Combo with "Epstein Barr Virus" and 1 other – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
how do viruses that infect the circulatory, reticuloendothelial, and lymphatic systems cause disease? 3
answer
-remain silent -cause hyper proliferation -cellular dysfunction in these organ systems.
question
Diseases caused by these viruses 4
answer
Cancer Birth Defects Immunosuppression Cardiac dysfunction
question
Epstein Barr Virus viral family genome
answer
Herpesviridae family member Enveloped dsDNA virus
question
Epstein Barr Virus mechanism of infection
answer
Uses C3d component of complement system for attachment and entry. Replication in epithelial and B CELLS
question
Epstein Barr Virus - MOA 5 steps
answer
1. infect B cell 2. cause B cell to proliferate and told to produce antibodies to EBV virus and other random antigens= heterophiles antibodies 3. T cells rec. infection and being fighting off infection 4. few b cells escape forming memory b cells -have EBV virus in genome in latent phase 5. stim--> moment from latency to productive phase--> asymptomatic shedding in saliva
question
Epstein Barr Virus - Virology Heterophile Antibodies
answer
random antibodies to seemingly random antigens
question
Epstein Barr Virus - Virology Latency -allows for what? 2
answer
ALL herpes viruses allow for cancer and delayed symptoms
question
Genes Involved in EBV Carcinogenesis
answer
genes produced during latency that allow for EBV to cause cancer
question
Genes Involved in EBV Carcinogenesis Latent Membrane Protein 1 (LMP1) -MOA= cancer -structure
answer
6 transmembrane-spanning domains CD40 Homologue Constitutively Active Receptor -Increased Growth - Suppressed Apoptosis
question
Genes Involved in EBV Carcinogenesis Latent Membrane Protein 2 (LMP2) -MOA= cancer
answer
Increased Growth of B cells
question
Genes Involved in EBV Carcinogenesis Epstein Barr Virus Nuclear Antigen 1 (EBNA1) -MOA= cancer
answer
-Transactivation of EBV transforming genes (LMP1 and LMP2) - Inhibition of Apoptosis
question
Epstein-Barr Virus transmission
answer
saliva high prevalent 90%
question
Epstein-Barr Virus primary infection population WW US
answer
Worldwide - before 5 years of age United States -adolescence and early adulthood
question
Epstein-Barr Virus factors contributing to cancer? 3
answer
-Immunosuppression ex. malaria -Genetic predisposition -Environmental factors
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Infectious Mononucleosis symptoms 5
answer
fever malaise exudative pharyngitis splenomegaly tender lymphadenitis
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Infectious Mononucleosis - biomarker
answer
Heterophile antibodies
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Infectious Mononucleosis main pop infected?
answer
Most common in young adulthood and in industrialized countries.
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Infectious Mononucleosis complications
answer
splenic rupture
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Infectious Mononucleosis main cause of symptoms?
answer
immune targeting of infected B cells
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Infectious Mononucleosis when do you see a rash?
answer
Rash - often accompanied by ampicillin treatment -may form complexes= rash
question
Epstein-Barr Virus progression symptoms
answer
1. fever + malasia + fatigue +virus shedding 2. lymphadenopathy + hepatospenomegaly +pharangitis
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Infectious Mononucleosis progression of antigen seen? progression antibodies
answer
EA = EBV Early Antigen (lytic) VCA = EBV Viral Capsid Antigen (lytic) EBNA = Epstein Barr Nuclear Antigen (latent) 1. anti EA antibody 2. anti VCA 3. IgM 4. IgG + anti ebna
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Infectious Mononucleosis diagnosis
answer
-mono spot -antibodies to EBV -downey cells
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Infectious Mononucleosis diagnosis -mono spot
answer
Heterophiles Antibodies -agglutinate sheep or horse RBC.
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Infectious Mononucleosis diagnosis -antibodies of EBV
answer
IgM to Viral Capsid Antigen (VCA) demonstrates primary EBV infection.
question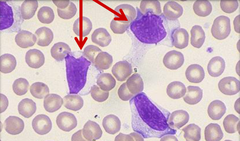
Epstein-Barr Virus Infectious Mononucleosis diagnosis -downey cells appearance 3 what are they

answer
Atypical T cell Vacuoles Altered Nucleus Indented Cell Margin
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Infectious Mononucleosis -treatment 2
answer
1. Rest and Hydration 2. Avoid strenuous activity to avoid splenic rupture. Anti-virals (acyclovir) - inhibit the viral polymerase - not used because cause is not virus but immune response to infected B cells 3. Avoid strenuous activity to avoid splenic rupture.
