Regulation of the cell cycle and cancer – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Cell cycle
answer
series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide; consists of phase: M, G1, G0, S, G2
question
M-phase time
answer
1 hour
question
Interphase time
answer
10-12 hours; no upper limit
question
S-phase time
answer
6-8 hours
question
G2 phase time
answer
2-4 hours
question
G1 phase time
answer
very variable
question
Interphase subdivisions
answer
G1 (gap 1), S (DNA synthesis phase) and G2 (gap 2)
question
G0
answer
in the absence of growth factors, the cell leaves the cell cycle at G1 and enters the resting phase (this phase)
question
Restriction point
answer
point when cells become committed to enter the cell cycle
question
M phase
answer
mitosis and cytokinesis
question
Mitosis

answer
separation of daughter chromatids; division of nucleus (karyokinesis); microtubule-dependent
question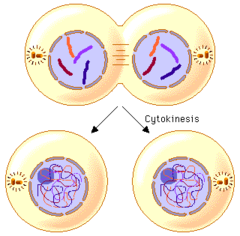
Cytokinesis

answer
part of M-phase; division of the cytoplasm; actin dependent
question
Stages of mitosis
answer
prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase (PPMAP)
question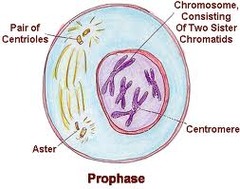
Prophase (mitosis)

answer
stage 1; chromosomes condense; nucleolus disappears; cytoplasmic microtubules break down; spindles being to form; centrioles migrate to poles
question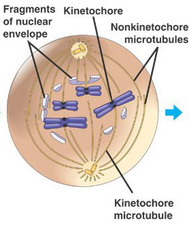
Prometaphase (mitosis)

answer
stage 2; chromosomes shorten & thicken, spindle forms between centrioles, moved to poles of the cell, kinetichores begin attaching to microtubules
question
Metaphase (mitosis)
answer
stage 3; pulling in between the kinetochore tubules results in the chromosomes and lining up at the metaphase plate
question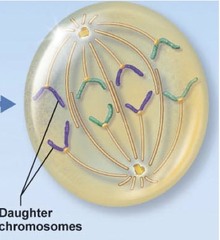
Anaphase (mitosis)

answer
stage 4; sister chromatids have separated and are now chromosomes; they are being pulled to opposite ends of the cell; kinetochore microtubules shorten; polar microtubules lengthen and slide; cleavage furrow appears and actin band form a contractile ring (start of cytokinesis)
question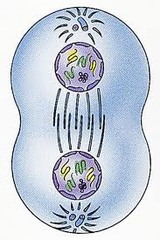
Telophase (mitosis)

