Veterinary Anaesthesia: Equipment – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What are two forms of administering a GA?
answer
1. injectable (IV) 2. inhalational
question
What equipment do you need for injectable?
answer
-Syringes, needles, catheters, syringe drivers -Inexpensive
question
What equipment do you need for inhalational?
answer
-Source of oxygen -Anesthesia machine -Breathing circuits
question
What is an adv of inj? inhalational?
answer
- inexpensive, more mobile - can ventilate, good life support
question
Catheter types?
answer
1. over the needle: common 2. through the needle catheter: less common, more for long term
question
What is inhalational anaesthesia?
answer
- Anaesthetic drug and carrier gas administered to lungs using an anaesthetic machine
question
Why is a patient usually intubated?
answer
artificial airway (endotracheal tube) -Allows ventilation -Airway protection -No leakage of gases, - accurate administration → animal getting the right amount of drug
question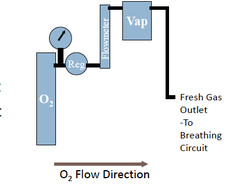
What is the order of components for the anesthetic machine?

answer
O2 Source (pressure gauge) Regulator Flowmeter Vaporiser Fresh Gas Outlet Breathing Circuit
question
What does the regulator do?
answer
- steps down the pressure - lower and maintain downstream pressure - cant give 02 at the high pressure its stored at
question
What are the types of carrier gases used?
answer
- medical grade N2O AND O2
question
What colour or O2 tanks? What colour are N20 tanks?
answer
- white or green or both - blue
question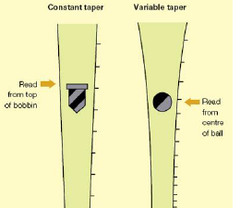
What are flowmeters? Where do you read the ball? the bullet?

answer
measure the gas flow Specific for gas (density, viscosity) Colour coded, Precision read from centre of ball, top of bobbin
question
What are precision vaporizers? Where are they situated?
answer
- Vaporizes anesthetic agent and delivers at set concentration (% output) - before breathing circuit
question
What are the compensated for?
answer
- temperature - sea level?
question
Can you use any vaporizer with any inhalant?
answer
- no, specific for agent
question
How is safety maintained with vaporizers?
answer
-Keyed filler systems -Colour coded
question
What are the functions of breathing circuits? 3
answer
Used to deliver O2 and anesthetic gases to patient Allow removal of waste gases (CO2) Allow ventilation of lungs
question
What are two designs of breathing circuits? What is this designs based on?
answer
1.Non-Rebreathing systems 2. Rebreathing systems - based on method of CO2 removal
question
What are basic components of all types of breathing circuits? 5
answer
- adapters: Attaches hoses to mask or endotracheal tube - rebreathing bag - breathing tubes/hoses - exhaust valves (pop off valve) - scavenging system
question
What size should the bag be?
answer
6-10 X TV ( 10-15 ml/kg) of patient
question
What is the function of this bag? 3

answer
-Reservoir of gases during inspiration -View respiratory movements -Ventilate lungs
question
What are breathing tubes? What is a potential problem associated with breathing tubes?
answer
-Provides connection and reservoir for gases -Apparatus Dead Space: Potential area for CO2 collection
question
What are exhaust valves? 2 What position should it always be left in? When is it closed?
answer
-Prevents excess pressure building up in circuit -Closing and squeezing bag allows lung ventilation -Leave open except when ventilating lungs
question
What is the scavenging system?
answer
-Conducts waste anesthetic gases away from workspace
question
Describe a rebreathing circuit? What does CO2 removal depend on?
answer
• Gases flow in circle so they go through soda-lime • Two unidirectional valves are included in circuit
question
Compare the resistance of a rebreathing to a bains?
answer
rebreathing has greater resistance
question
What patients do we usually use a rebreathing in?
answer
- > 10 kg
question
Why is a rebreathing used?
answer
- more economical → lower flow rates (10-30 ml/kg/min O2 flow) - less wasteful of gases → recycled - but to avoid build-up of CO2 → need soda lime - modern machines allow use of rebreathing in 2kg patients
question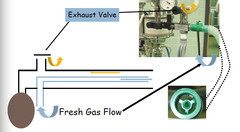
What is a non rebreathing circuit? What does CO2 removal depend on? What is fresh gas flow set at?

