ABA Basic Exam – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Median n stimulation
answer
Wrist flex Thumb opposition Flexion of radial half of digits Forearm protonation
question
Drugs administered via ETT
answer
Lidocaine Atropine Naloxone Epi LANE
question
02 content equation
answer
1.39 * Hemoglobin * saturation) + .003 * Pa02
question
2 equations to calculate GFR
answer
Cockcroft-Gault: (140-age)*weight (kg)/72*Cr Modification of Diet in Renal Disease 175*(Cr)-1.154*age-0.203*(.742 if female)*(1.212 if african american)
question
Von Bezold Jarisch Reflex
answer
Noxious stimuli to either ventricle a/w myocardial ischemisa, hypovolemia, coronary reperfusion, AS, neuraxial anesthesia results in decreased BP, coronary vasodilation, and inibition of sympathetic outlfow
question
Bainbridge atrial reflex
answer
Increased vagal tone and distention of right atrium or central veins results bradycardia, hypotension, decreased SVR
question
Gestational age that aortocaval compression begins
answer
20 weeks gestation
question
Average blood volumes
answer
Premature - 95 Full Term - 85 Infant- 80 Adult men - 75 Adult women - 65
question
Morphine equivalent dose
answer
Intrathecal duramorph is 10 times for IV dose and 100 times for PO dose
question
Changes in mixed venous oxygen saturation
answer
Increase - sepsis Decrease - Anemia, hypoxemia, low CO, Increased 02 consumption
question
Spinal cords ends and dural sac ends in adults and peds
answer
Spinal cord Adult - L1-L2 Peds - L3-L4 Dural Sac Adult - S2-S3 Peds - S3-S4
question
Uterine blood flow at term
answer
700 - 900 mL/min and is not autoregualted
question
Superficial peroneal nerve innervation
answer
Dorsum of foot
question
Posterior tibial nerve
answer
Plantar surface of food
question
Deep peroneal nerve
answer
Web space between the first and second toe
question
Sural nerve
answer
Posterolateral foot
question
Saphenous nerve
answer
anteromedial side of food
question
Landmark for superior hypogastric plexus block
answer
Plexus extends from L5-S1
question
Landmark for lumbar sympathetic block
answer
L3
question
Landmark for celiac plexus block
answer
L1
question
Afferent and efferent limbs of laryngospasm reflex
answer
Afferent - Internal branch of superior larygneal nerve Efferent - Reccurent laryngeal nerve
question
Number needed to harm
answer
1/ARI ARI = experiment event rate - control event rate
question
Infraclavicular blocks brachial plexus at what level?
answer
Cords
question
Foot drop
answer
Anterior tibial n or peroneal n
question
Weakness below the knee and dcreased sensation of all of the foot with exception of innter arch
answer
Sciatic
question
Loss of knee extensiion and hip flexion
answer
Femoral
question
Inability to abduct leg
answer
Obturator
question
Pierre Robin Syndrome abnormalities
answer
micrognathia - MC others - glossoptosis, cleft palate, laryngomalacia, and hearing loss
question
Total body bicarbonate deficit equation
answer
Weight kg * Deviation of [HCO3-] from 24 * 0.3
question
MAP equation
answer
(SBP + 2* DBP)/3
question
Cerebral perfusion pressuire
answer
MAP - CVP/ICP
question
Oculocardiac reflex
answer
Results in decreased HR with compresion of eyeball Afferent: ophthalmic bracnh (Trigeminal) Efferent: Vagus
question
Equation for vaporizer output of bubble through
answer
Output = Carrier gas flow* saturated vapor pressure of agent/Barometric pressure- saturated vapor pressure of agent
question
Pulmonary fucntion changes in patients with Acites
answer
Decreased - FEV1, DLCO, FVC, IRC
question
NNT
answer
1/ARR ARR - control event rate - experimental event rate
question
Interaction of muscle relaxants with antibiotics, lithium, antiepileptics, magnesium, volatiles
answer
Antibiotics (aminoclycosides, polymixins, lincomycin, clinda) - potentiate Antiepileptics - Resistance ot NDNMBs, Potentiate Succ Lithium - Potentiation of NDNMBs and Succ Mag - Potentiates NDNMBs and no effect on succ Volatiles - Potentiate - Des > Sevo>Iso>Hal>NO
question
Coronary artery perfusion pressure equation
answer
MAP-PAWP
question
Artery of Adamkiewitz
answer
T9-T12
question
Spinal cord perfusion pressure
answer
MAP- CSF pressure
question
SVR
answer
(MAP-CVP)*80/CO
question
PVR
answer
(PAMP-PAWP)*80/CO
question
Dextran SE
answer
Decrease platlet agreation, Anaphylaxes
question
Hetastarch SE
answer
Anticoagulatent effects - decrease F7, vWF, Fibringogen, decrease plately aggreation Pruitic crisis
question
Treatment of ventricular fibrillation in adults and peds
answer
Defibrillate at 2 J/kg followed by subsequent shocks at 4 J/kg
question
Fail safe valve
answer
Prevents delivery of hypoxic mixture to patient due to failure of 02 supply Pressure of 02 below which this valve with decrease or prevent flow of N20 = 25 psi
question
Stimulation of nerve will induce extension of the digits, wirst, and elbow as well as forearm supination
answer
Radial nerve
question
Lung parameter most affected with scoliosis curvature > 65 degrees
answer
Vital Capacity
question
Lung changes during pregnancy
answer
TV and Ispiratory reserve capacity increase Vital capacity remains the saem All other decrease
question
Filling SEVO vaporizer with Des
answer
HIgher output concentration
question
Exagerated pain in response to nonciceptive stimuli
answer
Hyperathia
question
Increased sensitivity to pain
answer
Hyperalgesia
question
Abnormal sensation without an apparent stimulus
answer
Paraesthesia
question
Pain in the distribution of nerve fiber or bundle
answer
Neuralgia
question
Perception on nonnoxious stimuli as painful
answer
Allodynia
question
Conditions a/w with low DLCO
answer
COPD CHF Anemia Sarcoidosis Asbestosis TB
question
Condtions a/w increase DLCO
answer
Asthma Polycythemia Left to right intracardiac shunt Exercise Pulmonary Hemorrhage
question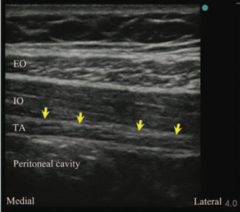
TAP Block

answer
Useful for procedures invovling lower abdomen Subcostal T12, Ilioinguinal L1, iliohypogastric (L1), genitofemoral nerves targeted Nerves travel in plan of internal obliquie, and transversus abdominal msucle
question
Predictors of operative risk for thoracotmy
answer
FEV1<40 DLCO<40 VO2<10
question
Intracranial hypertension exists when ICP is greater than...
answer
15
question
GAG Relfex
answer
Afferent - Glossopharyngeal n Efferent - Superior and recurrent laryngeal n
question
Cerebral blood flow
answer
Normal = 50 Slowing EEG = < 20 Isoelectric EEG = 15 Irreversibel brain damage = < 10
question
Signs of dehydration
answer
Mild - UOP < 2 Moderate (10% weight loss) - sunken fontanels, decreased skin turgur, and decreased mucous membraens Severe (15% weight loss) - reduced BP
question
Herbal drug interaction
answer
CV - Ephedra Bleeding - Garlic, ginko, ginsing, green tea, saw palmeta Hepatotoxic - echinacea, kava Changes drug metabolism - St johns wart Changes glucose metabolism - ginsing Immunosuppresant - echinacea
question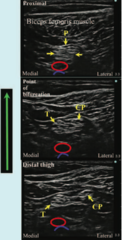
Popliteal nerve block - structures noted within popliteal fossa

answer
Sciatic, n,Tibeal n, Common peronial nerve, Popliteal A/V
question
Aphonia, and respiratory distress imeediately after thyroidectomy
answer
BL recurrent laryngeal nerve injury = VC close due to unoposed constriction of cricthyroid msuclle (intervated by external branch of recurrent larngeal n)
question
Afferent and efferent branches of laryngoaspm refelx
answer
Affferent - superior larngeal nerve
question
Bloow volume lost for ever 1% of the body surface area excised during burn repair
answer
3.5-5% Note - volume of tissue excised should exceed 10-15% of total body serface area at one procedure
question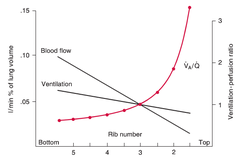
Ventilation/Perfusion throughout the lung

answer
V & Q both increase from the apex to the base, but base of the lung recieves more ventilation than the apex Base recieves the greatest amount of perfusion At apex of the lung there is less blood becasue gravity pulls it odwn and relatively high ventilation, so V/Q highest at apex and lowest at base
question
Blood loss of standard vaginal delivery
answer
500 C section - 1000
question
Myocardial oxygen consumption - normally, @ 22 degrees c, and after cardioplegia
answer
10 mL/100g/min - normal 5.5 mL/100 g/min - @ 22 degrees C 0.3 mL/100 g/min - cardioplegia
question
Most important mechanism of heat loss in OR following redistribution in first 30 mins
answer
Radiation - heat loss from skin to cold surroundings in OR
question
Paravertebral thoracic block
answer
Indications - thoracic procedures, masectomy Complications - pnumothroax (major), hypotesnion Thoracic paravertebral space - Posterior - costotransverse ligament Anterior - pleura of lung Medial - vertebrae/intervertebral foramina Inferior - Rib Superior - Rib
question
Neuromuscular blockers excretion
answer
Pancuronium - renal (avoid in renal failure) Vec/Roc - hepatic metbasolim and biliary excretion with slight renal excretion Mivacurioum - pseudocholinesterase Cisatracurium - hoffamn degradtion
question
Transtracheal block which nerve
answer
Recurrent laryngeal nerve Superior larngeal n - greater cornu of the hyoid
question
INcrease ventialtion increase FA/FI of which type of agents the most?
answer
Soluble agents
question
Side effects of terbutaline
answer
tachycardia hypotesnion MI Pulm edema inhibiition of hypoxic pulmnary vasoconstriciton Hyperglycemia Metabolic acidosis Hypoklaemia Axiety/nervousness
question
Reynolds Equation for gas flow
answer
Re = 2*radius*velocity*diameter/viscocity Re>4000- turbulent Re<2000- laminar Low numbers (e.g lminar ) - low gas density, low velocity, small radius of tube high numbers - (turblent) - low viscoity
question
Superior hypogastric pleux block
answer
Inidication - pelvis pain unresponsive to lumbar or caudal epidural blocks - cancer of the cervix, uterus, bladder, prostate, rectum Contains - postganglionic lumbar sympathetic fibers, viceral sensory fibers from cervi, uterus, bladder, and rectum, preganglionic parasympathetic fibers from S2-S4 Landmark - L5 Complications - Common illiac artery puncture
question
Stimulation of musculocutanous nerve
answer
Elbow felxion
question
forwarm supination
answer
radial nerve
question
forearm pronation
answer
median nerve
question
wrist flexion
answer
ulnar nerve
question
Intralipid dosing
answer
Bolus 1.5 ml/kg over one minute with a continuous infussion of 0.25 ml/kg/min conitniuning for at least 10 mins after cardiac stability is obtained Repeat bolous once or twice for persistent CV collpase Infusion rate can be doubled to 0.5 mL/kg/min if BP is low
question
Sensation to tongue
answer
General sensory - trigeminal (anterior two thirds) and glosspharyngeal (posterior one third) Tase - facial (anerior 2/3) and glosspharngeal (posterior 1/3)
question
Metbaolism of atracurium
answer
HOffman and nonspecific esterases A/W histamine release
question
Effect of transfudcer of a line blood pressure
answer
If transducer is placed lower than the set zero reference , the blood pressure reading will tend to overestmate IF the transfucer is placed high tahn the set zero, the blood pressure reading will tend to underestmate BP
question
Sevo put into a iso vaporizer
answer
Sevo VP 162, is filled in an iso cannister with a vapor pressure of 239, then it will deliver a lower concentration than expected IF sevo was filled in a cannister that has lower vapor pressure than 162, it would result in a high than expected concentration
question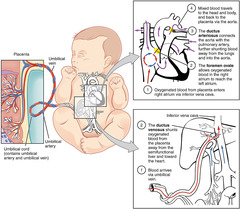
Neonatal circulation

answer
Oxygeanted blood from placenta travels via the inferior vena cava to right heart Venous oxygenated blood bypasses nonfunctional pulmonary system through the foramen ovale and the ductus arteriosus @ birth expansion of lungs with air decreases PVR
question
Initial fluid replacement for pyloric stensosis
answer
NS - add K once urine out put increased
question
Treatment of cyanide toxicity
answer
Discontinue infusion, adminster 100% O2 Administer amyl-nitrate (inhaler) or IV sodium nitrite and thiosulfate, except in those pateints with abnormal renal function, for whom hydroxocobalamin is recommended
question
Bohr effect vs Haldane effect
answer
Bohr - CO2/H are affecting the affinity of Hb for 02 Haldane - 02 is affecting the affivinty of Hb for CO2/H+
question
Cholindergic crissi
answer
DUMBELS Diaphrosies.Diarrhea Urination Miosis Bronchospasm/Bradicardioa Emesis Lacrimation Salivation
question
Most common nerve damaged during aortic arch repair
answer
Left recurrent laryngeal nerve - branches of left vagus in the chest vs right recurrent laryngeal nerve that branches off vegas lower in the neck Left recurrent largneal nerve injury - post op hoarseness a/w adducted left vocal cord and an abducted right vocal cord
question
Muscle relaxants associated with histamine release
answer
Succ Atracurium and tubocurare
question
Risk factors for PDPH
answer
Yougner age Feamel
question
Which patient not candate for tramadol?
