Surgery- Colon and Rectum – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What are the white lines of Toldt?
answer
Lateral peritoneal reflections of the ascending and descending colon.
question
What parts of the GI do not have a serosa?
answer
Esophagus, middle, and distal rectum.
question
What are the major anatomic differences between the colon and small bowel?
answer
Colon has taeniae coli, haustra, and appendices epiploicae, whereas the small intestine is SMOOTH.
question
What is the blood supply to the PROXIMAL rectum?
answer
IMA--> Superior hemorrhoidal (superior rectal)--> Proximal rectum.
question
What is the blood supply to the MIDDLE rectum?
answer
Internal Iliac-->Middle hemorrhoidal (middle rectal)-->Middle rectum
question
What is the blood supply to the DISTAL rectum?
answer
Pudendal artery-->Inferior hemorrhoidal (inferior rectal)--> Distal rectum * Pudendal artery is a branch of the hypogastric
question
What is a colorectal carcinoma?
answer
Adenocarcinoma of the colon or rectum
question
What is the incidence of colorectal cancer?
answer
Most COMMON GI cancer.
question
What are the dietary risk factors for colorectal cancer?
answer
Low-fiber, high fat diets.
question
What are the genetic risk factors for colorectal cancer?
answer
Family history is important when taking history (FAP, Lynch's syndrome)
question
What else puts one at risk for colon cancer?
answer
IBD, though UC;Crohn's. Age, previous colon cancer also factors
question
Lynch's syndrome?
answer
HNPCC- Hereditary NonPolyposis Colon Cancer- AD inheritance of high risk for development of colon cancer.
question
What are the current recommendations of screening for colorectal cancer?
answer
Starting at age 50, at least ONE of the following: - Colonoscopy every 10 years - Double contrast barium enema every 5 years - Flex sigmoidoscopy every 5 years - CT colonography every 5 years.
question
What are recommendations if someone in the family has contracted colon cancer, as far as screening is concerned?
answer
- Colonoscopy at age 40, OR at least 10 years before the age at diagnosis of the youngest first-degree relative, and every 5 years thereafter.
question
What percentage of adults with a guaic stool test positive for colon cancer?
answer
10%.
question
From which side is melena more common, as far as colon cancer is concerned?
answer
RIGHT-sided colon cancer
question
From which side is hematochezia more common, as far as colon cancer is concerned?
answer
LEFT-sided colon cancer
question
What are the signs/symptoms of colon cancer?
answer
- MOST COMMON: Hematochezia or mucus - Tenesmus - Feeling of incomplete passage of stool
question
What diagnostic tests are helpful for colon cancer?
answer
History and PE (10% of colon cancer cases are palpable on rectal exam)
question
What disease does microcytic anemia signify, until proven otherwise?
answer
COLON CANCER
question
What is the pre-op test panel for colorectal cancer?
answer
- History and PE - LFTs, CEA, CBC - Basically everything
question
Is CEA useful?
answer
Not for screening, but for progression. Offers no proven survival benefits.
question
What unique diagnostic test is helpful in patients with rectal cancer?
answer
Endorectal US
question
How are colorectal tumors staged?
answer
TMN Staging
question
What is stage 1 colon cancer?
answer
Invades the submucosa or muscularis propria (T1-2, N0, M0) Survival rate: 90%
question
What is stage 2 colon cancer?
answer
Invades through muscularis propria or surrounding structures, but no nodes are effected (T3-T4, N0, M0) Survival rate: 70%
question
What is stage 3 colon cancer?
answer
Positive nodes, but NO distant mets (T: Any, N1-3, M0) Survival rate: 50%
question
What is stage 4 colon cancer?
answer
Positive distant mets (T: Any N: Any M1) Survival rate: 10%
question
What percentage of patients presenting with colon cancer have liver mets?
answer
20%
question
What are the treatment options for colon cancer?
answer
- Resection: Wide resection of lesion and its regional lymphatic drainage
question
What do all rectal cancer operations include?
answer
Total mesorectal excision- Remove the rectal mesentery, including lymph nodes
question
What is the lowest LAR (low anterior resection) possible?
answer
Coloanal anastomosis (anastamosis normal colon directly to anus)
question
What surgical margins are needed for colon cancer?
answer
Traditionally, ;5 cm; margins must be at least 2 cm
question
What is the minimal surgical margin for rectal cancer?
answer
2 cm.
question
How many lymph nodes should be resected with a colon cancer mass?
answer
12 LNs minimum, for staging. May also improve prognosis.
question
What is the adjuvant treatment for stage 3 colon cancer?
answer
5-FU and chemo
question
What is the adjuvant treatment for T3-T4 colorectal cancer?
answer
Preoperative radiation therapy and 5-FU chemo as a radiosensitizer.
question
What is the most common site of distant mets from colorectal cancer?
answer
Liver
question
What is the treatment of liver metastases from colorectal cancer?
answer
Resect with ;1cm margins and administer chemo if feasible.
question
What is the surveillance regimen?
