Assessment Techniques and Diagnositc Testing – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Assessment
answer
FIRST step in the nursing process; systematic way of collecting data Objective data verifies the info obtained on health history
question
Skills Required for Assessment
answer
I.P.P.A Inspection Palpation Percussion Auscultation
question
Preparation
answer
Nurse: wash hands, confident, self-assured, comfortable with skills Patient: privacy, explanation Environment: warm, private, well-lit, eliminate distracting noises
question
Approaches
answer
~Cephalocaudal (HEAD TO TOE) ~LEAST to MOST invasive: used with pain ~Validate subjective data: episodic, c/o injury or discomfort ~Screening: hypertension, scoliosis, diabetes, hearing, vision ~Comparison: COMPARE one side of the body with the other
question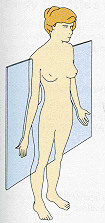
Coronal (Frontal) Plane

answer
Divides body into front (anterior) and back (posterior) [ventral and dorsal]
question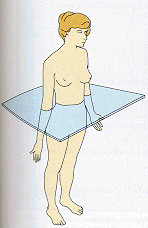
Transverse

answer
Divides the body into upper (superior) and lower (inferior) halves distal (away from) ->proximal (near the origin)
question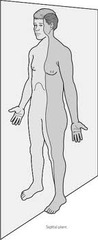
Sagittal Plane

answer
Divides the body into right and left parts medial (middle) -> lateral (to the sides)
question
Standing
answer
Position in which RN performs the musculoskeletal, neurological exam
question
Sitting
answer
Position in which RN can asess HEENT (head, ears, eyes, nose, throat), lung (posterior)
question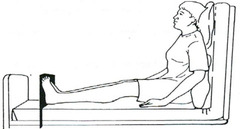
Fowler's

answer
Used with pt's who have cardiac and respiratory disease
question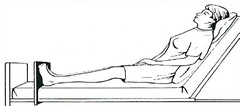
Semi Fowler's

answer
Used for cardiac exam, anterior lungs, thorax, breast exam
question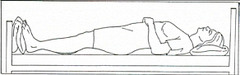
Recumbent (Supine)

answer
Used for abdominal exam, arms and legs, peripheral pulses
question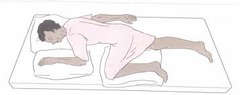
Sims

answer
Used for posterior exam and rectal exam
question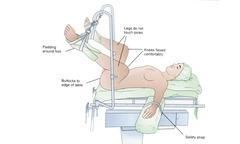
Lithotomy