answer
Alcoholic - Increased risk of seizure
question
Carotid Body chemoreceptors
answer
Located near bifurcation the internal carotids Afferent: glosspharygneal Senses: hypoxemia, Hypercapnia, , decreased pH, PO2<80 most potent stimulus leads to ventilator stimulation
question
Factors a/w with risk of ischemic optic neuropathy
answer
Spinal surgery, Cardiopulmonary bypass Males Prone position Intraoperative hypotesnion Massive fluid replacement Hx of diabets, HTN, vascular disease Long duration of surgery Obestiy Wilson frame use Massive blood loss
question
Stages of labor
answer
Latent - contractions become more regualr Active - Cervix dilates from 4 to 8 cm and contractions get more intesnse, about 3 minutes aprt, lasting aobut 45 seconds Transition - Cervix dilates from 8 to 10 cm, contractions are 2 to 3 minutes apart and last about 1 minute Fetal decent - Babys head more toward the pelvis Second stage - Cervix fully dialted @ 10 cm, followed by crowing of baby head Delivery Third stage - Begins after the baby is born and ends when the placenta seperates from uterus
question
Alveolar Ventilation
answer
TV - Dead space * RR
question
1 mac of N20
answer
500 mL/min
question
Vascualr suseceptibel to IV injection
answer
ICE Beyond Slight Freezing I=intercostal C= cuadal E=Epidrual B=Brachial plexus S=sciatic F=femoral
question
pH change for patients with chronic respiratory acodsis for incrase in PaCO2
answer
pH will change 0.03 units for every 10 mmHg change in PaCO2
question
Normal CBF
answer
45-55 mL/100g/min 75-80 gray matter 20- white matter
question
Boyles Law
answer
T=PV -at constant temperature th eprodcut of the pressure and volume is constant
question
PaPlaces Law
answer
T = P*R, T = suraface tension, P = intraalveorl pressure, R - radius of alvesuls
question
Normal mitral valve and aortic valve area
answer
Mitral - 4-6 cm2 Aortic - 2-4
question
Autoregulation range of the kideny
answer
60 - 160 thus GFR and RBF only begin to decrease at MAPS below 60 or above 160
question
Fast conducting fibers, responsible for intesnse sharp pain and paraesthesias
answer
A delta
question
Sensation of pressure, light touch, propioception and fine hair moment
answer
A-Beta
question
Delayed burning sensation after noxius stimuli
answer
Unmylinated C -fibers
question
Muscle spindles
answer
Gamma motor neurons
question
Shock dose for synchronized cardioversion for a flutter
answer
50 - 100 J
question
MAC by age for SEVO
answer
Neonates and infants 1 year - 2 %
question
Indications for cardiac pacemaker
answer
Symptomatic sinus or AV nod disease Long QT Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy Dialted cardiomyopathy Congestive heartfailure Severe bradyarrhytmia Afib
question
Lung volumes unchaged during obesity
answer
Unchanged - forced expiratory volume, forced vital capacity, peak expieratory flows Reduced - RV, Expieratory lung volume, Functional residual capacity, total lung capcity
question
Anesthetic changes for elderly
answer
MAC declines from young adulthood by 30% Dose of opoids decreases ED50 of NMB is increased Creatine increased Volume of LA recued
question
Autonomic hyperreflexia
answer
Chornic spinal cord injury above T5-T6 Symptoms: Vasodialtion above the leshion HTN below the leshion others sweating nasal congestion HA blurred vision bradycardia heartblock ventricular dysrhythmias
question
How much does PaCO2 increase during apena in first minute
answer
6 mmHg and then rises 3-4 mmHg each subsequent minute of apnea
question
Pre eclampsia risk factors
answer
Nulliparity (not having bared children) age>40 black family history chronic reanl disease chronic hypertension
question
4 distinct plans of stage 3 (surgical plane)
answer
1 - ocular movement 2 - decreased tidal voumes, low risk of larygnospasm 3 - respirations by diaphragm, ETT can be saefely placed 4 - flacid muscle tone
question
Characteristic of difficult mask ventilation
answer
Facial hair, edentia, over/under bite, facial deformity, enlarged tongue/tonsils
question
How many days after MI should surgery be delayed?
answer
30 days
question
Factor that demonstrates direct correlation with delayed gastric empyting in diabetic patient?
answer
Presence of autonomic nueropaty Features - Orthostatic hypotension, elevated resting heart rate, sexual disfunction, etc
question
Medications that decrease LES tone?
answer
IV anesthetics - propofol, thiopental, opoids, anticholinergics Volatiles B - agonists TCAs Antichoinergics - glyco
question
Medications that increase LES tone?
answer
Antacids Metoclopramide Cholinergics Succ A adrenergic agonists Metoprolol
question
Medications that done alter LES tone
answer
H2 antagonists NDNMBs
question
Sensitivity
answer
TP/TP+FN
question
Specificity
answer
TN/TN + FP
question
EEG changes with anesthesisa
answer
EEG in the awake pt - irregular rapid activty of low amplitude with a dominant frequent of 13 Hz EEG w/ anesthesia Beta type rapid oscillations increase in amplitude 13-20 Hz EEG w/deeper anesthesia a/w global slowing of theta, then delta (0-4 Hz) which becomes regular before disappearing into isoelectric EEG with very deep anesthesia (Burst suppression) Sevo A/W beta wave activity
question
Reccurent laryngeal nerve
answer
Branch of vagus Sensory - VC, and trachea Motor - all larynx muscles except cricothyroid Anesthesized by trastrachial block
question
Glosspharyngeal nerve
answer
Sensory - oropharynx, soft palate, psoterior third of tongue, tonsils, vallecula, and anterior surface of epiglotis Blocking this nerve blocks the gag reflex
question
Internal branch of the superior larygneal nerve
answer
Sensroy - base of tongue, posteror surface of epiglottis, aryepiglottic fold, and arytenoids
question
Diameter Index safety system
answer
noninterchangeable gas specific connections to the pipeline Note - if wrong gas connected e.g nitrous connected to oxygen site then hypoxic gas mixture could be delivered to patatient
question
Pin index safety system
answer
connects E cylinder tanks to the machine
question
Fail safe valve
answer
located in the intermediate pressure circuite - if pressure of oxygen drops below 28 psi it will stop the flow of nitrous oxide to the patient
question
Pressure regulator
answer
reduces cylinder pressure to 45 psi, which is lower than normal pipeline pressure of 50 psi malfunctioning regulator results in release of cylinder gas at high pressure and depletion of e cylinder
question
Lambert- Eaton syndrome
answer
Suseptible to NDNMBs
question
Conditions a/w difficult intubation
answer
Pierre Robin syndrome Treacher Collins Downs Acromegally
question
Check valve
answer
Present in the distal end of the low pressure circut - downstream from the vaporizers but upstream from oxygen flush valve Prevents pressure from the flush valve, ventilator or reservoir bag from renturing into the low pressure circuit Note - prevents positive pressure test from finding leak in low pressure circuit, need to use negative pressure test
question
Oxygen pressure failure alarm will be activated if the pipeline pressure drops below?
answer
30 psig
question
Laryngospasm
answer
Involuntary contraction of the cords Caused by stimulation of sensory paths of recurrent and supperior laryngeal nerves (branches of vagus) Triggered via secretions, blood, or debris Rx - 100 oxygen, jaw thrust, IV anesthesitcs or succ
question
BL recurrent laryngeal nerve injury (e.g after total thyroid removal)
answer
Stridor - unopposed adduction of vocal cords Note UL injury - hoarsness
question
BL superior laryngeal nerve injury
answer
Increased risk of aspiration as the vocal cords remain open and unable to protect the airwawy
question
Color code different gases?
answer
CO2 - grey NO - Blue Air - Yellow Nitrogen - Black 02 - Green
question
Low, Intermediate, and High pressure circuit contents
answer
Low - vaporizers, begins with flow meters Intermediate - begins at wall gas supply and the first stage regulators for the e cylinders and ends at the flow meters HIgh - contains just e cylinders and ffirst tage pressure regualtors
question
Gas flows - laminar vs turbulent
answer
Low flows - laminar - viscocity High flows - turbulent - density
question
Expiratory valve stuck in open position
answer
capnograph tracing failing to return to baseline
question
Expiratory vavle stuck in closed
answer
Breath stacking, volumtrauma and barotrauma Hyperinflation of the lungs could result in hypotesnsion 2/2 decreased venous return
question
Inspiratory and expiratory valve stuck in open position
answer
incrase in end tital c02
question
Coponents of soda lime
answer
75 % Calcium hydroxide 20% water 3% soium hydroxide 1% potassium hydroize Sodoum hydroixe, potassisum hydorixide are strong alkalis and implicated in the formation of CO, Compound A
question
Maximum pressure ETT cough should be inflated
answer
25-30 cm H20
question
3 rules to prevent rebreathing in a circle system
answer
Unidirectional gas flow Fresh gas flow does not enter circuit between patient and expiratory valve APL valve not located between inspiratory valve and patient
question
CO production
answer
Produced when volatiles passed through desiccated absorbents containg strong alkali (barium, potassium or sodium hydroxide) Des>en>iso>sevo
question
Contraindications to LMA use
answer
Aspiration risk - full stomach, hiatal hernia, GERD, intestinal obstruciton, delayed gastric emplyting Obestiy ok as long as no refulx present Not advised if postive pressure ventilation, peritoneal insufflation, or trendelenberg anticipated
question
Factors a/w Compound A formation
answer
Alkali absorbents - barium, sodium, and potassium hydroxide Higher concentration of Sevo Longer anesthetic Dessication
question
Alveolar concentration of a volatile that represents the ED 95?
answer
1.3 MAC
question
MAC that alows eye opening
answer
1/3 - 1/4 MAC
question
MAC BAR
answer
1.7-2.o MAC
question
ED 50 of dose response curve of volatile
answer
1 MAC
question
VP of DES
answer
669
question
Effect of volatiles on cerebral blood flow
answer
Increase CBF, especially N20 and HAL
question
Efffect of volatiles CMR02?
answer
Decrease, except N20 which increases
question
Effect of N20 on vascular resistance
answer
Decrease
question
Volume of distribution
answer
Apparent volume into which a drug is diluted Concentation = Dose/Volume Volume exceeds patient volume for fat soluble and highly protein bound drugs
question
Compare and contrast fentanyl and morphine during spinal injection
answer
Morphine - hydrophilic, leading to long duration of effect, slow onset, slow absorption into system ciruculation Fentanyl - lipophilic, quickly bind lumbosacral nerve roots
question
Conetext sensitive half life
answer
Concept that half life increases over time, especially for lipid soluble drugs
question
Effect of NDNMBs on MG?
answer
Exaggerated response
question
First order vs zero order kinetics
answer
First order -rate of the elimination is proportional to the concentration of the drug -exponential decay process Zero order -elimination is fized regardless of drug concentration
question
Drug potency function of...
answer
Drugs receptor and the receptor response to drug binding Drugs with higher potency have lower ED 50
question
Effect of Des at elevated altitude
answer
The des vaporizer delivers the correct dialed in percentage of desflurane at any altitude That dieled in percentage of DES at high altitudes results in a lower delivered partial pressure of DES, however, so one would need to use a DES vaproizer
question
Factors that increase and decrease MAC
answer
Increaese -Hypernatremia -Hyperthyroid -Alcoholism -Acute administraton of dextroamphetamine -Cocaine (acute) -Ephedrine -Younge age Decreases -Hypoxemia - Pa02 < 40 -Hyponatremia -Anemia - HC<10% Metabloic acid base status, hypercapnia, hypocapnia have no effect
question
Myasthenic vs Cholinergic crisis
answer
Myasthenic -an exacerbation of the myathenic symptoms caused by UNDERMEDICATION with anticholinesterases -priority to maintain adequate respiratory function -Tensilon test will help improve muscle tone Cholinergic Crisis -acute exacerbation of muscle weakness caused by overmedication with cholinergic anticholinesterase drugs -muscle twitching to the point of respiratory comprmise -symptoms improve with anticholinergic medis (atropine)
question
MAC value by age
answer
Peaks at age 1-6 months Lower in neonates, and decreases even further in premature infants in proportion to their prematurity Gradually decrease from age 1-6 months through the rest of ones life
question
Law of mass action
answer
Predicts that if you give larger mass of drug, the onset will be quicker
question
How does right to left shunt affect rise of Fa
answer
Repeate dilatuion of pulmonary blood affects lease soluble agents the most
question
Principle advantage of remifentanl
answer
Fast emergence - Metablized by plasma esterase and by hoffamn elimation - conext sensitive half life 2 to 3 minutes, no matter how long it has been infused
question
Primary disadvantage to remifentanl
answer
Acute opoid tolerence
question
Sufentanil
answer
Very lipophilic with large volume of distribution 2.48 L/kg
question
Drugs with zero order kinetics?
