Ch 92. Tumours of the Bladder – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
List the benign tumours of the bladder. (7)
answer
Cystitis cystica Cystitis glanduralis Leiomyoma Leukoplakia Epithelial metaplasia Nephrogenic adenoma Inverted papilloma
question
What kinds of transformed urothelium are seen epithelial metaplasia? Appearance? Association?
answer
Squamous and Glandular Squamous = knobby, white, flaky material on trigone Glandular = clumps of raised red areas *Females*, infection, trauma or surgery
question
Leukoplakia appearance? Malignant potential?
answer
Squamous metaplasia with keratin deposition = white flaky substance Benign in bladder.
question
What is characteristic of inverted papilloma ? Association and location? Treatment?
answer
Normal urothelial cells invaginating into lamina propria but not into muscularis propria Chronic inflammation, BOO Located usually on trigone TURBT. <1% incidence of recurrence
question
What do you pathologically see in nephrogenic adenomas and etiology? Usual presenting sign? Treatment?
answer
Tubules similar to renal tubules Metaplasia caused by chronic irritation Gross hematuria. Vascular tumours. TURBT. Eliminate source of irritation.
question
What is cystitis cystica/glandularis pathologically? Association? Presenting features ? Treatment ?
answer
Cystic nests lined by cuboidal and columnar cells, proliferation of von Brunn nests Inflammation, BOO Irritative voiding symptoms / hematuria TURBT, elimination of obstruction/inflammation
question
What can cystitis glandularis potentially transform into?
answer
Adenocarcinoma. Case reports.
question
What's the most common type of non epithelial benign tumour of the bladder? Appearance? How can diagnosis be confirmed?
answer
Leiomyoma Smooth indentations of bladder with normal urothelium overlying tumour MRI
question
Who is at highest risk of bladder cancer? Reduced risk?
answer
Old, white males African-american female ; african american male/white female
question
What is the median age of bladder cancer diagnosis?
answer
70 years
question
Lifetime risk of developing urothelial cancer for white male?
answer
3.7%
question
What histological types of urothelial cancer is most common in North America and Europe Africa and Egypt?
answer
Urothelial carcinoma SCC
question
What genes may be associated with bladder cancer and why?
answer
Null GSTM1 and slow NAT-2 Detoxify nitrosamines. Lead to high levels of 3-aminobiphenyl
question
What are risk factors for urothelial carcinoma?
answer
*Smoking* Caffeine Occupational exposure (aromatic amines) Family history (no clear mendelian inheritance pattern) Phenacetin Chronic inflammation/infection Radiation Cyclophosphamide
question
How is the risk of BCa related to the degree of smoking? Second hand smoke? Smoking cessation?
answer
Linear relationship between intensity and duration Low, not statistically different from that for nonsmokers Decreases the risk in a linear fashion
question
What nutritional behaviour is associated with a reduced risk BCa?
answer
Fruits and vegetables, mediterranean diet
question
What is the primary mutagenic metabolite from cyclophosphamide?
answer
Phosphoramide mustard
question
What are the different histologic proportions?
answer
90% urothelial 5% SCC 2-5% Adenocarcinoma / other variants
question
What are precursor lesions to BCa?
answer
Hyperplasia Atypia Dysplasia
question
What is the significance of dysplasia?
answer
Urothelial instability Can be a marker of recurrence and progression in those with know Ca
question
What does PUNLMP stand for? Natural history?
answer
Papillary urothelial neoplasia of low malignant potential Recur but rarely progress/invade
question
What is CIS characterized as ? Genetic abnormalities associated with CIS/high-grade disease? Cystoscopic appearance?
answer
Non papillary, flat, high-grade tumours Alteration of RB, TP53 and PTEN genes Reddish with heaped-up mucosa
question
What if CIS is associated with invasive tumour?
answer
Worse prognosis. Reduced OS.
question
How do you clinically distinguish between T3a and T3b disease?
answer
T3a = palpable mass at time of TURBT that can no longed be appreciated after resection T3b = palpable mass before and after TURBT
question
What's the significance of prostatic stromal invasion?
answer
Worse prognosis Extension to prostatic urethra without stromal invasion does not carry adverse prognosis
question
What falls under the classification of NMIBC?
answer
Tis Ta low grade Ta high grade PUNLMP T1
question
What percentage of low grade tumours recur and invade? High grade?
answer
60% recur, 10% progress to invasion 80% recur, ~50% progress to invasion
question
What's the earliest mutation seen in low risk NMIBC?
answer
Deletion of Xm 9, FGFR-3 gene mutation HRAS and PI3K
question
What are the theories for the recurrent nature of BCa?
answer
Field change effect Tumour implantation
question
What is pagetoid spread? Association?