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Infectious Mononucleosis vaccine
answer
none
question
Epstein-Barr Virus oral hairy leukoplakia -common in what patients
answer
-common in immunosuppressed (HIV) ~300 CD4 T-cell/mm3= seen early
question
Epstein-Barr Virus oral hairy leukoplakia -stage virus in in cycle
answer
Active EBV replication
question
Epstein-Barr Virus oral hairy leukoplakia treatment 2
answer
Antiherpetic drugs= acyclovir -b/c main cause= replicating virus Podophyllin resin
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Cancer Burkitt's Lymphoma -cause -main symptoms
answer
B-cell origin Often presenting in the jaw of children (endemic form)
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Cancer Burkitt's Lymphoma -location seen in world
answer
W africa
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Cancer Burkitt's Lymphoma -genetic cause -result?
answer
tranlocation event moving MYC gene from chromosome 8--> 14 up reg. E2F increase rate of cell cycle movement from G1--> S phase makes it the most rapidly progression tumor
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Cancer Burkitt's Lymphoma -treatment
answer
Treated with chemotherapy (70-80% cure rates).
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Cancer Burkitt's Lymphoma -endemic ass. -US ass
answer
100% with EBV= endemic 20%= US
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Cancer Burkitt's Lymphoma cofactors 2
answer
Chronic Malaria - endemic Immune Suppression
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Cancer Hodgkin's Disease -cause -genetics?
answer
B-cell origin Not linked to specific chromosomal translocation events.
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Cancer Hodgkin's Disease symptoms
answer
-Nontender, palpable, lymphandenopathy in neck supraclavicular, and/or axilla. -Commonly enlargement of lymph nodes deep within chest (medistinal adenopathy). Approximately 1/3 of patients -display fever -night sweats - weight loss
question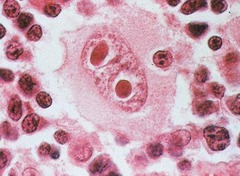
Epstein-Barr Virus Cancer Hodgkin's Disease Reed-Sternberg cell -appearance

answer
a large cell with two or more nuclei or nuclear lobes, each of which contains a large eosinophilic nucleolus classic presentation hodgkins disease
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Cancer Hodgkin's Disease treatment patients with EBV having this cancer?
answer
-radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy. -Localized Hodgkin's disease is cured in greater than 90% of patients. 20-40% contain proliferation of EBV-infected cells.
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Cancer Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma -location -cell involved?
answer
Originates in the nasopharynx. Epithelial cell cancer.
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Cancer Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma symptoms 3
answer
Facial pain Fullness in sinuses and throat Hearing loss
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Cancer Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma location globally
answer
SE asia
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Cancer Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma treatment
answer
Nasopharyngeal carcinomas are treated through chemotherapy and radiation treatment regimens.
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Cancer Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma cofactors 2
answer
-genetics -diet
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Cancer Post-transplantation Lymphoproliferative Disorder (PTLD) -association -spread -type of cell
answer
Abnormal proliferation of lymphoid cells in a transplant patient. malignant or benign
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Cancer Post-transplantation Lymphoproliferative Disorder (PTLD) symptoms 4
answer
-fever - fatigue - weight loss - progressive encephalopathy
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Cancer Post-transplantation Lymphoproliferative Disorder (PTLD) main risk factors
answer
transplant
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Cancer Post-transplantation Lymphoproliferative Disorder (PTLD) diangosis
answer
Histological analysis of tissue. Detection of EBV genomes (in situ hybridization)
question
Epstein-Barr Virus Cancer Post-transplantation Lymphoproliferative Disorder (PTLD) treatment progression 3 steps
answer
1. 1st Reduce Immunosuppression 2. 2nd Treatment with Rituximab (mouse human chimeric anti-CD20 antibody.) 3. 3rd conventional chemotherapy
question
Cytomegalovirus Diseases -based on what
answer
demographics patients -Normal= asym or mono -baby of sero negative mom= cytomegalic inclusion disease -AIDS or immunsuppres= multisigte symptomatic disease
question
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) family genome sym in healthy people?
answer
Herpesviridae family Enveloped dsDNA Reactivation is rarely symptomatic in immunocompetent individuals.
