Dosing of Propofol, Etomidate and Lidocaine
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Propofol (induction dose)
answer
1-2.5 mg/kg
question
Propofol (maintenance)
answer
100-200 mcg/kg/min
question
Propofol (conscious sedation)
answer
25-75 mcg/kg/min
question
Propofol (onset)
answer
30 seconds
question
Propofol (duration)
answer
3-8 minutes
question
Etomidate (induction dose)
answer
0.2-0.6 mg/kg
question
Etomidate (onset)
answer
30-60 seconds
question
Etomidate (duration)
answer
3-5 minutes
question
Lidocaine (induction dose)
answer
1.5 mg/kg
question
Lidocaine (max LA dose w/out Epi)
answer
4 mg/kg
question
Lidocaine (max LA dose w/ Epi)
answer
7 mg/kg
question
Ketamine (IV dose induction)
answer
2-4 mg/kg
question
Ketamine (PO)
answer
10mg/kg
question
Ketamine (IV infusion or iv push)
answer
15-45 mcg/kg/min (1-3 mg/min infusion) 0.5-1.0 mg/kg iv
question
Ketamine (IM dose)
answer
4-6 mg/kg
question
Ketamine (IV onset)
answer
1-2 minutes
question
Ketamine (IM onset)
answer
3-8 minutes
question
Ketamine (IV duration)
answer
6-15 minutes
question
Ketamine (IM duration)
answer
15-20 minutes
question
Ketamine (conscious sedation)
answer
0.25-0.5 mg/kg IV
question
Succinylcholine (IV onset)
answer
30-60 seconds
question
Succinylcholine (IM onset)
answer
2-3 minutes
question
Succinylcholine (IV duration)
answer
3-5 minutes
question
Succinylcholine (IM duration)
answer
10-30 minutes
question
Succinylcholine (IV induction)
answer
1-1.5 mg/kg
question
Succinylcholine (IM dose)
answer
3 mg/kg
question
Succinylcholine (laryngospasm dose)
answer
20 mg IV
question
Vecuronium (IV induction)
answer
0.1 mg/kg
question
Vecuronium (Maintenance gtt)
answer
1 mcg/kg/min
question
Vecuronium (onset)
answer
2-4 minutes
question
Vecuronium (duration)
answer
30-60 minutes
question
Cisatracurium (duration)
answer
30-60 minutes
question
Cisatracurium (onset)
answer
2-4 minutes
question
Cisastracurium (IV induction)
answer
0.1 mg/kg
question
Cisastracurium (maintenance)
answer
1-3 mcg/kg/min
question
Rocuronium (induction dose)
answer
0.6-1.2 mg/kg
question
Rocuronium (maintenance)
answer
5-12 mcg/kg/min
question
Rocuronium (duration)
answer
30-60 minutes
question
Rocuronium (onset)
answer
60-90 seconds
question
Atracurium (induction)
answer
0.5 mg/kg
question
Atracurium (duration)
answer
30-60 minutes
question
Atracurium (maintenance)
answer
3-5 mcg/kg/min
question
Atracurium (onset)
answer
2-4 minutes
question
Ofirmev (dose)
answer
1000mg q6 or 650mg q4 infused over 15 minutes. Max daily dose 4000mg
question
Ofirmev (onset/peak/duration)
answer
10 minutes/ 1hr/ 4-6 hours
question
Hydrocortisone (dose)
answer
250mg IV
question
Scopolamine (IV/IM dose)
answer
0.3- 0.6 IV/IM
question
Scopolamine Patch (dose/onset/ duration)
answer
1.5mg total dosage for patch; 4 hours/ 3 days
question
Scopolamine (onset IV)
answer
8-10 minutes
question
Scopolamine (onset IM)
answer
30 minutes
question
Scopolamine (duration IV)
answer
2 hours
question
Scopolamine (duration IM)
answer
4 hours
question
Dopamine (onset)
answer
5 minutes
question
Dopamine (duration)
answer
minutes after discontinuing
question
Dopamine (dosing)
answer
1-70 mcg/kg/min (Only dopaminergic receptors stimulated at less than 2 mcg/kg/min, Beta at 2-5 mcg/kg/min, Alpha at rates greater than 10 mcg/kg/min)
question
Phenylephrine (bolus dose)
answer
50-100 mcg/dose (do not exceed 0.5mg in adults)
question
Phenylephrine (duration)
answer
10-15 minutes
question
Phenylephrine (onset)
answer
immediate
question
Clonidine (dose)
answer
0.1-0.6 mg (in 2 or 3 dose orally)
question
Precedex (loading dose)
answer
1 mcg/kg IV over 10 minutes
question
Precedex (Maintenance Drip)
