Exam 18 Corrections – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Male newborn delivered at 28 weeks, neonatal respiratory distress syndrome, ABG shows decreased pH, decreased Po2 increased PCO2. A deficiency in which of the following most likely caused the disorder? A. Diacylglycerol B. Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine C. Phosphatidylserine D. Sphingomyelin E. Surfactant protein D
answer
B. Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine Most important lecithin in pulmonary surfactant! so deficiency in it would lead to neonatal respiratory distress syndrome with ground glass appearance of lung fields
question
35-year-old woman with fever and sharp chest pain for 3 days. T 101.3F. Friction rub heard. All causes of secondary pericarditis ruled out. Cause of primary pericarditis? A. Bacterium B. Fungus C. Parasite D. Tumor E. Virus
answer
E. virus (idiopathic but presumed to be viral)
question
Researching new cancer drug, effective at killing rapidly dividing cells, in mice caused profound myelosuppression. In patients, most appropriate to follow which when at risk for infectious complications? A. Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activity B. Natural killer cells C.Neutrophil counts D. Serum complement concentrations E. Serum IG concentrations
answer
C. Neutrophil counts Make up majority of WBC! A part of the first responding innate immunity! Myelosuppression means no Myeloid cells like monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, erythrocytes, dendritic cells, and megakaryocytes or platelets
question
Patient with orthostatic hypotension, loose stools for 1 year, and history of type 1 DM. Stool studies are normal. What is the pathophysiological mechanism of the diarrhea? A. Exudation B. Generalized malabsorption C. Motility disorder D. Osmosis
answer
C. Motility disorder DM nephropathy of the nerves so can control motility as well
question
Full-term newborn in respiratory distress. Imaging shows abdominal contents in left pleural cavity. Maldevelopment of which structure led to diaphragm defect? A. Esophageal mesoderm B. Left diaphragmatic crus C. Left pleuropericardial fold D.Left pleuroperitoneal membrane E. Septeum transversum
answer
D. Left pleuroperitoneal membrane Defect in it leads to diaphragmatic hernia where abdominal structures enter thorax. More prone to happen on the left side bc right hemidiaphragmn is relatively protected by liver
question
56-year-old exposed to possible chemical attack. Respirations labored, diaphoresis, excessive lacrimation, increased salivation, muscle strength 2/5, urinary and fecal incontinence. Besides atropine, another tx? A. Bethanechol B Phenoxybenzamine C. Pralidoxime D. Pyridostigmine
answer
C. Pralidoxime ( regenerates AchE if given early) Phenoxybenzamine= irreversible alpha blocker used pre-op for pheochromocystoma to prevent catecholamine ( hypertensive) crisis Pyridostigmine= tx for myastenia gravis
question
46. 34-year old man is brought to the ER semiconscious and combative. In addition to sedation , a short-acting neuromuscular blocking agent is administered for intubation to prevent aspiration. Within a few seconds after admin of the drug, he has transient muscle fasciculations in his face ; he develops generalized paralysis within 1 minute. Forty five minutes after completion of the procedure , he is still paralyzed. A genetic abnormality of which of the following enzymes is the most likely cause of his unusually slow recovery from paralysis? A. Choline O-acetyltransferase B. Monoamine oxidase C. Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase D. Pseudocholinesterase
answer
D. Pseudocholinesterase Pseudocholinesterase deficiency is a condition in which a person's body is abnormally slow at breaking down a certain class of drugs used for surgical anesthesia. Known as choline esters, the most commonly used of these drugs is called succinylcholine (suxamethonium). Different from malignant hyperthermia where person presents w/fever and muscle contractions and its due to mutation in voltage sensitive ryantodine receptor causing an increase in Ca release from sarcoplasmic reticulum
question
66-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department by her daughter because of a 2-day history of fever, flank pain, pain with urination, and nausea. Ten days ago, she was admitted to the hospital for similar symptoms and was diagnosed with acute pyelonephritis. She was discharged with instructions to take oral ciprofloxacin after a 3-day course of intravenous ciprofloxacin resulted in improvement. She also has hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and osteoporosis. Current medications also include alendronate, calcium carbonate, ezetimibe, hydrochlorothiazide, and simvastatin. Her temperature is 39.1°C (102.4°F), and blood pressure is130/80 mm Hg. The most likely cause of this patient's current condition is an interaction between her current oral antibiotic and which of the following medications? A. Alendronate B. Calcium Carbonate C. Ezetimibe D. Hydrochlorothiazide
answer
B. Calcium Carbonate= can chelate and decrease effectiveness of other drugs ( like abx)
question
45-year-old man comes to the physician because of an enlarging face shoulders and trunk and thinning of his arms and legs. Physical examination shows a large plethoric face, fat pad over the upper thoracic spine and purple striae on the abdomen. Serum studies show undetectable ACTH and an increased cortisol concentration. Administration of low dose dexamethasone would most likely result in which of the following sets of serum findings? A. ACTH= No change and Cortisol= Increased B. ACTH= No change and Cortisol= no change C. ACTH= No change and Cortisol= decreased
answer
B. ACTH= No change and Cortisol= No change Dexamethasone is supposed to provide negative feedback to pit suppressing ACTH secretion so more cortisol wont be produced but it not making a change means this process is outside the normal axis. ACTH is undetectable so ACTH independent Cushings syndrome (so doesnt involve the anterior pit) Most likely either exogenous glucocorticoids or adrenal tumor!
question
71-year old woman with coronary disease and well-controlled hypertension is brought to the physician 2 hours after sudden onset of weakness of her left leg. Her BP 145/85 mmHg. Neurologic exam: weakness and decreased sensation over the left lower extremity. There are no other sensory or motor deficits. Which labeled structure is site of injury? - A (Pre/postcentral gyrus; motor/sensory cortex)
answer
Only Lower Limb sensory loss and weakness-> Anterior cerebral artery infarct which impacts the motor/sensory cortex
question
11. 14-year-old girl with type 1 diabetes mellitus and 4-hour history of lethargy, confusion, disorientation. Symptoms gradually developed and she did not take her usual insulin dose during a sleepover. HR 110, RR 24 deep and rapid, bp 95/75. Labs: glucose 450, arterial pH 7.15. ABG? pCO2/HCO3-/Anion gap - decreased/decreased/increased
answer
Diabetic ketoacidosis= metabolic acidosis so primary disturbance is going to be a decrease in arterial HCO3! Due to hyperventilation will have decreased PCO2 and increased anion gap
question
Studying epithelial repair of small intestine in experimental animal. Wants to identify most active cell division location. Where is this cell activity found? A.Base of the crypt B. Brunner gland C. Peyer Patch D. Top of the villi
answer
A. Base of the crypt (contain stem cells that replace enterocytes/ globlet cells)
question
67-year-old man with 3 months fatigue and shortness of breath. Vitals HR 90, RR 15, bp 150/98. PE conjunctival pallor. Labs: hb 8.5, hct 26%, MCV 90, RDW 14.4% (N=13-15%), Cr 2.9, Ferritin 144, Iron 24, Transferrin saturation 23% (N=20-50%). Besides iron supplementation, most appropriate tx? A. Erythropoietin B. Folic Acid C. Granulocyte colony- stimulating factor
