DAT Organic Chemistry Reactions etc. – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion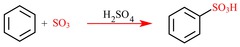
Aromatic Sulfonation

answer
Fuming sulfuric Acid (SO?/H?SO?) + Heat
question
Aromatic Nitration
answer
Nitric and Sulfuric acids (H?SO?/HNO?), nitronium intermediate
question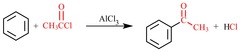
Aromatic Acylation (Friedel-crafts)

answer
Carbocation electrophile (usually acyl) is incorporated into aromatic ring, catalyzed by AlCl?
question
Activating Groups
answer
ortho/para-directing NH?>NR?>OH>NHCOR>OR>OCOR>R
question
Deactivating Groups (para)
answer
F>Cl>Br>I
question
Deactivating (Meta)
answer
(e? withdrawing): NO?>SO?H>carbonyl, COOH, COOR, COR, CHO
question
SN2
answer
Requires a good nucleophile
question
E2
answer
Requires a strong base
question
Alcohol Addition
answer
Addition of water to double bonds to form an alcohol
question
Alcohol Addition (Grignard)
answer
RMgBr + carbonyl -> Alcohol
question
Alcohol Reduction
answer
Aldehyde/Ketone/Carbox acid/Ester + LiAlH? or NaBH? -> Alcohol
question
Phenol Synthesis
answer
Hydrolysis of diazonium salts
question
Alcohol Dehydration
answer
Requires Strong acid i.e. H?SO? and heat
question
Alcohol Substitution
answer
-OH is not a good leaving group so hard to do. Best to add change -OH into a H?O or add tosyl chloride and form a tosylate (great leaving group)
question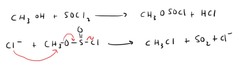
Alcohol Substitution (alkyl halide)

answer
Can also be done with PBr? to create alkyl bromides
question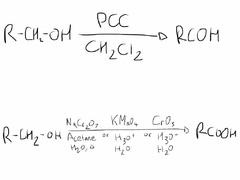
Alcohol Oxidation

answer
PCC yields aldehydes, KMnO? will create a carboxylic acid or ketone
question
Ether Synthesis

answer
Condensation of R-OH in ACID
question
Williamson Synthesis
answer
Follows SN2 mechanism
question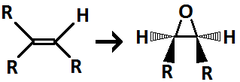
mCPBA

answer
Used to form an oxirane, can also be used on a hexene (1 double bond)
question
Aldehyde Oxidation
answer
Produces a carboxylic acid. KMnO?, CrO?, Ag?O or TOLLEN's Reagent
question
Ketone Oxidation
answer
Does not exist
question
Enolization
answer
Michael Addition
question
Hydration of Carbonyl
answer
H?O acts as the nucleophile
question
Cyanohydrin Formation
answer
Aldehyde and ketone react with HCN
question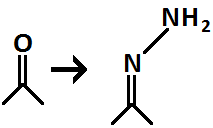
Hydrazone Formation from Carbonyl
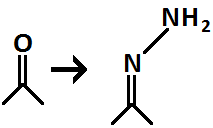
answer
Reagent = H?NNH?
question
Wittig Reaction
answer
C=O ?C=C
question
Carboxylic Acid Synthesis From 1° OH
answer
Reagents: KMnO?, K?Cr?O?, CrO?
question
Carboxylic Acid Synthesis from Alkene
answer
CH?CH=CHCH?CH? ?1)KMnO?, OH?, heat 2)H?? CH?COOH + CH?CH?COOH Yields two carboxylic acids at site of cleavage
question
Carbonation of Grignard Reagents
answer
(CH?)?CBr ?Mg/ether?(CH?)?MgBr ? 1.CO? 2. H?, H?O ? (CH?)?CCOOH
question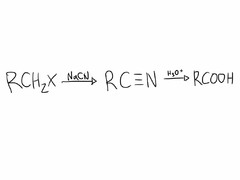
Hydrolysis of Nitriles
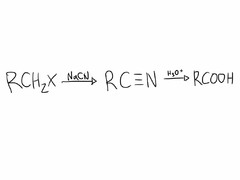
answer
Yields carboxylic acid and NH??
question
Nucleophilic Substitution of Carboxylic Acid (general)
answer
Yields a ketone where the Nu? takes the place of the alcohol
question
Reduction of Carboxylic Acids (general)
answer
Results in corresponding primary alcohol
question
Ester Formation from Carboxylic Acids
answer
Requires an alcohol under acidic conditions, yields an ester and water. Water is used as a leaving group
question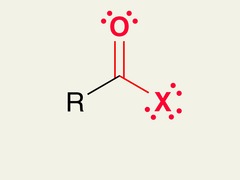
Acyl Halide Formation

answer
Reagents: Carboxylic acid and SOCl? or other halide
question
Soap Formation
answer
Carboxylic acids react with NaOH to form salts, organize non-polar tails around a non-polar substance and polar heads facing water. Spherical structure is called micelles.
question
Decarboxylation