answer
0.2-1.4 mcg/kg/hr
question
Precedex (fiberoptic intubation)
answer
0.7 mcg/kg/hr
question
Precedex (procedural sedation)
answer
start 0.6 mcg/kg/hr and titrate
question
Precedex (duration)
answer
10-30 min after infusion stops
question
Precedex (onset)
answer
10-20 minutes
question
Nitroglycerine (dose)
answer
25-50 mcg IV bolus 5-200 mcg/min IV infusion (200= max dose) 0.4 mg SL q5 x 3 doses
question
Nitroglycerine (duration)
answer
3-5 minutes
question
Nitroglycerine (onset)
answer
1 minute
question
Hydralazine (dose)
answer
2.5- 20mg IV (5-10mg q20 with a max dose of 40mg)
question
Hydralazine (duration)
answer
4-8 hours
question
Hydralazine (onset)
answer
15-20 minutes
question
Labetalol/ Trandate (non-selective) IV intermittent dose
answer
0.25mg/kg
question
Labetalol/ Trandate (non-selective) Infusion dose
answer
up to 2 mg/min
question
Labetalol/ Trandate (non-selective) IV bolus dose
answer
20mg-80mg q10 (start with 20 and work up 300mg max)
question
Labetalol (duration)
answer
2-4 hours
question
Labetalol/Trandate (onset)
answer
immediately
question
Metoprolol/Lopressor (dose)
answer
(selective) 2.5 to 5mg q5 max dose 15mg
question
Metoprolol/Lopressor (duration)
answer
(selective) 5-8 hours
question
Metoprolol/ Lopressor (onset)
answer
immediately
question
Esmolol/ Brevibloc (onset)
answer
(selective) 1-2 minutes
question
Esmolol/ Brevibloc (duration)
answer
(selective) 5-10 minutes
question
Esmolol/ Brevibloc (bolus and infusion dose)
answer
(selective) Bolus 10-15 mg Infusion: 25-350 mcg/kg/min (loading dose of 500mcg/kg/min for 1 min then titrate)
question
Propanolol/ Inderal (dose)
answer
(non selective) IV 1mg q5 minutes up to 5mg
question
Propanolol/Inderal (onset)
answer
(non selective) 15 minutes
question
Propanolol/Inderal (duration)
answer
6 hours
question
Epinephrine (onset)
answer
less than a minute
question
Epinephrine (duration)
answer
5-10 minutes
question
Epinephrine (peak)
answer
1-2 minutes
question
Epinephrine (iv push)
answer
10-100mcg
question
Epinephrine (Infusion)
answer
0.01-0.03 mcg/kg/min (Beta) 0.03-0.15 mcg/kg/min (alpha and beta) 0.15-0.3 mcg/kg/min (alpha
question
Norepinephrine (infusion dose)
answer
0.01-0.2 mcg/kg/min
question
Norepinephrine (onset)
answer
less than 1 minute
question
Norepinephrine (duration)
answer
2-10 minutes
question
Norepinephrine (peak)
answer
1-2 minutes
question
Albuterol/ Proventil/ Ventolin (dose)
answer
90 mcg/inhalation 2 puff MDI q4-6 hours 2.5mg neb q4-6 hours
question
Albuterol/ Proventil/ Ventolin (duration)
answer
6-12 hours
question
Albuterol/ Proventil/ Ventolin (onset)
answer
15-30 minutes
question
Zofran (dose)
answer
4-8mg IV (0.15mg/kg)
question
Zofran (duration)
answer
4-8 hours
question
Zofran (onset)
answer
rapid
question
Granisetron (Kytril; IV and PO dose)
answer
1 mg IV 2 mg PO
question
Promethazine (dose)
answer
12.5-25 mg IV 6.25mg/5ml PO
question
Promethazine (duration)
answer
4-12 hours
question
Promethazine (onset)
answer
3-5 minutes
question
Metoclopramide (dose)
answer
10-20mg IV
question
Metoclopramide (duration)
answer
1-2 hours
question
Metoclopramide (onset)
answer
1-3 minutes
question
Ranitidine (dose)
answer
50-100 mg IV (1-2.5 mg/kg) 150-300 PO
question
Flumazenil (dose)
answer
0.2 mg/kg (slow titration max 3mg)
question
Flumazenil (onset)
answer
1-2 minutes
question
Flumazenil (duration)
answer
45-90 minutes
question
Benadryl (dose)
answer
25-50mg (PO/IV/IM) (0.5-1.5mg/kg)
question
Benadryl (duration)
answer
3-6 hours
question
Dexamethasone (dose)
answer
5-10mg
question
Dexamethasone (duration)
answer
variable
question
Dexamethasone (onset)
answer
1 hour
question
Naloxone (dose)
