Social Psychology Exam Test – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
The scientific study of the way in which people's thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by the real or imagined presence of other people. Focuses on how an individual acts within a social context.
answer
Social Psychology
question
The effect that the words, actions, or mere presence of other people have on our thoughts, feelings, attitudes, or behavior
answer
Social Influence
question
The study of groups, organizations, and societies, rather than individuals.
answer
Sociology
question
Tendency to explain our own and other people's behavior entirely in terms of personality traits and underestimate the power of social influence. Ex. Molly thinks Bob purposefully and maliciously tripped her when really, he accidentally got his foot caught in hers
answer
Fundamental Attribution Error
question
The way in which people perceive, comprehend, and interpret the social world and social situations. Shaped by two human motives. 1. The need to be accepted 2. The need to feel good about themselves
answer
Construal
question
People's evaluations of their own self-worth; the extent to which they view themselves as good, competent, and decent
answer
Self-esteem Approach
question
How people think about themselves and the social world; how people select, interpret, remember, and use social information to make judgments and decisions
answer
Social Cognition Approach
question
A social psychologist would tend to look for explanations of a young man's violent behavior primarily in terms of: a. his aggressive personality traits. b. possible genetic contributions. c. how his peer group behaves. d. what his father taught him.
answer
c
question
The topic that would most interest a social psychologist is a. how the level o extroversion of different presidents affected their political decisions. b. whether people's decision to cheat on a test is influenced by how they imagine their friends would react if they found out. c. the extent to which people''s social class predicts their income. d. what passers-by on the street think of global warming
answer
b
question
How does social psychology differ from personality psychology? a. social psychology focuses on individual differences whereas personality psychology focuses on how people behave in certain situations. b. social psychology focuses on the shared processes that make people susceptible to social influence, whereas personality psychology focuses on individual differences. c. social psychology provides general laws and theories about societies, whereas personality psychology studies the characteristics that make people unique. d. social psychology focuses on individual differences, whereas personality psychology provides general laws and theories about societies.
answer
b
question
What is the "level of analysis" for a social psychologist? a. the individual in the context of a social situation. b. the social situation itself. c. a person's level of achievement. d. a person's level of reasoning.
answer
a
question
Which of the following research topics about violence is one that a social psychologist might investigate? a. how rates of violence change over time within a culture. b. why murder rates vary across cultures. c. brain abnormalities that produce aggression when a person is provoked. d. why some situations are more likely to provoke aggression than others.
answer
d
question
A school of psychology maintaining that to understand human behavior, one need only consider the reinforcing properties of the environment.
answer
Behaviorism
question
A school of psychology stressing the importance of studying the subjective way in which an object appears in people's minds rather than the objective, physical attributes of the object. Ex. focuses on a whole painting instead of focuses on its parts
answer
Gestalt psychology
question
What does the "Wall Street Game" reveal about personality and situation? a. competitive people will compete fiercely no matter what a game is called. b. cooperative people will try hard to get competitive opponents to work with them. c. the name of the game makes no difference in how people play the game. d. the name of the game strongly influences how people play the game.
answer
d
question
A stranger approaches Emily and tells her that he is a professional photographer and asks if she would like spend 15 minutes posing for pictures. According to social psychologists, Emily's decision depends on a. how well dressed the man is. b. whether the man offers to pay her. c. how Emily construes the situation. d. whether the man has a criminal record
answer
c
question
Social psychology had its origins in a. Gestalt psychology b. Freudian psychology c. Behavioral psychology d. Biological psychology
answer
a
question
"Naive realism" refers to the fact that a. most people are naive about psychology b. few people are realistic. c. most people would rather be naive than accurate. d. most people believe they perceive things accurately.
answer
d
question
Expecting a certain thing to happen so you behave in ways that make it come true
answer
Self-fulfilling prophecy
question
Researchers who study social cognition assume that people a. try to view the world as accurately as possible. b. can't think clearly with other people around them. c. distort reality in order to view themselves favorably d. are driven by the need to control others.