answer
Used for vaginal exam
question
Knee Chest
answer
Used for rectal and prostate exam
question
Inspection
answer
"Concentrated Watching" ~Inspect each body system ~Requirements: good lighting and adequate exposure
question
Smells: Fruity
answer
Sign of metabolic disorders accompanied by diabetic acidosis
question
Smells: Alcohol
answer
Imbibing, ingestion of drugs containing alcohol (cough syrup)
question
Smells: Smoke
answer
...
question
Smells: GI Bleeder
answer
Metallic smell
question
Smells: Pseudomonas
answer
Fruity smell
question
Smells: Offensive breath
answer
Poor oral hygiene, dental caries, bronchitis
question
Palpation
answer
Follows and confirms findings on inspection Factors to assess: Texture: smooth or rough Temperature: hot or cold Moisture: dry or mosit Organ location, size Vibrations, Pulsations Lumps, Masses: size, consistency Tenderness, pain: exact location
question
Percussion
answer
Gives palpable vibrations and characteristic sounds which depicts location, size and density of an organ (assess underlying structures) as air increases in organ, sound becomes LOUDER
question
Percussion
answer
~Size and location of organ: percussion note changes at borders ~Density of structure: air, fluid, solid organ produces a characteristic note ~Detects masses: superficial mass, palpation penetrates 5 cm ~Elicits pain: inflamed structures ~Deep tendon reflexes: intact neuromuscular system
question
Two Methods of Percussion
answer
Direct vs Indirect
question
Direct Percussion
answer
Immediate or Blunt Percussion; Percussing hand directly strikes the body wall (done w/ sinuses)
question
Indirect Percussion
answer
Mediate Percussion; Involves 2 hands
question
Stationary hand
answer
The Pleximeter How to Percuss
question
Striking hand
answer
The Plexor (middle finger of dominant hand) How to Percuss
question
How to Percuss
answer
Percuss in 2's (short gentle taps and enough force to get a good clear note)
question
Basic Principle of Percussion
answer
A structure with more air produces a longer, deeper sound because it vibrates freely
question
Resonant
answer
Medium loud, clear, hollow, heard over the LUNGS
question
Hyperresonant
answer
Louder, booming quality, heard over a CHILD's lung
question
Tympany
answer
Musical, drum-like, occurs over air-filled organs like the stomach, intestines
question
Dull
answer
Muffled thud, dense organs like the LIVER and SPLEEN
question
Flat
answer
Dead stop of the sound, over MUSCLE or BONE
question
Auscultation
answer
Listening to sounds through the use of stethoscope; Stethoscope blocks out environmental noise
question
Auscultation: Heart and blood vessels
answer
Listen for normal heart sounds (S1,S2), abnormal heart sounds, bruits (turbulent blood flow)
question
Auscultation: Lungs
answer
Listen for breath sounds, adventitious sounds (abnormal breath sounds)
question
Auscultation: Abdomen
answer
Listen for bowel sounds, bruits
question
Auscultation: Thyroid
answer
Listen for bruits
question
Stethoscope
answer
Ear pieces: point towards your nose Binaurals: should keep earpieces snugly in ears Tubing: 1/2 in diameter 12-14 in long Diaphragm- used to pick up HIGH pitched sounds, hold firmly against the skin Bell- used to pick up LOW pitched sounds, hold softly
question
Infant
answer
6 months are better on mom's lap take advantage of quiet baby-> auscultate heart, lungs, abdomen Developmental Considerations
question
Toddler
answer
Perform exam on parent's lap, allow choices Developmental Considerations
question
Preschooler
answer
Autonomy, cooperative, like to be involved, like to see how things work Let them listen to mom's heart Developmental Considerations
question
School-age child
answer
Modesty develops, they can decide if mom or dad can stay Developmental Considerations
question
Adolescent
answer
In tune to their body-> best time to do health teaching, use head to toe approach Developmental Considerations
question
Aging adult
answer
Allow for as few position changes as possible Developmental Considerations
question
Ophthalmoscope
answer
Apatures to examine different structures in the eyes
question
Otoscope
answer
Illuminates external canal and tympanic membrane, nasal canal
question
Tuning fork
answer
500 - 1000 Hz auditory fork; 100 - 400 Hz sensation fork
question
Percussion Hammer
answer
Deep tendon reflexes
question
Neurologic Hammer
answer
Has soft brush and sharp needle for detecting sensory perception
question
Tape Measure
answer