answer
Cancer cells growing underneath a layer of normal-appearing surface urothelium CIS and following multiple doses of intravesical therapies Supports need for random bladder/prostatic biopsies in pts with +cytology and negative cystos
question
What are predictors for poor prognosis?
answer
*Grade* *Stage* +LVI Genetic instability - molecular markers
question
What are the traditional pathways of urothelial cancer formation?
answer
Normal urothelium --> papilloma, PUNLMP, hyperplasia, low grade Ca Normal urothelium --> dysplasia --> CIS Normal urothelium --> hyperplasia/dysplasia --> high grade NMIBC
question
What is the genetic hallmark of invasive disease?
answer
Low to absent FGFR-3 High TP53 mutation Genetic instability
question
What gene mutations are associated with high grade cancer?
answer
TP53 mutation RB PTEN Loss of Xm17
question
What's the sensitivity and specificity of urine cytology?
answer
Sens: 40-60% Spec: 94-100%
question
What percentage of pts presenting with a painless gross hematuria will have a urological malignancy? What % of patients with a newly diagnosed bladder tumour will have gross hematuria as their presenting symptom?
answer
20% 85%
question
What role do urinary markers play in the detection of BCa?
answer
Little role. The current sensitivity is not good enough to replace cystoscopy *Remains the gold standard*
question
What current evidence exists for the prevention of BCa?
answer
Quitting or never smoking is best BCG with high dose vitamins may prevent recurrence
question
List some of the histologic variants of urothelial cancer (5) Which responds to chemotherapy?
answer
Micro papillary Nested variant Clear cell variant *Glandular or adenocarcinoma* Plasmacytoid
question
What is recommended treatment for micro papillary?
answer
Urgent surgical resection *Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is ineffective and will delay time to treatment*
question
What is significant about the clear cell variant?
answer
70% of urothelial carcinomas will have foci of clear cells *No worse prognosis*
question
How should glandular or adenocarcinoma differentiated variants be treated?
answer
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy with radical cystectomy
question
What is the growth pattern of plasmacytoid and why is this a problem? Treatment?
answer
Non papillary, sessile Delay of gross hematuria presentation Usually present at advanced stage Surgery. Poor response to chemotherapy
question
What can nested variant be confused with and why is this a problem?
answer
Benign von Brunn nests, cystitis cystica and inverted papilloma Very aggressive variant
question
What are some nonurothelial malignancies? (4)
answer
Sarcomas Small cell Signet Ring Cell SCC
question
What patients are at risk of developing SCC?
answer
Patients infected with S. haematobium SCI pts - those with chronic catheters/inflammation
question
How should small cell carcinoma be treated?
answer
Considered and treated as though metastatic disease is present even if not Chemosensitive Chemoradiation +/- surgery
question
How does signet cell cancer typically present?
answer
Typically understaged Usually locally advanced and metastatic at presentation
question
What is primary prostatic urethral cancer strongly associated with? Incidence of secondary prostatic urethral cancer? Risk factors for secondary prostatic urethral cancer?
answer
Urothelial cancer (CIS) 3%, increases with time *CIS and history of intravesical chemotherapy*
question
How should noninvasive prostatic urethral disease be treated?
answer
TURP + BCG
question
How is noninvasive prostatic urethral cancer at final pathology staged?
answer
No longer T4a Only T4a when there's stromal invasion (direct or indirect)
question
What % of women and men will have squamous metaplasia of the bladder?
answer
40% women 5% men
question
Where is the incidence of bladder cancer highest?
answer
In developed countries
question
Where is the mortality rate from bladder cancer highest in?
answer
Egypt
question
What is the increased risk of developing bladder cancer if you have a first degree relative with bladder cancer?
answer
2-fold increased
question
What was one of the first and most common chemical agents implicated in the formation of bladder cancer?
answer
beta-naphthylamine
question
What food compound is associated with a reduced risk of bladder Ca?
answer
Citrus
question
What is the increased risk with developing bladder cancer with radiation exposure (and what threshold of radiation)?
answer
2-fold increased if ;50 mSv Risk is not age dependent, latency period of 10-15 years
question
What is the risk of malignancy in a patient with recurrent gross hematuria who has had a previous negative workup?
answer
0 at 6 years
question
What % of bladder cancer is related to smoking in males?
answer
30-50%
question
What % of patients will have prostatic urethral disease when they undergo radical cystectomy?
answer
40%
question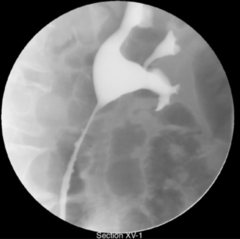
What is this image called and associated with?

answer
Pseudodiverticulosis Associated with bladder cancer



