn the murmur and heart sound
question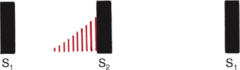
Late systolic murmur

answer
usually starts mid or late systole and persists up to S2
question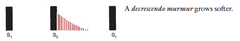
Early diastolic murmur
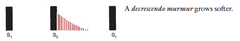
answer
starts immediately after S2 w/o a gap, then fades into silence before S1
question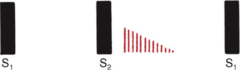
Mid Diastolic murmur

answer
starts a short time after S2, may fade away or merge into late diastolic murmur
question
Continuous murmur

answer
Some congenital and clinical conditions produce continuous murmur
question
Crescendo, Decrescendo, Crescendo decrescendo, plateau murmurs
answer
C: grows louder D: grows softer CD:rise and fall Plateau:same intensity thruout
question
In male breast exam, what is most concerning?
answer
Asymmetry
question
Breast cancer prevelance in women
answer
Breast cancer in up to 11% of women; 1-8 women; 80% of cases occur after 50 y/o; leading cause of cancer death in women
question
Modifable RFs for Breast Cancer
answer
breastfeeding < 1 yr., postmenopausal obesity, use of HRT, cigarette smoking, alcohol ingestion, physical inactivity, contraception type.
question
Grading of murmurs
answer
Grade 1 - very faint, heard only after listener has "tuned in"; may not be heard in all positions Grade 2 - quiet, but heard immediately after placing the stethoscope on the chest Grade 3 - moderately loud Grade 4 - loud, with palpable thrill Grade 5 - Very loud, with thrill. May be heard with the stethoscope is partly off the chest Grade 6 - very loud, with thrill. May be heard with stethoscope entirely off the chest
question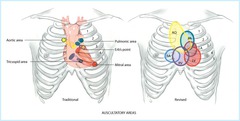
Where to auscultate aortic, pulmonic, tricuspid, mitral/apex valves