answer
a
question
Which of the following reflect(s) the motive to maintain high self-esteem? a. After Sarah leaves Bob, Bob decides that he never liked her much anyway. b. Students who want to take Prof. Lopez's class have to apply by writing a 10 page essay. Those selected to join end up loving the class. c. Janetta did poorly on her first test and admits that she didn't study enough and vows to study harder next time. d. Zach has been involved in several minor traffic accidents recently. "There sure are a lot of terrible drivers out here." he says. "People should learn to drive as good as me."
answer
abd
question
The "self-fulfilling prophecy" is the reason that many people a. love Doomsday predictions b. make a prophecy that they will fail their exams c. create a prophecy that they will succeed on their exams d. act in ways to make predictions of their own behavior or other's come true.
answer
d
question
How many of the following comments illustrate the fundamental attribution error? a. A woman comes home and nags her husband repeatedly. The husband thinks "my wife sure has become a grouchy person." b. A woman reads about high unemployment in poor communities and says "well if they weren't so lazy, they could find work." c. "The people who committed suicide at Jonestown were socially isolated and thus cut off from other points of view. d. "The people who committed suicide at Jonestown were mentally ill."
answer
abd
question
The tendency for people to exaggerate, after knowing that something occurred, how much they could have predicted it before it occurred.
answer
Hindsight Bias
question
If you give children a reward for something they already enjoy doing, they will subsequently like that activity a. more b. the same c. less
answer
c
question
A research method whereby a researcher observes people and systematically records measurements or impressions of their behavior
answer
Observational Method
question
The method by which researchers attempt to understand a group or culture by observing it from the inside, without imposing any preconceived notions they might have
answer
Ethnography
question
The level of agreement between two or more people who independently observe and code a set of data; by showing that two or more judges independently come up with the same observations, researchers ensure that the observations are not the subjective, distorted impressions of one individual
answer
Interjudge Reliability
question
A form of the observational research method in which the researcher examines the accumulated documents, or archives, of a culture (ex. diaries, novels, magazines, and newspapers)
answer
Archival Analysis
question
The research method whereby two or more variables are systematically measured and the relationship between them (how much one can be predicted by the other) is assessed.
answer
Correlational Method
question
A statistical technique that assesses how well you can predict one variable from another. Ex. how well you can predict people's weight from their height.
answer
Correlation Coefficient
question
A research method in which a representative sample of people are asked (often anonymously) questions about their attitudes or behaviors.
answer
Surveys
question
A research method in which the researcher randomly assigns participants to different conditions and ensures that these conditions are identical except for the independent variable ( the one thought to have a causal effect people's responses)
answer
Experimental Method
question
Making sure that nothing besides the independent variable can affect the dependent variable; this is accomplished by controlling all extraneous variables and by randomly assigning people to different experiment conditions
answer
Internal Validity
question
The extent to which the results of a study can be generalized to other situations and to other people
answer
External Validity
question
the extent to which the psychological processes triggered in an experiment are similar to psychological processes that occur in everday life.
answer
Psychological Realism
question
A description of the purpose of a study, given to participants, that isn't true and is different from the true purpose of the study and is used to maintain psychological realism
answer
Cover Story
question
A statistical technique that averages the results of two or more studies to see if the effect of an independent variable is reliable
answer
Meta-Analysis
question
Studies that are designed to find the best answer to the question of why people behave as they do
answer
Basic Research
question
Studies designed to solve a particular social problem
answer
Applied Research
question
The attempt to explain social behavior in terms of genetic factors that have evolved over time according to the principles of natural selection
answer
Evolutionary Psychology
question
Agreement to participate in an experiment
answer
Informed Consent
question
Misleading participants about the true purpose of a study or the events that will actually transpire. May be used as long as the participants are debriefed afterwards
answer
Deception
question
Explaining to participants at the end of an experiment what the true purpose of the study was and what transpired
answer
Debriefing
question
Thinking that is quick, no conscious deliberation of thought, unintentional, involuntary and effortless
answer
Automatic Thinking
question
Thinking that is effortful, deliberate, thinking about self and environment, and carefully selecting the right course of action
answer
Controlled Thinking
question
Mental structures that organize our knowledge of the social world. Encompasses our knowledge and impression of other people, ourselves, social roles, stereotypes.