answer
40-100 mcg
question
Naloxone (duration)
answer
20-60 minutes
question
Naloxone (onset)
answer
2 minutes
question
Ketoralac (dose)
answer
30 or 60mg
question
Ketoralac (duration)
answer
4-6 hours
question
Ketoralac (onset)
answer
30 minutes
question
Indigo Carmine
answer
(40mg/5ml vial) 5mg
question
Furosemide (dose)
answer
20-40mg IV (up to 200mg/dose for acute pulmonary edema) 20-80mg PO (qday or q6-8 hrs for edema, HTN; not to exceed 600mg/day)
question
Lasix (duration)
answer
2 hours IV 6-8 hours PO
question
Lasix (onset)
answer
5 min IV 30 min IM 30-60 min PO/SL
question
Lasix (peak)
answer
<15min IV 1-2 hours PO/SL
question
Oxytocin (dose)
answer
0.5-8 mU/min
question
Hemabate/ Carboprost tromethamine (dose)
answer
250mcg IM initial repeat PRN q 1.5-3.5 hours
question
Methergine/ Methylergonovine (dose)
answer
0.2 mg IM q2-4 (not to exceed 5 doses) (Then 0.2-0.4 mg PO q6-8 hours for 2-7 days)
question
Sublimaze/Fentanyl (IV dose)
answer
25-100mcg
question
Sublimaze/Fentanyl (IV duration)
answer
0.5-1 hour
question
Fentanyl (peak)
answer
20-30 minutes
question
Sublimaze/Fentanyl (IV onset)
answer
2-5 minutes
question
Hydromorphone (IV onset)
answer
15-30 minutes
question
Hydromorphone (IV duration)
answer
4-5 hours
question
Hydromorphone (IV dose)
answer
0.25 mg -1mg
question
Hydromorphone (peak)
answer
30-90 minutes
question
Morphine (IV dose)
answer
2-10mg
question
Morphine (IV duration)
answer
4-5 hours
question
Morphine (IV onset)
answer
20 minutes
question
Morphine (IV peak)
answer
30-60 minutes
question
Sufentanil (IV dose)
answer
0.5 mcg/kg
question
Sufentanil (IV onset)
answer
1-3 minutes
question
Sufentanil (IV duration)
answer
dose dependent
question
Remifentanil (IV induction and infusion dose)
answer
0.5-1 mcg/kg (induction) 0.05-2 mcg/kg/min (infusion)
question
Remifentanil (IV onset)
answer
1 minute
question
Remifentanil (IV duration)
answer
5-10 minute
question
Remifentanil (peak)
answer
1 minute
question
Midazolam (onset)
answer
IV 1-2 minutes IM 15 minutes PO 30 minutes
question
Midazolam (duration)
answer
IV 20-50 minutes IM up to 6 hours
question
Midazolam (IM, IV, Induction dose)
answer
IM 0.07 mg/kg IV 0.02-0.03 mg/kg Induction 0.1-0.2 mg/kg
question
Edrophonium (dose)
answer
0.05-0.1 mg/kg
question
Edrophonium (duration)
answer
30-60 minutes
question
Edrophonium (onset)
answer
5-10 minutes
question
Atropine (dose)
answer
0.4-1mg IV (bradycardia) (NMB Reversal 10 mcg/kg with edrophonium 0.02 mg/kg peds)
question
Atropine (duration)
answer
2-6 hours
question
Atropine (onset)
answer
30-60 seconds
question
Neostigmine (dose)
answer
0.05 mg/kg max dose 5mg (w/ robinul 0.2mg for every 1 mg of neostig)
question
Neostigmine (duration)
answer
45-90 minutes
question
Neostigmine (onset)
answer
5-15 minutes
question
Glycopyrrolate (dose)
answer
IV 0.1-0.2 mg for bradycardia 0.2 mg for every 1mg of neostig or 10 mcg/kg
question
Glycopyrrolate (onset)
answer
1-3 minutes
question
Glycopyrrolate (duration)
answer
Vagal effects about 2 hours, decreased salivation for 7 hours
question
Vasopressin (dose)
answer
Bolus 10-20 units 0.04-0.1 unit/min
question
Vasopressin (duration)
answer
10-30 minutes
question
Vasopressin (onset)
answer
1-5 minutes
question
Vasopressin (peak)
answer
5 minutes
question
Ephedrine (dose)
answer
5-10mg
question
Ephedrine (onset)
answer
less than 1 minute
question
Ephedrine (duration)
answer
10- 60 minutes
question
Atracurium
answer
0.5 mg/kg
question
Succinylcholine induction dose
answer
0.5-1 mg/kg RSI: 1-1.5 mg/kg
question
Succinylcholine onset
answer
30 sec
question
Succinylcholine duration
answer
4-6 min
question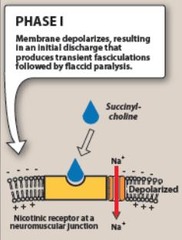
