Breast Cancer wk 6 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion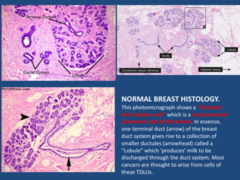
which is a structural and functional unit of the breast. In essence, one terminal duct (arrow) of the breast duct system gives rise to a collection of smaller ductules (arrowhead) called a "Lobule" which 'produces' milk to be discharged through the duct system. Most cancers are thought to arise from cells of these TDLUs.

answer
Terminal duct lobular unit
question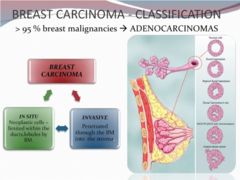
Neoplastic cells-limited within ducts, lubules by BM

answer
Breast carcinoma-In situ
question
penetrated through the BM into stroma
answer
Breast carcinoma-invasive
question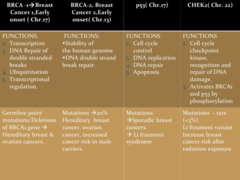
BRCA 1/2 P53 CHEK2

answer
Most common genes implicated in breast carcinoma
question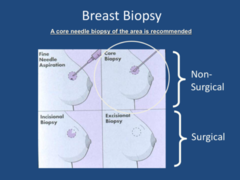
FNA: smaller needle, isolated cells, not useful for finding additional fetures Core Biopsy recommended

answer
Breast Biopsy
question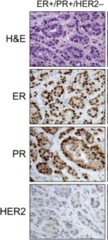
ER, PR, Her2, Ki67 proliferative index Prognosis: tells how well the patient will do Predictive: how well the tumor will respond to certain treatments

answer
Histological studies for BC
question
Big magnet, gadallenium for tracer Anything that has enhanced blood flow, has more gadallenium in it, and appears brighter on MRI (enhancing or lighting up) Important new tool for imaging the breast High sensitivity (low specificity) Detection and characterization of otherwise-occult breast carcinoma
answer
Breast MRI
question
If mastectomy is chosen, then no more treatment necessary, if lumpectomy is chosen then it should be followed by breast irradiation. Then no difference in survival; ( although there appears to be a higher risk of reoccurrence) Irradiation bear a small change of sarcoma (angiosacroma 5-10 years down the road)
answer
lympectomy vs. masectomy
question
Wire gets slipped in, make incision, take out the wire with the lump around it
answer
wire localization during lympectomy
question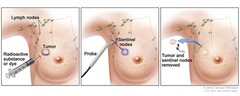
1. Inject around area of tumor with blue dye, radioactivity, or both 2. Track the lymphatic drainage of the tumor The purpose of the sentinel lymph node biopsy is to determine if the FIRST (sentinel) lymph node in the draining chain has cancer. IF the first lymph node is negative, you can assume the other lymph nodes are negative and don't need an axillary dissection.

answer
sentinel lymph node biopsy
question
whole breast irradiation The purpose of the radiation is to kill any residual neoplasm that wasn't removed at surgery. Spill of tumor during surgery Tumor does not grow in a tight little ball, there are tumor cells throughout; if you get radiation, it decreases recurrence
answer
to complete local regional therapy of BC
question
Anti-estrogen therapy
answer
systemic therapy for ER+/PR+/HER-
question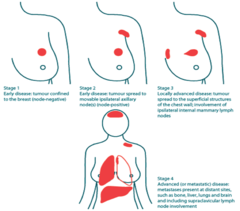

answer
BC staging
question
1. Tubule formation (if there is a lot, its like a breast tissue) 2. Mitotic figures (dividing more rapidly?) 3. Nuclear grade, nuclear: cytoplasmic ratio Stage III: Key here: no gland formation, solid sheet of cancer cells, giant nuclei, high mitotic rate = high grade tumor does not at all look like normal breast tissue
answer
Breast grading
question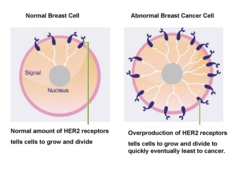