answer
Aortic: Rt 2nd ICS Pulmonic: Lt 2nd ICS Tricuspid: Lower Lt sternal border, 4th ICS Mitral/Apex: Lt 5th ICS, medial to midclavicular line
question
When to use diaphragm and bell for unique sounds
answer
Diaphragm=high pitch sounds (aortic regurgitation, S1, S2, murmurs) Bell=low pitch sounds (mitral stenosis, bruits)
question
Cardiovascular risk factors
answer
family hx, cigarette smoking, poor diet, physical inactivity, obesity, HTN, dyslipidemia, DM, pulse/high HR
question
Screening for cardiovascular risk factors
answer
Begin routine screening at 20 y/o for individuals with RFs for CVD
question
Criteria for DM
answer
Any one of the following: 1)HbA1c of 6.5% or higher 2)Fasting blood glucose of 126 mg/dL or higher 3)2 hour plasma glucose level of 200 mg/dL 4)Random plasma glucose of 200 mg/dL or higher with symptoms of hyperglycemia
question
Abnormal pulse: Paradoxical pulse
answer
Greater than normal drop in systolic BP during inspiration. Can check with cuff at systolic level (normal variant is 3-4 mmHg) if higher then be suspect and check closely
question
Abnormal pulse: Carotid artery thrills and bruits
answer
detection of vibrations or thrills (cat purring) during palpation. Bruits can be detected thru auscultation of the carotid arteries- murmur like turbulent sound (Best if pt stops breathing for 15 seconds, listen with diaphragm and repeat with bell. Place at upper end of thyroid cartilage below angle of jaw)
question
Special population at risk for CVD
answer
-Women and African Americans -Women's leading cause of death is CVD -AA men and women show marked ethnic disparities against white pops in US -Smokers
question
What is JVP
answer
Jugular Venous Pressure: reflects right arterial pressure (central venous pressure) and right ventricular end diastolic pressure JVP is estimated from right internal jugular vein; We see a wave prior to S1 when right atrium contracts and again during sytole when blood enters from the vena cava(Pt should be around 30 degrees elevated, supine)
question
Two cardiac maneuvers and what you are listening for during cardiac exam
answer
Left lateral decubitus: use bell at PMI to listen for mitral stenosis Aortic regurgitation: pt leans fwd, use diaphragm, exhale fully, stop breathing, left sternal border and apex
question
Peripheral vascular- grading of pulse
answer
3+ = bounding pulse 2+ = brisk, expected, normal 1+ = diminished, weaker than expected 0 = absent, unable to palpate
question
Peripheral artery disease
answer
-stenotic, occlusive and aneurysmal disease of abdominal aorta/mesenteric/renal branches, and arteries of lower extremities -Pain can arise from skin, musculoskeletal or nervous system -Note skin changes to lower extremities and report of claudication symptoms (with activity) -Risk of death from MI/stroke triples in adults with PAD -ABI(ankle-brachial index) can be used to diagnose PAD
question
Warning signs/symptoms of PAD
answer
-Fatigue, aching, numbness or pain that limits walking or exertion in the legs; if present, identify the location. Ask also about erectile dysfunction -Any poor healing or nonhealing wounds of the legs or feet -Any pain present when at rest in the lower leg or foot and changes when standing or supine -Abdominal pain after meals and associated "food fear" and weight loss -Any first-degree relatives with an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)
question
PAD RFs
answer
; 65 y/o ; 50 y/o with hx of diabetes or smoking Leg symptoms with exertion Nonhealing wounds
question
What is edema? What is pitting edema?
answer
accumulation of excessive fluid in extra vascular interstitial space; pitting= Pressing thumb firmly for 2 seconds over the: dorsum of each foot and behind each medial malleolus and over the shins Pitting - a depression caused pressure from your thumb
question
Venous tenderness or cords in calf
answer
can accompany DVT
question
ALLEN TEST BUERGER TEST VERICOSE VEINS VENOUS VALVES
answer
ALLEN TEST - compares patency of ulnar ; radial arteries BUERGER TEST - looks for arterial insufficiency by looking at postural color changes. VERICOSE VEINS - test for mapping by compression VENOUS VALVES - trendelenberg test
question
Know the artery layers and its unique qualities
answer
Intima - single continuous lining of endothelial cells with remarkable metabolic properties (innermost) Media - smooth muscle cells, dilate and constrict to accommodate BP and flow Adventitia - connective tissue with nerve fibers and vasa vasorum (outermost) Atherosclerosis (not a layer) - chronic inflammatory disease initiated by injury to vascular endothelial cells, promoting atheroma plaque formation and vascular lesions of hypertension
question
Layers of the veins
answer
Intima - nonthrombogenic Media - rings of elastic tissue and smooth muscle Externa - connective tissue Leg veins have weaker structures - susceptible to irregular dilation, compression, ulceration, and tumor invasion
question
PAD etiology
answer
Approximately 8 million ppl or 6-12% of pop (;40 y/o) affected; Silent in nearly 50%; Risk of death from MI/CVA triples in adults with PAD
question
Definitions of different uterine bleeding
answer
Menarche—age at onset of menses Dysmenorrhea—pain with menses, often with bearing down, aching, or cramping sensation in the lower abdomen or pelvis Premenstrual syndrome (PMS)—a cluster of emotional, behavioral, and physical symptoms occurring 5 days before menses for three consecutive cycles Amenorrhea—absence of menses Abnormal uterine bleeding—bleeding between menses; includes infrequent, excessive, prolonged, or postmenopausal bleeding Menopause—absence of menses for 12 consecutive months, usually occurring between ages 48 and 55 years Postmenopausal bleeding—bleeding occurring 6 months or more after cessation of menses
question
Abnormal Bleeding patterns: Polymenorrhea Oligomenorrhea Menorrhagia Metrorrhagia Postcoital bleeding
answer
Polymenorrhea - less than 21-day intervals between menses Oligomenorrhea - infrequent bleeding Menorrhagia - excessive flow Metrorrhagia - or intermenstrual bleeding Postcoital bleeding-bleeding after sex
question
Male exam: What do the structures feel like?
answer
Epididymis-light pressure, feels cordlike and minimally nodular Spermatic cord/vas deferens-feels stiff and tubular Prostate-rubbery and nontender with no evidence of fixity in surrounding tissue
question
Risk factors for testicular cancer
answer
-most common solid cancer of young men btwn ages 15-34 -history of carcinoma in the contralateral testicle, mumps, orchitis, inguinal hernia, hydrocele as child, positive family hx
question
Know clock on women exam
answer
-think of woman's breast as the face of a clock starting at 12 noon and moving towards 1 o'clock. Continue around the entire circle until you reach 12 noon again. We can use clock to determine locations of masses, nodes, lumps, etc. Also don't forget tail of spence!
question
Cardiac output
answer
the amount of blood pumped by the heart per minute CO=HRxSV Normally 5-6 liters/min at rest
question
What is important to remember when taking a sexual health history
answer
be sure to maintain a neutral, nonjudgmental tone so that your patients feel safe and trust you with their concerns
question
Most prevelant HPV types
answer
HPV 16 and 18 (70%)