answer
A. Erythropoietin Creatinine is high!! So something is going on with the kidney!
question
18-month-old girl with 2 day progressive cough and hoarseness. T 102.2F, HR 88, RR 24, bp 100/70. Oxygen saturation 95%. PE mild erythema of oropharyngeal and laryngeal mucosa no exudate, harsh, barking cough heard. Improves within 4 days. Cause? A. Bordetella pertussis B. Influenza A virus C. Parainfluenza virus D. RSV
answer
C. Parainfluenza Virus Harsh barking cough= croup! So parainfluenza virus! RSV= bronchiolitis
question
To decrease risk for cv disease 24 yo man begins diet. 1.53 cm 95 kg BMI 32, Intends to lose 16 kg by limiting caloric intake to 2000 cal. to maintain the recommended protein intake (56g day); a balanced decreased in carbs and fat is required (caloric radio of fat and carbs is 30:55). which best describes number of calories that should be provided by fat in this its diet each day? A. 370 B. 430 C. 510 D. 630 E. 740
answer
D. 630 1g carb or protein= 4kcal 1g alcohol= 7kcal 1g Fatty acid=9 kcal 56*4= 224 cal for protein 2000-224= 1776 cal for fat and carbs 30:55 (fat: carb) so 30/85= X/1776 x=626
question
41. 65-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 1-week history of a swollen, painful left knee. Her temperature is 38°C (100.4°F), and blood pressure is 110/65 mm Hg. Examination of the left knee shows erythema and swelling of the joint and decreased range of motion. A photomicrograph of synovial fluid obtained by arthrocentesis is shown. This patient's synovial fluid most likely contains which of the following? A. Uric acid B. Neisseria gonorrhoeae C. Treponema pallidum
answer
A. Uric Acid Monosodium urate crystal on photomicrograph of synovial fluid. S.aureus, strep, N. gonorrhoeae ( synovial fluid has lots of WBC! and is purlent!)
question
25-year-old woman with fatigue for 3 wks and intermittent fever for 7 days, had teeth cleaned a month ago, no abx for prophylaxis, and had rheumatic fever as child and endocarditis 4 y ago. PE shows 2/6 murmur, ultrasound shows abnormal mitral valve. Photo of growth from blood cultures shown (GP cocci in chains). Characteristic of causal organism? A. Greening reaction on blood agar B. Inhibition by optochin C. Resistance to novobiocin
answer
A. Greening reaction on blood agar bc alpha hemolytic!! optochin resistant! and catalase negative Strep Viridans!
question
65-year-old man with 4-hour history of intermittent severe pain in flank area radiating to genital region. History of hypercalciuria and renal calculi. Drug decrease the urinary excretion of calcium? A. Acetazolamide B. Furosemide C.Hydrochlorothiazide D. Spironolactone
answer
D. Hydrocholorothiazide MOA: inhibits NaCl re-absorption of in early DCT-> decreasing diluting capacity of the nephron. Decreases Ca excretion!
question
A 25-year-old man is admitted to the hospital because of severe crush injuries to the chest and extensive burns over 30% of his body surface area. Three hours later, he develops tachypnea and dyspnea. Arterial blood gas analysis on room air shows a decreased Po2 and Pco2. A chest x-ray shows bilateral interstitial and alveolar infiltrates. The patient is intubated and mechanically ventilated. Damage to which of the following is most likely to preclude restoration of normal tissue architecture and pulmonary function in this patient? A. Basement membranes B. Capillaries C. Fibroblasts D. Macrophages E. Mast cells
answer
Preclude= prevent from happening! A. Basement membrane (interstium btw the alveoli and the capillari) damage to this would lead to fibrosis and scarring reducing pulmonary function Acute respiratory distress syndrome
question
19-year-old woman is admitted to the hospital for antibiotic treatment of meningococcal meningitis. She is stabilized. Three days later, her pulse is 120/min, and blood pressure is 60/30 mm Hg. Physical examination shows bilateral flank tenderness. Serum studies show a sodium concentration of 128 mEq/L, potassium of 5.4 mEq/L, and bicarbonate of 20 mEq/L. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step to determine the cause of this patient's hypotension? A.Adrenocorticotropic hormone stimulation test B. Blood culture and antibiotic sensitivity test C. Urine culture and antibiotic sensitivity test
answer
A. Adrenocorticotropic hormone stimulation test. To see how well adrenal glands respond to ACTH! Decrease in Na and bicarb and increase in potassium s/p meningococcal meningitis= Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome: acute primary adrenal insufficiency due to adrenal hemorrhage associated with septicemia Adrenal insufficiency= deficiency of aldosterone and cortisol ( mineralcorticoids and glucocorticoids)
question
2-month-old female with T 102F, vomiting, diarrhea, dehydration. Exam of stool shows viral particles with wheel-like shape. Properties of virus? Type of nucleic acid/envelop/capsid symmetry - Double-stranded RNA, segmented/no/icosahedral
answer
- Double-stranded RNA, segmented/no/icosahedral Rotavirus! #1 cause of infantile gastroenteritis and fatal diarrhea in kids
question
32-year-old woman has new neuro finding while being tx for acute infection of sphenoid sinus. Imaging shows cavernous sinus thrombosis on left. Additional finding most likely? A. Central facial weakness B. Decreased sense of smell C. Inability to abduct the eye
answer
C. Inability to abduct the eye CN that pass thru cavernous sinus and could be impacted CN III (eye movement and pupil constriction) CN IV (eye movement) CN V1 (afferent nerve of lacrimation reflex) CN VI ( eye movement laterally)
question
83-year-old with arteriosclerosis undergoes repair of infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm. Graft extends just below the renal arteries to the bifurcation of the aorta. Which organ will lose primary blood supply and rely on collateral circulation? A. Adrenal gland B. Descending colon C. Pancreas D. Spleen
answer
B. Descending colon Branches off the abdominal aorta (Superior to inferior) Celiac trunk SMA Renal Gonadal (on left side) IMA Bifurcation at L4 in to Left and Right common illiacs! IMA supplies (Hindgut) Distal 1/3 of transverse colon to upper portion of the rectum.
question
39-year-old man with polycystic kidney disease has 6-month history intermittent blood in urine. T 98.6 F HR 100 RR 24 BP 160/90. Urea nitrogen 100, creatinine 8. UA shows blood. Arterial blood gas shows? pH/pCO2/HCO3- - 7.22/28/11
answer
Increase in creatinine and BUN--> renal failure Consequence of renal failure= Metabolic acidosis so Bicarb will be <20 and PCO2 will be decreased too due to hyperventilation.
