Greek Medicine (1500-200 BC) – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Greek society
answer
The success and wealth of the Greek Empire allowed the Greeks to develop a love of learning and to try to find answers to the mysteries around them. There were two main strands to Greek medicine. The first stemmed from their strong belief in the gods. The god of healing was Asclepius (also spelt Asklepios or Aesculapius). The second stemmed from new ideas from Greek doctors, the most famous of whom was Hippocrates
question
Greek gods and medicine

answer
The Greeks believed in gods for almost all aspects of life. Poseidon was god of the sea; Ares was god of war; Asclepius god of healing. Temples were built to him, called Asclepeia. It was believed that if a sick person went to sleep in an Asclepion, Asclepius and his daughters would visit him in his dreams and cure them. Asclepius was the Greek god of healing. The temples that were built to worship him were called 'asclepions' and used for treating the sick. The cult of Asclepius became more important during the 5th century bc and the three most important asclepions - in Epidaurus, Pergamum and Cos - were all built or rebuilt around 350 bc. Asclepius had two daughters, Panacea and Hygieia. As you can see from Source C, the asclepions were large and complicated sites. People who were ill would go to an asclepion and spend at least one night there, praying to Asclepius and being treated. They would usually go through the following processes:• make an offering or sacrifice to Asclepius • bathe in the sea to cleanse and purify themselves • sleep for at least one night in the abaton, a long, narrow building open to the air on each side. While sleeping in the abaton, patients expected to be visited by the god. Some had dreams. Others were probably treated by the priests. The snake was Asclepius' sacred animal. In Greek carvings, he is usually shown holding a staff with a snake wound round it. The priests used snakes as part of the treatment in the abaton. Ointments were often rubbed into the part of the body where symptoms occurred. Sometimes the snakes licked the sick part as well. The patients were supposed to wake up cured the next morning, and some did. Others did not. One of our most important sources about what happened in an asclepion is an account written by Aristides, a philosopher from Athens, about his treatment in ad 150. Aristides had spent years visiting different asclepions.
question
New Greek medical ideas
answer
As well as believing in the healing powers of Asclepius, there was also a lot of respect for other medical theories. The Greeks loved philosophy and came up with lots of new ideas as a result. One important Greek philosopher was Aristotle, who originally developed the Theory of the Four Humours which became the basis for Greek medical practice. Hippocrates developed the theory further. Despite being wrong, it was a theory which was to be widely used by doctors for nearly 2,000 years. The reliance on the theory was so heavy that it prevented doctors from looking elsewhere for causes of disease.
question
The Theory of the Four Humours

answer
Aristotle suggested that the body was made up of four liquids or 'humours' - blood, phlegm, yellow bile and black bile. He connected these with the four seasons - yellow bile with summer, black bile with autumn, phlegm with winter, blood with spring - and said that there could therefore be too much of the connected humour in the body in a particular season. This would be a problem because, according to Aristotle, a person needed to keep the humours in perfect balance in order to be healthy.
question
Clinical observation

answer
Clinical observation is the careful noting of all the symptoms of a disease and of the changes in the patient's condition during the course of an illness. A doctor was supposed to follow four steps: • Diagnosis. Study the symptoms of the patient. In what ways is the patient different from normal? • Prognosis. Try to predict the course the illness will follow, by thinking about previous patients with the same symptoms. • Observation. Continue to observe the patient. noting changes in their condition and comparing these to the prognosis. • Treatment. Treat the patient, but only when observations have confirmed the prognosis and previous exp
question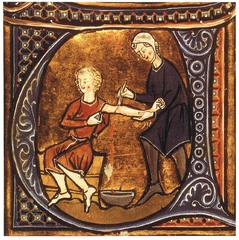
Treating illness

answer
Greek medical treatments aimed to re-balance the humours. Treatments prescribed included: bleeding vomiting purging Bleeding a patient was a treatment which was used right through to the 19th century. A scratch was made in the skin and the blood was let out into a cup.



