First Aid – Primary Brain Tumors (do pics first so flip) – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Adult brain tumor characteristics
answer
Most are supratentorial, half are metastases (well circumscribed at gray-white junction)
question
Cause of clinical presentation
answer
Mass effects (seizures, dementia, focal lesions)
question
Three most common adult primary brain tumors
answer
glioblastoma multiforme>meningioma>schwannoma
question
grave prognosis (<1 year), cerebral hemispheres, can cross corpus callosum ("butterfly glioma") stain for GFAP, what term goes with this?
<img src="https://chmanchacentro.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/grave-prognosis.jpg" title="grave prognosis (<1 year), cerebral hemispheres, can cross corpus callosum ("butterfly glioma") stain for gfap, what term goes with this?" alt="grave prognosis (
answer
Glioblastoma multiforme pseudopalisading (pleomorphic tumor cells with central areas of necrosis and hemorrhage)
question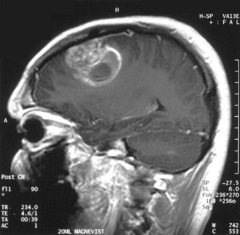
Glioblastoma multiforme: how common? survival? location? stain? histo?

answer
common; <1 year; cerebral hemispheres and can cross corpus callosum; GFAP; histo= pseudopalisdading pleomorphic tumor cells that border areas of necrosis and blood
question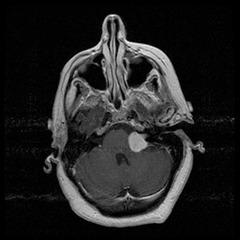
Antoni A and B

answer
Schwannoma
question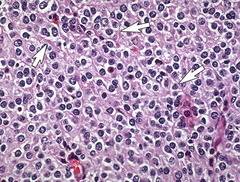
Oligodendrocytes = fried eggs cells

answer
Oligodendroglioma
question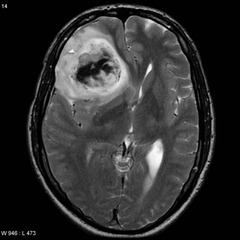
relatively rare, slow growing, usually frontal lobes, chicken-wire capillary pattern with "fried-egg" oligodendrocytes often calcified

answer
oligodendroglioma
question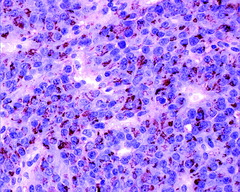
Hyper or hypopituitarism

answer
pituitary adenoma
question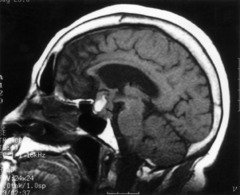
most commonly prolactinoma bitemporal hemiaopia (pressure on optic chiasm), hyper or hypopituitary sequelae from Rathke's pouch

answer
pituitary adenoma
question
childhood peak incidence primary brain tumors
answer
pilocytic astrocytoma, medulloblastoma, ependymoma, hemangioblastoma, craniopharyngioma
question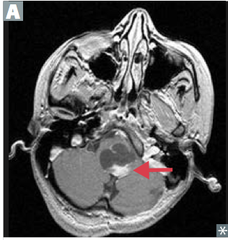
usually well circumscribed, most often in posterior fossa (in kids), may be supratentorial GFAP positive, benign, good prognosis Rosenthal fibers—eosinophilic, corkscrew fibers, cystic and solid; has a CYST with PROTRUDING NODULE

answer
pilocytic astrocytoma
question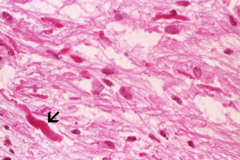
Rosenthal fibers

answer
pilocytic astrocytoma
question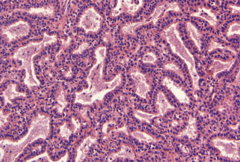
Solid, small blue cells. Radiosensitive

answer
Medulloblastoma
question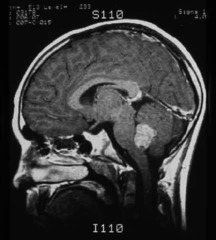 hydrocephalus" alt="A form of primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET); present with coordination problems; occurs in cerebellar vermis; compress 4th ventricle --> hydrocephalus">
hydrocephalus" alt="A form of primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET); present with coordination problems; occurs in cerebellar vermis; compress 4th ventricle --> hydrocephalus">
A form of primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET); present with coordination problems; occurs in cerebellar vermis; compress 4th ventricle --> hydrocephalus
 hydrocephalus" alt="A form of primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET); present with coordination problems; occurs in cerebellar vermis; compress 4th ventricle --> hydrocephalus">
hydrocephalus" alt="A form of primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET); present with coordination problems; occurs in cerebellar vermis; compress 4th ventricle --> hydrocephalus">answer
Medulloblastoma
question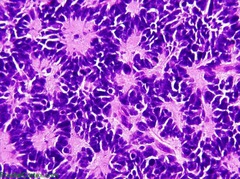
highly malignant cerebellar tumor—can compress 4th ventricle causing hydrocephalus PNET—primitive neuroectodermal tumor rosettes/pseudorosettes, solid, small blue cells, radiosensitive

answer
medulloblastoma
question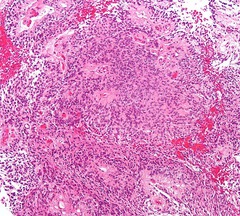
ependymal cell tumor usually in the 4th ventricle (hydrocephalus). poor prognosis perivascular pseudorosettes, rod-shaped blepharoplasts (basal ciliary bodies) near nucleus.