question
48-year-old man 2-month increasing abdominal girth and inability to achieve erection. Smoked 1 pack cigarettes for 20 years and drug 1 pint of liquor daily. Vitals normal. PE shows scleral icterus, spider angiomata, gynecomastia, ascites and prominent umbilical venous pattern. Tests small. Cause of gynecomastia? A. Excessive estrogen production by the adrenal glands B. Failure of liver to conjugate testosterone to its carrier molecule C.Failure of liver to degrade estrogen
answer
C. Failure of liver to degrade estrogen Liver cirrhosis leads to gynecomastia Estrogen stimulates breast development!
question
19-year-old man with gastrointestinal bleeding. Laparotomy done and 5-cm blind outpouching on antimesenteric side of terminal ileum 15 cm from ileocecal valve resected. Pathology shows? A. Angiodysplasia of the colon B. Crohn disease C. Heterotopic gastric mucosa
answer
C. Heterotopic gastric mucosa Meckel's Diverticulumn= partial closure of the vitelline duct w/ patent portion attached to ileum (blind pouch with opening to illeum). May have heterotopic gastric or pancreatic tissue--> melena, hematochezia, abdominal pain. About 2 feet away from illeoceccal valve
question
68-year-old man with creatinine 2.3 due to chronically increased hydrostatic pressure in Bowman space. Cause? A. Benign prostatic hyperplasia B. Congestive Heart Failure C. Hypertension D. Type 2 Diabetes
answer
A. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia BPH is an obstruction of male urinary tract! Outflow obstruction has potential to create hydronephrosis or post renal azotemia. Back pressure of urine will lead to increased hydrostatic pressure in bowman's space.
question
Child with XXY karyotype, genetic studies showed he received the extra "x" from his father. An error of chromosome segregation occurred during anaphase at which of the following stages of spermatogenesis in the patient's father? A. Early spermatid B. Late spermatid C.Primary spermatocyte D. Primodrial germ cell E. Secondary spermatocyte
answer
C. Primary spermatocyte Diploid so 2N! (X-X Y-Y) Primary spermatocyte goes thru meiosis I to become secondary spermatocyte haploid so 1N (X-X) or (Y-Y)
question
50-year-old woman with COPD comes with 3 months of progressive shortness of breath. Physical shows JVD, loud pulmonary component of S2. Pulmonary function tests show FEV1:FVC ratio of 20% and decreased diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide. Which is decreased in pulmonary vascular smooth muscle? A. Adventitial collagen matrix deposition B. Cytosolic phospolipase A2 activity C. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase production D. Endothelin expression
answer
C. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase producition COPD-> Hypoxemia->Alveoli constrict in attempt to send blood to more diffused part of lung)-> high pressure in pulmonary circuit-> atherosclerosis of pulmonary trunk, smooth muscle hypertrophy of pulmonary arteries, & intimal fibrosis so less vasodilation happening and less endothelial nitric oxidase synthase production
question
25-year-old woman with polycystic kidneys and 3-month history of weakness, fatigue, headaches, hypertension, loss of appetite and itching. Cr 4. Labs? - bicarb (HCO3-) decreased, inorganic phosphorous (PO4) increased, parathyroid hormone increased
answer
Chronic renal disease-->(Renal osteodystrophy) secondary hyperparathyroidism--> Hypocalcemia, hyperphophatemia, failure of vit d hydroxylation (decreased ca intestinal absorption) Renal failure: Metabolic acidosis (decrease in bicarb) and renal osteodystrophy
question
Patient making sexual advances towards physician. Appropriate measure? A. Have a chaperone join them B. Stop the history taking and refer the patient to another physician
answer
A. Have a chaperone join them
question
65-year-old with sudden onset generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Personality change last 6 months; used to be mild mannered and now verbally abusive. CT shows single mass enhances with contrast in right frontal lobe and crosses to left hemisphere through corpus callosum. Dx? A. High-grade fibrillary astrocytoma B. Malignant meningioma C. Metastatic carcinoma D. Metastatic melanoma
answer
A. High grade fibrillary astrocytoma Astrocytoma= Glioblastoma multiforme Agressive malignant tumor found in cerebral hemisphere can cross cropus callosum! Mets present as multiple well circumscribed lesions at the gray white junction
question
67-year-old woman with atrial fibrillation with sudden onset severe abdominal pain. Ex-lap shows embolus in superior mesenteric artery with complete occlusion of middle colic artery. Ischemic changes where? A. Descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum B. Distal one third of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum C. Small intestine, ascending colon, and part of the transverse colon D. Stomach duodenum, and small intestine
answer
C. Small Intestine, ascending colon, and part of the transverse colon. SMA: Midgut! so distal duodenumn to proximal 2/3 of transverse colon. Celiac trunk: foregut! so Pharynx and lower esophagus to proximal duodenum, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen!
question
60-year-old man 1 day of fever, chills, confusion and memory loss. Returned from Gulf coast where he walked barefoot. Hx of severe cirrhosis and portal hypertension. T 39C (102.2 F), RR 22, bp 90/48. Physical shows early blister formation on right lower extremity. Blood culture: gram-negative, lactose-fermenting organism. Bug? A. Haemophilus influenzae B. Salmonella typhi C. Vibrio vulnificus
answer
C. Vibrio vulnificus V. vulnificus can cause a wound infection from contact with contaminated water or shellfish. Salmonella is not a lactose fermenting organism Haemophilus influenzae is a respiratory gram negative that lactose fermenting doesnt test for.
question
An experimental animal is created that has a defect in an innate gastrointestinal defense mechanism. Organism is found to have decreased HCl prod. After 2 months on biopsy gastric fundus and body show decreased mucosal thickness and hyperplasia of enterochromaffin like cells. This closely resembles? A. Barrett esophagus B. Chronic gastritis C. Whipple disease D. Zollinger- Ellison syndrome
answer
B. Chronic gastritis Decreased HCL production->hypergastrinemia (high gastrin) increases acid secretion primarily thru its effects on enterochromaffin like cells (hyperplasia) and mucosal inflammation
question
35-year-old woman with 3-month progressive shortness of breath with exertion. RR 26. Physical shows jvd and prominent a wave. Lungs clear. Cardiac exam shows loud pulmonic component of S2 and right-sided S4 gallop. Increased pulmonary expression of what? A. Endothelin-1 B. Nitric oxide C. Prostacyclin D. Thrombomodulin
answer
A. Endothelin-1 Causes vasoconstriction that plays a role in pulmonary hypertension and cor pulmonale
question
30-year-old woman with 2-years of numbness, blanching, and bluish color to ears, fingers and toes after emotional upset or cold exposure. Vitals and PE normal. Avoid taking which drug? A. Acetaminophen B. Dextromethorphan C. Diphenhdramine D. Phenylephrine
answer
D. Phenylephrine= Alpha adrenergic agonist: increase in vasoconstriction Raynaud's phenomenon happens due to arteriolar (small vessel) vasospasm in response to cold or stress. Dextromethorphan= antitussive (antagonizes NMDA glutamate receptors). Synthetic codeine analog Diphenhdramine= 1st gen antihistamine so get reversible inhibition of H1 receptors (decrease in nasal and bronchial mucus production and decrease in vascular permeability)
question
A new antiplatelet agent is developed for the prevention of recurrence of stroke. In a large randomized clinical trial with equal numbers of men and women, the rates of stroke are lower in patients receiving the new agent than in patients receiving the standard treatment. Results are shown: Recurrent Stroke Rates per 1000 Person-Years Standard Treatment vs. New Antiplatelet Drug Women .12 .04 Men .24 .08 Overall .18 .06 Based on these results, which of the following is the relative risk reduction in women? A. 8% B. 12% C. 50% D. 63% E. 67%
answer
E. 67% Relative risk reduction= portion or risk reduction attributable to the intervention as compared to the control= 1-RR RR= risk of developing dz in exposed group/risk of developing dz in unexposed group or standard treatment .04/.12= .3333 1-0.333=.67
question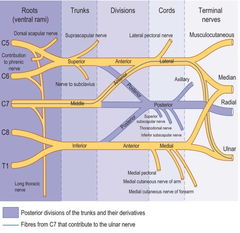
30-year-old man in bicycle collision and hits right shoulder forcefully. Unable to flex right elbow with decreased sensation to pinprick over right lateral forearm. Brachial plexus lesion?