answer
Schema
question
Neurological disorder characterized by the inability to form memories, each situation is new
answer
Korsakov's Syndrome
question
The process by which recent experiences increase the accessibility of a schema, trait, or concept
answer
Priming
question
The extent to which schemas and concepts are at the forefront of people's minds and are therefore likely to be used when we are making judgments about the social world
answer
Accessibility
question
A mental rule of thumb whereby people base a judgment on the ease with which they can bring something to mind. Ex. people think shark attacks happen often because we hear about it a lot whereas it doesn't happen as often as we think. (John Stewart example)
answer
Availability Heuristic
question
A mental shortcut whereby people classify something according to how similar it is to a typical case. Ex. Blonde haired guy with surf board - from Virginia or California? Most would say California
answer
Representative Heuristic
question
thinking style associated with Western cultures where people focus on objects without considering surrounding context
answer
Analytic Thinking Style
question
thinking style associated with Eastern cultures where people focus on overall context, relation between objects
answer
Holistic Thinking Style
question
a heuristic in which a person thinks the probability of an outcome has changed, when in reality, it has stayed the same. If a coin is flipped 10 times and lands on "heads" everytime, a person employing gambler's fallacy would believe the probability of the coin landing on "heads" the 11th time would be very low. The truth, however, is that the probability of a coin being "heads" or "tails" is 50% everytime the coin is flipped. The probability remains the same.
answer
Gambler's Fallacy
question
Mentally changing some aspect of the past in imagining what might have been. Ex. "If only I had answered that one question differently, I would have passed the test"
answer
Counterfactual Reasoning
question
The study of how we form impressions (perceptions) of and make inferences about other people
answer
Social Perception
question
way in which people communicate without words; nonverbal cues include facial expressions, tone of voice, gestures, body position and movement, the use of voice, and gaze
answer
Nonverbal Communication
question
To express or emit nonverbal behavior, such as smiling or patting someone on the back
answer
Encode
question
To interpret the meaning of the nonverbal behavior other people express, such as deciding that a pat on the back was an expression of condescension and not kindness
answer
Decode
question
Anger, Happiness, Surprise, Fear, Disgust, and Sadness
answer
Six Major Emotions
question
facial expressions in which one part of the face registers one emotion while another part of the face registers a different emotion
answer
Affect Blends
question
Culturally determined rules about which nonverbal behaviors are appropriate to display
answer
Display Rules
question
Nonverbal gestures that have well understood definitions within a given culture; ex. the okay sign
answer
Emblems
question
drawing meaningful conclusions about another person's personality based on an extremely brief sample of behavior
answer
Thin-Slicing
question
When it comes to forming impressions, the first traits we perceive in others influence how we view information that we learn about them later. ex. Keith versus Kevin's list of characteristics ordered differently
answer
Primacy Effect
question
The tendency to stick with an initial judgement even in the face of new information that should prompt us to reconsider
answer
Belief Perseverance
question
A description of the way in which people explain the causes of their own and other people's behavior
answer
Attribution Theory
question
inference that a person is behaving in a certain because of something about the person such as attitude, character, or personality
answer
Internal Attribution
question
inference that a person is behaving a certain way because of something about the situation he or she is in; the assumption is that most people in this situation would respond the same way
answer
External Attribution
question
A theory that states that to form an attribution about what caused a person's behavior, we systematically note the pattern between the presence or absence of possible causal factors and whether the behavior occurs
answer
Covariation Model
question
part of the covariation model and is the information about the extent to which other people behave the same way toward the same stimulus as the actor does. Ex. Joe screams at dog but it is high consensus b/c everyone screams at the dog
answer
Consensus Information
question
part of the covariation model and is the information about the extent to which one particular actor behaves in the same way to different stimuli Ex. Joe screams at dog but it is high distinctiveness because Joe doesn't react to other people's pets or dogs in general this way
answer
Distinctiveness Information
question
part of the covariation model and is the information about the extent to which the behavior between one actor and one stimulus is the same across time and circumstances. Ex. Joe always screams at dogs and people's pets
answer
Consistency Information
question
The seeming importance of information that is the focus of people's attention. What we see (police interrogation camera angles) plays a big part in whether we think of it as an internal or external attribution. Our ___________ , or point of view, helps explain why the fundamental attribution error is so widespread. We focus our attention more on the person than on the surrounding situation because the situation is so hard to see or know.
