Chapter Ii In Depth (plus – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
List the relative boiling points of carbonyl groups. Why are they this way?
answer
Amide > Carboxylic acid > Nitrile > (Ester~acyl chloride~aldehyde~ketone) > ether. Amides have the highest bp bc of the strong Dipole-Dipole interactions of resonance contributors and Hydrogen bonds form between the molecules. Caboxylic acids bc of intermolecular Hydrogen bonding and Nitriles bc of Dipole-dipole interactions.
question
Draw the intermolecular Hydrogen bonding of Carboxylic acids.
answer
...
question
Draw the intermolecular Hydrogen bonding of Amides
answer
...
question
Draw the intermolecular bonding of Dipole-Dipole interactions in amides.
answer
...
question
draw the intermolecular Dipole-Dipole bonding in Nitriles.
answer
...
question
What is the difference in the smell between aldehydes and ketones?
answer
Aldehydes have pungent odors (like vanilla extract or cinamaldehyde) and Ketones tend to smell sweet (the sweet odors of spearment and caraway seed (carvone).
question
What is Ketosis?
answer
A pathological condition that can occur in people with diabetes in treatment of paediatric epilepsy or on a ketogenic (very low carb diet like the Atkins diet and fatburning bodybuilding diets) when the body produces more acetoacetate than can be metabolized. The excess acetoacetate breaks down to acetone (the simplest ketone). Ketosis can be recognized by the smell of acetone on a person's breath.
question
3-chlorobutanal (beta-chlorobutyraldehyde)
answer
...
question
trans-2-methylcylohexanecarbaldehyde
answer
...
question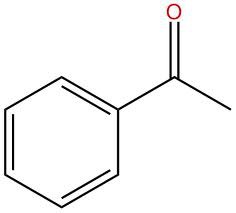
(acetophenone) ((methyl phenyl ketone))

answer
...
question
Name Functional Group Priority Class, Suffix, Prefix
answer
Carboxylic (-oic,Carboxy) Ester (-oate, Alkoxycarbonyl) Amide (amide, Amido) Nitrile (-nitrile, Cyano) Aldehyde (al, Oxo ( =O ) Aldehyde (al, Formyl (CH=O) Ketone (-one, Oxo ( =O ) Alcohol (-ol, Hydroxy) Amine (-amine, Amino) Alkene (-ene, Alkenyl) Alkyne (-yne, Alkynyl) Ether (---, Alkoxy) Alkyl halide (---, Halo)
question
What is the relative reactivity greatest to least of carbonyl compounds and why?
answer
Formaldehyde, Aldehyde, ketone. 1.) Hydrogen is more electron withdrawing so the carbonyl carbon charge will be more partial positive and more reactive to nucleophiles and therefore more reactive to nucleophilic addition. While alkyl groups more stabalize the ketone making it less reactive. 2.) Steric factors - hydrogen's small size make the carbonyl carbon on the aldehyde more accessible. Ketones have greater steric crowding in in their transition states. Therefore the alky groups on the ketone stabilize the ketone and destabilize the transition state making it less reactive than aldehydes
question
What are the 4 types of nucleophilic addition reactions that aldehydes and ketones undergo? Why these three?
answer
irreversible (if the nucleophile is a strong base) reversible (if the nucleophile is a weak base) Addition-elimination (if the attacking nucleophile has a lone pair and there is enough acid in the solution to protonate the OH group of the tetrahedral compound then water can be eliminated from the addition product. This reaction is also reversible). Gringnard reactions Can also be considered a strong base reaction and is irreversible).
question
how do you use Grignard reactions to form a) A primary Alcohol b) A secondary Alcohol c) A tertiary Alcohol d) A Carboxylic acid
answer
a) formaldehyde b) Aldehyde c) Ketone d) carbon dioxide ----------------------------> 1.R-Grignard 2. H3o+ (dilute acid)
question
Why don"t grignard reagents add to the carbonyl carbon of a carboxylic acid?
answer
A carboxylic acid has an acidic proton that reacts first converting the reagent into an alkane.
question
From ethyne Sythesize 1)1-pentyn-3-ol 2)1-phenyl-2-butyn-1ol 3) 2-methyl-3-hexyn-2-ol
answer
#1.) ethyne + NaNH2 2.)Propanal 3.) HCl #2) ethyne + NaNH2 2.) CH3MgBr (this gives Methylacetylene) 3) NaNH2 4)benzaldahyde 5) HCl #3)