answer
Musculocutaneous nerve lesion leads to difficulty flexing elbow variable sensory loss over lateral forearm
question
4-day-old boy with vomiting after breastfeeding. PE shows lethargy and dry mucous membranes. Labs: Na 139, Cl 90, K 7, HCO3 17, Glucose 42, BUN 25, Cr 0.4, 17-hydroxyprogesterone increased. Enzyme deficiency? A. 11B-Hydroxylase B. 17A-Hydroxylase C. 21-Hydroxylase E. 17-Ketoreductase
answer
C. 21-Hydroxylase Most common deficiency causing congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Presents in infancy with salt wasting and increase in renin activity and increase in 17-hydroxyprogesterone and in potassium!
question
52 yo man is brought to er 30min after the onset of chest pain and shortness of breath. He had played tennis all day and he does not remember how much fluid he had consumed. His temperature is 36.7 oC, pulse 122min, respirations 28min and BP 90/50 mmHg. PE shows dry skin and decreased capillary refill. An ECG and evaluation of cardiac enzymes show no abnormalities. Which of the following findings in the nephron best describes the tubular osmolarity, compared with serum in this patient? PT //macula densa //medullary collection duct - Isotonic, hypotonic, hypertonic
answer
Proximal tubule= isotonic Macula Densa (combo of cells from ascending loop of henle and distal tubule)= reabsorption of all of the Na, H2O, HCO3--Dilute tubular fluid--> Hypotonic Medullary collection duct: draws H2O and urea out to create a hypertonic interstitium
question
35-year-old woman with 2-day history of blistering lesions on sun-exposed face, arms and hands. Recurrent episodes of skin lesions over several years. Taking oral contraceptives for 15y. PE shows fluid-filled vesicles and bullae. Labs: AST increased, ALT increased, total porphyrin increased, urine uroporphyrin III increased. Precursor to uroporphyrin? A. Hippuric acid B. Histidine C. Lysine D. Pyruvic acid E. Succinyl CoA
answer
E. Succinyl CoA Glycine+Succinyl CoA in mithochondria are precursors to uroporphyrin synthesis which is what accumulates in Porphyria cutanea tarda (most common prophyria presents with blistering cutaneous rash in photoexposed areas) Heme= Fe+protoporphyrin Prophyrias develop due to enzyme deficiency leading to defective protoporphyrin synthesis-> defective heme synthesis
question
48. A sexually active 32-year-old woman has vaginal pain with urination. Pelvic examination show bilateral vesicoulcerative lesions of introitus (entrance to the vagina) . Tx? A. Acyclovir B. Amoxicillin/Clavulanate C. Ganciclovir
answer
A. Acyclovir Tx HSV genital lesions which are vesicoulcerative lesions Ganciclovir tx for CMV
question
34-year-old man with a 3 month history of a progressive rash on his feet. Rash is not itchy or painful. A photograph of feet is shown. HIV+. In addition to HAART, which of the following pharmacotherapy is most appropriate? A. antibacterial B. Antifungal C. Antineoplastic D. Antiparasitic
answer
C. Antineoplastic Kaposi's Sarcoma which is associated with HHV8 but is considered a neoplasm
question
7-year-old boy is about undergo an appendectomy. An intravenous catheter needs to be inserted, but the patient is fearful of being stuck with needle. The most appropriate anesthesia administered by mask to anesthetize this patient quickly would have which of the following characteristics? A. High Blood solubility B. High cerebrospinal fluid solubility C. High lipid solubility D. Low blood solubility E. Low lipid solubility
answer
D. Low blood solubility Drugs with low blood solubility give rapid induction and recovery times Drugs with high lipid solubility are highly potent blood solubility--> speed of onset lipid solubility--> potency
question
During a clinical study of calcium and phosphorus metabolism, a 50-year-old man undergoes series of lab studies. His serum Ca, PO4 and PTH are normal. He is given infusion 2 g Calcium chloride over 2 hours. His serum Ca concentration now is 11.5mg/dl. Compared with pre infusion levels, the serum concentration of which of the following substances is likely to be increased at this time? A. 7-Dehydrocholesterol B. 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol C. 24,25 Dihydroxycholecalciferol D. Vitamin D3
answer
C. 24, 25 hydroxycholecalciferol=inactive form of vit D increase in calcium concentration-> decreases PTH--> decreases activation of Vit D so theres more inactive vit D!
question
45-year-old homeless man found unconscious. Breath smells of alcohol. Vitals stable. PE shows bronzed skin and spider angiomata on chest. Labs: hemoglobin 10, hematocrit 30%, MCV 110, WBC 9000, platelets 160,000, ferritin 200, b12 500, folate 20. Blood smear shows hypersegmented neutrophils and 3+ oval macrocytes. Labs? Methylmalonic Acid/ Homocysteine A. Increased/increased B. Increased/ normal C. Normal/increased D. Normal/ Normal E. Normal/ Decreased
answer
C. Methylmalonic Acid normal and Homocysteine increased. Alchy with a Folate Deficiency! Folate and B12 needed for: Homocysteine->Methionine-> DNA synthesis B12 only needed for: Methylmalonic acid-> Succinic acid-> Myelin synthesis
question
55-year-old man with elevated LDL cholesterol is prescribed lovastatin. This treatment would result in which adaptive responses at the cellular level? A. Decreased hepatic expression of LDL cholesterol receptors B. Decreased transcription of HMG-CoA reductase C. Increased transcription of HMG-CoA reductase
answer
C. Increased transcription of HMG-CoA reductase Statins competitively and reversibly inhibits HMG-CoA reductase which is the rate limiting enzyme of cholesterol synthesis. So transcription of enzyme would be upregulated to compete
question
Persons are at risk of influenza are vaccination every year because of antigenic variation, which can be drift (minor) or shift (major). Mechanism of antigenic shift? A. Frameshift B. Reassortment C. Recombination
answer
B. Reassortment Reassortment= when viruses with segmented genomes (influenza) exchange genetic material.Can create antigenic shift. Ex: Complex viral reassortment of genes from human, swine, and avian viruses led to H1N1 influenza A epidemic Recombination= exchange of genes between 2 chromosomes by crossing over within regions of significant base sequence homology.