answer
Perceptual Salience
question
Analyzing another person's behavior first by making an automatic internal attribution and only then thinking about possible situational reasons for the behavior, after which one may (usually not enough of an adjustment) adjust the original internal attribution (Sometimes we skip the whole second step altogether)
answer
Two-Step Attribution Process
question
A form of defensive attribution wherein people assume that bad things happen to bad people and good things happen to good people. When we see tragedies we assume it was b/c people made mistakes or poor choices and this alleviates our anxiety that the tragedies could happen to us
answer
Belief in a Just World
question
Explanations for one's successes that credit internal, dispositional factors and explanations for one's failures that blame external situational factors. We make _______________ when our self-esteem is threatened.
answer
Self-Serving Attributions
question
The tendency to think that other people are more susceptible to attributional biases in their thinking than we are.
answer
Bias Blind Spot
question
Occurs when we conform because we see others as a source of information to guide our behavior. Believe others interpretation of an ambiguous situation is more correct than ours.
answer
Informational Social Influence
question
conforming to other people's behavior out of a genuine belief that what they are saying/doing is right
answer
Private Acceptance
question
conforming to other people's behavior publicly without necessarily believing what the other people are saying/doing
answer
Public Compliance
question
Occurs when we conform because we want to be liked and accepted by others. Results in public compliance with the group but not necessarily private acceptance.
answer
Normative Social Influence
question
The theory that conforming to a social influence depends on -Strength (importance of group to person) -Immediacy (closeness in time & space) -Number of people in group
answer
Social Impact Theory
question
The tolerance a person earns, over time, by conforming to group norms; if enough credits are earned, the person can, on occasion, deviate from the group without retribution. Ex. Matt Louis can deviate w/o retribution because he has earned enough credits
answer
Idiosyncrasy Credits
question
A type of norm that is people's perception of what behaviors are approved or disapproved by others
answer
Injunctive Norms
question
A type of norm that is people's perception of how other's actually behave in given situations, regardless of whether the behavior is approved or disapproved.
answer
Descriptive Norms
question
Getting people to agree first to a small request makes them more likely to agree later to a second, larger request
answer
Foot in the Door Technique
question
First asking people for a large request that they will probably refuse makes them more likely to agree later to a second, smaller request
answer
Door in the Face Technique
question
Attitudes that we consciously endorse and can easily report. Rooted more in recent experiences. Ex. Robert believes that all races are equal and abhors racial bias.
answer
Explicit Attitudes
question
Attitudes that are involuntary, uncontrollable, and at times unconscious. Rooted more in childhood experiences. Ex. Johnny grew up in a culture where there were many negative stereotypes about minority groups and negative feelings are triggered when he is around these groups
answer
Implicit Attitudes
question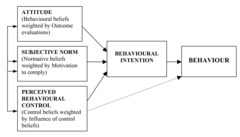
The theory of how attitude predict deliberate behaviors

answer
Theory of Planned Behavior
question
Behaviors that we think about
answer
Deliberate Behavior
question
A type of norm where it encompasses people's beliefs about how other people will view the behavior in question
answer
Subjective Norms
question
Intentions are influenced by the ease with which they believe they can perform the behavior.
answer
Perceived Behavioral Control
question
The strength of the association between an object and a person's evaluation of that object, typically measured by the speed with which people can report how they feel about the object
answer
Attitude Accessibility
question
Theory that when people behave inconsistently with their attitudes and cannot find external justification for their behavior, they experience discomfort/dissonance
answer
Cognitive Dissonance Theory
question
An explanation of the two ways in which persuasive communications can cause attitude change Specifies when people will be more influenced by what the speech says (i.e. the WHAT; the logic) and when they will be influenced by more superficial characteristics (i.e. the WHO; the deliverer)
answer
Elaboration Likelihood Model
question
Route in the elaboration likelihood model when people are motivated and have the ability to pay attention (e.g., listen carefully and think) to the arguments in the communication
answer
Central Route
question
Route in the elaboration likelihood model when people do not pay attention to the arguments but are instead swayed by surface characteristics (e.g., who is delivering the speech)
answer
Peripheral Route
question
Making people immune to attempts to change their attitudes by initially exposing them to small doses of the arguments against their position
answer
Attitude Inoculation
question
People feel their freedom to perform a certain behavior is threatened, an unpleasant state of reactance is aroused, which they can reduce by performing the threatened behavior. Ex. telling your kids they can't go out and then they sneak out.