answer
Ependymoma
question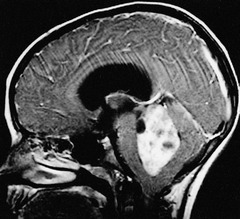
Characteristic perivascular pseudorosettes. Rod-shaped blepharoplasts

answer
Ependymoma
question
usually cerebellar—foamy cells and high vascularity associated with vHL syndrome if found with retinal angiomas can produce EPO causing secondary polycythemia see thin walled capillaries with minimal intervening parenchyma
answer
Hemangioblastoma
question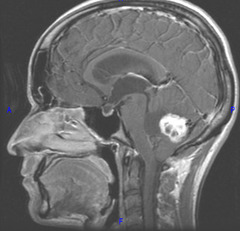 secondary polycythemia" alt="Foamy cells and high vascularity; associated with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome when found with retinal angiomas; can produce erythropoietin --> secondary polycythemia">
secondary polycythemia" alt="Foamy cells and high vascularity; associated with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome when found with retinal angiomas; can produce erythropoietin --> secondary polycythemia">
Foamy cells and high vascularity; associated with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome when found with retinal angiomas; can produce erythropoietin --> secondary polycythemia
 secondary polycythemia" alt="Foamy cells and high vascularity; associated with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome when found with retinal angiomas; can produce erythropoietin --> secondary polycythemia">
secondary polycythemia" alt="Foamy cells and high vascularity; associated with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome when found with retinal angiomas; can produce erythropoietin --> secondary polycythemia">answer
Hemangioblastoma
question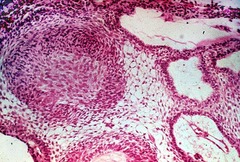
From Rathke's pouch (derived from outpouching of mouth), can have calcifications; benign; bitemporal hemianopsia

answer
Craniopharyngioma
question
benign childhood tumor (most common childhood supratentorial tumor), confused with pituitary adenoma (because it can also cause bitemporal hemianopia). derived from remnants of Rathke's pouch, calcification is common
answer
craniopharyngioma
question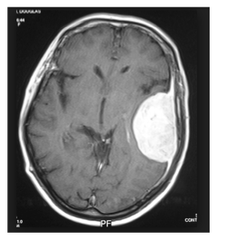
meningioma: how common? aggressive or benign? location? arises from? histo?

answer
common; benign; usually asymptomatic but can present with seizures; occurs in convexities of hemispheres and parasagittal region; arises from arachnoid cells and is extra axial (so external to brain parenchyma) and can have a dural attachment called a tail (see picture); histo= spindle cells concentrically arranged in whorled pattern; psammoma bodies are laminated calcifications
question
brain tumor with estrogen r's
answer
meningioma
question
s100 + & location
answer
schwannoma; cerebellopontine angle usually but possible along any peripheral nerve; often with CN VIII--> vestibular schwannoma, see bilaterally with NF-2
question
mneumonic for oligodendroglia
answer
"oh leg go my ego" for fried egg appearance
question
pituitary adenoma
answer
prolactinoma; bitemporal hemianopsia due to pressure on optic chiasm; hyper or hypopituitarism are sequelae (prolactinoma --> hypogonadism)
question
mnemonic for adult brain cancer causes
answer
MGM Studios Mets, Glioblastoma, Meningioma, Schwannoma (also have hemangioblastoma -von HL w/ retinal angiomas and can produce erythropoietin-; Oligodendroglia and Pituitary adenoma- prolactinioma)
question
mnemonic for childhood brain cancer causes
answer
Animal Kingdom, Magic Kingdom, Epcot Astrocytoma, Medullobastoma, Ependymoma (also have craniopharyngioma)
question
which brain tumor matches the following: pseudopalisading necrosis polycythemia neurofibromatosis type 2 assoc w/ von hippel-lindau foamy cells, high vascularity hyperprolactinemia --> galactorrhea, amenorrhea, anovulation
answer
glioblastoma multiforme hemangioblastoma schwannoma hemangioblastoma hemangioblastoma pituitary adenoma
question
which brain tumor matches the following: psammoma bodies fired egg appearance perivascular pseudorosettes bitemporal hemianopia worst prognosis child w/ hydrocephalus homer-wright pseudorosettes
answer
meningioma oligodendroglia ependyoma pituitary adenoma (adult); craniopharyngioma (child) glioblastoma multiforme meduloblastoma or ependyoma meduloblastoma