question
73-year-old man has poor appetite and lost 25 lb over 4 months. Labs show normochromatic normocytic anemia. Xray of chest shows 2-cm perihilar mass. Biopsy shows small cell carcinoma of lung. Which is responsible for weight loss? A. Cytokine effect B. Infection C. Renal failure D. Superior vena cava syndrome E. Tumor hormone production
answer
A. cytokine effect Cachexia= weight loss, muscle atrophy, fatigue that occurs in chronic dz (cancer, AIDs, HF). Mediated by cytokines like TNF, IFN-gamma, IL-1, and IL-6.
question
36-year-old F with 2 week history of fatigue, bleeding of the gums, and bone pain. Physical examination shows pallor, hepatosplenomegaly, and ecchymotic lesions over extremities. Labs: Hb 8g/dl Ht 25% Leukocytes: 36,000 segm neutr 4% eosinophils 4% lymph 6% mono 6% promyelo 80% platelets 25,000 Polymerase chain reaction test shows an mRNA corresponding to the retinoic acid receptor- alfa/promyelocytic leukemia fusion gene resulting from a reciprocal translocation of chromosomes 15 and 17. Treatment w/ all-trans retinoic acid is started. In response to the therapy, the fusion protein will most likely attract which of the following proteins to form a pre-transcriptional complex? A. Histone acetylase B. Histone kinase C. Histone N-methyltransferase D. Nitric oxide
answer
A. Histone acetylase Histone acetylation relaxes DNA coiling, allowing for transcription. "Histone acetylation makes DNA Active" Tx APL with Vit A derivative that can bind mutated receptors of cells stuck in blast stage (promyelocytes) and allow them become PMNs.
question
48yo man with possible hypertension. based on 20 measurements, his average diastolic pressure is 94mmHg, SD is 8mmHg. If only four measurements were made rather than 20, which of the following statements would best describe the width of the 95% Confidence Interval with regard the mean blood pressure? A. Smaller B. Larger C. The same D. Changed, but the direction cannot be predicted
answer
A. Larger Confidence Interval (CI)= range of value within which the true mean of the population is expected to fall with a specified probability CI=mean+/- Z(SEM) SEM= standard error of the mean= an estimate of how much variability exists between the sample mean and population mean. Increases as the sample # (n) decreases. So sample n decreased-> increased SEM and made CI larger!
question
18-year-old woman comes 12 hours after ingesting 100 aspirin tablets in suicide attempt. PE shows tachypnea. Labs? pH/pCO2/HCO3- A. 6.90/60/10 B. 7.30/60/29 C. 7.32/15/8 D. 7.44/60/40
answer
pH/pCO2/ HCO3- C. 7.32/15/8 Aspirin= Salicylates! so can cause and increased anion gap metabolic acidosis with immediate hyperventilation as compensatory response. Primary disturbance= decreased HCO3- Also have decreased PCO2 (from hyperventilation) Metabolic acidosis: Both HCO3 and PCO2 is decreased
question
65-year-ld man with cancer of cecum found to have metastatic lesion to liver. Venous route of mets? A. Ileocolic --> superior mesenteric --> portal --> right hepatic branch of portal B. Ileocolic --> Inferior mesenteric-->portal--> right hepatic branch of the portal C. Middle colic -->Inferior mesenteric--> splenic--> portal--> right hepatic branch of the portal
answer
A. - Ileocolic --> superior mesenteric --> portal --> right hepatic branch of portal Remember SMA supplies and superior mesenteric vein drains distal duodenum to 2/3 of transverse colon so cecum is included in this section!
question
35yo F has congestive cardiomyopathy and pitting edema. Her serum urea nitrogen concentration is 25mg/dl and serum creatinine is 1.8mg/dl. Furosemide therapy is started. After 5 days, labs show: Na 130 K 4.5 Cl 90 HCO 30 BUN 85 Creatinine 2.2 Albumin 3 Urine specific gravity 1.023, rbc 0 wbc0 sediment none Urinary fractional excretion of sodium is less than 1%. Explanation? A. Acute tubular necrosis B. Prerenal Azotemia C. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus D. Renal Artery Stenosis
answer
B. Prerenal Azotemia Loop diuretic like furosemide is used to treat edematous states bc inhibits ascending loop of henle which prevents concentration of urine. But in this case it doesnt work in stopping kidney injury and BUN/ Creatinine increases so most likely: Prerenal Azotemia due to decrease in renal blood flow which decreases GFR. Na/H2O and BUN held on to by kidney in attempt to conserve volume (kidney thinks there isnt enough due to lack of blood flow)--> increase BUN/ Creatinine ratio (BUN is reabsorbed but creatinine is not) and decrease in fractional excretion of Na.
question
2-year-old girl with febrile seizure. PE shows nuchal rigidity and bacterial meningitis suspected. LP and immediate abx therapy planned, but parents unavailable for consent. Next step? A. Initiate the procedure and treatment without consent B. Do not initiate any procedure or treatment until a legal guardian arrives
answer
A. Initiate the procedure and treatment without consent
question
57-year-old man with alcoholism dies of klebsiella pneumonia. Abscess cavities filled with purulent exudate on autopsy. Pattern of necrosis in lung tissue? A. Caseous B. Fat C. Fibrinoid D. Gangrenous E. Liquefaction
answer
E. Liquefaction Associated with bacterial abscesses and brain infarcts! Caseous is associated with ischemia and infarcts in most tissue except the brain. Fibrinoid is associated with immune reaction in vessels Gangrenous is associated with distal extremity after chronic ischemia
question
44-year-old woman 15 weeks' gestation with uterus consistent size with gestational age. Amniocentesis shows increased alpha-fetoprotein (AFP). Fetus at greatest risk for which defect? A. Congenital heart defects B. Horseshoe kidney C. Hypergonadism D. Malrotation of the gut E. Spina bifida
answer
E. Spina bifida Alpha fetoprotein: High levels associated with neural tube defects (spina bifida) and abdominal wall defects. Low level associated with downs syndrome
question
50-year-old man with pulmonary embolus. Treated with intravenous heparin. 24 hours later, warfarin added. Day 2, partial thromboplastin time is 52 seconds (control 26 sec), and prothrombin time is 12 seconds (control 12.1 sec; INR = 1). Best explanation for normal prothrombin time and INR? A. Heparin-warfarin interaction B. Long half-life of factor II (prothrombin) C. Too low a dose of heparin D. Too low a dose of warfarin E. Undetected liver disease
answer
B. Long half life of factor II (prothrombin) Heparin= activates antithrombin which decreases the action of IIa (thrombin) and factor Xa. So it prolongs the PTT with in hours Warfarin= impairs the synthesis of vit k dependent clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X and anti-clotting protein C and S. Slow onset of action but duration of action is for days Protein C and Protein S have shorter half-lives than factors II, VII, IX, and X which can explain the normal PT time and if not monitored can cause early transient hypercoagulability.