Circumference, length (liver span, diaphragm)
question
Penlight
answer
View lesions with tangenital lighting (lighting from the side), pulsations
question
Calipers for skinfold thickness
answer
Measures thickness of subcutaneous tissue
question
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
answer
Basic screening test Hemoglobin and Hematocrit Red Blood cell count (RBC) White Blood cell count (WBC)
question
Hemoglobin
answer
~Main intracellular proteins ~Carries O₂and removes CO₂ ~Measures total_________ in the blood ~Increases with polycythemia (increased in RBC) ~Decreases with blood loss, anemia or bone marrow supression
question
Hematocrit
answer
~Measures PERCENT of red blood cells in the total blood volume ~Increases with polycythemia, dehydration, burns ~Decreases with blood loss, overhydration, dietary deficiency, anemia
question
H and H (Hemoglobin and Hematocrit)
answer
Will INCREASE in dehydration WIll DECREASE in hyperbalemia
question
Red Blood Cell Count (RBC)
answer
Number of RBCs per cubi millimeter of whole blood Low RBCs -> anemia High RBCs -> polycythemia, may develop secondary to chronic hypoxia
question
White Blood Cell Count (WBC)
answer
Determines the number of circulating WBCs per cubic millimeter of whole blood High WBCs -> bacterial infection Low WBCs -> viral infections
question
Serum Electrolytes
answer
Used for electrolyte and acid-base imbalances; Check for sodium, potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate ions; glucose (Ordered as Chem 7 or BMP or basal metabolic panel) Urea Creatinine
question
Urea
answer
End product of protein metabolism, measured as (BUN)
question
Creatinine
answer
Produced by muscles and excreted by kidneys
question
Visualization Procedures: GI Tract
answer
Direct visualization of the GI tract (looking right at the tissue)
question
Anoscopy
answer
Display anal canal Direct Visualization of GI Tract
question
Proctoscopy
answer
Display of the rectum Direct Visualization of GI Tract
question
Proctosigmoidoscopy
answer
Display of the rectum, sigmoid colon Direct Visualization of GI Tract
question
Colonoscopy
answer
Display of the large intestine Direct Visualization of GI Tract
question
Indirect Visualization
answer
Done with x-rays; Enhanced by radiopaque substances such as barium
question
Nursing Considerations: Direct Visualizations of the GI Tract
answer
~pt needs to be cleaned out; Strong cathartic (GoLytely) and Dulcolax given 24 hours before test ~signed informed consent ~monitor VS and for bowel perforation ~inform pt that air is introduced during test (flatulence) ~if tissue samples were removed -> pt may experience bleeding in their stool
question
Visualization Procedures: Urinary
answer
KUB IVP Renal Ultrasonography Cytoscopy
question
KUB
answer
X-ray of the kidneys/ureters/bladder
question
Intravenous Pyelography (IVP)
answer
Radiographic study to evaluate the urinary tract
question
Nursing Considerations: IVP
answer
~Contraindicated for those who are allergic to shellfish or IDODINATED dye, dehydrated, renal failure ~Signed consent ~Metformin (medication for diabetes) is held for 24 hours ~Laxative or enema is given before test Post-op ~Maintain hydration ~Monitor I & O
question
Renal Ultrasonography
answer
Non-invasive procedure that uses sound waves to visualize kidneys
question
Cystoscopy
answer
BLADDER and URETHRAL orifices are visualized with a cytoscope
question
Nursing Considerations: Cystoscopy
answer
~signed consent ~light sedation ~restrict fluid/food for 8 hours ~monitor I & O, character of urine, hydration ~check for signs and symptoms of flank pain, chills, difficulty urination
question
Visualization Procedures: Cardiopulmonary
answer
Electrocardiography Angiography Echocardiogram Lung Scan (V/Q ventilation/perfusion scan) Laryngoscopy Bronchoscopy
question
Electrocardiography
answer
Provides graphic recording of the heart's electrical activity; ECG can be examined to determine dysrythmias, myocardial damage, enlargement of the heart, drug effects
question
Stress Electrocardiography
answer
Assess pt's response to increased cardiac workload
question
Nursing Considerations: Stress Electrocardiography
answer
~Review test ~Comfortable clothes and shoes ~Review history and meds ~Check for chest pain within past 48 hours ~baseline ECG ~Monitor VS post test
question
Angiography
answer
Radiopaque dye is injected into a vessel, flow thru vessel is assessed Coronary angiography Pulmonary angiography
question