answer
ETOH Heparin Pheytoin Warfarin ASA
question
Ciatracurium
answer
Larger molecular weight and is highly polar - low volume of distribution
question
Diazepam
answer
Metabolized in the liver to active metabolites that prolong diazepams sedative effects
question
Propofol
answer
Total body clearance exceeds hepatic blood flow Anti- emetic Promotes bacterial growth - ampual must be used within six hour of opening Children require higher induction dose of propofol per kg 2/2 larger central distribution volume Decreases BP
question
Ketamine
answer
Induces sympathetic nervous system - increased BP, and HR
question
Etomidate
answer
Hemodynamically neutral
question
How does ESLD, PNA, increased age, and pregnancy affect albumin and alpha glycoprotein levels?
answer
Increased albumim Decreased albumin - ESLD, Increased age, Pregnancy Increased glycoprotein - PNA Decreased glycopretoin - Pregnancy
question
Factors that alow drugs to pass membranes
answer
low molecular weight lipophilic low degree of ionization large concentration gradient
question
Propol binds which receptor
answer
GABA A
question
MOA of ketamine
answer
NMDA antagonist
question
MOA of dexmetatomidine and clonidine
answer
alpha 2 adrenergic agonists
question
MOA of droperidol
answer
Dopamine receptor antagnoist
question
Metabolite of midazolam
answer
Hydroxymidazolam, may lead to progloned sedation in renal failure
question
pKa deffiniton?
answer
pKA of a drug is defined as pH at which half the drug is in the its ionized form and half is in its unionized form
question
How to decrease pain a/w propofol injection into small vein?
answer
larger veins Prior lidocaine, thiopental, or fent/remi Diluting the formulation with additional solevent - intralipid Sodium metabisulfite as antimicrobial agent Note ampofol has more pain with injection
question
Sulfite containing medicaitons that increase indicence of bronchospasm
answer
Generic propofol Epineprhine Dexamethasone/Hydrocortisone
question
Effect of benzos of CO2 reponse curve?
answer
Shift it down
question
Effect of PNA on lidocaine bioavailability?
answer
PNA increases alpha glycoprotein which binds more lidocaine decreasing the bioavailability
question
IV anesthetic effect on respirations?
answer
Propofol - apnea Thiopental - apnea Ketamine/etomidate - preservation
question
Alpha 2 subunit of GABA - A responsible for?
answer
anxiolysis, and muscle releaxation
question
Alpha 1 subunit of GABA A receptor responsible for?
answer
sedation, anticonvulsant, and amnesia
question
Of the IV anesthetics which is not chiral?
answer
Propofol Chiral ones include - Thiopental, etomidate, Ketamine
question
Characteristic of Tetralogy of Fallow
answer
VSD Right ventricular outflow tract obstruction Over riding aorta Right ventricular hypertrophy
question
pKA that produces drugs with smallest amount of its molecules ionized, hence the largerst percentage in neutral form?
answer
pKA closest to blood stream pH, e.g the lowest pKa
question
Active metabolites of diazepam?
answer
Oxazapam Desmethyldiazepam Both prlong clinical effect Note enterohepatic circulation produces secondary peak in diazepam after 6-12 hours
question
Propofol infusion syndrome
answer
Critically ill children and adults on long term infusion in ICU Sx - lactic acidosis, lipemic serum, cardiac dysfunction, heart failure, V- fib, tachycardia, heart block, rhabdo, hyperkalemia, renal failure, fatty liver Mechanism - inhibition of fatty acid oxidation and mitochondrial ETC RFs - TBI, airway infection, peds, total cumulative dose, high catecholamine levels, criticall illness, inborn errors of metabolism
question
How should induction dose of propofol be calculated?
answer
Lean body weight
question
Treatment of propofol infusion syndrome?
answer
Hemodyalsis
question
How should propofol infusion be dosed?
answer
Total body weight
question
Metabolite of meperdine
answer
Normemperdine, in renal failure can cause irritability, tremors, muscle twitching, myoclonus and even seizure
question
Opoid a/w prlonging QT interval?
answer
Methadone
question
Tolerance
answer
reduction in effect of drug over time a/w repeated delivery of agonist, or increase in dose required to yield an equivalent response
question
Propylene glycol toxicity a/w what drug and symptoms?
answer
Parenteral - Lorazepam Sx- metabolic acidosis, and AKI, ELEVATED osmolar gap (>12)
question
Phase 1 vs phase 2 block?
answer
Phase 1 -TOF >0.7 -Sustained tetanus Phase 2 block -antagonized by anticholiesterase -Fade on TOF -Post tetanic facilitaton -TOF <0.3
question
Buprenorphiene mechanism
answer
Partial Mu receptor opoid agonist
question
Nalbuphine
answer
Mixed agonist antagonist with agonist at K receptors and antagonist a Mu recpeotr Releaves pruritis without reversing analgesia
question
Methylnatrexone mechnasim of reversing opoid induced constipation?
answer
Peripherally acting opoid Mu rec antagonist
question
Homozygote butrylcholinesterase number
answer
20 -30, duration of suc inuced paralsysis of 4-8 hourss
question
Heterozygote dibucaine number
answer
50-60,
question
Dose required for phase 2 block with suc?
answer
>5 mg/kg for over 60 minutes
question
Level of GABA - A receptor ccoupancy that will lead to amnesia, anxiolysis, sedation, and unconsciousness?
answer
Amnesia, Axiolysis - 20% Sedation 30-50% Unconsciousness - > 60%
question
List the endogenous opoid ligands
answer
Endorphins Enkepalins - delta rec Dynorphins - kappa rec Endomorphins - Mu rec Nociceptin or orphanin - don't bind opoid receptors, may be involved in opoid induced hyperalgesia
question
T1/2 of plasma cholinesterase?
answer
8-16 hours
question
Most important side effect of Benzos
answer
Respiratory depression, but apnea uncommon at sedative doses
question
M2 receptor
answer
respirtaroy depression
question
Mu 1 receptor
answer
Analgesia
question
Kappa opoid receptor
answer
dysphoria, diuretic effects (negative regulation of ADH)
question
Delta opoid rec?
answer
Modulate Mu recptor activity
question
Cirrhosis effect on plasma cholinesterase?
answer
Decreases it
question
2nd dose of Succ likely to...
answer
Cause bradycardia, especially in children
question
Echthiphate
answer
Prolongs succ
question
Antibiotic should be used with caution in patient receiving benzos?
answer
Macrolides - erythromycin - inhibits p450 3A4, leading to increased level of midazolam and prolonged sedation
question
Opoids most likely to cause skeletal fidgety?
answer
Sufenta + Fent
question
Muscle relaxants most effect by renal failure?
answer
Pancuronium - T1/2 increased 97 % with prolonged duration of action
question
Muscle relaxants a/w histamine release?
answer
Atracirum
question
Muscarinic side effects?
answer
Bradycardia Bronchospasm INcreased secretions Diarrhea Urination Miosis Lacrimation
question
Muscle relaxant a/w tachycardia
answer
Pancuronium - atropine like effect
question
Muscle relaxant metabolized by plasma cholinesterase and terminated by hoffman elimination?
answer
Atracurium
question
Muscle relaxant metabolized by plasma cholinesterase alone?
answer
Mivacurium
question
Muscle relaxant whose metabolite with 80% of the activity of the primary drug?
answer
Vec - 3 OH compound Note 30-40% of ven excreted unchanged in bile 25% excreted unchanged in urine
question
Aminosteroid muscle relaxant with least renal clearance?
answer
Roc - cleared over 90% by the liver
question
Class of muscle relaxants most likely to cause histamine release?
answer
Benzylisoquinolinium NDMRs - Mivacurium, cisatracurium, atracurium However atracurium most likely to cause histamine release
question
Muscle relaxant that is prolonged in renal failure?
answer
Pancurionium - excreted largely unchanged by the kidneys
question
Muscle relaxant a/w laudanosine metabolite?
answer
atraciurym - lowers seizure threshold
question
Myasthenia graves response to muscle relaxants?
answer
Sensitive to non depolarizes (requires less) Resistant to such (requiring more)
question
Metoclopramide effect on NDMRs?
answer
Has plasma cholinesterase inhibition activity - prolonging NDMRs metabolized by them - mica curium, atracurium, cisaracium, and suc
question
Effect of carbamazepine on NDMR function?
answer
Increased plasma clearance of vec, panc, and roc however atracurium, and mivacurium not affected Note phenytoin can enhance the function of NDMRS
question
What is sugammadex incompatible with?
answer
verapamil, ranitidine, and odansetron
question
How is sugamedex eliminated/
answer
unchanged in the urine
question
Volatile with most reduction on hepatic blood flow?
answer
Hal
question
Volatile most likely to cause renal failure after 12 hours of use?
answer
Enflurane
question
Order in which volatiles depressed hypoxic ventilatory response?
answer
Hal;En;Iso;Sevo;Des;;NO
question
Antihypertesnives that potentiate myocardial depressant effects of volatiles?
answer
beta antagonists, calcium channel blockers, or hypoglycemia (e.g high dose insulin)
question
ED 95 of Roc and effect of Des?
answer
ED 95 (average dose producing 95% twitch suppression) is 0.6 mg/kg However Des at 1 MAC nearly doubles potency of roc, so dose of 0.3 mg/kg would acomplish same goal
question
NO a/w with what deficiency?
answer
B12 def - Magloblastic anemia - presents with paresthesias in hands and feet, anorexia, fatigue, glossitis
question
How does bilateral carotid endarterectomies affect hypoxemia response?
answer
Pt with BL CEA - likely have decency of their peripheral chemoreceptors located in the carotid bodies which are sensitive to changes in arterial oxygen tension
question
Effect of volatiles on cortical evoked potentials?
answer
Decrease amplitude, and increase latency
question
Effect of volatiles of hemodynamics
answer
Increases Heart rate Decreases SVR Presereved CO Decreased MAP
question
How do muscle relaxants contribute to muscle relaxation and imobilzation
answer
Desensitize the Act receptor spinal NMDA type glutamate rec and glycine rec contribute to mobilization
question
In the presence of apnea how long does it take for CO2 to increase
answer
Increase 5 mmhg in first minute, and 3 mmHg every minute thereafter
question
Snydrome associated with cardiac arrest with volatiles on induction?
answer
Williams syndrome - higher percentage of these patients have prolonged QT intervals
question
Effect of N20 on hemodynamics?
answer
Sympathomimetic effect - under most clinical circumstances maintains CO, heart rate, and BP however does have tendency to increase heart rate and BP if given alone
question
What agents to avoid in atrial and ventricular arrhythmia ablation procedures?
answer
Volatiles - suppress atrail and ventricular arryhtmias Note propofol - only suppreses atrial arryhmias, but not ventricular
question
Inhibition of movement by volatiles mediated by?
answer
Resides in spinal cord and NMDA and glycine receptors appear to be involved Note: GABA - loss of consciousness mediated at supratentorial level Acetycholine recptors - muscle relaxation
question
Volatile that causes greatest decrease in hepatic blood flow?
answer
Halthane
question
myocardium supplied by circumflex
answer
lateral wall
question
Air embolus mostly likely to go where in heart?
answer
Right ostium - leading to RCA infarction - supplied posterior wall and posterior septum
question
CRH
answer
Produced in hypothalamus, stimulates anterior pit to release ACTH - which subsequently stimulates the adrenal cortex to release cortisol
question
Lowest PO2 value of blood?
answer
Coronary sinus - heart maximally extracts 02
question
LAD supplies
answer
Anterior LV, apex, anterior septum
question
Treatment of negative pressure pulmonary edema?
answer
Constant positive airway pressure
question
S4
answer
Aortic stenosis - concentric LV hypertrophy Atrial contraction against non compliant ventricle
question
Law of Laplace?
answer
Wall stress is equal to the product of intracavitary pressure and the radius of the chamber divided by the thicken of the cavity or P*r/2T
question
S3
answer
Heart failure
question
AV node supplied by?
answer
RCA - if included results in complete heart block with slow, wide complex, ventricular escape rhythm
question
Management of patient with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
answer
Obstruction worse with decrease preload, or after load or increases contractility or heart rate thus... Ensuring adequate preload wihtvolume Maintenance of after load Avoid increases in HOUR and contravitly
question
Muscarinc receptor most prominent in myocardium?
answer
m2
question
Best vasopressor hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy?
answer
Phenelephrine - increases after load and lowers heart which both decrease left ventricular outlet obstruction
question
Oculocardiac reflex
answer
Afferent - Trigenminal CN 5 Efferent - Vagus CN 10
question
New S3 during pregnancy?
answer
Benin - due to increase circulating volume
question
Best echo view to visualize stenotic aortic valve as well as determination of gradients across the left ventricular outflow tract and the aortic valve
answer
Deep transgastric long axis view
question
SA node location and intervention?
answer
Supplied by RCA and located at junction of the RA and SVC
question
Primary determinants of myocardial oxygen demand?
