Pathoma- Chapter 9: Lung Cancer – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What is the most common cause of cancer mortality in the US (high-yield)?
answer
-Lung Cancer
question
What are the most common cancers by incidence?
answer
1.) Breast (women); Prostate (men) 2.) Lung cancer 3.) Colorectal carcinoma
question
What is the average of presentation for lung cancer?
answer
-60 y.o.
question
What are the key risk factors for lung cancer?
answer
-Smoking (85% of lung cancers occur in smokers)
question
What is the key carcinogen in cigarette smoke? (very high-yield)
answer
-Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons -Arsenic
question
What does arsenic increase the risk of?
answer
-Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung
question
How is the risk of lung cancer related to smoking?
answer
-Cancer risk is directly related to the duration and amount of smoking ('pack years')
question
Risk Factors for Lung Cancer Where does radon come from?
answer
-Radon is formed from the radioactive decay of uranium- which is present in the soil all around us -Can accumulate in closed spaces such as basements- as a colorless, odorless gas -It can go into the lung cancer
question
What is the 2nd most frequent cause of lung carcinoma in the US?
answer
-Radon exposure -It is responsible for most of the public exposure to ionizing radiation, too
question
Radon exposure is the cause of increased risk of lung cancer in what profession?
answer
-Uranium miners
question
Patients who are exposed to asbestos are much more likely to develop what form of lung neoplasm?
answer
-Lung cancer rather than mesothelioma
question
How do pts. who have lung cancer present?
answer
-They present with non-specific symptoms, i.e., cough, weight loss, hemoptysis, post-obstructive pneumonia
question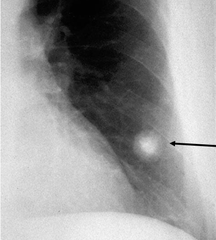
What will CXR classically reveal in a pt. with lung cancer?

answer
-A 'coin lesion' or a solitary nodule
question
What is the next step after you have identified a solitary nodule in a pt. (very high-yield)?
answer
-Go back and compare this x-ray to a prior x-ray -If the coin lesion has been there for quite sometime and has been stable- much morel likely that it represents something benign -If the coin lesion is new or has been growing- it would require a biopsy in order to ascertain the diagnosis of cancer
question
What are some benign lesions that could present as coin lesions?
answer
-Granuloma -Bronchial hamartoma; often calcified on imaging -A young pt. with a coin lesion- say less than the age of 40 is much more likely to have a benign lesion than they are to have cancer
question
What would the granuloma that presented as a coin lesion be due to?
answer
-TB or a fungus
question
In the midwest, which fungus would you think about as the cause of a coin lesion (very high-yield)?
answer
-Histoplasma
question
What is a hamartoma?
answer
-A benign mass comprised of tissue that normally belongs in that location, but it is disorganized
question
What do bronchial hamartomas contain (very high-yield)?
answer
-Lung tissue and cartilage
question
How will a bronchial hamartoma appear on imaging?
answer
-It is often calcified on imaging
question
What are the classic division of lung carcinoma?
answer
-Small-cell carcinoma (15%) -Non-small cell carcinoma (85%) -This distinction is made by the pathologist when looking at the cells under the microscope
question
How is small cell carcinoma treated?
answer
-It is usually not amenable to surgical resection (treated with chemotherapy and radiation instead) "cells of small cell carcinoma are so small that the surgeon can't see them"
question
How is non-small carcinoma treated?
answer
-Treated upfront with surgical resection and is usually not amenable to chemotherapy
question
What are the major subtypes of non-small cell carcinoma?
answer
-Adenocarcinma (40%) -Squamous cell carcinoma (30%) -Large cell carcinoma (10%) -Carcinoid tumor (5%)
question
What are the 2 key features of an adenocarcinoma of the lung (very high-yield)?
answer
-Glands and mucus production
question
What are the key features of a squamous cell carcinoma of the lung (very high-yield)?
answer
-Keratin pearls and intracellular bridges
question
If we don't see glands, mucus production, keratin pearls, or intracellular bridges, what kind of non-small cell carcinoma is it?
answer
-Large cell carcinoma
question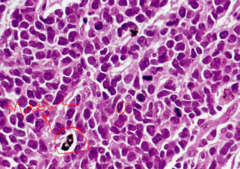
What is the characteristic histology of small cell carcinoma?

