AP Human Geography – Unit 1 Vocabulary (Articulation) – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
geography
answer
the study of the physical features of the earth and its atmosphere, and of human activity as it affects and is affected by these, including the distribution of populations and resources, land use, and industries
question
spatial relationships
answer
two (or more) phenomena may be related, or associated with one another
question
human-environment interaction
answer
the connection and exchange between humans and the natural world
question
location
answer
position; situation of people and things
question
place
answer
uniqueness of a location (or similarity of two or more locales); phenomena within an area
question
scale
answer
the amount of territory that a map represents
question
pattern
answer
general arrangement of things being studied
question
regionalization
answer
the process geographers use to divide and categorize space into smaller areal units
question
globalization
answer
expansion of economic, political, and cultural processes to a global scale and impact (transcend state boundaries)
question
physical map

answer
primary purpose is to show landforms like deserts, mountains, and plains
question
political map
answer
designed to show governmental boundaries of countries, states, and counties, and the location of major cities
question
thematic map
answer
show spatial aspects of information or of a phenomenon
question
reference map
answer
generalized map type designed to show general spatial properties of features
question
choropleth map
answer
uses various colors, shades of one color, or patterns to show the location and distribution of spatial data
question
dot map

answer
used to show the specific location and distribution of something across the territory of the map
question
graduated symbol map

answer
uses symbols of different sizes to indicate different amounts of something
question
isoline map
answer
uses lines that connect points of equal value to depict variations in the data across space
question
cartogram map

answer
the sizes of countries (or states, counties, or another areal unit) are shown according to some specific statistic
question
map projections
answer
process of showing a curved surface on a flat surface
question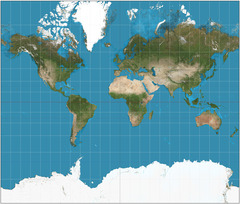
Mercator projection

answer
straight meridians and parallels that intersect at right angles, used for marine navigation; most distortion at the poles (high latitudes)
question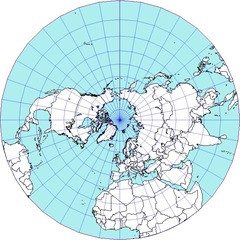
Polar projection

answer
directions from a central point are preserved; usually these projections also have radial symmetry; also known as Azimuthal projections
question
region
answer
area on Earth's surface marked by a degree of homogeneity (uniformity) of some phenomenon
question
formal (uniform) region
answer
homogeneous region is an area within which everyone shares in common one or more distinctive characteristics. The shared feature could be a cultural value such as a common language, or an environmental climate
question
perceptual (vernacular) region
answer
a place that people believe exists as a part of their cultural identity. Such regions emerge from peoples informal sense of place rather than from scientific models developed through geographic thought
question
functional (nodal) region
answer
area organized around a node or focal point; the characteristic will diminish in importance as it spreads outward. This region is tied to the central point by transportation or communication systems or by economic or functional associations
question
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
answer
collection of computer hardware and software permitting spatial data to be collected, recorded, stored, retrieved, used, and displayed
question
Global Positioning System (GPS)
answer
satellite-based system for determining the absolute location of places
question
remote sensing
answer
method of collecting data or information through the use of instruments (e.g., satellites) that are physically distant from the area or object of study



