Crack the PCAT: Organic Chemistry – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Atom
answer
Basic building block of matter, representing the smallnest unit of a chemical element
question
Amine
answer
organic compounds that contain only hydrogen, carbon , and nitrogen
question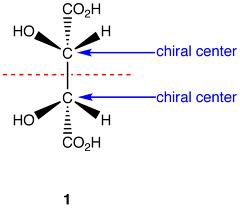
Meso compound

answer
Achiral compound w/chiral centers
question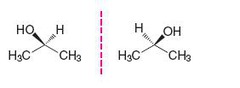
Achiral

answer
Symmetrical (mirror image is same)
question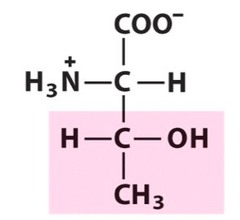
Chiral

answer
Asymmetrical (different from mirror image)
question
Enantiomers
answer
Pair of nonsuperimposable mirror image molecules/mirror-image isomers
question
Diastereomers
answer
Stereoisomers that are not mirror images
question
Constitutional isomers
answer
Compounds with different sequence in atoms (different order bonding)
question
Structural isomers
answer
Compounds that have the same molecular formula but differ in the covalent arrangements of their atoms
question
Geometric isomers
answer
Compounds that differ in position of substitutents attached to a double bond or cycloalkane (Ex: cis or trans, E or Z)
question
Polar protic solvents
answer
Solvent that gives off H+ atoms (Ex: water, most alcohols, formic acid, hydrogen fluoride, and ammonia. Polar protic solvents are favorable for SN1 reactions)
question
Alpha beta unsaturated aldehydes
answer
A special group of carbonyl compounds; saturated because they are conjugated to an alkene group; electrophilic b/c the carbon atoms are e- deficient; participate in addition reactions with Nu's where Nu's add atoms to the alpha carbon
question
Miscible with water
answer
Ketones, polar bonds, free election pairs Immiscible with water: Lipids, long hydrocarbon chains (like octanol), dichloromethane (CH2Cl2)
question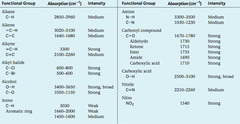
Infrared absorption (IR) spectra

answer
C=O 1680-1750 cm-1 C-O 1000-1300 cm-1 O-H 2500-3300 cm-1 C-H 2850-2960 cm-1 C-C wide range of values
question
SN1 reactions
answer
Unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reactions. Leaving group leaves, forming a carbocation that then reacts with a nucleophile. Reactivity increases from methyl to primary to secondary to tertiary with increasing carbocation stability. The rate determining step is dependent on the electrophile
question
Electrophile
answer
"Electron loving"; are electron deficient and typically react with nucleophiles by accepting electrons
question
Nucleophiles
answer
"Nucleus-loving" atoms with either lone pairs or ? bonds that can be used to form new bonds with electrophiles by donating electrons. 3 trends: 1) Nucleophilicity increases as charge on atom is more (-) 2) " " increases with basicity 3) " " increases with polarizability
question
Solubility in water
answer
Amide > Acid > Alcohol > Ketones & aldehydes > Amine > Ester > Ether > Alkane
question
Polymerization
answer
A chemical process that combines several monomers to form a polymer or polymeric compound; changes a simple chemical into another substance that contains the same elements
question
Density gradient centrifugation graph
answer
Two separate peaks indicate that both are pure



