Applied Genetics and Cancer – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Overall cancer death rates continued to ___ in the United States among both _____ and ____, among all major racial and ethnic groups, and for all of the most common cancer sites, including ____________.
answer
decline; men and women lung, colon and rectum, female breast, and prostate.
question
Death rates continued to ____ during the latest time period (2000 through 2009) for _____ (among men only) and for cancers of the ___________.
answer
increase melanoma of the skin liver, pancreas, and uterus
question
Most human cancers are _____ because there is no identifiable inherited gene involved, but the cancers developed as a result of _________ (carcinogens such as cigarette smoke) that randomly induced mutations in cells that led to uncontrolled growth.
answer
"sporadic" environmental factors
question
Environmental factors are encountered throughout life and act over ______; hence, most _____ occur in ____ .
answer
a long period of time sporadic cancers adults
question
Most affected persons have _____, and that site is where you would expect most cancers to be (breast, lung, prostate, colon, etc.)
answer
one primary site
question
Sporadic Cancer is a ________ of a specific cancer in _____. It is _____ and a _______ in paired organs. It has a ______ of onset, starting with a ____________.
answer
Single occurrence the family Monoclonal Unilateral tumor Later age Single primary tumor
question
In sporadic cancer, _____ generally not at increased risk. It is rarely seen in ________.
answer
Relatives 'wrong' sex. (breast cancer in females)
question
Cancer has a misregulation of cell cycle. What mechanisms cause this?
answer
1. Activation of growth activation pathways 2. Loss of function mutations in growth inhibitors • Both mechanisms account for multistep hypothesis of cancer progression
question
Benign - X - Metastatic
answer
X = Malignant
question
Types of Proto-Oncogenes
answer
1. Secreted growth factors 2. Cell surface receptors 3. Intracellular signal transducers (Ras) 4. DNA-binding nuclear proteins, including transcription factors (Myc) 5. Cell cycle regulators - cyclins, cyclin dependent kinases
question
Ras proteins are molecular switches controlled by GTPase and nucleotide exchange
answer
Normal: Ras G12 "Activated": RasG12V Glycine to Valine mutation caused constitutively active state of Ras protein. This locks Ras in the activated state because the inhibitor of Ras cannot bind. This increases cell proliferation. HUGE in pancreatic cancer.
question
Drugs targeting Ras Pathways
answer
Drugs try to block all Ras pathways, depending on where the mutation is. You need to know where the molecular defect is to know if it is up or downstream. Ex Herceptin is upstream.
question
Histology slides of neuroblastoma shows:
answer
-Neuro-rosettes -Neuropil cells -Stage IV disease -Multiple bony metastasis -Bone marrow involvement
question
Neuroblastoma
answer
cancer of nerve cells (neurons) usually appearing in the embryo or shortly after birth in adrenal cortex
question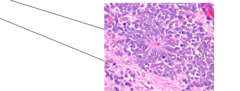
Neuro-rosettes? Neuropil cells (neuropile cells)?

answer
(or neural rosettes) rosette-like cluster of neural progenitor cells. (top) synaptically dense region with mostly unmyelinated axons, dendritic cells and glial cells.
question
Degree of oncogenic expression correlates with:
answer
stage of disease at diagnosis response to treatment prognosis
question
Greater than _____ of _______ is associated with amplification of N-Myc oncogene.
answer
One third neuroblastoma
question
_____ amplification is one mechanism of activation of cancer. If you increase the copies of it, you get _________. If you decrease the copies, you get ____.
answer
N-myc diagnosis of cancer at an earlier age diagnosis of cancer at a later age
question
Prognostic factors of Neuroblastoma
answer
predicting disease outcome based on: -patient's age at diagnosis stage of disease at diagnosis -ploidy level of tumor -presence/absence of N-Myc -gene amplification
question
Good outcome of Neuroblastoma
answer
-Infants -Hyperdiploid (;46) or near-triploid (69) chromosome number -No amplification of N-Myc gene
question
Poor outcome of Neuroblastoma
answer
-Age ;1 year -Near diploid (~46) or near-tetraploid (92) chromosome number -Amplification of N-Myc gene
question
Oncogenes- dominant oncogenes via 3 ways.
answer
1. Growth Activators- many steps 2. Mutational Activation (Ras, example) 3. Amplification (myc, example)
question
Knudson's Two Hit Hypothesis:
answer
A tumor ensues when two events occur in the same cell lineage, both copies of the gene need to be "hit" a "reminder" that dominance and recessiveness are properties of phenotype, not of genes or mutations
question
Familial tumor:
answer
individual born with mutation already so every cell susceptible only one additional mutation needed to develop the tumor family susceptibility inherited as a dominant trait whereas the the need for a second hit is a recessive pattern
question
Sporadic tumor:
answer
two events in same founder cell, likely to be rare
question
Retinoblastoma (Rb) tumor suppressor gene
answer
-Most common eye tumor in children -Occurs in heritable and non-heritable forms
question
Tumor Suppressor Genes
answer
Genes whose normal activity is to restrain cell growth and activity
question
______ in tumor suppressor genes, creates forms that lose their ____ function
answer
Loss of function mutations inhibitory
question
The TSG mutation converts the function of a normal tumor suppressor gene into a _________.
answer
cancer promoting function
question
G1-S checkpoints:
answer
genes should not be able to start replicating their DNA until all DNA damage has been repaired Unrepairable genes are triggered to undergo apoptosis
question
S phase checkpoint:
answer
operates whilst DNA is being synthesized. Different replication origins become active at different times during S phase
question
G2-M checkpoint:
answer
prevents cells from initiating mitosis when there is unrepaired DNA damage
question
_______ control Checkpoints.
answer
Tumor Suppressors
question
Function of recessive oncogenes
answer
-Encode growth inhibitors (brakes on cell cycle) -Requires loss of both alleles for cancer phenotype Examples Rb and p53
question
Multi-step nature of tumor genesis; What are 3 things needed for tumor genesis?
answer
1. Cancer progression requires a series of mutations 2. Gain of function (activators) and loss of growth inhibitors 3. Mutations that alter cell cycle increase subsequent mutation rates.
question
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis
answer
-Clinically defined as: at least 100 adenomatous polyps -often thousands of polyps present throughout the colon with early age of onset average ~16 yrs, range 8-34 yrs
question
Mutations in ____ Gene are Responsible for Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP).
answer
APC
question
APC is a ____ gene. Mutations in the APC gene ____ account for ~95% cases of FAP.
answer
tumor suppressor 5q21



