Biology: Meiosis, Mitosis, Stem Cells & Cancer – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Mitosis
answer
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle process (five stages) by which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus.
question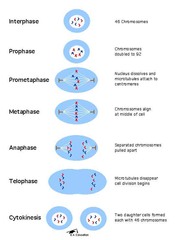
Stages of Mitosis

answer
#1. Interphase #2. Prophase #3. Metaphase #4. Anaphase #5. Telophase
question
Interphase
answer
(not an actual phase, because its the cell's everyday life.) Chromatin is loose and visible, Chromosomes are not.Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division by copping (doubling) DNA; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases.
question
Prophase
answer
2nd phase, which separates the duplicated genetic material (carried in the nucleus of a parent cell) into two identical daughter cells. During prophase, the complex of DNA & proteins contained in the nucleus, known as chromatin, condenses into chromosomes. The nucleus starts to disappear, so that the DNA can be accessed.
question
Metaphase
answer
3rd phase (M=middle), where the chromosomes aline in the middle of the cell, and are at their most condensed and coiled stage. Spindle fibers form and attach to the chromosomes. If this does not happen, mitosis wont continue, bc its the "checkpoint"
question
Anaphase
answer
4th phase, where the chromosomes are separated and pulled apart to opposite sides of the cell, by the spindle fibers. As the cell starts to elongate, the spindle fibers shorten.
question
Telophase
answer
Last phase of Mitosis, also known as Cytokinesis. The process that separates the duplicated genetic material (carried in the nucleus of a parent cell) into two identical daughter cells. Cell division begins once the replicated, paired chromosomes have been separated and pulled to opposite sides, or poles, of the cell.In a plant, and new cell wall is built to separate the two cells, in an Animal cell the membrane is "pinched" to separate the two cells. Chromosomes unwind & become chromatin, once again.
question
Cytokinesis
answer
Division of the cytoplasm during cell division
question
Microtubules
answer
A hollow rod of the protein tubulin in the cytoplasm of all eukaryote cells that make up spindle fibers, & are involved in nucleic and cell division.
question
Meiosis
answer
Cell division that produces reproductive cells (gamates) in sexually reproducing organisms.
question
Gamates
answer
Specialized sex cells (sperm/ egg) produced during meiosis.
question
Mitosis VS Meiosis
answer
Mitosis: one division forming 2 identical cells (clones) is an asexual process Meiosis: two divisions forming 4 genetically different cells, by a sexual process.
question
Embryology
answer
Branch of biology that deals with the development of an embryo from the fertilization of the ovum to the fetus stage.
question
Stem Cells
answer
Unspecialized cells that retain the ability to become a wide variety of specialized cells, bc they were not assigned jobs
question
Adult Stem cells
answer
They have less potential and are more specialized, which makes them harder to work with, then regular stem cells.
question
Stem Cells VS Normal Cells
answer
Stem Cells are unspecialized that retain the ability to become a wide variety of specialized cells and Adult Stem Cells have less potential and are more specialized, which makes them harder to work with, then regular stem cells then regular cells are.
question
Importance of Stem Cells
answer
Stem cells represent an exciting area in medicine because of their potential to regenerate & repair damaged tissue. Some current therapies, such as bone marrow transplantation, already make use of stem cells and their potential for regeneration of damaged tissues
question
Cancer
answer
A malignant growth or tumor caused by abnormal, uncontrolled cell division, which damages the body parts around them. Cells will continue to grow and divide, even if your body does not need them too. This means that the body does not know when to start and stop mitosis.
question
Cancer Cells VS Normal Cells
answer
#1. Cancer cells spend less time in interphase then regular cells do, therefore they are dividing more. #2. They have uncontrollable mitosis, where as normal cells are able to control it, this means they do not stop divsion even after a certain point, like a normal cell would. #3. Cancer cells grow faster then normal cells #4. Cancer cells are able to break away fro, groups of cells and travel to other parts in the body. #5. They have a different physical makeup, cancer cells often have parts that allow the, to grip and grab onto other cells and tissues, where as normal cells do not have that.
question
What causes Cancer
answer
Cells do not respond to the signals that regulate the growth of cells, which causes them to non-stop rapidly divide.Genetic predisposition, lifestyle choices, environmental factors, and/or a combination of all are factors that can cause or increase the risk of cancer.
question
Cancer caused by genetics
answer
Some people are born with a gene mutation, inherited from their mother or father. The damaged gene increases their risk of cancer, much higher than most peoples. When cancer occurs because of an inherited gene mutation, its known as a "hereditary cancer".
question
Cancer caused by environmental factors
answer
Certain types of infections and environmental exposures to different types of chemicals and radiation, can cause cancers. HIV (virus) is associated with risks for cervical cancer, skin cancer & etc. Environmental air pollution increase the risk of cancers, especially lung cancer.
question
Cancer caused by lifestyle choices
answer
Lifestyle factors such as smoking tobacco leads to lung cancer. A poor diet (heavy red meat consumption), with a lack of physical activity (obesity) can lead to colon, breast, kidney cancer, etc. Too much UV rays can cause wrinkles & skin cancer, very important to use sunscreen.
question
Tumors
answer
A group of cells that have lost their ability to control the rate at which mitosis grow and divide, which forms a mass. Tumors may be classified by location, tissue type, or degree of malignancy.
question
#2 Types of Tumors
answer
Begnin: remains in place, but can interfere with surrounding tissue development Malignant: invasive tumors, grows into surrounding tissues, if not stopped tumors can metastasize or spread to other sites, by getting into the blood stream and traveling throughout the body.
question
What Makes a Mole Possibly Cancerous
answer
Look out for abnormal size, if its bigger then a pencil's eraser. The shape should not have irregular, ragged borders (edges) of the mole. The color should not vary or be too dark. And the asymmetry of the mole should match the other half.