answer
Her2 receptors
question
Standard of care for locally advanced breast cancer Potential for improved surgical outcome Allows "in vivo" test of tumor responsiveness to therapy Exposes micrometastatic tumor cells to chemotherapy at an earlier time point (? better chance for cure) **prior workup should include: Breast MRI (if poorly visualized on mammogram and ultrasound Bone scan CT of the chest, abdomen and pelvis This screens for distant metastasis!!!! Stage 3 versus stage 4 If patient also has headaches, then a Brain scan is also performed The key is that stage 4 brearst cancer can not be cured, however, for stage 3 there is a chance for a cure!!!!!
answer
Preoperative (Neoadjuvant) Chemotherapy
question
This patient has a bad tumor with a high proliferative rate == you will kill proliferating cells with chemotherapy, but need also anti-Her2 (Trastuzumab (Herceptin)) to potentially also target non-proliferating tumor cells and to aid killing of proliferating cell. -mastectomy and auxillary node dissection, and then radiation
answer
treatment for BC with high proliferative rate and HER2+
question
BRCA1, BRCA2, (account for up to 10% of breast cancer types, 25-50% of hereditary breast cancer) PALB2 Next-Gen sequencing done for several genes in hereditary cancer panels (BRCA1/2) Oncotype testing on RNA for RECURRENCE (Breast cancer assay and Mammaprint, i.e. ); Oncotype DX helps predict the chance of metastasis for breast cancers
answer
Types of genetic testing
question
-immunohistochemical staining assay
answer
Types of hormone or receptor testing
question
surgery to remove one or more lumps
answer
lumpectomy
question
remove one or more breasts
answer
mastectomy
question
occur after the primary treatment They may include radiation treatment, chemotherapy, and targeted treatments that are based on the specific characteristics of a particular breast cancer.
answer
Adjuvant treatments
question
done before the primary treatment Neoadjuvant chemo- or targeted therapy may be attempted before surgery to promote shrinkage of a large breast tumor can also give info about tumor responsiveness to drug
answer
Neoadjuvant treatments
question
Higher prevalence of BRCA 1 and 2 in Ashkenazi Jewish ethnicity and others
answer
BRCA mutations are associated with different ethnic groups
question
If you have ER+ breast cancer, your cancer cells grow in the presence of the hormone estrogen By blocking estrogen, doctors can improve the likelihood of controlling ER+ breast cancers. ER+ breast cancers have the most favorable prognosis of all subtypes typically responds to hormone therapy
answer
Estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer
question
The Oncotype DX test is a genomic test that analyzes the activity of a group of genes that can affect how a cancer is likely to behave and respond to treatment Normalized for RNA content using expression of 5 control genes Expression of 16 cancer-related genes analyzed obtain recurrence score
answer
OncotypeDx Breast Cancer Assay
question
breast cancer cells that have hormone receptors. These receptors are special proteins that the hormones estrogen and progesterone bind to. Breast cancer cells that are HR positive depend on estrogen and progesterone to grow. Hormonal therapy blocks the receptors or reduces the amount of hormones that can get into the receptors. As a result, the cancer cells shrink or die.
answer
HR+
question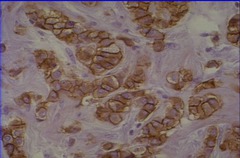
human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 HER2 is a member of the human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER/EGFR/ERBB) family. Amplification or overexpression of this oncogene has been shown to play an important role in the development and progression of certain aggressive types of breast cancer. amplification=>2 HER2 genes/nucleus