answer
-Poorly-differentiated small cells -The tumor is mitotically-active and exhibits necrosis
question
Small Cell Lung cancer is highly associated with what risk factor?
answer
-Male smokers
question
Where will the small cell lung cancer be located in the lung?
answer
-Central tumor
question
What are the paraneoplastic syndromes seen in small cell lung cancers?
answer
-SIADH (+ hyponatremia) -Ectopic ACTH production -Lambert-Eaton Syndrome
question
Small Cell Lung Cancer: Paraneoplastic Syndromes What is Lambert-Eaton Syndrome?

answer
-Pts. develop antibodies against presynaptic Ca2+ channels causing muscle weakness
question
Mnemonic for Small Cell Lung Cancer
answer
-Small Cell -(male) Smokers -Central -Paraneoplastic Syndromes (small, smoke, ssentral, syndromes)
question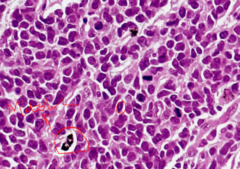
Histology of Small Cell Carcinoma

answer
-Relatively small cells that mimic lymphocytes in their size -There is also a significant degree of mitotic activity
question
Small Cell Carcinomas arise from what cells (very high-yield)?
answer
-Arise from neuroendocrine (Kulchitsky) cells
question
What stain is positive in small cell carcinomas (very high-yield)?
answer
-Chromogranin positive
question
What two tumors will be chromogranin +?
answer
small cell carcinoma carcinoid tumor (non-small cell)
question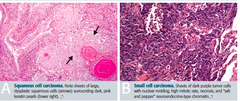
How is squamous cell carcinoma defined on histology?

answer
-Have to see keratin pearls or intercellular bridges
question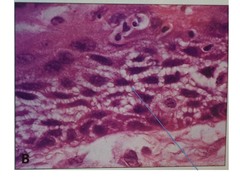
Intercellular Bridges in Squamous Cell Carcinoma

answer
-These lines represent the desmosomal connections between the squamous cells -This is because squamous cells are normally connected to each other via desmosomes
question
What is the most common tumor seen in male smokers?
answer
-Squamous cell carcinoma
question
Where will squamous cell carcinoma tumors be located in the lungs?
answer
-Central tumor
question
What is the paraneoplastic syndrome associated with squamous cell carcinoma (very high-yield)?
answer
-May produce Parathyroid-related peptide- resulting in hypercalcemia
question
How is an Adenocarcinoma defined?
answer
-The presence of glands or mucin production
question
What is the most common lung cancer in nonsmokers and female smokers (high-yield)?
answer
-Adenocarcinoma
question
Where is adenocarcinoma classically located in the lung?
answer
-Peripheral tumor
question
Gross Image of an Adenocarcinoma of the Lung

answer
-Notice that the tumor is way out at the edge of the lung- up against the pleura- it is peripherally located
question
How is a large cell carcinoma defined?
answer
-Poorly-differentiated large cells (no keratin pearls, no intercellular bridges, no glands, and no mucin production)
question
Characteristics of Large Cell Carcinoma?
answer
-Not related to smoking -Can be central or peripheral -Hs a poor prognosis
question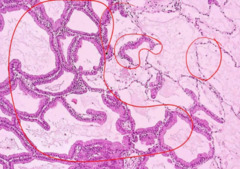
What is bronchioloalveolar carcinoma (Adenocarcinoma in-situ)?

answer
-Columnar cells that grow along preexisting bronchioles and alveoli
question
Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma arises from what cells (very high-yield)?
answer
-Clara cells
question
Bronchioloalveolar carcinomas are located where in the lung?
answer
-Peripheral tumors
question
How can Bronchioloalveolar carcinomas present on imaging (very high-yield)?
answer
-Can present with pneumonia-like consolidation on imaging (very high-yield)
question
What is the prognosis of Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma?
answer
-It has an excellent prognosis
question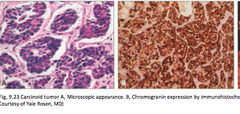
What is a carcinoid tumor?