Coronary Angiography
answer
Used to evaluate extent of CORONARY ARTERY disease
question
Pulmonary Angiography
answer
Used to assess pulmonary vascular system
question
Nursing Considerations: Cardiopulmonary
answer
~Use of iodine dye ~Informed consent ~Test takes 1-2 hours ~When dye is injected, there is burning, flushing feeling ~Must lie motionless ~NPO for 8 hours ~Post-op: check VS, insertion site, pulses in extremity ~hydration
question
Echocardiogram
answer
Uses ultrasound to visualize structures of the heart and evaluate left ventricular functioning
question
Lung Scan: V/Q (ventilation/perfusion)
answer
Scan used to how well GAS and BLOOD travel thru the LUNGS, radioisotope is injected intravenously
question
Fingertips
answer
Used for texture, swelling, pulsations, presence of lumps Part of the Hand Used in Palpation
question
Fingers and Thumb
answer
Used to detect position, shape, consistency of an organ or mass Part of the Hand Used in Palpation
question
Dorsa of the Hand
answer
Used to assess temperature Part of the Hand Used in Palpation
question
Base of the Fingers (Ulnar Surface)
answer
Used to feel vibrations Part of the Hand Used in Palpation
question
Light Palpation
answer
~surface characteristics, lesions, superficial masses ~press 1/2-3/4 inch ~check muscle tone, tenderness
question
Deep Palpation
answer
~encourage pt to used imagery, slow deep breaths to relax muscles ~intermittent palpation is best ~press 2 inches to identify organs ~hold hand <60 degrees, use pads of fingers ~identify abdominal organs or masses
question
Bimanual Palpation
answer
~Requires TWO hands ~Used to capture a body organ (kidneys, uterus, adnexa)
question
Laryngoscopy and Bronchoscopy
answer
Test used to look at the larynx and bronchi of the lungs; local anesthetic is given to prevent the gag
question
Nursing Considerations: Laryngoscopy or Bronchoscopy
answer
~NPO for 6-8 hours ~informed consent ~remove dentures ~provide mouthcare ~may be given general anesthesia Post-op -> semifowler's ~frequent VS ~expectorate (spit their secretions) until gag returns
question
Computerized Tomography or Computerized Axial tomography (CAT) Scan
answer
~Distinguished minor difference in the denisty of the tissue ~Produces a 3 dimensional image ~More sensitive than X-ray
question
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
answer
Non-invasive (pt is placed in a magnetic field) Pts cannot have implanted metal device: ~pacemakers ~artificial joint ~body art (may contain metal pigments) ~metal body piercing jewlery ~transdermal patches Pt cannot be pregnant or clostrophobic
question
Position Emission Tomography (PET) Scan
answer
Involves inhalation or injection of a radioisotope; Images are created as the isotope is distributed in the body Allows for the study of organ function, blood flow and tumor growth
question
Nursing Considerations: PET Scan
answer
~Restrict alcohol, tobacco, caffein for 24 hours ~informed consent ~no metal objects Post-Op ~hydration ~radioisotope is eliminated in 6-24 hours ~flush toilet immediately, wash hands
question
Aspirations
answer
Lumbar punctures Abdominal paracentesis Thoracentesis
question
Lumbar Punctures
answer
Cerebrospinal fluid is drawn thru a needle inserted into the subarachnoid space between the 3rd and 4th lumbar vertebrae; Pt is positioned on side with back arched
question
Nursing Considerations: Lumbar Puncture
answer
~baseline VS ~knee chest position Post-Op ~hydration ~pt flat -> 30 degrees for 8 hours ~check puncture site for leakage ~check for neurological changes
question
Abdominal Paracentesis
answer
Used with patients with ascites; strict sterile technique is used ~Cannula is inserted into abdominal cavity to withdraw fluid ~Normally no more than 1500 is drained out at once to prevent hypovolemic shock ~Nursing: observe site for hematoma, pressure bandage
question
Thoracentesis
answer
Remove excess fluid or air in the pleural space to ease breathing; Can also be used to insert chemotherapeutic drugs Strict sterile technique is used Nursing: pressure bandage on puncture site; assess for bleeding, hematoma
question
Biopsies
answer
Removal and examination of tissue Bone marrow Liver biopsy
question
Bone Marrow Biopsy
answer
Used to detect specific diseases of the BLOOD; Sternum, anterior or posterior iliac crest of the hip
question
Liver Biopsy
answer
Pt will have a pressure dressing over site, lie on right side after procedure, frequent vital signs