answer
HER2
question
Elevated HER2 activity can reduce the growth factor dependence of cells -HER2 does NOT bind a ligand itself, but dimerizes with HER1, HER3, or HER4 (no HER2 dimers) and initiates MAPK pathway -HER3 in a dimer activates prosurvival PI3K signaling -HER2/HER3 heterodimers activate both MAPK and PI3K pathways Consequences Prolonged stimulation of signaling pathways (e.g. MAPK, PI3K) Uncontrolled growth of breast cancer cells Inhibition of apoptosis Resistance to chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and other targeted therapies
answer
Consequences of increased HER2 activity
question
Mediates antibody dependent cytotoxicity (flags HER2+ cancer cell for destruction by immune system) Suppresses HER2 signaling causing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis Herceptin responders often build up RESISTANCE within a year or two Can cause reduced heart function and congestive heart failure
answer
Herceptin (Trastuzumab)
question
normal proteins involved in multiple cellular functions including repair of double-strand breaks in DNA BRCA1 gene is sometimes hypermethylated, which inhibits its expression
answer
BRCA 1 (Breast cancer 1, early onset) and BRCA 2
question
includes RNA Pol II and histone deacetylases. BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 interact with a wide range of proteins involved in transcription, chromosome maintenance, DNA repair and cell cycle control
answer
BRCA 1-associated genome surveillance complex" (BASC)
question
-BC diagnosed before age 50 in family member -Cancer in both breasts in same woman in family -BC and ovarian cancer in same woman or in same family -Multiple BCs in same family -2 or more BRCA-related cancers in single family member -Cases of male BC -Ashkenazi Jewish ethnicity
answer
Family factors associated with increased risk of harmful BRCA mutation in an individual
question
NF1 is a GTPase-activating protein (GAP) aiding hydrolysis of GTP in MAPK signaling NF1 defect present in many other cancers, notably neurofibromatosis NF1 mutants usually cause hyperactivation of MAPK pathway
answer
NF1 (Neurofibromin 1)
question
The ATM gene provides instructions for making a protein that is located primarily in the nucleus of cells, where it helps control the rate at which cells grow and divide. This protein also plays an important role in the normal development and activity of several body systems, including the nervous system and the immune system. Additionally, the ATM protein assists cells in recognizing damaged or broken DNA strands. disease association: ataxia telangiectasia
answer
ATM
question
checkpoint kinase 2 The CHEK2 gene provides instructions for making a protein called checkpoint kinase 2 (CHK2). This protein acts as a tumor suppressor, which means that it regulates cell division by keeping cells from growing and dividing too rapidly or in an uncontrolled way. The CHK2 protein is activated when DNA becomes damaged or when DNA strands break.
answer
Chek2
question
partner and localizer of BRCA2 it interacts with BRCA2 to fix broken DNA
answer
PALB2
question
Chek2 mutant, ATM mutant, PALB2, BRCA 1/2
answer
Genes associated with inherited breast cancer
question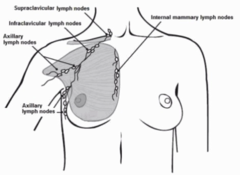
supraclavicular intraclavicular axillary (75%) internal mammary

answer
axillary and other draining lymph nodes
question
fine needle aspiration biopsy non-surgical, distinguish between cyst and non-cyst
answer
FNA
question
biopsy like FNA, uses larger needle to remove sample
answer
core
question
entire lump removed (lumpectomy)
answer
open excision
question
radioisotope to trace lymph node drainage before mastectomy If negative, conclude that cancer has not spread LN-/LN+ (lymph node affected with cancer) status affects how aggressive the breast cancer will be treated