answer
Results in loss of CO? and thus loss of entire carboxyl when heated
question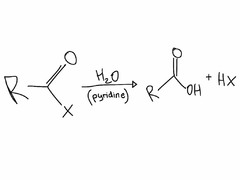
Hydrolysis of Acyl Halide

answer
Very rapid reaction
question
Anhydride Formation from Acyl Chloride
answer
Reaction of carboxylate salt (RCOO?) and acyl chloride (RCOCl) produces an anhydride
question
Acyl Halide ? Ester
answer
Nucleophilic attack by an alcohol results in replacement of the halide in an acyl halide with an ester EtOH + CH?COX -; CH?COOEt + HX
question
Acyl Halide ? Amide
answer
Nucleophilic substitution CH?COX + 2NH? ? CH?CONH? + NH?Cl
question
Acyl Halide Reduction
answer
CH?COX + H?/Pd/BaSO?/quionoline/Lindlar's Catalyst ? CH?OH
question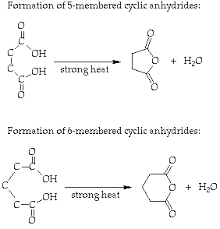
Cyclic Anhydride Self-condensation

answer
Only 5 and 6 membered rings are easily made
question
Condensation of 2 Carboxylic Acids
answer
Carboxylic acids under anhydrous conditions results in an anhydride and loss of H?O
question
Hydrolysis of Anhydrides
answer
Results in 2 equivalents of carboxylic acids when exposed to water
question
Anhydride ? Amide
answer
Cleaved by NH? to produce an amide and a carboxylic acid. The COOH and NH? can react further to create an ammonium carboxylate
question
Anhydride ? Ester + Carboxylic Acids
answer
Reacting with -OH will produce one ester and one molecule of COOH. "Splits" the original molecule
question
Anhydride acylation
answer
Reagents: AlCl? or other Lewis acid will produce an aryl ketone (benzene with a ketone) and a carboxylic acid
question
Transesterification
answer
Transform one ester into another, -OH acts as a nucleophile and displaces alkoxy on original ester
question
Grignard Addition to Ester
answer
Results in a tertiary alcohol if enough reagent is added and the intermediate ketone is not too bulky (MgBr)
question
LAH Reduction of Ester
answer
Produces two different alcohols
question
Amide Hydrolysis
answer
Results in COOH + NH?, occurs under acidic conditions via nucleophilic substitution
question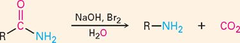
Hofmann Rearrangement
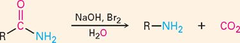
answer
Converts amides to 1° amines with loss of carbonyl as CO?
question
Amide Reduction
answer
Reagent: LAH, results in corresponding amine, no C atom is lost
question
Acyl Halides
answer
Most reactive (least stable) carboxyl derivative, can do Friedel-Crafts acylation, and can be reduced to alcohols or aldehydes
question
Anhydrides
answer
Second most reactive carboxyl derivative, can be formed via substitution or condensation and can perform Friedel-Crafts acylation
question
Esters
answer
Not very reactive carboxyl derivative, hydrolyze to yield acids + alcohols, can react with Grignard reagents to produce a 3° alcohol
question
Amides
answer
Least reactive carboxyl derivative, can be formed by reacting many substrates with amines or ammonia, can be transformed to 1° amines via Hofmann rearrangement
question
Amine Synthesis from -NO?
answer
Iron or Zn as a catalyst
question
Nitrile ? Amine
answer
LAH = lithium aluminum hydride, produces a primary amine
question
Imine ? Amine
answer
Aldehyde or ketone reacted with ammonia, then reduced with hydrogen and a Ni catalyst
question
Amide ? Amine
answer
Reacting an amide with LAH produces RCH?NH?
question
Exhaustive Methylation
answer
Amine ? ammonium iodide ?ammonium hydroxide ? least substituted alkene
question
C=O IR Peak
answer
1750-1800 (sharp)
question
O-H IR Peak
answer
3200 - 3600 (broad)
question
N-H IR Peak
answer
3400 - 3500 (sharp)
question
What is the relationship between the H and LG during an E2 reaction?
answer
They must be anti-periplanar to one another
question
When determining a molecules stero-center configuration (R+S), what direction should the lowest priority group face?
answer
The lowest priority group (usually H) should be facing away from you in a Fischer projection
question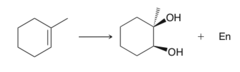
OsO4 / t-BuOOH / base

answer
Syn-diol addition
question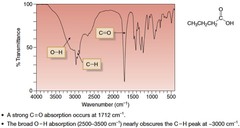
COOH IR Peak

answer
Peak at ~1710 cm?¹
question
What does non-volatile refer to in organic chemistry?
answer
A substance that does not turn into a gas easily, i.e. thing layer chromatography is a method sufficient for separating non-volatile substances
question
Geometric isomer
answer
isomer that differs in the placement of groups around a double bond; cis/trans isomerism