question
4-year-old boy with fatigue and irritability for 2 months. Family visited rural Louisiana 5 months ago and ran around barefoot. Conjunctivae are pale. Labs shows normal wbc with 15% eosinophils. Stool prep shows parasite egg (picture). Cause of fatigue? A. Activation of IgE B. CNS infestation C. Circulation immune complexes D. Microcytic anemia E. Myocarditis
answer
D. Microcytic anemia (Necator americanus/Ancylostoma duodenale) Can get it from running around barefoot the larvae penetrate the skin can cause a rash (cutaneous larva migrans) or can cause an intestinal infection causing anemia by sucking blood form the intestinal wall
question
6-year-old boy with 5-day history of intermittent vomiting and 3-month hx of progressive clumsiness. Can no longer ride bicycle and difficulty getting out of car. Funduscopic exam shows bilateral papilledema. Neuro exam shows impaired upward gaze and pupil response to light. Walks shuffling gait. CT shows enlarged lateral and third ventricles and a 2-cm mass. Location of mass? A. Cerebellar hemisphere B. Frontal Lobe C. Lateral medulla D. Pineal gland
answer
D. Pineal gland Pinealoma: cause parinaud syndrome (compression of tectum-> vertical gaze palsy); obstructive/ non-communicating hydrocephalus (compression of the cerebral aqueduct-> enlarged lateral and third ventricles) and precocious puberty in males (BhCG production)
question
A normotensive 54-year-old man with normal renal functions gets a heart transplantation. One year later, bp 170/110 and serum creatinine 2.1. Which immunosuppressive drug caused these findings? A. Azathioprine B. Corticosteroid C. Cyclophosphamide D. Cyclosporine E. Muromonab-CD3 (OKT3)
answer
D.Cyclosporine Calcineurin inhibitor:Binds cyclophilin. Blocks T-cell activation by preventing IL-2 transcription. Used for transplant rejection prophylaxis Nephortoxicity! (both calcineurin inhibitors are) Can cause hyperkalemic renal tubular acidosis (type 4) Cyclophosphamide is used to tx solid tumors, leukemia, and lymphoma. AE: myelosuppression & hemorrhagic cystitis
question
72-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 6-month history of increased bruising on her forearms. She appears alert and well nourished. Physical examination shows extensive wrinkling, scaly erythematous patches on the face, and irregularly shaped brown macules on the face and forearms. There are ecchymoses in various stages of healing on both forearms; the ecchymoses are more numerous on the right side. Laboratory studies, including a complete blood count and coagulation studies, are within the reference ranges. She has noticed no bleeding from her gums after brushing her teeth. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the ecchymoses in this patient? A. Extensive solar elastosis B. UV destruction of Langerhans cells in the epidermis
answer
A. Extensive solar elastosis Actinic elastosis, also known as solar elastosis is an accumulation of abnormal elastin (elastic tissue) in the dermis of the skin, or in the conjunctiva of the eye, which occurs as a result of the cumulative effects of prolonged and excessive sun exposure, a process known as photoaging.
question
Investigator studying immune response to fungi. Fungi express beta-glucans on cell surface and that triggers innate immune response. Which tx decreases glucan expression? A. Amphotericin B B. Caspofungin C. Flucytosine D. Tebinafine E. Voriconazole
answer
B. Caspofungin An Echinocandin: which inhibits cell wall synthesis by inhibiting B-glucans Used for Invasive aspergillosis, Candida AE: GI upset, flushing (by histamine release)
question
45-year-old man comes to physician for follow up after appendectomy. There is mild scleral icterus and well healing surgical incision. Lab values show Total bilirubin 3.2 (high) Direct: 0.2 Indirect 3 mg/dL (high) High ALT and AST Dx? A. Cholelithiasis B. Gilbert syndrome C. Hepatitis D. Liver failure E. Surgical bile duct trauma
answer
B. Gilbert's syndrome AR Hereditary hyperbilirubinemias Mildly decrease UDP-glucuronosyltransferase conjugation and impaired billirubin uptake. Asymptomatic or mild jaundice. Increase unconjugated bilirubin with overt hemolysis. Billirubin increase with fasting and stress
question
33-year-old woman who three weeks ago, underwent oophorectomy for epithelial ovarian cancer. Recommends adjuvant chemotherapy with paclitaxel. Mechanism? A. Alkylates DNA B. Destroys asparagine C. Inhibits dihydrofolate reductase D. Inhibits microtubule disassembly E. Prevents microtubule polymerization
answer
D. Inhibits microtubule disassembly
question
Man comes to doc for cast removal. Fracture of left humerus that required open reduction, internal fixation, cast immobilization. Muscle strength is 2/5 with extension of elbow and 1/5 with extension of wrist and fingers. Patient most likely sustained a fracture at (which location in humerus)? A. Coronoid fossa B. Distal shaft C. Medial epicondyle D. Radial groove E. Surgical neck
answer
D. Radial Groove aka midshaft fracture of humerus. Radial nerve is the extensors of arm, wrist and fingers. Wrist drop, loss of elbow, wrist, and finger extension. Decrease in grip strength Could have loss of sensation over posterior arm/ forearm and dorsal hand
question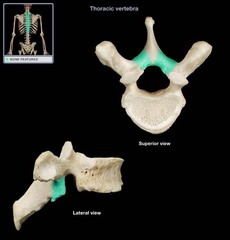
34-year-old man with herniated lumbar intervertebral disc. Laminectomy and removal of hernia scheduled. CT scan of vertebrae shown, which is surgical entrance location into neural canal?

answer
D (the lamina - called a laminectomy)
question
52-year-old female with a history of breast cancer who received 4week course of radiations 6 months ago comes for followup. Exam shows no cancer recurrence. rr 26/min. CT chest shows bilateral atelectasis in upper lung fields. Primary pathophysiological cause? A. Compression B. Consolidation C. Contraction D. Obstruction E. Resorption
answer
C. Contraction (secondary to radiation) Atelectasis= loss of lung volume due to inadequate expansion of air space. Contraction Atelectasis: radiation causes local or general fibrotic changes in lung or pleura which makes full expansion not possibly and causes and increase in elastic recoil during expiration (stiffer lungs).