Succinylcholine MOA

answer
binds to nicotinic ACh receptors at the NMJ causing depolarization
question
Rocuronium induction dose
answer
o.6-1.2 mg/kg
question
Rocuronium onset
answer
45-90 sec
question
Rocuronium duration
answer
15-150 min
question
Non-depolarizing NMBA MOA
answer
competitive binding of nicotinic ACh receptors at the NMJ, preventing depolarization
question
Cisatracurium induction dose
answer
0.2 mg/kg
question
Cisatracurium onset
answer
90-120
question
Cisatracurium duration
answer
20-40 min
question
Fentanyl dose
answer
50-150 mcg
question
Fentanyl onset
answer
within 30 sec
question
Fentanyl peak
answer
3-5 min (6.8 min)
question
Fentanyl duration
answer
30-60 min
question
Fentanyl MOA
answer
Mu 1&2 agonist
question
Fentanyl issues
answer
muscle rigidity, bradycardia w/large dose, potency 100x morphine
question
Remifentanil dose
answer
0.05-2 mcg/kg/min
question
Remifentanil onset
answer
within 30 sec
question
Remifentanil peak
answer
3-5 min
question
Remifentanil duration
answer
5-10 min
question
Remifentanil metabolism
answer
plasma cholinesterases
question
Dilaudid dose
answer
0.5-2 mg
question
Dilaudid onset
answer
almost immediate
question
Dilaudid peak
answer
5-20 min
question
Dilaudid duration
answer
2-4 hrs
question
Dilaudid issues
answer
muscle rigidity
question
Morphine dose
answer
1-15 mg
question
Morphine onset
answer
<1 min
question
Morphine peak
answer
5-20 min
question
Morphine duration
answer
2-7 hrs
question
Morphine issues
answer
avoid in asthma and hypotension because of histamine release
question
Propofol dose
answer
1-2 mg/kg
question
Propofol maintenance dose
answer
50-150 mcg/kg/min
question
Propofol onset
answer
30 sec
question
Propofol peak
answer
1 min
question
Propofol duration
answer
5-10 min
question
Propofol MOA
answer
increasing the duration of the GABA-activated opening of the chloride channel with resulting hyperpolarization of cell membranes
question
Propofol properties & issues
answer
anti-emetic hypotension, irritation on injection
question
Ketamine dose
answer
0.5-1 mg/kg
question
Ketamine onset
answer
<30 sec
question
Ketamine peak
answer
1 min
question
Ketamine duration
answer
5-15 min
question
Ketamine MOA
answer
inhibits glutamate @ the NMDA receptor
question
Ketamine metabolism
answer
cytochrome P450 system
question
Ketamine S/E
answer
++ MAP, ++ HR, + CO, no respiratory depression, bronchodilation, analgesic properties, decrease CBF but increase CPP CMRO2 ICP & IOP
question
Midazolam dose
answer
0.1-0.2 mg/kg
question
Midazolam onset
answer
30-60 sec
question
Midazolam peak
answer
3-5 min
question
Midzaolam duration
answer
15-80 min
question
Midazolam MOA
answer
GABA agonist- opening of Cl channels leading to hyper polarization
question
Dexmedetomidine dose
answer
1 mcg/kg over 10 min
question
Dexmedetomidine maintenance dose
answer
0.2-0.7 mcg/kg/min
question
Dexmedetomidine peak
answer
2-6 min
question
Dexmedetomidine duration
answer
0.5-2 hrs
question
Dexmedetomidine MOA
answer
presynaptic Alpha-2 agonist inhibiting Ca channels and activating K channels causing hyperpolarization and decreased release of catecholamine vesicles
question
Dexmedetomidine issues
answer
hypotension & bradycardia
question
Neosynephrine dose
answer
50-100 mcg
question
Neosynephrine onset
answer
<1 min
question
Neosynephrine peak
answer
<1 min
question
Neosynephrine duration
answer
15-20 min
question
Neosynephrine indication & MOA
answer
hypotention w/o bradycardia selective alpha-1 agonist causing vasoconstriction of arterioles and venuoles
question
Neosynephrine issues
answer
bradycardia
question
Ephedrine indication & MOA
answer