answer
- PE - Stool guiac - CBC - CEA, - LFTs Every 3 months for 3 years, then every 6 months for 2 years.
question
Why is follow up so important within the 3 years post-op?
answer
~90% of colorectal occurences are within 3 years of surgery.
question
What are the most common causes of colonic obstruction in the adult population?
answer
Colon cancer, diverticular disease, colonic volvulus.
question
What are colonic and rectal polyps?
answer
Tissue growth into bowel lumen, usually consisting of mucosa, submucosa, or both.
question
How are polyps classified?
answer
Sessile: flat Pedunculated: On a stalk
question
What is the histologic classification of inflammatory polyps?
answer
As in Crohn's Disease or UC
question
What is the histologic classification of hamartomatous polyps?
answer
Normal tissue in an abnormal configuration
question
What is the histologic classification of hyperplastic polyps?
answer
Benign- normal cells with no malignant potential
question
What is the histologic classification of neoplastic polyps?
answer
Proliferation of undifferentiated cells, premalignant or malignant.
question
What are the subtypes of neoplastic polyps?
answer
- Tubular adenomas: Usually pedunculated - Tubulovillous adenomas - Villous adenomas (usually sessile and look like broccoli heads)
question
What determines malignant potential of an adenomatous polyp?
answer
Size, histologic type, atypia of cells.
question
What is the most common type of adenomatous polyp?
answer
Tubular (85%)
question
What is the correlation between size and malignancy?
answer
The larger the polyp, the more likely the malignancu
question
Which histology of adenomatous polyps carry with it the greatest chance of malignancy?
answer
Villous>tubovillous>tubular ** This is also the order of most common... Sadly VILLANY!
question
Where are most polyps found?
answer
Rectosigmoid
question
What are the signs/symptoms of polyps?
answer
Bleeding (red or dark blood), change in bowel habits, mucus per rectum, electrolyte loss, totally asymptomatic
question
What are the diagnostic tests for polyps
answer
Colonoscopy is best
question
What is the treatment for polyps?
answer
Endoscopic resection (snared)
question
What is familial polyposis?
answer
FAP (familial adenomatous polyposis
question
What are the characteristics of FAP?
answer
Hundreds of adenomatous polyps within the rectum and colon that begin developing at puberty, cancer will develop by the age of 40-50 if not treated.
question
What is the inheritance pattern of FAP?
answer
Autosomal dominant (i.e. 50%)
question
What is the genetic defect in FAP?
answer
APC (Adenomatous polyposis coli) gene
question
What is the treatment of FAP?
answer
Total protocolectomy and ileostomy
question
What is Gardner's Syndrome?
answer
Neoplastic polyps of the small bowel and colon. Cancer by age 40 in 100% of patients untreated (like FAP)
question
What are other associated findings in Gardner's Syndrome?
answer
Desmoid tumors (in abdominal wall cavity) osteomas of the skull (seen on x-ray), sebaceous cysts
question
What is a neumonic for Gardner's Syndrome?
answer
Gardner's plant SOD: S- Sebaceous cysts O- Osteomas D- Desmoid tumors
question
What is a desmoid tumor?
answer
Tumor of the musculoaponeurotic sheath, usually of the abdominal wall. Benign
question
What is the treatment of Gardner's Syndrome?
answer
Total proctocolectomy and ileostomy
question
What is Peutz-Jegher's Syndrome?
answer
Hamartomas throughout the GI tract (mostly in the Jejunum ileum)
question
What is the associated cancer risk from polyps?
answer
Increased
question
What is the associated cancer risk for women with Peutz-Jeghers?
answer
Ovarian cancer
question
What is the inheritance pattern of Peutz-Jeghers?
answer
AD
question
What are other signs of Peutz-Jeghers?
answer
- Melancotic pigmentation of buccal mucosa (black/brown)
question
What is the treatment of Peutz-Jeghers?
answer
Removal of polyps if symptomatic.
question
What are juvenile polyps?
answer
Benign hamartomas in the small bowel and colon. Not premalignant, also known as retention polyps.
question
What is Cronkite-Canada syndrome?
answer
Diffuse GI hamaratoma polyps (no cancer potential) associated with malabsorption/weight loss, and LOSS OF ELECTROLYTES
question
What is Turcot's Syndrome?
answer
Colon polyps with malignant CNS tumors.
question
What is diverticulosis?
answer
Condition in which diverticula can be found within the colon, especially the sigmoid. Usually false diverticula.
question
What is the pathophysiology of a diverticulosis?
answer
A weakness in the bowel wall that develops at points where nutrient blood vessels enter between antimesenteric and mesenteric taeniae, increased intramural pressures then cause herniation through these areas.
question
What is the incidence of diverticulosis?
answer
50-60% in the US by age 60. Only 10-20% become symptomatic.
question
Who is at risk for diverticulitis?
answer
People with low fiber diets, constant constipation, and positive family history. Incidence also increases with age.
question
What are symptoms/complications?