answer
Wall tension, contractility, and HOUR
question
Hyperventilation effect on PVR?
answer
Decreases resistance
question
Most important determinat of cardiac output?
answer
Venous return
question
Factor controling venous return?
answer
Mean systemic filling pressure, right atrial pressure, and blood flow resistance between the peripheral veins and the right atrium VR=Mean systemic filling pressure - right atrail pressure/resistance to venous return
question
Flow equation (Poiseulles law)
answer
Pie *r^4/8*nL
question
Nor - epi effect
answer
Increases SVR
question
Dobutamine
answer
Inodilator - increase CO, and decrease SVR
question
Milrinone
answer
PUlmonary vasdodilation and decrease PVR and SVR while increase CO and contractility
question
Acute aortic insufficiency
answer
Decrease dialtolic pressure HR and contractility will increase - wawter hammer pulse - maintains CO
question
Diuretics that cause hyperkalemia
answer
triamterene amiloride spironolactone
question
Pulmonary edema associated with which diuretic?
answer
Mannitol
question
Fenoldopam
answer
Selective dopamine rec 1 agonist Increase renal blood flow and sdoium excretion while decreaseing afterload SE - tachycardia 2/2 baroreceptor response to decrease bp
question
Spironolactone
answer
competes with aldo sterone receptor SE - gyncomasatia, hirsutism, and mestral irregulatires
question
Urine electrolytes associated with intrinsic renal failure?
answer
Urine Na ; 40, Urine osms ; 400
question
Urine electrolytes associated pre - renal cauase?
answer
Urine Na 400
question
Mechanism reponsible for rewakening on ketamine?
answer
Redistribution
question
Effect of ketamine of IOP?
answer
Increase - avoid in open eye procedures
question
Diuretics to avoid in chronic renal failure?
answer
Potassium sparing because they increase K - e.g spironolactone
question
DIfference between PO and IV ketamine?
answer
PO about 20% of IV bioavailability, so peak effect similar but oral would result in a slower onset and loger duration of action
question
Recptors affected by ketamine?
answer
Mu agonist - analgesia Inhibits NMDA Muscarinic Ach antagonist NMDA antagonist
question
Excitaory NMDA agonists?
answer
Glutamic acid, aspartic acid, and glycine
question
EEG waves seen with ketamine?
answer
Theta waves
question
Mecahnism of oliguria during laparoscopic surgery?
answer
Decreased renal blood flow 2/2 decreased CO, and increased SVR Increased levels of renin, ADH, and aldosterone Increased renal vein pressures
question
Which opoid receptor does ketamine bind?
answer
MU
question
Electrolytes abnormalies a/w PVCs
answer
Hypomag and hypokalemia
question
Diuretics that increase serum glucose?
answer
Loops - furosemide, torsemide HCTZ Triamterene
question
Changes the kidney undergoes during pregnancy?
answer
Kidneys and ureters increase in size Increase plasma flow Increase in GFR Decreased BUN Glucosuria
question
RFs for prolonged weaning from vent?
answer
Advanced age COPD Plueral effusions Pulmonary Hypertension Delerium Metabolic alkalosis
question
Acute changes after rapid bolus of manitol
answer
Increase in intravascular volume leading to increaed ICP, CVP, BP, CO
question
Prostaglandin E2 effect on kidney?
answer
renal vasodilation
question
Tase and sensation to the tongue?
answer
Anterior - facial nerve (taste), trigeminal (sensation) Posterior - glospharngeal for tase and sensation
question
Nerve injury associated with vocal cord paralysis and haorsness?
answer
Recurrent laryngeal nerve
question
Determines when ventilator assisten inspiration terminates in pressure support?
answer
pressure support breaths terminated when inspiratory flow decrease to a certeain percentage (typically 25%)
question
SIMV
answer
Combines assist control ventilation (either pressure or volume) and on breats above the set rate, will alow for pressure support ventilation Used for weaning
question
High freq oscillatory ventilation
answer
Pressure and volume are both variable and affected by lung mechanics, time (inspiratory and expiratory) is sthe only controled variable
question
Pressure regulated volume control
answer
Each breath is pressure controlled and has a variable or decelerating flow cruve however the clinician enters a target folume for each breath Every several breaths, the computer calcualets the driving pressure needed to achieve that volume Compliance can can change and high pressure alrms must be set
question
Presure support ventialtion
answer
RR is set by the patient When patient achieves a triger, a pressure is then generated by the vent Flow are meastured throughout the breath When the flow rate achieves approxmately 1/3 the intial flow rate, the pressure support is ended and the vent will await the next triger THe mode is pressure controlled, flow triggered (by patient) and flow cycled Differes from assist control pressure since inspiration is determied by time in that mode
question
Surfae landmark of trachea?
answer
extends from C6-T4/5
question
Costodiphragmatic recess
answer
Extends from eighth to tenth ribs along mid axialy lines
question
Volume control ventilaton
answer
Desired TV, flow rates, and inspirtaory time are set by clinician A decrease in compliance with the same delivered tidal volume results in an increase in peak inspirtory pressure
question
Pharynx
answer
Tube extending from base of skull to cricoid cartilage
question
Sternal angle
answer
T4/T5
question
Anatomic relation between neurvascular structures in costal grove
answer
Vein (superior), Artery (midle), and nerve (inferior)
question
Angle of the scapula
answer
T7
question
Xiphoid process
answer
T6
question
Umbilicus
answer
T10
question
Increased peak airway pressure, no change in plateau?
answer
Increased airway resitance
question
Increased peak airway pressure, increased plateau presssure
answer
Decreased lung compliance
question
RIse in PaCo2 in ashmatic?
answer
implies impending airway obsturction
question
High peak inspiratory pressure, normal plateau DDX
answer
HIgh resistance to air flow mucous plug foreign body bronchospasm kinged endotracheal tube compression of the external vent circuit
question
Extrahoric obsutruction
answer
Normal epiration, but inhalation is decreased
question
Fixed intra or extra thoracic obstruction
answer
Both inhalation and expiration are affected
question
Unilateral recurrent largngeal nerve injruy
answer
Hoarseness and paralyized ovcal cords that assume intermediate position
question
Bilateraly recurrent largnyeal nerve injury
answer
Aphonia, and paralyzed VC that flap together producing obstruction
question
Cricoid cartilage
answer
C6
question
Carina
answer
T5
question
Diaphgram acounts for what percentae of the inhaled tidal volume in normal adults?
answer
70%
question
Pulse oximeter - X and Y axis?
answer
X - time Y - absoprtion
question
Vagus nerve trajectory
answer
Runs posterolateral to the distal (intrathoraic) trachea and typically position in grove between the trachea and esophagus
question
Elecated peak airway pressure, normal plateau pressure
answer
Bronchoaspm - adminster inhaled beta agonist
question
Increased peak and plateau pressure?
answer
Migraation of ETT into right mainstem
question
Red:IR Modulation Ratio in pulse ox
answer
R = (Ared,AC/Ared,DC)/(Air,AC/Air,DC) R is a double ratio of the pulsatile and non - ppulsatile components of red light absoprtion to IR absorption
question
Beer Lamberts Law
answer
Intensity of transmitted ligh is inversly proportional to the concentration of the substance thourhg which the lighth passes
question
Pulse ox reports?
answer
Functional saturation
question
Co oximeters report
answer
Fractional saturatiion
question
Gass exchange occurs.....
answer
Respiratory bronchiole Alveolar ducts Alveolar sacks
question
Pleural pressure gradient
answer
Difference between intrapleural and intra alveolar pressure
question
Venturi effect
answer
Reduction in fluid pressure that results whne a fluid flows through a contricted section of pipe Pnumotachometers mreasures the flow rate of gases by detecting pressure differences across a fine mesh
question
Airleak in ETT for peds?
answer
Air leak below 25
question
Resistance proportion too?
answer
R^4 for laminar flow R^5 for turbulent flow
question
Effect of moving blood pressure cuff from proximal (e.g arm) to distal (e.g ankle)
answer
BP reading will increase
question
IV agent with imidazole structure?
answer
Etomidate
question
Etomidate physologic effects?
answer
Slightly decresases SVR CO unchanged IOP, CMR2, and ICP all decrease RR increases, and TV decreases
question
BP measurement technqiues that only provide systolic measurement
answer
Doppler and palpation Note asuculation - Systolic and diastolic
question
Etomidate acts at what recepotr?
answer
GABA A agonist
question
Oscillometric NIBP directly measures?
answer
MAP Systolic and diastolic calculated
question
How to calculate actual blood pressure if cuff is below level of the heart?
answer
Falsly elevated due to hydrostatic effect of blood Multiply height in cm of cuff below the heart * 0.7 then subtract that product from the falsly elevated measured pressure
question
what percentage of etomidate is protein bound?
answer
75%
question
Effect of etomidate on EEG
answer
Biphasic - low concentrations, activation occurs and at high concentrations inhibition occurs
question
HIccups at induction a/w what IV anesthetic?
answer
Etomidate
question
How is etomidate eliminated and metabolized?
answer
Metabolised by plasma esterases and hepatic enzymes and elimated in urine
question
Side effects of Etomidate
answer
Thrombophlebitis 20% Myoclonus 30-60%
question
MAP
answer
DBP + 1/3 pulse pressure
question
Effect of etomidate of auditory eoked potentials?
answer
Decreased amplitude, and increased latency In contrast to SSEPs which the amplitude is increased
question
Hyponatremia sighs
answer
confusion, malaise, lethardy
question
Digoxin toxicity a/w
answer
Hypokalemia
question
Hypernatremia signs
answer
irritability, spacticity, tremor
question
Fluid associated with reduction in factor 8 and vWF
answer
Hetastarch
question
Fluid a/w decreased platlet aggregation and prolonged bleeding time?
answer
Dextran
question
Colloid a/w allergic reaction
answer
Dextran has been a/w allergic reactions, interference with blood typing and renal failure
question
Fluid assoicated with pruritis
answer
Hetastarch
question
Recomended dural antiplatelet therapy after DES, baremetal, and baloon angiolasty?
answer
DES - 365 day BM - 4-6 weeks BA - 14 days
question
Tolerance Dependence
answer
Tolerance - escalating dose required for same effect Dependence - withdrawl
question
Cross tolerance
answer
Occurs between etoh and hypnotics/sedative requiring larger dose to achieve same effect
question
Addiction
answer
compulsive suse of a substance and seeing to aquire a substance to the exclusion of other activites, despite evidence of harm
question
Tachyphylaxis
answer
Rapid devlopment of tolerance to a drug after large, repeated doses or infusion
question
TBW
answer
Females 50% and males 60% of body weight
question
Crystaloid that does not contain potassium?
answer
NS
question
Mechansim responsible for long term tolerance with chronic opoid use?
answer
NMDA activation Ketamine and methadone, both antagongist at the NMDA receptor have been show to slow the onset of tolerance
question
Clincal risk factors predtive of periopertive CV complications (Revised cardiac risk indiex)?
answer
Ischmeic heart disease Heart failure Stroke or TIA Insuilin dependent DM Renal impartiment Cr;2
question
Two things that do not delop tolerance while on opoids?
answer
Miosis, Constipation
question
Blood loss to crystaoloid replacement
answer
1:1.3 to 1:1.6
question
Symptoms of cyanide toxicity from nitroprusside?
answer
Tachyphlaxis Metabolic acidosis Elevated mixed venous Pa02
question
Meperidine CI in patients taking what due to increased risk of serotonin syndrome
answer
MAO inhibitors - Selegiline
question
Fluid replacement on top of maintence for fever?
answer
2.5 mL/kg over 24 hours
question
Nicardipine
answer
DHP calcium channel blocker Used to decrease SVR and MAP after cardiac surg Bolus 0.5-1 mg, followed by infusion 2.5-10 mg/hr
question
Diltiazem
answer
Non DHP calcium channel blocker Rate control for Afib Bolus, followed by infusion 1-15 mg/hr
question
Antibiotifcs a/w renal dysfunction?
answer
Gentamycin (5-10%) Levofloxacin (1%)
question
Best antbiotic for lower GI procedures?
answer
Cefoxitin
question
Antiotiotic that increases QT interval?
answer
Macrolide -Erythromycin Levofloxacin can also increase QT but association less common
question
Dobutamine effects
answer
Increases CO with SVR Se - itachyarrhymias and PVC's
question
Ionotrope associated with decreased platlet count?
answer
Amrinone
question
Common EKG finding in digoxin tocity
answer
Atrial tachycardia with variable degree of heart block
question
Ionotrope that is Beta 1 selective?
answer
Dobutamine - B1 agonist and increases cAMP increasing intra celluar calcium concentration
question
Effects of ACE inhibitor
answer
Block ACE on Ang1 in the kidney blunting Ang 11 production and subsequent effects on vasocontriction, aldo synthesis, and ADH release Increase bradykinin levels 2/2 inhibition of ace
question
Compounds responsible for vasopressin release?
answer
Ach Histamine Nicotine Prostagandins
question
Hydralazine associated with?
answer
Lupus like syndrome
question
HR, SV, SVR, Mv02 all increased
answer
High dose epineprhine - >.1 mcg/kg/min
question
Increase HR, Increaed SV, Decrease SVR, increase Mv02?