answer
-A tumor of well-differentiated neuroendocrine cells -Will see nests of cells
question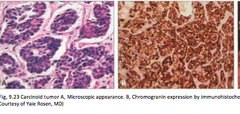
The cells in a carcinoid tumor will be positive for what markers (very high-yield)?

answer
-Chromogranin positive (very high-yield) -Neuroendocrine cells will contain neurosecretory granules within their cytoplasm- those neurosecretory granules will stain chromogranin positive on IHC
question
Where can carcinoid tumors be located?
answer
-Can be either central or peripherally located
question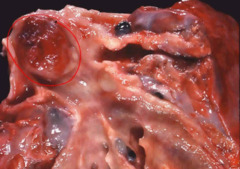
What is the classic tumor seen with a carcinoid tumor (very high-yield)?

answer
-A polyp-like mass in the bronchus -This is how it shows up on examinations!!!!
question
What is the prognosis of a carcinoid tumor?

answer
-Low-grade malignancy -Rarely can cause carcinoid syndrome
question
What are the most common sources of metastasis to the lung?
answer
-Breast and colon carcinoma -Will appear as multiple 'cannon ball' nodules on imaging
question
Which form of cancer is more common in the lungs: metastasis or primary tumors?
answer
-Metastasis is more common than primary tumors
question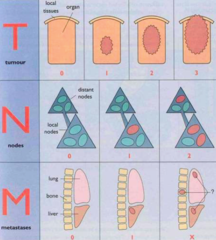
TNM Staging What is the T?

answer
-T- size and local extension of the tumor -N- spread to regional lymph nodes (hilar and mediastinal) -M- unique site of distant spread is the adrenal gland
question
What is a unique site for lung metastasis (very high-yield)?
answer
-The adrenal gland -Very high-yield!!!!!
question
What is the overall 5-year survival for lung cancer?
answer
-15% (fairly poor) -This is because it presents so late in the course of the disease
question
Local Complications of Lung Carcinoma Which type of lung cancer will involve the pleura?
answer
-Adenocarcinoma- because adenocarcinoma is usually peripheral -Adenocarcinoma is the most common tumor seen in non-smokers and female smokers
question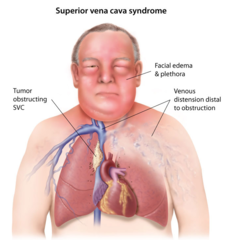
Local Complications of Lung Carcinoma What is SVC Syndrome?

answer
-This is when pts. have distended head and neck veins with edema and blue discoloration of the arms and face
question
Involvement of recurrent laryngeal or phrenic nerve would present as?
answer
Recurrent laryngeal: This would result in hoarseness Phrenic - Diaphragmatic paralysis
question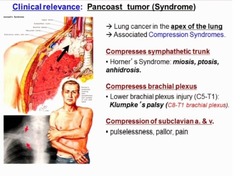
Local Complications of Lung Carcinoma What happens if the tumor compresses the sympathetic chain?

answer
-This happens when a tumor is located in the apex of the lung, i.e., a pancoast tumor -It results in ptosis, pinpoint pupil, and anhidrosis aka: Horner's syndrome
question
Large Cell Carcinoma IHC for Adenocarcinoma
answer
-TTF-1
question
Large Cell Carcinoma IHC for Squamous Cell Carcinoma
answer
-p40
question
Large Cell Carcinoma IHC for Neuroendocrine tumors?
answer
-Chromogranin (Small Cell and Carcinoid tumors)
question
What is the recommended screening for patients with long smoking history?
answer
-Screening by low-dose CT recommended for pts. with long smoking history
question
Lung Cancer and Driver Mutation Testing What mutations are particularly common in adenocarcinoma?
answer
-EGFR mutation -ALK translocation
question
Lung Cancer and Driver Mutation Testing What drug is used to treat adenocarcinomas with EGFR mutations?
answer
-Erlotinib
question
Lung Cancer and Driver Mutation Testing What drug is used to treat adenocarcinomas with ALK translocations?
answer
-Crizotinib
question
Lung Cancer and Driver Mutation Testing What mutation can be seen in any non-small cell lung cancer?
answer
-PD-L1 expression
question
Lung Cancer and Driver Mutation Testing What drug is used to treat lung cancers with PD-L1 expression?
answer
-Pembrolizumab