answer
sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB)
question
- Mass detected in breast - Calcifications seen in Xray - Architectural distortions (MRI)
answer
why perform biopsy?
question
Radioisotope injected several hours before surgery. Location of probe located visually (dye) and with Geiger counter (99mTc) Sentinel Lymph Nodes (SLNs) and tumor removed
answer
Sentinel Node Lymphoscintigraphy
question
Non-invasive breast cancer with cells only in the ducts, not in breast tissue, with low risk of being lymph node positive
answer
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
question
Cancer cells escaped ducts or lobules and invaded breast tissue; higher risk of lymph node positive than with DCIS (ductal-IDC, lobular-ILC)
answer
Invasive (inflitrating) carcinoma (IDC or ILC)
question
-Uncommon (1-3% of all breast cancers) -Usually no lump, but skin red, pitted, or feel warm -Breast may be enlarged, hard, tender or itchy -May be unremarkable on mammogram
answer
Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC)
question
actin-rich protrusions of the plasma membrane that are associated with degradation of the extracellular matrix in cancer invasiveness and metastasis. how cancer cells escape primary tumor
answer
Invadopodia
question
are a group of enzymes that in concert are responsible for the degradation of most extracellular matrix proteins during organogenesis, growth and normal tissue turnover. how cancer cells escape primary tumor
answer
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)
question
ER+: cells grow in response to the hormone estrogen PR+: cells grow in response to progesterone HER2: human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; HER2 proteins are receptors on breast cells. Normally, HER2 receptors help control how a healthy breast cell grows, divides, and repairs itself
answer
receptors and breast cancer
question
Invasive vs in situ disease Presence of distant metastasis (Stage IV) Presence of lymph node metastasis (*most important factor in cases without distant metastases) Size (cutoffs 5 cm) Inflammatory, chest wall or skin invasion (Stage III) used to assign stage
answer
major prognostic factors
question
Nottingham grade Histologic type Hormone receptor status HER2 status Proliferative rate Lymphovascular invasion predictive of response to therapies
answer
minor prognostic factors
question
Score of 1-3 assigned in 3 categories: Tubule formation Mitotic count Nuclear pleomorphism (how much variation there is in nuclear size, shape and staining properties)
answer
Nottingham grade
question
Classification based on: -Extent of primary tumor -Presence in lymph nodes -State of metastasis to other organs (e.g. brain, bone, lung, liver, other)
answer
Traditional Breast Cancer Staging (TNM)
question
This parameter assesses what percent of the tumor forms normal duct structures. In cancer, there is a breakdown of the mechanisms that cells use to attach to each other and communicate with each other, to form tissues such as ducts, so the tissue structures become less orderly.
answer
Tubular formation
question
This parameter assesses whether the cell nuclei are uniform like those in normal breast duct epithelial cells, or whether they are larger, darker, or irregular (pleomorphic). In cancer, the mechanisms that control genes and chromosomes in the nucleus break down, and irregular nuclei and pleomorphic changes are signs of abnormal cell reproduction.
answer
Nuclear Pleomorphism
question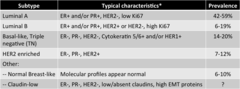
1. luminal A 2. Luminal B 3. Basal-like, Triple negative (TN) (15%) 4. HR2 enriched others: Normal breast-like, claudin-low