answer
- bain system - CO2 Removal dependent on fresh gas flow: 150 - 200 ml/kg/min during expiratory pause - hi flow flush out co2 away from vacninity where it might be inhaled
question
Is the CO2 in the bag in a bain system a concern?
answer
- no, generally patient too small to inhale from the bag
question
what size patients do you use bain in?
answer
- <10 kg
question
What is a Ayres T piece?

answer
- Fresh gas flow 200-300 mL/kg/min (use - on <10 kg) CO2 flushed to expiratory limb during expiratory pause - common in dentals
question
When is the O2 flush system used? What is this flush system? What is it not used for? When don't you ever used it? What can be a complication?
answer
Only use with circle rebreathing system 30 L/min oxygen bypasses vaporizer to circuit -Not used to deepen anesthesia Used to flush out circle system of anesthetic → emergency NEVER use with Bain circuit!!!! -Barotrauma likely
question
What is a circuit pressure gauge? What should the pressure never exceed when bagging? What else can you observe to guide how much pressure you are adding while bagging?
answer
Guide for ventilation of lungs Not greater than 10 - 25 cm H2O pressure -But watch chest expansion as well
question
What are scavenging systems? What must you ensure about the strength of the system? Where can you scavenge out to? How long should your tubing be leading to the scavenging system? What is a charcoal absorption system?
answer
Exhaust valve shrouds •Active extraction systems • Ensure not too strong • Hose outside wall/window • Not longer than 2 metres • Charcoal adsorption system • Throw out when gains 50g
question
What are two types of ET? Which one is used in birds? why?
answer
- cuffed → seals of with tracheal wall - non - cuffed → good for birds, otherwise too much pressure, have complete tracheal rings
question
What Size tube should you choose?
answer
- choose the one with the largest diameter - have 3 out to pick from - always check your tubes first for any abnormalities - check cuffs for leaks
question
How are the airways secured?
answer
Inflate cuff as soon as possible Deflate at last minute before extubation
question
Describe correct placement of ET?
answer
- Select range of 3 possible diameters - Pre-measure before anesthesia from mid - lower neck to incisor teeth
question
Describe correct cuff inflation?
answer
Test for leaks first Ventilate lungs Listen for leak Inflate cuff repeat
question
Describe your do's and don'ts for equipment?
answer
Always check anesthetic equipment prior to use Understand how the equipment functions Anticipate problems and prepare Service anesthetic machine and vaporizer regularly Never use O2 flush system with Bain circuit Never leave exhaust valve closed down for lengthy periods -Pressure will build up and patient cannot exhale Keep environment free from waste gas contamination
question
What 2 breathing systems are in use today?
answer
Semi-closed and Closed systems fully bound systems, closed to atmospheric air inhaled gas is controlled, fresh gas ex high pressure cylinder and reducing valve
question
Semiclosed system
answer
high flow
question
Closed system
answer
low flow
question
non-rebreathing system examples
answer
all Semiclosed, high flow systems: Ayres T piece Bain coaxial system Magill attachment Lack coaxial system Parallel lack system
question
rebreathing system examples
answer
closed (low flow) or semi-closed (medium to high flow) systems: circle absorber waters to and fro
question
Carbon dioxide removal - 2 ways
answer
1. high gas flow flushes CO2 into atmosphere 2. Absorption CO2 by chemical reaction soda lime - calcium hydroxide baralyme - calcium hydroxide (80%) and barium hydroxide PLUS need KOH, NaOH (more reactive hydroxides) and Water for the reaction summarised as Ca(OH)2 + CO2--> CaCO3 + H2O
question
How can you establish whether absorbent is active?
answer
chemical indicators change colour with pH - don't rely on colour alone as colour can bleach out if not changed 2. exothermic reaction--> heat where reaction taking place 3. granules- fresh crumble easily, exhausted granules are hard