answer
Reactance Theory
question
The rapid spread of emotions or behaviors through a crowd
answer
Contagion
question
the occurrence of similar physical symptoms with no known physical cause in a group of people
answer
Mass Psychogenic Illness
question
In a series of studies of normative social influence, participants judged which of the three comparison lines on the right was closest in length to the standard line on the left. The correct answer was always obvious. However, members of the group (actually confederates) gave the wrong answer out loud. Now the participant faced a dilemma: Give the right answer and go against the whole group, or conform to their behavior and give an obviously wrong answer? 76% of participants conformed.
answer
Asch's Line Judgment Study
question
In a study to test obedience, Milgram had participants ask other participants (confederates) questions and when the question was answered correctly the participant had to shock the confederate. Milgram told them it was essential that they continue despite the confederate crying out in pain. Continued giving the shocks even after the learner cried out in pain, said heart was bothering him.
answer
Milgram's Studies
question
Evaluation of people, objects, and ideas.
answer
Attitude
question
The tendency for individuals to increase their liking for something they have worked hard to attain. Ex. getting hazed in a frat works because the members like the frat more when they get in
answer
Justification of Effort
question
A reason or an explanation for dissonant personal behavior that resides outside the individual (e.g., to receive a large reward or avoid a severe punishment)Ex. justifying lying because it is a white lie and it will make the other person feel better
answer
External Justification
question
The reduction of dissonance by changing something about oneself (e.g., one's attitude or behavior) ex. a person who does volunteer work will internally justify their lack of pay because they're doing something good.
answer
Internal Justification
question
Stating an opinion or attitude that runs counter to one's private belief or attitude .
answer
Counterattitudinal Advocacy
question
The dissonance aroused when individuals lack sufficient external justification for having resisted a desired activity or object, usually resulting in individuals' devaluing the forbidden activity or object
answer
Insufficient Punishment
question
the arousal of dissonance by having individuals make statements that run counter to their behaviors and then reminding them of the inconsistency between what they advocated and their behavior. Ex. the study where they made the smokers make an anti-smoking PSA video for high schoolers.
answer
Hypocrisy Induction
question
Dissonance theory predicts that when we dislike someone, if we do them a favor, we will like them more.
answer
Ben Franklin Effect
question
Dissonance aroused after making a decision, typically reduced by enhancing the attractiveness of the chosen alternative and devaluating the rejected alternatives. More importance = more dissonance More permanence = more dissonance The most permanent and important a decision, the more a person will like the choice because they will try harder to reduce dissonance.
answer
Postdecision Dissonance
question
Reducing dissonance by adding a cognition about other positive attributes - e.g., smoker who fails to quit. Not very smart of me to be smoking, but, I'm really a very good mathematician!
answer
Self-Affirmation
question
The tendency to overestimate the intensity and duration of our emotional reactions to future negative events. Ex. We overestimate how bad negative events, like a relationship ending will make us feel but we don't account for dissonance reduction.
answer
Impact Bias
question
- Salesperson induces a customer to agree to purchase a product at a very low cost, subsequently claims it was an error, and then raises the price. - Frequently, the customer will agree to make the purchase at the inflated price. - Works b/c Sense of commitment - Sense of commitment triggers the anticipation of an exciting event - Price only slightly higher than other prices elsewhere
answer
Lowballing
question
Sometimes people do not know how they feel until they see how they behave - Can form our attitudes based on our observations of our own behavior Lying about how we feel, may end up believing the lie
answer
Self-Perception Theory