hypotension w/ bradycardia & bronchospasm Beta & Alpha agonist mix direct & indirect
question
Ephedrine dose
answer
5-20 mg
question
Ephedrine onset
answer
immediate
question
Ephedrine peak
answer
2-5 min
question
Ephedrine duration
answer
10-60 min
question
Ephedrine issues
answer
increased risk of arrhythmia
question
Epinephrine indication & MOA
answer
other vasopressors fail, total spinal, bronchospasm Alpha & Beta agonist, increased HR, bronchodilator
question
Epinephrine dose
answer
2-10 mcg
question
Epinephrine onset
answer
<1 min
question
Epinephrine peak
answer
<1 min
question
Epinephrine duration
answer
5-10 min
question
Esmolol indication & MOA
answer
Tachycardia, HTN Selective Beta-1 antagonist
question
Esmolol dose
answer
0.5-1 mg/kg
question
Esmolol onset
answer
1-2 min
question
Esmolol peak
answer
5 min
question
Esmolol duration
answer
10 min
question
Esmolol metabolism
answer
RBC esterases
question
Metoprolol indication & MOA
answer
HTN, SVT, Acute MI Selective Beta-1 antagonist
question
Metoprolol dose
answer
2-15 mg
question
Metoprolol onset
answer
<15 min
question
Metoprolol peak
answer
20 min
question
Metoprolol duration
answer
5-8 hrs
question
Metoprolol contraindications
answer
bradycardia & heart block
question
Labetalol indications & MOA
answer
HTN Alpha & Beta antagonist (1:7 - Alpha/Beta)
question
Labetalol dose
answer
2.5-20 mg
question
Labetalol onset
answer
2-5 min
question
Labetalol peak
answer
5-15 min
question
Labetalol duration
answer
2-4 hrs
question
Labetalol contraindications
answer
asthma, HF, bradycardia
question
Hydralazine indications & MOA
answer
HTN, SVR reduction in CHF patients activation of K channels causing hyperpolarization of smooth cells preventing vasoconstriction (requires Nitric Oxide for vasodilation)
question
Hydralazine dose
answer
0.1-0.2 mg/kg
question
Hydralazine onset
answer
5-20 min
question
Hydralazine peak
answer
10-80 min
question
Hydralazine duration
answer
2-4 hrs
question
Hydralazine S/E
answer
reflexive bradycardia (minimal with co-administration w/Beta Blocker)
question
A 23 yo F presents to your office for an evaluation of her third molars. Teeth #1 and #16 are erupted/malposed, and #17 and #32 are slightly mesioangular PBIs. On history you discover that she has asthma and smokes cigarettes, 1 PPD for the past 10 years. Her medications include Advair Inhaler BID, Proventil prn, and orthotrycycline BCP (although she occasionally misses a dose and she has not had her period for a couple months). On further questioning, you also find out that she takes a MVI, additional vit E, and an herbal "mood pack" containing St John's Wort, ecchinacea, ginko biloba, and garlic. She wants to be "asleep" during her surgery. What questions would you ask this patient, pertaining to the findings in the medical history?
answer
Aside from CC, HPI, PMedHx, PSurHx, FamHx, ALL, ROS... How frequent and severe are the asthma attacks, what precipitates them, has she ever been to the ER or hospitalized for them. Is she sexually active, and is there a possibility she could be pregnant?
question
What are your concerns and perioperative recommendations for any of the medications or supplements that this patient is taking?
answer
I am concerned that she is not very compliant with her BCPs. I am also concerned about the additional vitamin E and herbals, which can cause excessive bleeding. I would instruct her to stop those supplements 2 weeks prior to any surgical procedure. In addition, I would counsel her to use alternate forms of birth control for the remainder of her current menstrual cycle if antibiotics are prescribed during treatment, because they can render BCPs ineffective.