question
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) location of viral replication
answer
1. Mucosal epithelium 2. Viremia
question
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) latency in what cells
answer
monocytes
question
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) transmission 4
answer
-Saliva -Breast milk -Urine -Fomites -Sexual contact
question
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) diagnosis 2
answer
-Detection of viral DNA or virus culture from diseased tissue= not necessarily acute b/c patient can shed for years w/out sym -Seroconversion= timing matters and multiple samples
question
CMV Antivirals 1st line 2 antivirals - negatives of these drugs?
answer
Gancyclovir Valganciclovir toxicity to bone marrow + drug related neutropenia
question
CMV Antivirals 1st line -Gancyclovir
answer
converted to viral polymerase inhibitor by CMV enzymes (i.v. or oral).
question
CMV Antivirals 1st line -Valganciclovir
answer
converted to gancyclovir within the body. Increased bioavailability. (oral)
question
CMV Antivirals 2nd line -name 2
answer
Cidofovir Foscarnet given if gancyclovier or valganciclovir don't work MORE toxic
question
CMV Antivirals 2nd Cidofovir
answer
converted to viral polymerase inhibitor by cellular enzymes. More toxic than gancyclovir .(i.v.)
question
CMV Antivirals 2nd Foscarnet
answer
direct inhibitor of the CMV polymerase. renal toxicity. (i.v.)
question
CMV Infectious Mononucleosis-Like Illness -incubation -symptoms 5 and duration
answer
Incubation period 20-60 days Symptoms duration 2-6 weeks -Fever -Fatigue -Pharyngitis (usually non exudative) -Abnormal T cells -No heterophile antibody production
question
CMV Infectious Mononucleosis-Like Illness infection seen in what pop?
answer
primary infection healthy individuals
question
CMV Cytomegalic Inclusion Body Disease -how common -in what pop. ass. with -mortality rate
answer
Occurs in ~5% of congenital CMV infections. Most common with primary infections in mom during pregnancy Mortality rate in severe cases is 20-30% CONGENITAL INFECTION
question
CMV Cytomegalic Inclusion Body Disease -symptoms -when are they seen? 7
answer
Infants that are asymptomatic at birth can develop abnormalities later in life. -Hepatosplenomegaly -Jaundice -Petechiae/Rash -Microcephaly -Growth retardation -Inguinal hernias -Chorioretinitis
question
CMV- Cytomegalic Inclusion Body Disease how common in US
answer
Most common congenital viral infection 30,000 children per year in US
question
CMV- Cytomegalic Inclusion Body Disease how does it occur?
answer
30 - 50% women childbearing age seronegative for CMV. - 1-4% of these women will be exposed during pregnancy. Risk of transmission from primary CMV infection during pregnancy = 1/3
question
Cytomegalic Inclusion Disease prevention 3 and what pop
answer
for women seronegative at time of pregnancy prevent woman from getting -handwahsing -avoid sharing drinks + toothbrushes with children -avoid kissing children
question
Cytomegalic Inclusion Disease treatment
answer
Maternal treatment with CMV immunoglobulin during pregnancy currently under investigation
question
CMV in Immunosuppressed Populations what 2 groups effected?
answer
-highest risk in 1-4 months following transplant - predominant disease in AIDS patients 50-100 T cells/ ul
question
CMV in Immunosuppressed Populations main symptoms
answer
Spiking Fever (100- 104 ºF)
question
CMV in Immunosuppressed Populations 2 sources
answer
-reactivation of latent CMV -transplanted organ
question
CMV disease transplant patients 3 disease
answer
-CMV pneumonitis -GI disease -graph vs host
question
CMV disease transplant patients CMV pneumonitis -symptoms
answer
Fever Hypoxia Interstitial Lung Infiltrates
question
CMV disease transplant patients -GI disease symptoms 4 complication
answer
Diarrhea Abdominal Pain Nausea Vomiting Complication: perforation and hemorrhage of GI epithelium
question
CMV disease AIDS patients 3 diseases
answer
CMV retinitis GI CMV pneumonitis
question
CMV disease AIDS patients CMV retinitis -symptoms 3 -diagnosis
answer
Blurred Vision "Floaters" White lesions Lesions with irregular, white necrotic border Diagnosis Pupil dilation and ophthalmoscope examination
question
CMV in Immunosuppressed Populations prevention organ transplant prevention 3
answer
-Donor matching -Prophylaxis or preemptive therapy with antivirals -CMV immunoglobin
question
CMV in Immunosuppressed Populations prevention AIDS
answer
Maintenance therapy with antivirals when reaching a threshhold level of CD4+ T-cells.
question
CMV in Immunosuppressed Populations treatment indications
answer
immunocompromised patients with severe disease are treated with I.V. antivirals. basically watch patient for symptoms