answer
Bleeding: may become a massive diverticulitis
question
What is the treatment of diverticulitis?
answer
A high fiber diet is recommended..
question
What are the indications for operation with diverticulosis?
answer
Complications (which include fistula, obstruction, stricture), recurrent episodes, hemorrhage
question
When is it safe to get a colonoscopy/endoscopy in a patient with diverticulitis?
answer
Due to risk of perforation, this is performed 6 weeks after inflammation resolves to rule out colon cancer.
question
What is diverticulitis?
answer
Infection or perforation of a diverticulum.
question
What is the pathophisiology of diverticuliitis?
answer
Obstruction of diverticulum by a fecalith leads to inflammation and microperforation
question
What are the signs/symptoms of diverticulitis?
answer
LLQ pain, diarrhea, fever, chills, anorexia
question
What are the associated lab values in one with diverticulitis?
answer
Increased WBC
question
What are the associated radiographic findings?
answer
On X-Ray: Ileus- Partially obstructed colon, air-fluid levels, free air if perforated
question
What are the associated barium enema findings?
answer
Barium enema should be avoided in acute cases. (colonoscopy increases risk for perforation as well)
question
What are the possible complications?
answer
Abscess, diffuse peritonitis, fistula, obstruction, perforation, stricture
question
What is the most common fistula with diverticulitis?
answer
Colovesical fistula (to bladder)
question
What is the best test for diverticulitis?
answer
CT Scan
question
What is the initial therapy for diverticulitis?
answer
- IV fluids - NPO - Broad spectrum ABx
question
When is surgery indicated for diverticulitis?
answer
- Obstruction - Fistula - Free perforation
question
What is the lifelong risk after development of the first one?
answer
33% after the first, 50% after the second.
question
What surgery is usually performed ELECTIVELY for recurrent bouts?
answer
One-stage operation: Resection of involved segment and primary anastomosis
question
What type of procedure is usually performed for an ACUTE case of diverticulitis with a complication (perforation, obstruction)?
answer
Hartmann's procedure. Resection of involved segment with and end colostomy and stapled rectal stump
question
What is the treatment for a divertucular abscess?
answer
Percutaneous drainage; if abscess is not amenable to percutaneous drainage, then surgical approach for drainage is necessary.
question
How common is massive lower GI bleed with diverticulitis?
answer
VERY rare. Seen with DiverticuloSIS, not diverticulitis.
question
What is the most common cause of lower massive bleeding in the lower GI in adults?
answer
Diverticulitis.
question
What is Colonic volvus?
answer
The twisting of the colon about its mesentery, resulting from obstruction and if complete, vascular compromise with potential necrosis, perforation, or both.
question
What is the most common type of colonic volvulus?
answer
Sigmoid
question
What is a sigmoid volvulus?
answer
A twist of the sigmoid colon
question
What are the etiologic factors of a volvulus??
answer
High residue diet resulting in bulky stools and tortuous, elongated colon, chronic constipation
question
What are the signs/symptoms of a volvulus?
answer
- Acute abdominal pain - Abdominal distention - Obstipation - N/V
question
What findings are found on an abdominal film of a volvulus?
answer
- Distended loop of sigmoid colon, often in the classic 'bent inner tube'
question
What are the signs of necrotic bowel?
answer
Free air, pneumatosis (air in the bowel wall)
question
How is the diagnosis of a volvulus made?
answer
Sigmoidoscopy or radiographic film.
question
Under what condition is gastrogafin enema used?
answer
If sigmoidoscopy and radiographic films fail, a 'bird's beak' can be seen with a barium enema
question
What are the signs of strangulation?
answer
- Discolored or hemorrghic mucosa on sigmoidoscopy - Bloody fluid in the rectum - Fever, hypotension, high WBCs
question
What is the initial treatment of a volvulus?
answer
Nonoperative. If there is no strangulation, sigmoidoscopic reduction is successful in 85% of cases.
question
What are the indications of surgery for a volvulus?
answer
Emergently if strangulation is suspected or nonoperative reduction unsuccessful (Hartmann's Procedure)
question
What is a cecal volvulus?
answer
Twisting of the cecum upon itself and the mesentery
question
What are the signs/symtoms of a cecal volvulus?
answer
- Acute onset of abdominal or colicky pain beginning the RLQ and progressing to a constant pain, vomiting, obstipation.
question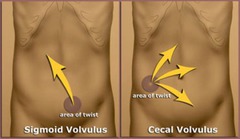
How is the diagnosis of a cecal volvulus made?

answer
Abdominal plain film. Large air/fluid level, dilated, ovoid colon. COFFEE BEAN sign
question
What is the treatment of a cecal volvulus?
answer
Emergent surgery, right colectomy with primary anastomosis or ileostomy.
question
What is the MAJOR difference between a sigmoid volvulus and a cecal volvulus?
answer
- Cecal volvulus REQUIRES surgery - Sigmoid volvulus undergoes initial endoscopic reduction of the twist.