question
What is Advair?
answer
A combination B2 agonist/corticosteroid inhaled asthma medication used for prevention, not acute attacks. It contains salmeterol (slow acting B2 agonist) and fluticasone (corticosteroid), and comes in a diskus inhaler, that is activated by the patient's inhalation.
question
Describe your physical examination:
answer
I perform a head & neck exam, visualization/palpation/auscultation, cervical LAD, TMJ exam, intraoral exam looking for soft tissues lesions, infections, ulcerations, and evaluate the airway using the mallampati classification (I - entire pharynx visualized, II - most of uvula visualized, III - only soft palate visualized, IV - soft palate not visible) & physical factors like mandibular position/size and ability to extend neck. I look at pupils for size and reactivity, and assess CN V & VII function as pertinent to any potential surgical procedures. I auscultate the heart and lungs.
question
On auscultation, her lungs are clear and you hear a soft, but unmistakeably present systolic ejection murmur at the left sternal border. She has never been told that she has a murmur. How would you grade the heart murmur?
answer
Levine scale: 1. The murmur is only audible on listening carefully for some time. 2. The murmur is *faint* but immediately audible on placing the stethoscope on the chest. 3. A loud murmur readily audible but with no palpable thrill. 4. A loud murmur with a palpable thrill. 5. A loud murmur with a palpable thrill. The murmur is so loud that it is audible with only the rim of the stethoscope touching the chest. 6. A loud murmur with a palpable thrill. The murmur is audible with the stethoscope not touching the chest but lifted just off it.
question
Location refers to where the heart murmur is usually heard best. There are 4 places on the anterior chest wall to listen for heart murmurs; each of the locations roughly corresponds to a specific part of the heart and should be listened to (through the stethoscope) with the patient lying down, face up. The four locations are?
answer
Aortic region - the 2nd RIGHT intercostal space. Pulmonic region - the 2nd left intercostal spaces. Tricuspid region - the 5th left intercostal space (STERNAL) Mitral region - the 5th left mid-clavicular intercostal space. (near nipple)
question
What are possible etiologies for the murmur?
answer
Innocent or physiologic murmur, pregnancy, anemia, VSD, tricuspid or mitral valve dysfunction.
question
What actions would you take?
answer
Medical consultation to evaluate the murmur and need for bacterial endocarditis prophylaxis prior to dental/surgical procedures. I would order a urine pregnancy test immediately, and in my hospital setting, I would refer the patient to cardiology, who would evaluate her with auscultation using different maneuvers (left lateral decubitus brings out mitral murmurs and sitting forward accentuates aortic murmurs), likely an ECG, and possibly an echocardiogram to rule out valvular dysfunction.
question
What does inhalation do to accentuate the murmur?
answer
Inhalation leads to an increase in intrathoracic negative pressure, which increases the capacity of pulmonary circulation, thereby prolonging ejection time. This will affect the closure of the pulmonary valve. This finding, also called Carvallo's maneuver, has been found by studies to have a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 80% to 88% in detecting murmurs originating in the right heart. specifically positive Carvallo's sign describes the increase in intensity of a tricuspid regurgitation murmur with inspiration.
question
On referral to her physician, a pregnancy test is ordered and comes back positive. She is near the end of her first trimester. What is the likely etiology of the murmur?
answer
Physiologic murmur caused by the hyperdynamic state of pregnancy (increased cardiac output). These murmurs do not require SBE prophylaxis.
question
What will you advise her about the timing of her surgery?
answer
She should ideally wait until after delivery. Any procedures that must be performed, are most safely performed in the *2nd trimester* using local anesthesia, although severe infections and trauma must be managed at the time they present in most cases.
question
She develops a moderate to severe pericoronitis involving tooth #32 (with occlusal trauma from tooth #1) during her pregnancy. She has tender right submandibular nodes, localized erythema and swelling around tooth #32 with mild suppuration, and a temperature of 99.8 F. How would you manage this situation?
answer
I would extract tooth #1 with local anesthesia (lidocaine or mepivacaine, but not bupivacaine - it can cause CV collapse) and irrigate the #32 site with Chlorhexidine 0.12% oral rinse, and have the patient irrigate at home BID. I would prescribe PCN 500mg PO QID for 7 days, or Clindamycin 300mg PO QID for 7 days if she is PCN allergic. I would see her in 48 hours for a follow-up appointment.
question
What antibiotics are safe to use during pregnancy?
answer
PCN, cephalosporins, clindamycin
question
What local anesthetics are safe to use?