answer
4 main molecular subtypes of breast cancer
question
Typically are larger and a higher TNM grade High rate of recurrence High rate of distant metastasis Not susceptible to therapies targeted against cancer cells with estrogen, progesterone, or HER2 receptors
answer
Triple Negative Breast Cancers (TNBC)
question
chemotherapy PARP inhibitors
answer
Treatment of Triple Negative Breast Cancers (TNBC)
question
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase catalyzes ribosyltransferase addition of ADP-ribose units Under normal conditions, PARP activity is associated with converting chromatin to a transcriptionally active unit PARP is involved in several cellular processes -Transcriptional activation via chromatin opening -Programmed cell death (Apoptosis) -DNA repair PARP deficiency Causes defect in DNA repair and other consequences
answer
PARP
question
PARP inhibitors prevent base excision repair and cause death in cells with BRCA defects (which would normally repair dsDNA breaks) BRCA-deficient cancer cells don't repair the multiple dsDNA breaks observed, and cell dies (PARP catalytic inhibitors) DNA replication blocked by trapped PARP; cell dies (PARP poison)
answer
PARP inhibitors
question
nuclear protein present in actively dividing cells; marker of proliferation
answer
Ki67
question
heterodimer of cytokeratins 5 and 6; subunits of keratin-containing intermediate filaments found in the basal/myoepithelial cells in the breast Primary tumors and metastases of a given carcinoma share the same pattern of cytokeratins, that distinguishes them from other types of carcinomas
answer
Cytokeratin 5/6
question
are a family of proteins that are the most important components of the tight junctions, where they establish the paracellular barrier that controls the flow of molecules in the intercellular space between the cells of an epithelium. cellular tight-junction proteins; absence of claudins is characteristic of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) leading to cancer development
answer
Claudin
question
is a process by which epithelial cells lose their cell polarity and cell-cell adhesion, and gain migratory and invasive properties to become mesenchymal stem cells; these are multipotent stromal cells that can differentiate into a variety of cell types.
answer
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)
question
non-coding RNAs regulating gene expression post-transcriptionally by binding to complementary sequence and causing degradation or inhibition of translation of that mRNA potential: stimulate miRNAs binding to oncogene mRNAs or inhibit miRNA binding to tumor suppressor mRNAs
answer
miRNAs
question
Delivery of 1-5 high-potent biological doses of radiation to the tumor Multiple radiation beam angles used to deliver the radiation A sharp dose gradient outside of tumor protects healthy tissue: minimize dose to any individual region of tissue outside of tumor; reduced tissue damage and reduced incidence of radiation burns
answer
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT)
question
Radioactive seeds (commonly iridium) fed through flexible, plastic catheter(s) into lumpectomy cavity to kill any tumor cells
answer
Breast Brachytherapy
question
Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) and epirubicin (Ellence) Adriamycin replaced earlier treatments with cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and 5-FU Most effective for HER2+ breast cancer Side effects Short term: nausea, hair loss Long term: heart damage (1-2%) and leukemia (;1%)
answer
Anthracycline Chemotherapy
question
A taxane that binds beta-tubulin and stabilizes mitotic spindles, thus inhibiting required tubulin depolymerization cycle Cyclophosphamide: "Nitrogen mustard alkylating agent" adds group (CnH2n+1) to guanine at position 7; causes intra- and interstrand DNA cross-links
answer
Taxotere (docetaxel) Chemotherapy
question
-Alter estrogen receptor activity (selective estrogen receptor modulator, SERM,) e.g. Tamoxifen -Inhibit estrogen synthesis (Aromatase Inhibitor, AI) -Selective estrogen receptor down-regulator (SEDR) e.g.fulvestrant (Faslodex); used for metastatic ER+ BC if get disease progression post anti-estrogen therapy -Interfere with hypothalamopituitary-gonadal regulatory axis to suppress estrogen formation (ovarian ablation/suppression)
answer
Targeting of Estrogen Response in Breast Cancer
question
SERM, e.g. Tamoxifen, competes with estrogen for binding to receptor Tamoxifen blocks binding of co-activators to receptor, so inhibits activation of gene expression
answer
(selective estrogen receptor modulator, SERM,) e.g. Tamoxifen
question
1. Estrogen receptor (ER) interacts with estradiol (E2) 2. Hormone/receptor complex binds estrogen DNA response elements (ERE) 3. Genes with ERE are transcribed
answer
Normal Estrogen Receptor Binding to Estradiol (E2) Ligand
question
Cytochrome P450 enzymes are involved in metabolizing Tamoxifen 4 phenotypes of CYP2D6: UM = Ultrarapid Metabolizer EM = Extensive Metabolizer IM = Intermediate Metabolizer PM = Poor Metabolizer Women with CYP2D6 *4/*4 genotype tend to have poor-metabolizer status for Tamoxifen (less ability to make metabolites (endoxifen) that block ER binding?)
answer
CYP2D6
question
Tamoxifen used in treatment of ER+ breast cancer Tamoxifen converted to various metabolites that have a greater affinity for the ER 4-hydroxytamoxifen 4-hydroxy-N-desmethyl tamoxifen ("Endoxifen") Cytochrome P450 enzymes are involved in metabolizing Tamoxifen, mainly CYP2D6
answer
Tamoxifen
question
The cytochrome P450 (CYP) family of enzymes is responsible for primary metabolism of many drugs. UM = Ultrarapid Metabolizer* EM = Extensive Metabolizer* IM = Intermediate Metabolizer PM = Poor Metabolizer *good for tamoxifen treatment
answer
Cytochrome P450 2D6 Testing for Tamoxifen Resistance
question
is a cytochrome P450 (CYP19) enzyme catalyzing conversion of androgens to estrogens
answer
Aromatase
question
Aromatase inhibitors block all estrogen production, thus used in postmenopausal women (otherwise instant menopause) Overall aromatase inhibitors do a slightly better job in decreasing recurrence and mortality Aromatase inhibitors work by blocking the enzyme aromatase, which turns the hormone androgen into small amounts of estrogen in the body causes the opposite offect in pre-menopausal women.
answer
Aromatase Inhibitors (AIs)
question
Oophorectomy or Radiation
answer
Permanent ovarian ablation
question
Used in premenopausal women Interferes with hypothalamopituitary-gonadal axis to suppress estrogen formation Give LHRH analog Zoladex (goserelin) which inhibits FSH and LH production from pituitary Consequence is inhibition of ovarian follicle estrogen production
answer
Temporary ovarian suppression