question
35-year-old woman with infertile, receive injection of contrast material into cervix. On hysterosalpingogram (shown), contrast material (indicated by arrows) also seen in peritoneal cavity, which explain this finding? A. Rupture of the fallopian tube B. Rupture of the uterine body C. Spillage of contrast which in an artifact D. Spillage of contrast which is normal
answer
D. Spillage of contrast which is normal
question
48-year-old woman with gradual onset back pain past 2 weeks. No trauma. Doesn't smoke cigarettes, drink alcohol or use drugs. Hemogram, serologic studies and urinalysis unremarkable. Xray of spine shows two lytic lesions, in T-10 and L-1. Dx? A. Avascular necrosis B. Metastatic carcinoma of breast C. Osteosarcoma D. Renal osteodystrophy E. Thyroid carcinoma
answer
B. Metastatic carcinoma of breast Bone Mets (most to least common): Prostate, breast>lung, thyroid, kidney
question
A 68-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 1-month history of light-headedness and tightness in his chest with exertion. He adds that the pain is worse after arguing with his wife, and the symptoms resolve with rest. He has a past history of lower gastrointestinal bleeding; evaluation at that time was negative on upper endoscopy and colonoscopy. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 85/min, respirations are 15/min, and blood pressure is 110/75 mm Hg. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. His hemoglobin concentration is 8.2 g/dL, and hematocrit is 24%. Test of the stool for occult blood is positive. An ECG shows no abnormalities. Repeat colonoscopy shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's gastrointestinal symptoms? A. Adenocarcinoma of the colon B. Angiodysplasia C. Diverticulitis D. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome E. Ulcerative colitis
answer
B. Angiodysplasia Tortuous dilation of vessels--> hematochezia. Most often found in cecum, terminal ileum, ascending colon. More common in older patients. Confirmed by angiography
question
25-year-old man just returned from Africa and begins oral chloroquine therapy for malaria caused by Plasmodium vivax. His initial therapeutic response is good, but he develops recurrent parasitemia 2 months later. Which of the following best explains the recurrence ? A. Chloroquine is ineffective as oral therapy for P.vivax malaria B. Chloroquine is ineffective as the exoerythrocytic malarial tissue stages C. Chloroquine is only effective against P.Vivax when combined w/ metronidazole D. The patient has a second previously occult malarial infection E. The patient is infected with a chloroquine-resistant strain of P.vivax
answer
B.Chloroquine is ineffective on the exoerythrocytic malaria tissue stages It blocks detoxification of heme into hemozoin. Heme accumulates and is toxic to plasmodia. P.vivax has a 48 hour cycle (fevers on first and third day). Dormant forms in liver (hypnozoite) and these would not be destroyed by cholorquine and could cause repeated parasitemia. Samething for P.ovale
question
17-year-old boy in septic shock unresponsive to ADH (vasopressin). Treatment is discontinued, and high-dose dopamine in started. Which receptors are stimulated and are of benefit to this patient? A. A1 adenoreceptors B. A2 adenoreceptors C. B1 adenoreceptors D. B2 adrenoreceptors E. D2 receptors
answer
A. A1 adenoreceptors A1 (Gq protein linked phosphlipase C receptor) when stimulated VASCONSTRICTS Dopamine is a sympathomimetic! At high doses: provides vasoconstriction due A1 effects! At low doses: inotropic (modify force or speed of contraction of heart muscle) and chronotropic effects ( change heart rate and rhythm by affecting heart's conduction system and the nerves that influence it)
question
24-year-old man with 3-day progressive numbness of both feet that has ascended to thighs. Last 24 hours, numbness and tingling of hands. PE ataxic gait. Deep tendon reflexes diminished in upper extremities and absent in knees and ankles. Vibration and joint position absent in fingertips and feet bilaterally. Mild weakness distal upper extremities ad moderate weakness of lower extremities. Structure involved in creating these sensory findings? A. Dorsal spinocerebellar tract B. Fasciculus cuneatus C. Fasiculus gracilisi D. Myelinated primary afferents E. Unmyelinated primary afferents F. Ventral spinocerebellar tract
answer
D. Myelinated primary afferents Guillain-Barre syndrome: Ascending symmetric numbness and paralysis that begins in the lower extremities. Due to autoimmune destruction of schwann cells--> inflammation and demylination of peripheral nerves and motor fibers.
question
55-year-old man northern European descent with 2-month weakness, altered skin color, bilateral knee pain. Siblings have type 2 diabetes and cirrhosis. His PE bronzed skin, hepatomegaly, arthritis. Increased saturation of transferrin and ferritin. Liver biopsy increased iron content and cirrhosis Greatest risk?
answer
Hemochromatosis! From multiple blood transfusions or hereditary HFE mutation (can result in heart failure, "bronze diabetes," and increase risk of hepatocellular carcinoma Classic triad= cirrhosis, DM, and skin pigmentation
question
45-year-old man bmi 26, total cholesterol 200(boderline high) , HDL 50, triglycerides 550 (high). In addition to lifestyle changes. Which drug to prescribe? A. Colestipol B. Ezetimibe C. Fenofibrate D. Orlistat E. Simvastatin
answer
Main issue is high triglycerides!! C. Fenofibrate Upregulates LPL-> increase in triglyceride clearence and it will activate PPAR-A to induce HDL synthesis Colestipol= Bile acid resin which actually slightly increases triglycerides and predominately used to decrease LDL by preventing intestinal reabsorption of bile acids; liver must use cholesterol to make more
question
A 25-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 2-year history of intermittent, diffuse, cramping lower abdominal pain. The pain is usually associated with 2 to 6 days of loose, watery stools, and is typically relieved with defecation. Between these episodes, her stools are normal. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies, including complete blood count, metabolic panel, and thyroid function tests show no abnormalities. A drug targeting which of the following mechanisms of action is most appropriate for this patient? A. Accentuation of bile salt reabsorption B. Accentuation of Mu opioid myenteric plexus receptor C. Inhibition of colonic water reabsorption D. Inhibition of 5-hydroxytryptamine 1 receptor E. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor alpha
answer
B. Accentuation of Mu opioid myenteric plexus receptor Loperamide= agonist at Mu opiod receptors; slows gut motility. Poor CNS penetration (low addictive potential) Used to treat diarrhea AE: Constipation, nausea Odansetron=5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT3) antagonist (d). Used to control vomiting postop and in patients undergoing cancer chemo
question
35-year-old from group home comes for worsening behavior for 2 weeks. He believes CIA is spying on him through television set. Reports hearing voices in hall outside and that CIA now plans to kill him. Appears disheveled with unkempt hair and poor hygiene, difficulty answering questions because listening to internal stimuli. Mental status exam will show which? A. Flattened effect B. Inability to state his name C. Inability to write his name D. Lack of orientation to place or time
answer
A. Flattened effect Schizophrenia Diagnosis: Need at least 2 of the following with one of them being a positive symptom (the first three listed) 1. Delusions= unique false, fixed idiosyncratic beliefs that persist despite the facts and arent typical of a patients culture or religion 2. Hallucinations (often auditory) 3. Disorganized speech 4. Disorganized or catatonic behavior 5. Negative symptoms ( affective flattening, avolition, anhedonia, asociality, alogia)
question
47-year-old woman with irregular, raised, multicolored dark lesion on left forearm with frequent sunlight exposure. Biopsy shows malignant pigmented cells. Worst prognosis with involvement of which layer? A. Basement membrane B. Epidermis C. Papillary dermis D. Reticular dermis E. Subcutaneous tissue
answer
E. Subcutaneous tissue Deepest layer/ deeper the tissue involvement is the worse the prognosis Layers of the skin: EPIDERMIS (surface to base): Stratum Corneum (keratin), Stratum Lucidum, Stratum Granulosum, Stratum Spinosum, Stratum Basale. DERMIS SUBCUTANEOUS FAT (hypodermis, subcutis)
question
69-year-old woman with 3-week history of muscle cramps, weakness, abdominal pain, and constipation. Hypertension treated with metoprolol and hydrochlorothiazide for past 4 months. Labs show hypokalemia. Which drug should be added? A. Bumetanide B. Cholrthalidone C. Furosemide D. Indapamide E. Triamterene
answer
E. Triamterene Potassium sparing diuretic (like Spironolactone and Amiloride) Blocks Na channels in the cortical collecting tubules. HCTZ (hydrochlorothiazide) is a thiazide diruetic: which inhibits NaCl re-absorption in early Distal Convoluted Tubule-> decreases diluting capacity of nephron. AE: hypokalemia
question
Lab Workbench wiped down with alcohol, successfully inactivates viruses with which characteristic? A. DNA genome B. Enveloped virion C. Helical capsid D. Icosahedral capsid E. Naked virion F. RNA genome