answer
Lidocaine and mepivacaine
question
What would be your anesthesia plan?
answer
Topical and local anesthesia. Fentanyl and Demerol are ok in small amounts during pregnancy, but benzodiazepines can cause birth defects (such as cleft lip & palate) early in the pregnancy.
question
You are taking out tooth #1 to alleviate a p-cor involving tooth #32. During the procedure the patient becomes light headed. Why is this occurring and what actions are you going to take?
answer
Likely compression of the Vena Cava, with decreased blood return to the heart. The treatment is to place the patient on her left side with her hip slightly elevated. I would also administer supplemental O2 by NC.
question
The patient recovers from the p-cor and goes on to an uncomplicated delivery. She presents 6 months later for removal of her remaining third molars. She no longer has a murmur on auscultation. She wants to be "completely asleep" for the surgery this time. What additional questions will you ask her?
answer
Is she breastfeeding? If she is, then she should pump and freeze breast milk to have available for several days after the surgery (until the anesthesia medications and any prescribed narcotic analgesics or antibiotics are out of the patient's system).
question
What is this patient's ASA classification?
answer
ASA 2 ASA 1-Normal healthy patient ASA 2-Controlled systemic disease without functional limitation ASA 3-Severe systemic disease with functional limitation ASA 4-Severe systemic disease that is a constant threat to life ASA 5-Moribund patient, not expected to survive without operation ASA 6-Brain-dead, organ donor (E)-Designator for any patient requiring an emergency operation
question
What are your preoperative instructions for this patient?
answer
Stop the vitamin E and herbals 2 weeks prior to surgery. NPO 6 hours prior, with small amounts of water allowed up to 2 hours prior to surgery. She must perform a urine HCG within 72 hrs prior to the surgery and she must have an adult escort with her to drive her home. She needs to bring her albuterol inhaler with her to the appointment, and continue to use her Advair BID throughout the perioperative period. She should ideally stop smoking several weeks prior to her surgery and refrain from smoking for at least a week postoperatively to minimize her risk of alveolar osteitis or impaired healing. I ask patients to remove any nail polish from their fingernails before the appointment and to wear comfortable, non-restrictive clothing.
question
Describe your anesthetic technique for an OPGA:
answer
I perform and supervise intubated general anesthetic cases in my hospital clinic, as a part of a residency training program. One surgeon performs the anesthesia and another performs the surgery. I have a nurse monitoring and recording vital signs during the procedure and recovery. After an immediate preoperative re-assessment, an 18-20ga peripheral IV is started, and a bag of LR is connected. Any indicated preoperative antibiotics are administered IVPB over 20-30 min. I pre-oxgenate for several minutes while placing monitors (pre-cordial stethoscope, pulse-ox, BP, and EKG leads). I give the patient midazolam for anxiolysis if indicated, but don't usually need it, and avoid it if possible to minimize recovery time. After obtaining the first set of vitals, I give 50 to 100 mcg of fentanyl over several minutes. Until recently, I used to give tubocurarine 3mg IVP, as a defasciculating dose at this point, telling the patient that they may have blurred vision and feel a subjective weakness or difficulty breathing. It has not been available recently. I induce general anesthesia with 2.5mg/kg Propofol IVP. I then make an attempt to mask ventilate the patient in order to assess the airway. If the airway is patent, then I administer Succinycholine 1.5mg/kg IVP, and wait approximately 1 min, until after muscle fasciculations subside. Decadron 8mg IVP is administered if indicated for the procedure. I then perform a direct laryngoscopy and administer approximately 50mg of lidocaine in the trachea with an LTA, to prevent stimulation of the airway with movement of the ETT. Without removing the laryngoscope, I pass an endotracheal tube, watching the cuff go past the cords. The stylet is removed, and the cuff inflated. I then hook up the anesthesia circuit to the ETT and verify position by auscultation, condensation in the ETT, ; ETCO2, and note the tube position at the teeth. The tube is secured and a throat pack placed. I place the patient on 60/40 nitrous oxide/O2 at a flow of about 4-5 l/min, and place them on the ventilator with a TV of approximately 8-10 ml/kg and a rate to keep the ETCO2 around 35. I administer a continuous propofol infusion, using a Baxter infusion pump, initially at 100mcg/kg/min. I administer local anesthetic, and perform the surgery. The propofol is gradually weaned down during the case, and the infusion stopped near the end of the procedure. The nitrous oxide is weaned and the patient placed on 100% O2 as the throat pack is removed. I allow the patient to emerge, through stage 2 (following commands and demonstrating good strength and respiratory pattern), prior to extubation. The patient is asked to open, inhale and hold it, and the bag squeezed to fill the lungs with air, just before dropping the cuff and gently pulling the endotracheal tube. The mask is placed and the patient monitored for adequate respirations prior to transport to the recovery room where the patient is constantly monitored until discharge.