answer
Dobutamine
question
Increased HR, Inreased SV, Increased SVR, INcreased Mv02
answer
Dopamine @ >10 mcg/kg/min - predominately alpha effects Dopamine stimulates D1, alpha, and B receptors, so its expected to increase HR and SV (B1), increase SVR (alpha), and increase Mv02 (B1)
question
Antibotics that potentiate neuromuscular blockade?
answer
Gentamicin, neomycin, tobramycin, amikacin Doxy, tetracycline Clinda
question
CI to MB andministration?
answer
Renal failure
question
Vasodilators associated with blunting hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction?
answer
Nitroglycerin and Nitroprusside
question
Hypoxic pulmonary vasocontriction
answer
Local hypoxia causes vasocontriction in pulmonary arteries, redirecting blood flow away from hypoix areas to areas with better oxygenation
question
Coronary vasospsm RX
answer
Diltiazem
question
Desmopressin (DDAVP)
answer
V2 specicic
question
Nicardipine
answer
INcrease HR, Decrease SVR, CO no change, Decrease contracility Coronary vasodilator
question
High risk patients for infective endocarditis?
answer
Prosthetic valve History of EC Unreparied cynatotic congenital heart disease Cogenital defect with prosthetic material reparied within last 6 months Cardiac transplant patient with vlave defects
question
Nesiritide
answer
Decreases vascular resitsance while having minimal effect on contractility and oxygen demane
question
PDE 2 inhibitors - milrinone and amrinone
answer
Only inotropic class that decreases Mv02 Inodilator, Increaes SV and CO and decreases SVR and PVr
question
Prolongs effects of calcium channel blockers and thus dose needs to be reduced?
answer
Liver failure
question
Location of V1a receptors?
answer
Vascular smooth muscle mainly resulting in vasocontriction other locations platelets, liver, adrenal glad, myometrium, brain and kidneys
question
Adverse effects of vasopressin
answer
Decreased CO Angina Myocardial ischemia Metbolic acisosis Ventricular dyshyhmia
question
Vasopressin use
answer
Control GI bleeding 2/2 decreased splanchnic blod flow
question
Nesiritide
answer
Binds to the A and B natriuretic peptide receptors, incrasing cGMP resulting in relaxation of smooth muscle, resulting in decrease preload, afterload and PVR
question
Nrepinephrine
answer
A, B agonist with predominatley alpha 1 effects Commonnly adminstered with milrinone after CPB
question
Acidosis effect on vasocontrictors
answer
Catecholamines less potent in setting of metabolic acisosis, so epi, phenylephrine and dopamine will not help Vasopressin and desmopressin work in acidotic enviroemnts however desmopressin tends to decrease BP (V2 selective) whereas vasopressin increases it (nonselective, V1a)
question
Procaineamide
answer
Sodium channel blocker, proloing duration of action potential and repolarization Bradycardia and prolong QT interval - Torsodes A/W lupus like syndrome
question
Hypophosphatemia
answer
Muscle weakness (poor tidal volumes), seizure, confusion, and peripheral neurpathy Increased sensitivity to NMBs
question
Diagnosis - head trauma causing LOC, with lucid period followed by rapid deterioration
answer
Epidrual hematoma - middle meningeal artery injury
question
Spinothalamic pathway
answer
Spinal cord - VPL nuc of thalamus - synapse - posterior limb of internal capsule - postcentral gyrus of the cortex Conveys temp, pain and touch sensation
question
EKG changes in hypercalcemia?
answer
Short QT, prolonged PR
question
Basal ganglia structures
answer
Corpus stratum: caudate, putamen and accumbens
question
Adenosine
answer
AV node blocker Used to stop reentrant circuit AV nodal reentrant tachycardia
question
EKG changes of hypokalemia
answer
Increaed ampltide and width of the P wave Prolongation of PR interval T wave faltening and inversion ST depression Prominant U wave Long QT due to fusion of teh T and U waves
question
EKG changes of hyperkalemia
answer
Peaked Ts Prolonged PR Wide QRS Decrease P wave amplitude/p wave disappearence Short ST V-fib/asystole
question
First treatment for ischemic head injury?
answer
Dexamethasone
question
Antiarryhmic assocaited with Torasades?
answer
Quinidine but procaineamide too
question
Mechanism of parkinsons?
answer
Neuronal depletion in the substantia nigra leads to a decrease in dopamine stores in the striatum
question
Class 3 antiarrhymthmics
answer
Potassium channel blocking class Amiodarone Sotalol Ibutilide Dofetilide Bretylium All lengthen the rate of cardiac depolarization, the APD, and ERP
question
Class 1B antiarrhymtic
answer
Shorten the APD, and the ERP Lidocaine Mexilitiine Tocainide Phenytoin
question
Class 1 A antiarrhymthic
answer
Lengthen the APD adn ERD, OTC A/W Torsades Quinidine Dispyramide Procainamide
question
Class 1 C antiarrhythmic
answer
Decreases rate of phase 0 AP and increase APD Prodyshythmic Metabolized in liver Propafenone, and Flecainide
question
Cerebral steal syndrome
answer
Redistribution of blood from ischemic areas of brain to vasodilated non ischemic areas
question
For each degree Celsius decrease in body temp, by how much will CMR02 be reduced?
answer
6%
question
During hyperventilation how much would you expect blood flow to reduced to brain
answer
CBF changes by 1-2 mL/100g/min per mmHg change in PaC02
question
Carotid Cavernous Fistula
answer
Presents - headache, pulsating exophthalmos, and extraocular nerve palsies Communication between internal jugular with venous outflow and resulting back pressure on the oculomotor, trochlear, and abducens nerves
question
HA prior to LOC, LOC followed by N/V, generalized headache and neck stiffnes
answer
Ruptured cerebral aneurysm
question
Head trauma
answer
Subdural hematoma - rupture of a bridging vein
question
Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis DDX
answer
Sickle cell Pregnacny Nephrotic syndrome Hormone replacement Dehydration Thrombophilia Inflamatory disease Polycthemia Meningitis Direct injury Head/neck procedures Homocystinuria
question
How long can a patient be in deep hypothermic circulatory arrest ?
answer
40 mins
question
Autoregulatory range at which cerebral blood flow is normally kept constant under autoregualtion?
answer
MAP 70-150
question
Where is serotonin release from?
answer
Raphe nuc
question
Where does NE synthesis occur?
answer
Locus coeruleus
question
Cerebral blood flows a/w EEG slowing and Flat EEG?
answer
Slowing - 20 mL/100g/min Flat - 10-12 mL/100g/min Irreversible damage - 6-10 mL/100g/min
question
Volatile agent that best preserved autoregulation?
answer
Sevo
question
How to calculate blood pressure in sitting postion?
answer
multiply the number of centimeters between cuff and external auditory meatus X .74 and then subtract this number from the blood pressure
question
Comparison of CSF components to blood?
answer
Higher - sodium, chloride, mag Lower protein, glucose, calcium, potassium
question
Genetic predisposition to Post operative cognitive dysfunction?
answer
E4 allele
question
Post operative delerium pre op RFs and periop risk factors?
answer
advanced age pre op cognitive impariment etoh abuse hip fracture surgery decreased functional status vison or hearing impariment cognitive imparment BUN:Cr>18 Use of physical restraints >3 medications added 24-48 hours prior to the onset of delerium Periopertive -Greater blood loss, pain, blood transfussions, post op hct<30%
question
Is there a difference between GA and RA in terms of indicidence of post opertive cognitive dysfunction
answer
NO
question
Emergence delerium
answer
Seen during or immediately after emerging Directly correlates with duration of anesthesia Peak incidence is children 2-4 years Frequent assicated with rapid emergence from sevo or des
question
Does on pump vs off pump cabg effect incidence of POCD?
answer
NO
question
Oxygen uptake across the alveolar membrane determined by?
answer
Diffusion capability -surface area of alveolus, thickness of membra,e, pulmonary capilary blood volume (similar to CO) and hemoglobin concentration
question
Mechanism of increasing ventilation
answer
Ventilation determined by CO2, wihch crosses blood brain barrier and alters the pH in the central medually chemorecptors. Thus increase in CO2 results in an increase in minute ventilation
question
Effects of hypercarbia
answer
Increased CBF Splanchnic and hepatic vasocontriction Decreased MAC Compesatory metabolic alkalsois Acidosis decreases th affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen, as decribed by the bohr effect
question
Oxygen consumption formula (Ficks principle)
answer
CO * C(a-v)O2 Ca/v02=hemogobin*1.34*Sa/vO2/100 + Pa/vO2*.003
question
Oxygen delivery formula (D02)
answer
CO * Ca02 (note Ca02 in mL02/dL blood) CO out usually given in liters/minute so you need to converte it to dL/min so times it by 10
question
Adult, and fetal hemoglobin p50
answer
p50 - 27 p50 - 18 (decreased 2,3 DPG)
question
Transient neurologic symptoms
answer
Pain and dysethesia 12 to 24 hours after spinal raidiating to ass Lidocaine A/W outpatient surgery, lithomy, positioning for arthroscopic proceudres Rx. NSAIDS
question
ortho toluidine metabolite of what and what does it cause
answer
Metabolite of prilocaine and can cause methemoglobinemia
question
Why add epi to local anesthetics?
answer
INcrease duration of the block
question
Factors that increase diffusion of across the epidural space?
answer
Larger drug dose Volume Lipid solubilty
question
What determines the spread of spinal?
answer
Dose volume baricity Patient position
question
What determiens duration of a spinal anethetic?
answer
Amoutn of drug adminstered Lipid solubulity
question
Difference between epidural and spinal?
answer
Epidural -slower onset and less predictable -increased volume needed -additional time for LA to cross dura to subarachnoid space Spinal -Faster, more reliable -Less durg is needed but both are dpeendent on dose to ryield optimal results
question
Lipophilic intrathecal opoids
answer
Faster onset Shorter duration Respiratory depressant effects usually occur in the first 2 hours of administration
question
Effect of adding lipophilic fentanyl to LA spinal?
answer
LA anesthetic alone results in N/V Adding fentanyl works synergistcally with LA to block visceral pain stimulating, leading to less intraopertive N/V compared to the same dose of LA alone
question
Bohr effect
answer
Describes the small impact of pH and PaCO2 on the position of the oxyhemoglobin disssociation curve
question
Right shift of oxy hemoglobin curve
answer
Sicke cell thalassemia acidosis (bohr) Hypercarbia (bohr) hyperthermia increased 2,3 DPG volatiles Pregnancy Hypophosphatemia
question
What is 2,3 DPG
answer
Allosteric inhibitor of oxygening binding to hemoglobin Byproduct of anarobic metabolism INcreaed in states of chronic hypoxia
question
Leftward shift of oxy hemoglbin curve
answer
INcreaesd pH Decreased PaCo2 Decreaed 2,3 DPG Hypothermia Fetal MEthemoglobinemia Sulfhemoglobinemia Carboxyhemogobinemia
question
Effect of Oxygen and hyperbaric oxygen therapy on carboxyhemoglobin levels
answer
Therapy with Fi02 1 decreases the half life of CO-Hb from 4-6 hours to 1 hour Hyperbaric oxygen therapy with Fi02 1 at 3 ATM redusced the T1/2 to 15 - 30 mins
question
Predicting post operative complication in lung resection
answer
VO2 max - 6 minute walk test of 2000 ft or 612 meters is equivlant of V02 max of 15 mL/kg/min and predicts low post operative risk VO2 max best predictor in patients with normal lung parenchma e.g no COPD while the DLco better predictor in pateints with lung disease
question
How much pressure is needed to expand atelectatic lung?
answer
40 cmH20
question
Hypoxic ventilatory response
answer
Type 1 glomus cells of carotid body sense partial pressure of Pa02 slight below 100 but substantial increase in ventilaton does noto occur until Pa02 falls below 70 mmHg. Ventilatory response does not maxmize until Pa02 falls below 60
question
Location of generation vs rhythm of respiration
answer
Generation - medualla - dorsal respiratory group Modulation of respiratroy rhythem - Pons via apneutic center and pnumotaxic center
question
How does pKa effect LA
answer
Onset of action for local anesthetics determied by pKa Lower the pKA, the fasater the onset Exception chlorprocaine with pKa of 9.1 can give greater concentration
question
Differenec between ester and amide anesthetics?
