Ap Human Geography Unit 5 Vocab Answers – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Agriculture

answer
Deliberate modification of Earth's surface through cultivation of plants and rearing of animals to obtain sustenance or economic growth
question
Domestication
answer
The conscious manipulation of plant and animal species by humans in order to sustain themselves Examples: Crops and animals on farms
question
Hearths of Domestication
answer
Areas of settlement during the Neolithic period, especially along major rivers, from where farming and cultivation of livestock was created
question
First Agricultural Revolution (Neolithic Rev.)

answer
Humans were able to stay in one place, grow their populations, and start to build communities. The ability to produce food without roaming for it increased the carrying capacity of Earth, which charted the path towards the development of civilization.
question
The Fertile Crescent
answer
An area of river valleys in the Near East where conditions are optimum for crop production.
question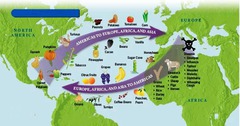
Columbian Exchange

answer
The exchange of plants, animals, diseases, and technologies between the Americas and the rest of the world following Columbus's voyages.
question
Terrace Farming
answer
Cutting of "steps" into the mountains that allowed for more agriculture
question
Irrigation
answer
A way of supplying water to an area of land
question
Deforestation
answer
The removal of trees faster than forests can replace themselves.
question
Wetland Draining
answer
Draining water from a wetland to clear an area for farming; may have negative affects on the environment
question
Second Agricultural Revolution

answer
Tools and equipment were modified, methods of soil preparation, fertilization, crop care, and harvesting improved the general organization of agriculture made more efficient
question
Third Agricultural Revolution (Green Rev.)
answer
Began in 1960's - the application of Genetically Modified Organisms, improved techniques and technologies to agriculture like pesticides - greatly increased production
question
High-yield Seeds
answer
Genetically modified seeds that survive longer and produce more crop
question
Chemical Farming
answer
Application of synthetic fertilizers to the soil and herbicides, fungicides, and pesticides to crops in order to enhance yields
question
Mechanized Farming
answer
The replacement of human farm labor with machines; characteristic of large scale commercial or plantation farming.
question
Pesticides
answer
Chemicals used on plants that do not harm the plants, but kill pests and have negative repercussions on other species who ingest the chemicals.
question
Herbicide
answer
A substance used to destroy plants, especially weeds
question
Fertilizer
answer
A chemical that provides nutrients to help crops grow better. Example: animals poop on plants which helps them grow
question
Bioclimatic Zones
answer
Areas that have similar climate and biological makeup of plants and animals
question
Mediterranean Climate
answer
Mild and constant climate thought to be ideal for most crops to grow in
question
Shifting Agriculture

answer
Method of farming where farmer clears a field using the slash and burn technique that he uses for about 3 years before letting the depleted soil rest for 6-20 years and moving to a new field
question
Pastoral Nomadism
answer
Type of agriculture that relies on animals rather than crops where a group wanders its territory with a herd that represents the group's power and prestige but still eats grain usually farmed by the women and children
question
Subsistence Farming
answer
The production of food primarily for consumption by the farmer's family Example: Developing countries
question
Commercial Farming
answer
The production of food primarily for sale off the farm Example: Developed Countries
question
Intensive Land Use
answer
Using a little bit of land for a crop that requires more individual care Example: Flowers
question
Market Gardening
answer
The small scale production of fruits, vegetables, and flowers as cash crops sold directly to local consumers.
question
Plantation Agriculture
answer
Production system based on a large estate owned by an individual, family, or corporation and organized to produce a cash crop.
question
Mixed Crop/Livestock Systems
answer
Type of agriculture where both plants and animals are grown for their produce and often the leftover plants are used to feed the animals, who in turn produce dung that is used as fertilizer for the plants
question
Extensive Land Use
answer
Farming that uses large area farms and has low input per acre (von Thunen outer rings) Example: Ranching
question
Shifting Cultivation
answer
From of agriculture in which an area of ground is cleared of vegetation and cultivated for a few years and then abandoned for a new area until its fertility has been naturally rest
question
Nomadic Herding
answer
The raising of livestock for food by moving herds from place to place to find pasture and water
question
Transhumance
answer
The seasonal migration of livestock between mountains and lowland pastures.
question
Ranching
answer
A form of commercial agriculture in which livestock graze over an extensive area.
question
Agribusiness
answer
Commercial agriculture characterized by integration of different steps in the food-processing industry, usually through ownership by large corporations.
question
Commodity Chain
answer
Series of links connecting the many places of production and distribution
question
Global Supply Chain
answer
The network created among different worldwide companies producing, handling, and distributing specific Example: Countries work together to trade crops that they produce
question
Clustered Settlement Pattern
answer
A settlement that is arranged in a roughly concentric shape around a central point
question
Dispersed Settlement Pattern
answer
A settlement that has no specific arrangement and has a large amount of space between houses
question
Linear Settlement Pattern
answer
A settlement arranged around a central linear object that goes through it, like a river or a road
question
Von Thünen's Model
answer
A circular model created by Johann Heinrich von Thunen in the early 1800s arranged in concentric rings containing different agricultural activities of varying distance from the market or city, with the first being perishables like dairy, fruits, and vegetables, the 2nd being lumber, the third being grain farming, and the fourth being livestock grazing grounds
question
Specialty Farming
answer
Farming that grows crops to provide small upscale niche markets with fresh produce
question
Desertification

answer
Degradation of land, especially in semiarid areas, primarily because of human actions like excessive crop planting, animal grazing, and tree cutting.
question
Biotechnology
answer
A form of technology that uses living organisms, usually genes, to modify products, to make or modify plants and animals, or to develop other microorganisms for specific purposes.
question
Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs)
answer
Foods that are mostly products or organisms that have their genes altered in a laboratory for specific purposes, such as disease resistance, increased productivity, or nutritional value allowing growers greater control, predictability, and efficiency.
question
Organic Farming
answer
A method of farming that does not use artificial means such as synthetic pesticides and herbicides, antibiotics, and bioengineering
question
Aquaculture
answer
Raising fish and other aquatic species in captivity for harvest.
question
Sustainability
answer
A set of policies or practices by which societies can ensure that the people of the future have the same access to resources and thus the same economic and environmental opportunities as people living today.
question
Soil Degradation
answer
The decline of the quantity and quality of soil.
question
Biodiversity
answer
The number of species within a specific habitat.
question
Overgrazing

answer
Destruction of vegetation caused by too many grazing animals consuming the plants in a particular area so they cannot recover
question
Aquifer Depletion
answer
The removal by humans of more groundwater than can be recharged by precipitation or melting snow
question
Value-Added Specialty Crops
answer
Crops that have another item added to them that increases the value and price)
question
Fair Trade
answer
System where producers get fair prices on their produce Example: Farmer gets good amount of money for their crops.
question
Local-Food Movements
answer
Increase in demand for locally grown foods due to a resulting sense of community