question
The patient desires a general anesthetic and you decide to treat her in the Outpatient Surgery Center of your local hospital. The anesthetist induces anesthesia with Propofol, and is using Sevofluorane for maintenance. What are Propofol and Sevofluorane?
answer
Propofol is a substituted isopropylphenol IV sedative-hypnotic agent used for induction and maintenance of anesthesia. It is in a soybean fat emulsion with egg phosphatide, and is highly lipophilic, which increases it's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier. It produces a dose dependent CNS depression, has a fast onset and short duration, and is easily titrated, but can cause marked hypotension when administered in rapid bolus. The usual induction dose is 2-2.5mg/kg. Infusions of 25-200mcg/kg/min are useful for sedation or maintenance of general anesthesia. Sevofluorane is a fluorinated volatile anesthetic agent with a low blood/gas partition coefficient, therefore a rapid onset and recovery from anesthesia. The MAC is 1.71. It is useful in mask inductions for children, because it has less a less pungent odor and airway irritability than other volatile anesthetics. When used in combination, sevo and propofol may cause profound hypotension.
question
What is MAC, pertaining to volatile anesthetics?
answer
The concentration of an inhaled anesthetic, at 1ATM, that prevents skeletal muscle movement in response to a painful stimulus (skin incision) in 50% of patients. A MAC of 1.3 prevents movement in approximately 95% of individuals undergoing surgery. MAC can be used to compare potency of anesthetic gases.
question
During the case, the anesthetist complains of increasing airway pressures. What could be the cause?
answer
Circuit or ETT obstruction (kinking), airway secretions or mucous plugging, bronchospasm.
question
How should potential bronchospasm be treated intraoperatively, in this intubated patient?
answer
Suction ETT and trachea with suction catheter. Albuterol MDI 8-10 puffs into endotracheal tube on inspiration, through chamber, or a 60cc syringe connected to the anesthesia circuit close to the ETT. If this doesn't work, then epinephrine 0.3mg SC.
question
Near the end of the case, the anesthetist is now complaining that the ETCO2 is abnormally high, and non-responsive to increasing the ventilatory rate. The patient has also become mildly tachycardic. The CRNA asks you what you think is going on?
answer
Suspect Malignant Hyperthermia.
question
What is Malignant Hyperthermia?
answer
An inherited disease that manifests most often in children (1:12,000 pediatric anesthetics, 1:40,000 adult anesthetics). The gene for MH is also the genetic coding site for the calcium release channel of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. It is presumed that a defect in the calcium release channel permits sustained higher concentrations of calcium in the myoplasm and persistent muscle contraction when susceptible patients are exposed to triggering agents (depolarizing muscle relaxants and volatile anesthetics). The eventual result is an extreme hypermetabolic state, leading to respiratory and metabolic acidosis and death is not treated.
question
How do you recognize and treat Malignant Hyperthermia?
answer
Identifying individuals at risk, through a thorough history (and family history) of previous anesthetics is necessary. 70% of MH-susceptible patients have increases of resting concentrations of creatine kinase. The definitive diagnosis of susceptibility to MH requires skeletal muscle biopsy and in vitro isometric contracture testing in the presence of caffeine or halothane, or both. The earliest clinical signs of MH include unexplained sustained elevation in ETCO2, and tachycardia. Arterial hypoxemia, metabolic (due to lactic acidosis) and respiratory acidosis are followed by an eventual profound increase in body temperature (late finding). Treatment includes: initiating the emergency plan/activating EMS, stopping the triggering agent and changing the anesthesia circuit, hyperventilating with 100% O2, administering 2.5mg/kg Dantrolene Sodium IVP and repeat every 10-15 minutes as needed (up to 10mg/kg), initiate active cooling (cold IV saline, gastric lavage with cold saline, surface cooling), Sodium bicarbonate 1-2mEq/kg IV as guided by arterial pH, induce diuresis (hydration, mannitol, lasix), and monitor electrolytes (treat hyperkalemia with insulin and glucose). The patient must be transported to and managed in an ICU setting at the appropriate time.