answer
Ester local anesthics - hydrolyis via pseudochoinesterase Amide - hepatic metabolism via p450
question
EMLA
answer
2.5% lidocaine and 2.5 % prilocaine Effective in penitrating skin Requires dosing 30-60 minutes prior to procedure
question
RFs for local anesthetic toxicity from amides
answer
Very young or old Cardiac disease Hepatic dyyfucntion
question
ECG cahnges associated with inravenous injection to test dose
answer
increaed amplitude of t waves on ecg increased or a decreased heart rate increased blood pressure
question
PABA
answer
Para aminobenzoic acid Allergic reactions Metabolite of preservitive methylparaben
question
Bupivicaine cardiac toxicty RX
answer
bolus 1.5 mL/kg of intralipid
question
Cauda equina syndrome
answer
Caused by lidocaine toxicty Order an MRI Sx inculude bowel and bladder incontience and perineal sesory loss (Note no sensory changes or incontenence in TNS)
question
Inflamation effects on LA
answer
Inflamation leads to acidosis, or decreased pH which lowers the unionized fraction of LA and creates unfavorable absorption because only the unionized lipophilic portion of the drug is able to penitrate
question
Haldane effect
answer
Decribes the fact that the oxygenation state of hemoglobin affects the positon and slope of CO2 reposne cruve Deoxyhemoglobin better able to bind CO2 and H+ facilitating greater CO2 clearence from tissues When 100% of hemoglobin exits as doxyhemoglobin the blood conceration of CO2 (y axis) is high for a give pCO2, as proportion of oxyhemoglobin increased, the total blood carbon dioxide concenrtaiton dorps
question
Dynamic lung volumes and capacities
answer
TV Inspiratory reserve volume Expiratory reserve volume Inspiratory capacity Vital capacity
question
How can dynamic lung volumes and capcities be measured?
answer
Simple spirometry
question
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis managment
answer
Smooth muscle proliferation lungs casue sever obstructive pattern After initation of ventilaton patients become high risk for auto peep (refractory hypotension 2/2 decreased venous return) Disconect patient from vent Vent stratagies - slow RR, prolonged I:E ratio HIgh risk for pneumothorax
question
Reduction in FRC
answer
Changing from standing to supine (30-40%) Sitting Induction of general anestheisa (20%) Lower abdominal surgery (30%)
question
Afferent branch of aortic body chemorecptors
answer
Vagus nerve
question
Afferent branches of lung mechanorecptors and activaiton?
answer
Vagus and spinal nerves Activation of these recptors occurs via maximal inspiration, irritant stimuli (secretions, gastric contents, and foregin bodies) Resulting in cough
question
Complication of bilateral carotid endarterectomies
answer
Patient loose the carotid body chemorecptors, and hypoxemia does not generate increase in ventilation Hypercapneic ventilatory drive also blunted
question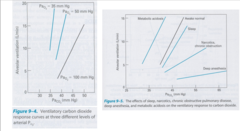
CO2 response curve

answer
Opoids - shift curve to the right (slope may change at high dose) Benzos/Roc - decrease slope (lessen response) wihtout affect the intercept or apenic threshold Propofol: decreases the slope of ventilaatory response curve Hypoxemia: at less than 65 mmHg pa02, the CO2 response curve is left shifted Volatiels: decrease the response (slow and right shift) to CO2 (although low doses - .1 MAC controversal)
question
LA that cause methemoglobinemia
answer
Prilocaine Benzocaine
question
Channels in the heart affected by local anesthetics?
answer
sodium, potassium, and calcium affecting depolarization, repolarization and contractility
question
Assesory muscle of breathing
answer
Scalene, sternocledomastoid, alae nasi
question
How much does 1 mmHGg increase in CO2 increase minute ventilatoon?
answer
2-3 liters/min/mmHg
question
Sequence of LA absorption from fastest to slowest
answer
IV>Tracheal>intercostal>caudal>paracervical>epidural>brachial>sciatic>SQ
question
Bupivicaine cardio toxicity risk factors
answer
Pregnant patients - due to effects of progesterone on myocardium Hypoxemia Respiratory acidosis Hyperkalemia
question
Inferior tip of scapula?
answer
T7
question
Postive test dose?
answer
INtraosseous or intravasucalr injecction positve when there is increase in heart rate of more than 15 beats per minute and increase in T wave amplitude of 25%
question
Superior aspect of illiac crest corrosposponds to waht level?
answer
L4-L5
question
Dural sac extends to what level in new borns?
answer
S3 -4 by 1 year of age its S1-S2 spinal ends at L1 by one year of age
question
Nipple line corrosponds to what level?
answer
T4
question
5th finger corresponds to what level?
answer
C8
question
DDx of SOB after spinal?
answer
Diaphgramatic weakness - C3-C5 Intercostal nerve - T1-T12 - all of these nerve typically affected in spinal for c - section
question
Anestheitc concern in RA patients
answer
Periopertive cervical flexion extension radigraphs should be obtained in RA pateints with limted neck movement and neuro symptoms On lateral flexion view, a distance >3 mm from the anterior arch of the atlas to the odontoid process indicates atlantoaxial subluxation Aneiro subluxation of C1 to C2 most common form of sublaxation and may occur in 40% of RA patients
question
CI to neuraxial blockade?
answer
Tethered cord syndrome
question
Epidural hematoma assocaited with rupture of what structure
answer
Middle menigeal arter Briding veins = sub dural hematoma
question
Structures transversed in midline epidural placement?
answer
SKin, supraspinous, interspinous, ligamentum flavm Ligamentum flavum you hear a "pop"
question
Subarachnoid space
answer
Filled with CSF Continous space with brain Bounded by pia matter and the arachnoid matter
question
Timming of epidural abscess after spinal?
answer
2 to 3 days More common if catheter has been in place for 3-5 days Epidraul hematomas usually occur within hours of cathiter placement or removal
question
Meralgia paraesthetica
answer
Mononeuropathy of the lateral femoral cutanous nerve presseting with loss of senation limited to the aterolateral thigh
question
Speed of onset of LA
answer
Determined by how many molecules are in the non ionized form LA with pKa closest to physiologic pH 7.4 have molecules in the non ionized form verse LA with high pKa
question
Duration of LA
answer
Dependent on the amount of protein binding
question
Structures transversed during paramedian approach epidural
answer
SKin, superficial and deep fascia, paraspinous msucles and ligamentum flavum
question
Layer of menignes repsponse for most of the resistance to durg movement from epdural space to the intrathecal space?
answer
Arachnoid matter 2/2 tight junctions
question
Ebtifibatide
answer
Glycoprotein 2 B/3 A inhibiotor REgional techniques avoided for 8 days
question
Monitor heparin?
answer
PTT
question
Warfarin interfesres with the snytehsis of waht factors?
answer
2, 7, 9, 10 and Protein C, S
question
How long to wait for neuraxial injection after clopidogrel and ticlopidine?
answer
Cloidogrel 7 days Ticlopidine 10 to 14 days
question
How does midazolam exert its effects?
answer
Water solbule durg that is converted into a lipid soluble form on exposure to the bloods pH, which can readly cross BBB and exert its effects
question
How much shoudl the most common test dose increase heart rate?
answer
MC test done 3 mL of 1.5 % Lido containg 5 mcg/mL epi (1:200,000) typically raises heart rate 20-30 beats/minute
question
What does a 1:200,000 epi mixture mean?
answer
1:200,000 - 1000 mg/200,000cc 1g=1000 mg=1,000,000 micrograms
question
Which needle types are most likely to laed to PDPH?
answer
Cutting needles (quinke) have higher incidence of PDPH than pencit point needles Also larger bore needles (smaller gauge) will increase PDPH
question
Risk factors for post dural puncture headache?
answer
Smaller guage and cutting needles (quinke) Younger age Female Pregnancy
question
Cardaic accelerator fibers?
answer
T2-T4
question
How long should you wait to perform a spinal for patients on lovanox?
answer
Full dose - 24 hours Prophylactic - 12 hours
question
Spinal epidural space
answer
Extends from the foramen magnum to sacral hiatus
question
Most significant factors that affect spread of LA in epdural space?
answer
Level of injection and volume/dose of LA Baricty of LA more significant with spinal anesthesia
question
Absolute contraindication to epidural ?
answer
Infection at enry site
question
Final anatomic sturcutre traversed by the needle prior to entering the caudal epidural space?
answer
Sacrococcygeal membrane
question
1ml/kg volume of LA will provide reliable sensory block up to what level if injected in the caudal space?
answer
T10
question
Stucture not covered during caudal block?
answer
Manipulation of teh testicle will pull on the upper peritoneal fibers not covered by the T10 level of caudal block
question
CI to caudal block
answer
Septicemia
question
Most sensitve sighn of intravascular injection of LA
answer
Peaked T waves
question
At this gestational age there is minimal risk for teratogencity but peak risk for fetal loss during anesthesia and surgery?
answer
Surgery during the first 2 weeks of gestation may increase change of fetal loss Mild cellur damage is generally fully recoverable during the first 2 weeks without teraogency By third trimester, the risk of preterm labor is increased
question
Heart other other vital organs deveop within which period making them susceptible to structural defects
answer
3-9 weeks
question
Predicts pulmonary complications during thoracotomy?
answer
PpoFEV1% = preoper FEV1% * (1-% functional lung tissue removed/100) if >40% low risk If <30% high risk for pulmonary complications
question
Times after smoking
answer
12-24 hr - decrease carboxyhemoglobin, right shift of hemoglobin dissociation curve 1-2 weeks - decreased sputum 12 weeks - improvement in small airway function
question
Muscle relaxants a/w histamine release?
answer
Atracurium and mivacurium
question
A/w skeletal abnormalities during first trimester?
answer
N20
question
During what trimester is a fetus at highest risk for dead associated with anesthesia and surgery?
answer
1st trimester
question
Maximal volatile concenetration allowablle?
answer
Alone - 2 ppm Volatile + N20 = 0.5 ppm
question
Or personell exposure to volatiles puts patietn at risk for stucturel abnormaliees in fetus - True or false
answer
No data has proven increaed risk to fetus from personnel expsoed chronically to trace anestheitc agents However association have been made with spontaneous abortion
question
Hoarse voice after intubation associated with wht neve?
answer
Unilateral vocal cord paralysis - pasly prevents abduction of ispilateral cord thus it becomes stuck in the adduction positon
question
Lingual nerve pasly
answer
Tongue numbness due to compression with oral airway, laryngeal mask or intubation Brnch of trigeminal V3 Somatic snsation to anetior 2/3 of tongue and gingiva along the lingual side of the mandibular teeth
question
Ischmeic optic neuopathy
answer
Number one diagnosis for non periopertive acute visual loss in pateints over the age of 50 Arteritic form - temporal arteritis, involing the anterior portion of optic nerve Rx. steroids
question
Posterior ischemic optic neuropathy
answer
Most common cause of POVL in spinal surgeries, more common when spinal fusion or instrumentation is involved Imeddiate post bilateral vision loss Fundo exam: optic disc pallor over weeks to months
question
Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy
answer
Most commonly reported after CABG, but also associated with bilateral neck, spine orthopedic procudres Vison loss dealyed up to one week post op Fundo: optic disc edema and pallor Afferent pupilalry defect
question
Common perionail nerve injury
answer
Lithotomy postion impared ankle dorsiflexion or foot drop
question
Ulnar nerve injury
answer
Most common peripheral neuropthy in supine patient Men>women, thinner Weakness of lumbrical in 4th, 5th digits with loss of flexion at MCP join and loss of extension at the IP joints, or "claw hand"
question
Conduction
answer
Transfer of heat betwen two adjacent srufaces
question
Convection
answer
Transfer of heat via air currents
question
Mechanism of negative pressure pulmonary edema?
answer
Negative intrahtoracic pressure 50 to 100 cmH20 rsults in sudden increase in venous return of blood to heart, which increase preload and an increase in both end diastolic and end systolic ventricular volumes
question
Patient biting down on tube, what dose of succ to give?
answer
0.1-0.2 mg/kg
question
Mechanisms for development of increase interstial lung fluid?
answer
Increased hydrostaric pressure in pulm cap bed Decreased interstitial space pressure Decreased osmotic pressure of plasma Increased permiability of membrane Decreased return of fluid to the circulation via lympathic
question
Particulate antaacids
answer
Sodium bicarbonate Magnesium hydroxide Calcium carbonate Aluminnim hydoxide
question
Non particulate antiacids
answer
Sodium citrate Sodium citrate + citric acid Sodium citrate + citric acid + potassium citrate
question
Pink frothy sputum diagnositic for waht?
answer
Negative pressure pulmonary edema
question
How long to avoid nitrous oxide following intravitreal injection of a gas bubble (ie Sulfur hexafluoride)?
answer
10days
question
Cotton wool exudates on the retina
answer
Retinal bleeding that orginates from the arterial circulation is often assicated with head trauma other event - severe chest or abdominal truama, acute pancreatitis, fat or amnotic fluid embolus
question
RF's for posterior iscemic optic neuropathy?
answer
Most common cause of post op visual loss Most commonly a/w spinal fusion procedures in prone position Other RFs - hemodilation, large volume of crystaloid, hypotension, prolonged surgical time, vasocontriction or pressure support, male, EBL;1000 mL, facial edema Patients typically report visual symptoms within 24 hours, most often while still in recovery room Fundo exam reveals - normal appearing optic disc, that begin to look pale over weeks to months Leshion: Retrobulbar portion of optic nerve
question
Normal optic disc and intact pupilary reflex?
answer
Cortical blindness note pupilary light reflex normaly absent in AION, PION, Central retinal artery occlusion
question
RF's for ION?
answer
Spinal fushion Male Obesity Wilson fram Longer anesthetic duration - This is by far the most significant factor and surgergy with >6 hours as an apparent inflection point Greater EBL Lowe amonts of colloid anministration Recomendations: Avoidi wilson head frame If using prone position put reverse t berg Staging long complex procedures
question
Nuropathy from retractor injury druing open abominal hysterectomy?