answer
B. Enveloped virion Alcohol's denature proteins and disrupts cell membrane.
question
82-year-old woman comes to the physician because of constant severe lower abdominal pain and fever for 24 hours. Laproscopic examination shows severe diverticulosis and perforated diverticulitis. In spite of appropriate therapy she dies 2 days later. Liver autopsy shown. Which of the following is the primary component of the material shown on the hepatic surface? A. Collagen Type I B. Collagen Type III C. Fibrin D. Fibronectin E. Proteoglycans
answer
C. Fibrin 1-3 days after: yellow pallor on liver lots of neutrophils! Fibrinous so material shown on hepatic surface is made up of fibrin
question
35-year-old woman pain in left leg 2 days. PE shows deep venous thrombosis. Labs: platelet 200,000, PT 12 (INR 1), PTT 37. Heparin started. Five days later, platelet 120,000(low). Reason for decreased platelets? A. Antithrombin III deficiency B. Cold agglutin disease C. DIC D. Drug related antibodies E. Spelnomegaly
answer
D. Drug related antibodies HIT: heparin induced thrombocytopenia. Development of IgG antibodies against heparin
question
28-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 4-day history of palpitations, severe neck pain, fatigue, and malaise. Her pulse is 120/min and regular. Physical examination shows a diffusely tender, mildly enlarged thyroid gland. There is no exophthalmos. Serum studies show a thyroid-stimulating hormone concentration of 0.01 μU/mL. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? A. Graves Disease B. Subacute granulomatous thyroiditis C. Thyroid abscess D. Toxic multinodular goiter
answer
B. Subacute granulomatous thyroiditis aka de Quervain This is a self limited disease often following a flu like illness (eg viral infection) Maybe hyperthyroid early in course followed by hypothyroid. VERY TENDER THYROID Graves Disease: diffuse goiter with pretibial myxedema and exophthalmos
question
After operation, 65-year-old patient has lung region that is underventilated but well perfused. Which increases? A. Alveolar dead space B. Anatomic dead space C. Physiologic dead space D. Physiologic shunt
answer
D. Physiologic shunt Decrease in PAO2 causes a hypoxic vasconstriction that shifts blood away from poorly ventilated regions of lung to well ventilated regions of lung
question
32-year-old man with HIV infection follow up examination, has been treated with HAART for the past 6 years HIV plasma viral load has been undetectable. HIV viral load now increase, antiretroviral resistance suspected. HIV genotype analysis confirms that the virus has resistance mutations, which of the following most likely mutated? A. Capsid and gp120 B. CD4 and CCR5 C. Nucleocapsid and gp41 D. Reverse transcriptase and protease
answer
D. Reverse transcriptase and protease (the two targets of HAART therapy, therefore if therapy stopped working, must be these two target proteins of virus mutated)
question
1-year-old has numerous infection of skin and oral mucosa since birth. Infections slow to respond to antibiotic therapy. T 100.4F. PE multiple erythematous lesions of skin some with superficial ulceration. WBC 21,000 (high) 77% segmented neutrophils, 6% bands, 14% lymphocytes and 3% monocytes. Biopsy shows no neutrophils in dermis or epidermis. Culture of lesion grows Staphylococcus aureus. The patients recurrent infections are caused by defective production of which of the following? A. Addressin B. A component of complement C. An integrin D. An interleukin
answer
C. An integrin Integrin= membrane proteins that maintain the integrity of basolateral membrane by binding to collagen and laminin in basement membrane Leukocyte adhesion deficiency Type 1 (AR) Defect in LFA-1 integrin (CD18) protein found on phagocytes--> impaired migration and chemotaxis Increase in neutrophils but no neutrophils at lesions Leads to recurrent bacterial skin and mucosal infections with absent pus formation, impaired wound healing, and delayed separation of umbilical cord (>30 days)
question
35-year-old primigravid woman 36 weeks' gestation with 6-hour history of heavy vaginal bleeding. No prenatal care. Ultrasound shows placenta over cervical os. Can't stop bleeding and has cesarean. Dx? A. Placenta accreta B. Placenta percreta C. Placenta previa D. Placenta infarction
answer
C. Placenta previa Attachment of placenta to lower uterine segment over internal cervical os. Associated with painless third trimester bleeding Placenta accreta/increta/percreta= defective decidual layer->abnormal attachment and separation after delivery Placenta accreta= placenta attaches to myometerium without penetrating it. Placenta percreta= placenta penetrates through myometrium and into uterine serosa (invades entire uterine wall) can lead to attachment to rectum or bladder
question
19-year-old woman 2-day history of pain in left index finger. Injured it when catching a ball. PE shows erythema of left index finger. Unable to flex the distal phalanx when proximal interphalangeal joint metacarpophalangeal joints restratined. Xray normal. Injured structure? A. Extensor digitorum indicis B. Extensor digitorum tendon C. Flexor digitorum profundus tendon D. Flexor digitorum superficialis tendon E. Median nerve F. Ulnar nerve
answer
C. Flexor digitorum profundus tendon Flexes distal phalanx at the distal interphaphalangeal joint (at the tip of the finger) of digits (2-5) Flexor digitorum superficialis tendon flexes the middle phalanx at the proximal interphalangeal joint.
question
Study designed to test the effectiveness of a new drug in the treatment of endometriosis, 100 women randomly assigned to one of two groups. 48 of women receive new drug, 52 receive standard therapy. The primary purpose of this method of assigning patients to different groups is to create which of the following ? A. Double blind study B. Single blind study C. Two groups with similar sample size D. Two groups with similar underlying characteristics
answer
D. two groups with similar underlying characteristics
question
1-year-old boy with rash for 2 weeks. 10th percentile for height and weight. PE scaly, seborrheic eruption over scalp, palms, back, diaper region and soles of feet. Generalized lymphadenopathy and hepatosplenomegaly. Xray of skull shows osteolytic lesions. EM biopsy of skin shows tennis racket-shaped bilamellar granule in cytoplasm. Immuno studies show CD1a antigen expression. Abnormal cells in patient are derived from which cell? A. Dendritic cells B. Keratinocytes C. Mast cells D. Merkel cells E. T-cells
answer
A. Dendritic cells Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (CD1a and Birbecks granules= tennis racket shaped bilamella granule in the cytoplasm of cells on EM) Proliferative d/p DENDRITIC (Langerhans) cells. Present in kids as bone lytic lesions (skull), skin rash, or recurrent otitis media w/ mass involving mastoid bone. Cells are functionally immature so dont stimulate primary T-cell via antigen presentation.