answer
Lumbar pleux or proximal femoral nerve resulting in loss of leg extension
question
Neuropathies: neuropraxia, axonotmesis, neurotmesis
answer
Neuropraxia -No disruption of anatomical nerual elements -Resolved in a few weeks Axonotmesis -Axons are disrupted, but nerve sheats remain intact -Wallerian degeneration, but axon regeneration results in recovery of funtion over weeks to months Neurotmesis -trasection of axons and myelin sheats -prevents regeneration and recovery
question
Most common periop neuropathies?
answer
Ulnar 25% Brachial plexus 19%
question
Weak leg abduction
answer
Obturator
question
Loss of sensation over the anterolateral thigh?
answer
Meralgia paresthetica - injury to lateral femoral cutanous nerve MOst common neuropathy related to child birth
question
Volume and pH necessary for developement of aspiration PNA?
answer
Gastric volume >0.3 mL per kg of body weight (20-25 mL adults) with a pH<2.5
question
Concentration effect
answer
Comprises concentrating effect and augmented tracheal inflow Desribes teh effect that a high concentration of N20 has on its own uptake and is independent of the other gases that are administered
question
Second gas effect
answer
requires borht nitrous oxide and a volatile agent
question
Which nail polish has greatest effect on accuracy of pulse ox?
answer
Blue nail polish -similar absorbance as deoxygenated hemoglobin - near 660
question
Augmented tracheal inflow
answer
Component of the concentration effect that involves gas from more proximal areas of the airway and lung replacing the alveolar gas that has rapidly diffused across the alveolar memebarane Requires a high FiN20 and the abiity to augment tidal volume Becasue volume control ventilation delivers fixed tidal volume prevents augmenation of tracheal inflow, note airway obstruction would have the same effect
question
Dry skin indiactor of what
answer
Indicatior of prolonged or severe hyperthermia Sweating decreases to conserve body fluids
question
Wavelength of light used in pulse ox?
answer
660 nm (red) 940 nm (infared)
question
Consequences of intraoperative hypothermia..
answer
Post op myocardial ishcemia wouund infection Impared coagulation Decreased drug metabolism
question
What increases partial pressure of agent?
answer
Increased input to the alveoli -Inspired anesthetic partial pressure -minute ventilation -Inspired gas flow Decreased uptake from the alveoli -Solubility -CO -Alveolar to venous partial pressure difference
question
Effect of right to left intracardiac shunt on N2O
answer
Decrease uptake of N20 Note a left to right shunt would have minimal effect
question
Vapor pressure is a function of...
answer
Temperaure VP increases in a non linear fashion as temperature incresaes
question
Safety features on modern anesthesia vaporizer
answer
Agent specifc keyed filling ports that prevent fill its rervoir using a bottle keyed for a different agent Low filling port with a fill line to provide a visual indicator and prevent overfilling INterlocks that prevent administration of more than one volatile at a time Cocentration dial taht increases out when rotated counter clockwise
question
VP of des
answer
681 - high est of all voaltiles
question
Filling a vaporizers calibrated for an agent with lower VP with one with a higher VP results?
answer
Patients higher than the amount being deliverd VP sevo - 157 VP hal - 243
question
How mcuh oxygen flow into the vaporizing chamber calculation
answer
Basically use the splitting ratio: e.g 12:1 Divide the fresh gas flow by 13 this nymber is the amount of fresh gas flow that flows into the vaporizer
question
What do the number on the dial of a vaporizer represent?
answer
Indicates volume precent, which is partial pressure of anesthetic vapor, as a percentage of total ambient pressure, calculated at sea level Vol % = (partial pressure due to vapor/total ambient pressure) * 100%
question
Relative humidity
answer
Partial pressure of water vapor in the air divided by the partial pressure of the water vapor when the air is saturated with water vapor at the same temperature, expressed as a percentage RH=Pwater/Psasturated water
question
Contraindications to N20 use?
answer
Pnumothorax INtravitreal gas injection Typnaoplasty Open crani as it could increase volume of gas embolus Acute intestinal obstruction
question
What increases when a variable bypass vaporizer, calibrated at sea level, experiences a decrease in barometric pressure (increase in altitude)?
answer
Partial pressre of anesthetic in the vaporzing chamber is unaffected by change in ambient pressure to the output in clincal temrs (MAC units of partial pressure) remains constant THe vaprizer output in % increases with decrease in barometric pressure
question
Critical temperature
answer
Temp above which a gas cannot be liquefied no matter how much pressure is applied
question
Ideal gas law
answer
One mole of an ideal gas will ocupy 22.4 liters at standard temp (273.15 K or o C) and pressure 101.325 PV=nRT
question
Daltons Law
answer
Mixture of gases in a volume, each gas exerts the partial pressure in the mixture that it would exert if it occupied the volume alone
question
Albumin
answer
Increased risk of mortality in patients with TBI
question
Cryoprecipitate
answer
Contains F8, vWF, fibrinogen Check fibrinogen level before replacement
question
Hetastarch
answer
Associated with acute renal failure Coagulopathy at larage doses
question
Platlets
answer
Stored at room temp which increases risk of bacterial infection
question
Symptoms of citrate intoxication?
answer
Hypotension Narrow pulse presure Increased intraventricular end diastolic pressure Lengthening of the QTc interval
question
Which stage of liver transpalnt are patients most susecptible to citrate intoxication?
answer
Anhepatic phase - portal vein cross clamped and patient unable to metabolize citrate from transfused blood products
question
Universal recipient blood type?
answer
AB postive - becasuse all antigens are present they do not make any antibodies
question
Blood Cold Chain to RBCs
answer
After fractionation, RBCs sotred between 2-6 C and 2-10 C for transportation until the point of use The 30 minute rulel states that RBC units should not be kept outside this temperature range for any period exceeding 30 minutes RBCs may travel back to blood bank in approved container capable of maintiang temps of 2 -10 C for up to 24 hours
question
Blood cold chain
answer
Specifies appropriate storage conditions for all blood components dervied from human volunteers from the time of harvest until the point of use - applied to all blood derived components, regardless of optimal temp and storage conditions This includes -Platlets - stored at 20-24 C Albumin -Whole blood/RBCs - Refridgerated @ 2-6 degrees -Cryopercipitate/FFP - frozen at temp below -20 C Recominant factors are not regualted under the blood cold chain e.g rF7
question
Monitors capable of measuring oxygen?
answer
Mass specctrometry Ramen Spectrometry
question
Bivalirudin
answer
Direct thrombin inhibitor Substitute for heparin in patients with heparin allergy orheparin induced thrombocytopenia
question
What is the only paramagnetic gas used in anestheisa?
answer
Oxygen -
question
Electrolyte abnomralities assoicated with transfusion?
answer
Potassium increase Hypocalcemia Hypomagnesium Sodium unaffected
question
What temperature should platlets be sotred at?
answer
Sotred at room temp 20-24 C,
question
Infared spectrometers detect what gases?
answer
CO2, N20, and volatiles They cannot measure symetic molecules ie 02, N2
question
Albuterol effect on monitoring volatile anesthetic agents?
answer
Albuterol contains halogenated propellants that absorb infared light in the range of volatile anesthetics. After treating with bronchodialtor, the machine may alrm "mixed agents" and show halothane as a detected gas
question
Lethal triad of trauma patients?
answer
Hypotension, Hypothermia, and acidosis
question
RBC changes with storage?
answer
Decreased 2,3 DPG Cells become more spherical with surface projections (spheroechinocytosis) Increased K outside of cells and increase Na within cells
question
Methods that can be used to measure volatiles?
answer
Infrared Piezoelectric Refractometry
question
Abnormalies that contribute most importantly to coagulopathy during massive transfusion?
answer
Dilution thrombocytopenia and hypofibrinogenemia
question
Platelet storage leshion
answer
When platlets are cooled their surface proteins change that trigger the rapid elimination from circulation by hepatic macropahges
question
What is leading cause of death related to transfusion?
answer
TRALI
question
Transfusion filters?
answer
170 micrometer - leukoreduced blood 40 mm - cell saver, massive transfuion
question
Adverse effects of sodium bicarbonate
answer
Hyperosmolarity Paradoxical CSF acdiosis Hyernatremia Hypercarbia
question
When is dextran indicated?
answer
a/w strong anticoagulant properties and would not be indicated in most operations It may sometimes be indicated in vascular or plastic surgeries where improving perfusion and avoiding thrombosis is desirable such as a musclar free flap
question
Diagnostic criteria for TRALI
answer
ALI -acute onset -hypoxemia Pa02/Fi02<300 -Bilaeral opacities -No left atrail hypertension PAOP <18 + the following: -Onset of signs <6 hours after administration -ALI not present before transfusion -NO temporal relationship to an alternative risk factor for ALI
question
Bronchial aspirate findings in TRALI
answer
Increased permiablitly of pulmonary capillaries results in exudative pulmonary edema Asspirate would contain: -High protein -High specific gravity >1.020 -Pleural fluid protein/serum protein >0.5 -Pleural fluid LDH/serum LDH>0.6
question
Mechanism of urticarial reaction following blood transfuion
answer
Reaction to donor plasma proteins
question
Mechanism of febrile hemolytic reaction?
answer
Reaction to donor leukocytes
question
What has been shown to reduce incidence of TRALI?
answer
Avoidng blood products from multiparous women and using male dominat plasma pool
question
RFs for TACO
answer
extremes of age CHF Renal impairment Hypoalbumin Fluid overload
question
Mechanism febrile non hemolytic transfusion reactions?
answer
Result cytokines and intracelluar contents released by donor leukocytes Reaction minimized with leiukoreduced blood
question
Type of pulmonary edema seen in TACO?
answer
Transudative pulmonary edema
question
When are irradiated RBCs useful?
answer
Preventing graft vs host disease
question
What is the first sign of ABO incompatibility in anestheized patient?
answer
Hemoglobinuria followed by hypotension and DIC
question
What inteventions have shown no use in TRALI?
answer
Diuretics, antibiotics, and steroids Note maintaing oxygenation (intubation) and pressor support only things that help
question
Treatment of TACO?
answer
Mild (cough, dypnea) - stop transfusion, supplemental O2 Severe (cyanosis, frothy fluid in ETT) - diuretic
question
Purpose of irradiating blood products to prevent graft vs host disease
answer
Irradiating blood renders T-cells incapable of repilicating and attacking host
question
What is the second most common cause of mortality realted to blood transfuison?
answer
TACO
question
What increases risk of graft vs host disease?
answer
Transfusion of RBCs from first or second degree relatives because they share HLA haplotypes, the recipients immune system cannot recognize and destory the donor T cells that can cause GVHD
question
What differentiates a dealyed hemolytic transfusion reaction from an immediate one?
answer
DIC does not occur in delayed type
question
RFs for TRALI
answer
Sepsis Liver Disease ETOH abuse Mechanical ventialtion
question
Pathophysiology of TRALI
answer
MOst cases due to antibodies from donor May require two hit immune mechanism Final common path involves neutrophil activation, endothelial injury, and capilalary leak May require pressure support
question
heterophil antibody negative, and prsents with enalrged lymph nodes in neck
answer
CMV
question
What carries highest risk of transfusion transmitted infection?
answer
Hep B 1:205,000
question
1:2,135,000
answer
HIV risk in blood
question
1:2,993,000
answer
Risk of HTLV 2 in blood
question
1:1,935,00
answer
Risk of hep c in blood
question
What is not tested for in blood?
answer
Hep A
question
Bacterial infections associated with blood products stored at room temp vs frozen
answer
Platlets stored at room temp have high risk of gram + infection e.g staph, and bacillus RBCs stored at 4 C increases liklihood of contamination with gram - bacteria such as Yersinia and psudomonas
question
What disqualifies a person from donating blood prodcut?
answer
One year band on donors who recenetly traveled to malaria edemeic countries Men who have had sex with men in the last year Sex with prostiute or injected drugs in last year
question
Massive transfusion definition?
answer
Replacement of a patients blood total blood volume -Greater than 10 units of PRBCs over a 24 hour period or Replacment of half a patients blodo volume within 3-4 hours -Greater than 4 units of PRBCs in 1 hour with a foreseeable ongoing need
question
Hyperkalmeic arrest
answer
In setting of massive transfuion and rapid infsuion rates, hyperkalemia can cause wide complex tachycardia potassium level in a unit of PRBCs - 77 meq/L and infusion rates of 100-150 mL/min can cause hyperkalemic arrest
question
Symptoms of citrate toxicty
answer
Tetany (lower calcium) Prolonged QT Decreased myocardial contracitliy Hypotesnion (Lower SVR) Narrow pulse pressure Eleavated CVP Pulseless electrical activity Ventricular fibrilation
question
What treatment is a JW most likely to accept in the circumstance of large blood loss?
answer
Intraoperative autotransfusion
question
Universal donor and recipient of blood?
answer
Donor: O negative Recipient: AB
question
Universal donor and recipeint for plasma?
answer
Type 0 patients can receive any type of plasma, because their RBCs lack antigen to attack either A or B antibodies AB type patients, as in this case shoudl only receive AB plasma
question
Monitoring heparin
answer
Low dose - pTT High dose - ACT
question
Anticoagulants to avoid in patients with renal disease?
answer
Dabigatran Rivaroxaban LMWH
question
Treatment of HIT
answer
Parenteral anti 10 a agents -Fondaparinux Parenteral Direct Thrombin inhibitors -Lepirudin -Argatroban -Bivalirudin
question
LMWH briding dose for pateint taking warfarin?
answer
D/C warfarin 5 days before procedure Start LMWH 1.5 mg/kg s.c. qd or 1 mg s.c. bid Therapeutic doses should be stopped 24 hours prior to neuraxial procedure and normal INR should be documented prior to neuraxial block
question
Drugs that decrease warfarin effect?
answer
barbiturates carbamazepine cholestyramine nafcillin phenobarbital phenytoin rifampin
question
Drugs that increase warfarin effect
answer
Levofloxacin Omeprazole Amidoarone
question
How long does it take for dabigitran to clear your system and coagulation normalize?
answer
Dabigatran should be stopped 1-2 days before surgery for CrCL>50 mL/min and 3-5 days before surgery for CrCl<50 mL/min
question
Natural course of HIT
answer
Antibody disappears over time, usally within 3-6 months Upon re exposure to heparin it reappears typically within 1-3 days There should be a 12 -24 hours period in which its safe to use unfractionated heparin
question
How long does intramuscular vitamin K take to nomralize INR
answer
12-24 hours no appropraite for emergent reversal of warfarin
question
Side effect of protamine?
answer
IgG or complement driven reaction resulting in severe pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular failure MOre common in patietns with fish allergy, previous vasectomy, or prior exposure to protamine or NPH insulin
question
Drugs most likely to cause fevers and anaphylaxis?
answer
Monocloncal antibodes and globulin prodcuts
question
What drug increases immunosuppresent levels and results in additive QT prlongation?
answer
Amiodarone
question
Gentamicin effect on immunosuppresnts?
answer
INcreases risk of nephrtoxicity
question
Amphotericin effect on immunosuppresnats
answer
Increases risk of nephrotoxicity
question
Rifampin effect on tacrolimus?
answer
decreases concentration
question
Effect of levofloxacin on immusppresants?
answer
Increases concentration
question
Side effect from adding tacrolimus to voriconazole or fluconazole?
answer
QTc prolongation
question
Effect of cyclosporin on benzo levels?
answer
Casues moderate increase in benzo concentration
question
Effect on immunosuppresent levels BBs CCB Amidarone DIgoxin
answer
BBs- no signficnat interactions CCB - increase concentration Amiodarone - increase immunosuppresnt concentrations and worsen QT Dogoxin - involved in the p glycoprotein pathway and can have interactions
question
Stimulus for vasopressin release?
answer
Released from posterior pituitary when the hypothalamus senses hyper osmolality (not hypo osmolality) or the carotid or aortic baroreceptors are not stimulated (as in hypotension)
question
Water compartments in body (%)
answer
TBW 60% of total body weight Intravascular 5 Intracellar 60 Interstitial 35
question
Rivaroxiban
answer
Oral factor 10 a inhibitor
question
Bivalirudin
answer
Direct thrombin inhibitor
question
Unfractionated heparin
answer
Indirectly inhibits factos 2 a (thrombin) and 10 a' Reuires antithrombin as cofactor
question
WIth decreasing temperature, gas solubility?
answer
Increase
question
With increasing temperature, pH...
answer
Decreases
question
A hypothermic pateints blood gas is heated to 37 C. The PCO2.... in the same sample when compared to the patients much colder blood?
answer
Increases
question
Combitube
answer
2 lumen decidce that contains latex used to secure airwawy in patints with facial trauma or vomitting
question
Rusch Easy tube
answer
Similar to combitube but contains no latex
question
Gag relfex
answer
Glossopharygneal
question
Must be anestized to provide tracheostomy?
answer
Recurrent laryngeal nerve
question
Touch sensation to anterior 2/3 tongue
answer
CN V - trigeminal
question
Benzocaine
answer
Methemoglobinemia
question
How mcuh does pH change for every degree C chnage?
answer
pH will change by 0.015 E.g Patients with ABG measures pH of 7.33 at temp of 37. What would the temperature corrected PH be if the patietns bladder temp is 20? pH will be higher as the patient cools and lower as the patient warms up 7.33 + (37-32)(0.015) =7.585
question
How much does bicarbonate rise for an acute respiratory acidosis?
answer
Bicarb rises 1 mEq/L for every 10 mmHg rise in pC02
question
You are cooling patient down to 17 C . You are following pH stat strategy. Th blood gas is 7.20. What do you do?
answer
First solve for corrected pH -Cooling patient down, so pH is gonna be increased... -7.20 + (37-17)(0.015)=7.5 Pt is alkalotic according to pH stat managment which strives to keep pateints pH at 7.4 There you would adise perfusionist to increase the patients C)2
question
Clark electrode
answer
Used to measure Oxygen - note falsly low 02 may result from build up of protein on semipermable membrae
question
How does laryngeal tube differ from combitube?
answer
Basically the same thing but LT does not contain latex
question
How does clark exlectrode work?
answer
Oxygen diffuses across the membrane, and undergo reduction at the cathode. The voltage difference betwewen the cathode and anode is directly proptional to the amount of oxygen in the same
question
What happens when yoy manage patient with pH stat?
answer
Increases cerebral blood flow
question
Total bicarbonate deficit
answer
base deficit * 0.3 * bodyweight (kg)+ deficit in meq
question
Which nerve affected if patient has low pitch voice?
answer
Sup Larygenal Nerve - external branh resposible for producting high pitch phonation
question
Acute respiratory compensation for metabolic acdisois?
answer
PaCO2 = 1.5 (HCO3) + 8
question
INferior boarder of scapula
answer
T7
question
Ach binding to 1. nicotinic and 2 msucarinic receptors result in what?
answer
1. sodium channels opening 2. Activation of G protein
question
Dermatomes needed to be covered for lower abdominal surgery e.g insciion from umbilcus to pubus?
answer
Sensory block extending cephlatad to T6-T8
question
Common legnth of gudie wire of retrograde wire intubation?
answer
100 cm
question
Cause of urinary retention during spinal?
answer
Inhibition of sacaral parasympathetic outflow
question
M2 receptor
answer
Located in heart - slows heart down
question
M1 receptor
answer
exocrine galnds and CNS
question
M3 receptor
answer
smooth muscles of the blood, as well as the lungs M3 receptors are G coupled and mediates increases in intracellar calcium resulting in contraction of smooth muscle such as bronchocontriction however withrespect to vasculature, M3 activation on vascular cells increases NO resulting in vasodilation
question
M4
answer
CNS, inhibition
question
CI to cricothyroidectomy
answer
Patients less than 5 years old due to larnygeal collapse
question
dermatome needed for c section
answer
T4 - nipples
question
A. of Adam kiewicz
answer
T8-L1
question
Oculocardiac reflex
answer
AFrrent - CN V, X Efferent - CN X
question
In supine spinal where would you expect densest block to be achieved?
answer
T5-T7 - most dependent area
question
What intervatioes small intestines and and trnsverse colon
answer
vagus nerve
question
What inetervates decending colon, sigmoid, and rectum
answer
Sacral portion S2-S4
question
Contraindaciton to jet ventilation
answer
Upper aireway obstruction - barotrauma
question
Cook exchange cathiters
answer
Usufel for bridege to extubation esepcially if known difficlut airway
question
Escherman vs Frova introducers
answer
Scenario may present a patient with tiny portion of aretnoids showing and needs intubation -Eschmann and Frova introducers coudl both be used in this situiation becasue they have angualted tips diesinged to hook uner epiglotis in Grade 3 or worse views -However Eschemann is lower cost and but cannot not deliver oxygen so in the scenario that you dotn need to deliver oxyggen this is the better option+ its more widely available
question
Arndt airway exchange catheter
answer
placed through an LMA using fiberoptic scope using gudie wire to exchamge LMA for ETT
question
Parasmypathiic nervous syem orgin?
answer
Cell bodies orignate form cranil nerves 3, 7, and 10 of the midbrain and medulla Sacral fibers orinate from the 2, 3, and 4th sacral semgement
question
SSEPS monitor?
answer
dorsla column function
question
MEPs meaure what pathwyay?
answer
lateral corticospinal tract and and anterior corticospinal tract
question
Where does the sympathetic NS originate from?
answer
T1-L2
question
Effect of volatiles, narcoitics, NO, and ketamine on SSEPS
answer
Volatiels - attenuation N20 - decreases amplitude IV agents/narcotics - incnrease latency, decrease amplitude Etomidate - increase latecny, increase amplitude Ketamine prodcues increase in amplitdue but no effect on latency
question
MEPS indication of what blood suppy?
answer
anterior spinal artery
question
Stellate ganglion comprsied of what structures?
answer
inferior cervical and first thoracic ganglion LOcated at the level of the 7th cervical vertebrae, anetior to the transverse process of C7
question
Most important sign of sucessful stellate ganglion block?
answer
2 degree temeprature increase in affected limb 2/2 to sympathetic block aide and vavsodilation Horners - side effect of stellate gagnlion block but does not confirm it
question
What neruo monitoring is most suseptible to volatiles?
answer
MEP BAEPs are the most insenstive agents and SSEPs are intermediate
question
When inducting patient with pheo what agents shoudl typically be avoided?
answer
Drugs casuing histamine realease (morphine) or increased catecholamines e.g ketamine, pancuronium
question
Explain increased temperature in upper extremity after stellate ganglion block but no decrease in pain
answer
Nerve of Kuntz -interostal nerve carrying sympathetic innervation to upper extremity that bypasses stellagte gangion -Location T1-T4
question
Procedures EMG is useful for monitoring nerve roots?
answer
urethral and rectal sphinters during a relase of tethered cord Identifying cortical bone breeches during pedicle screw placement and monitoring nerve root function anterior cerivcal disectomy and fushsion
question
Autonomic hyperrlexia
answer
Stimulation below level of leasion results in unopposed vasocontrisction below the level of the leashion - occurs becasue there is loss decending inhibition in th espinal cord THe carotid sinus senses this elevation in pressure and triggers vasodilation above the leshion
question
Wind up
answer
sensitizatioon of second order neurons where repeated high intesnistiy nociceptive inputs leads to a cellular such that the neruons become more easily activated
question
First site of nocicpetive sensory processing occurs?
answer
Second order neruons in nociceptive pathways are located in the doral horn of the spinal cord
question
M1
answer
analgesia
question
M2
answer
hypoventialtion, bradycardia and physical dependence
question
Kappa opoid receptors
answer
sedation, dysphoria, DIURESIS
question
Periaqueductal gray area of midbrain function
answer
Reponsible for descending inhibition at the level of the doral horn of the spinal cord where it inhibits afferent nociceptive transmition Mu agonism removes the inhibitory tone at PAG allowing it to inhibit transduction at spinal cord
question
Buprenorphine
answer
partial agonist of mu opoid receptor with high potency at low doses Ceiling affect where increased doses does not result in increased effect High afficnty but low intrinsic activatiy at mu recptors Displaces morphine, methadone and full opoid agonists from recpetor rsulting in increased opoid requirments in order to provide analgesia
question
Allodynia
answer
Pain to a stimulus that normally does not provoke pain
question
Anesthesia dolorosa
answer
Pain in an area without sensation
question
Hyperalgesia
answer
Increaeed pain assocaited with a normally painful stimulus
question
Dysesthesia
answer
spontaneously prodcued painful sensation
question
Superior hypogastric plexus recieves affernt pain fibers from where?
answer
Bladder, urethra, uterus, vagina, vulva, perineum, prostae, penis , testes, rectum, and decesing collon
question
Celiac plexus tranmits what information
answer
visceral pain from liver, pancreas, and biliary tree
question
Ganglion impar transmits what information
answer
recieves afferent pain fibers from the perninium, distal rectum, anus, distal urethra, vulva, and distal third of vaigina
question
Complex regional pain syndorme divided into type 1 and type 2 baed on what?
answer
Type 2 associated with specific nerve injury
question
Contraindicaiton to celiac plexus block?
answer
Bowel obstruction - unopposed parasymapthic stimulation with increased owel motility can result in perforation
question
How does sympathetic block reduce pain in CRPS?
answer
Reduces pain by disrupting sympatheic efferent pathway to the affected extremity THe amount of circulating catechoolamines in that extremity is reduced rsutling in decreased adrengergic recptor stimulation of the nociceptive afferent fibers
question
How does TENS unit relieve pain?
answer
Gate control theory of pain proposed as the potential mechanism Stimulation of large myelinated non nociceptieve (A-beta fibers interfers with the ability of small nociceptive fibers to transmit pain signals to secondary neurson at the level of the dorsal horn,
question
NSAID associated with reductions in GI side effects?
answer
COX 2 selective - Celecoxibib
question
Prilocaine
answer
Methemoglobinemia
question
Lidocaine a/w
answer
TNS
question
Best opoiod for renal failure?
answer
Fentanl - no active metabolites
question
Opoids associated with post histamine release?
answer
Morphine, meperdine, and codeine