answer
stage 5; nuclear envelope forms; spindles disappear; nuclear envelope forms; nucleolus re-forming; chromosome decondense; midbody contains spindle remnants
question
Return to interphase
answer
cytokinesis complete; cytoplasmic microtubules reforming
question
Spindle formation
answer
depends on the centrosome; a microtubule organising centre
question
Spindle formations contains
answer
a pair of centrioles
question
Centrosome location during interphase
answer
adjacent to the nucleus
question
Centrosome
answer
a structure present in the cytoplasm of animal cells that functions as a microtubule-organising centre and is important during cell division; composed of two centrioles
question
Centrioles
answer
cylindrical structures about 0.5 x 0.2 micrometers in diameter; made up of 9 triplets of microtubules; can act as a template for making cilia
question
Centriole duplication at each pole begins during
answer
interphase
question
Procentriole
answer
daughter centriole; grows out at right angles to the base of the mother centriole; one at each pole
question
By late _____ phase, the procentriole is full length but still attached
answer
G2
question
Mother/daughter centriole pairs seprate and spindles forms between them during the onset of ______
answer
mitosis
question
Detachment of mother and daughter centrioles occurs in _____ phase
answer
G1
question
Mitosis promoting factor
answer
causes entry into mitosis; cell fusion experiments revealed its existence
question
Rao and Johnston, 1970
answer
revealed the existence of mitosis promoting factor; shows that mitotic cells contain an inducer of mitosis (=MTF) which is dominant over all other phases of the cell cycle; what the MTF actually is not discovered
question
Fusion of a mitotic cell with an interphase cell
answer
causes the interphase nucleus to enter mitosis prematurely
question
Mitotic cell + G1 cell fusion
answer
results in single, thin chromosomes that have not replicated yet
question
Mitotic cell + S cell fusion
answer
replication forks everywhere; some replicated bits and some un-replicated bits of the genome; chromatin gets smashed to pieces > complete chaos
question
Mitotic cell + G2 fusion
answer
chromosomes become visible but much less visible than mitotic cell; thicker chromosomes than G1 chromosome; duplicated structures
question
Frog eggs
answer
MPF from them purified from them; found the MPF in it; found that the MPF is a cyclic-dependent protein kinase (already discovered in something else)
question
Protein kinase
answer
an enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to a protein, thus phosphorylating the protein
question
Protein kinase
answer
made of a catalytic subunit and a regulatory subunit
question
Cdk1
answer
catalytic subunit; first identified by Paul nurse through cell cycle genetics in yeast
question
Cyclin B
answer
regulatory subunit; first identified by Tim Hunt; in cleaving sea embryos; drives the mitosis;
question
Levels of Cdk1 during mitosis
answer
changes little during the cell cycle
question
Levels of Cyclin B during mitosis
answer
accumulates steadily during interphase and peaks during M
question
Degradation of Cyclin B
answer
essential to exit mitosis
question
S phase entry
answer
also depends on a dominant inducer
question
Fusion of S phase cell with G1 cell
answer
causes G1 nucleus to entre S phase prematurely
question
SPF
answer
cyclin-dependent kinase consisting a regulatory and catalytic subunit; triggers firing of replications origins and the initiation of DNA synthesis
question
Cdk2
answer
catalytic subunit of SPF; remains steady throughout cell cycle
question
Cyclin E or Cyclin A
answer
regulatory subunits of SPF
question
Cyclin E
answer
accumulates and peaks at the start of S phase but drops midway through
question
Cyclin A
answer
accumulates at the start of S phase and drops off at the end of G2 phase
question
Quiescence
answer
inactivity, stillness
question
G0 cells
answer
lack the machinery for replicating DNA because transcription of genes needed for the cell cycle entry by E2F transcription factors is repressed by Rb
question
E2F
answer
transcription factors that allow replicating DNA to transcribe the genes needed for cell cycle entry;
question
E2F target genes include
answer
thymidine kinase, DNA polymerase alpha, Cdc6, Cdk1, cyclin A, cyclin E, E2F-1
question
Rb gene
answer
protein that repress E2F transcription factors necessary for a cell to enter the cell cycle
question
Mutations in Rb gene
answer
responsible for retinoblastoma and are found at high frequency in many other tumours i.e. Rb acts as a tumour suppressor; inherited results in high susceptibility
question
Retinoblastoma
answer
tumour arising from a developing retinal cell; found in children
question
Passage of the restriction point (R)
answer
repression of EF2 is removed by phosphorylating Rb which is believed to correspond with...
question
Activate protein kinase complex
answer
ckd4 or ckd6 plus cyclin D1; phosphorylate Rb
question
Cyclin D1 expression
answer
point of convergence of numerous signalling pathways; expression strongly growth factor dependent
question
Over-expression of cyclin D1
answer
due to gene amplification or chromosome translocation; can drive entry into the cell cycle in the absence of growth factor stimulation
question
Oncogene
answer
cancer-causing genes that are formed due to mutations; e.g. mutated cyclin D1
question
Over-expression of cyclin D1 due to gene application
answer
common in breast cancers
question
Over-expression of cyclin D1 due to chromosome translocation
answer
common in B-cell lymphomas
question
Cell cycle deregulation
answer
found in many cancers
question
Most cancer cells have a
answer
reduced dependence on growth factors to enter the cell cycle
question
Common cell cycle deregulations (3)
answer
1) loss of Rb 2) upregulation of cyclin D 3) constitutive activation (continuous syntheis regardless of inducer of repressor molecules)) of growth factor signalling pathway
question
Pathway typically mutated in cancer cells
answer
Ras-Raf-MAPK pathway
question
Ras-Raf-MAPK pathway location
answer
downstream of receptor tyrosine kinase
question
Growth factor action
answer
(1) binds to GF receptor on plasma membrane, which have a tyrosine kinase unit which is activated (2) TK enzyme unit recruits Ras-GTP (3) Ras recruits another protein kinase, Raf (4) activates MAP kinase cascade (5) alters transcription in the nucleus
question
GF affects of transcription in nucleus
answer
increases the activity of transcription factors (fos, jun, myc) resulting in increased production of Cyclin D
question
MAP Kinase pathway
answer
only active when phosphorylated by MAPK; acts as an amplification pathway; amplification of transcription
question
MAPK
answer
only active when phosphorylated by MAPKK
question
MAPKK
answer
only active when phosphorylated by MAPKKK
question
Raf-1
answer
MAPKKK
question
Ras
answer
activated by growth factors by causing the replacement of its bound GDP with GTP
question
Active form of Ras
answer
Ras-GTP
question
G protein
answer
a GTP-binding protein that relays signals from a plasma membrane signal receptor; known as a G protein-coupled receptor, to other signal transduction proteins inside the cell
question
GEF
answer
guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) activate monomeric GTPases by stimulating the release of guanosine diphosphate (GDP) to allow binding of guanosine triphosphate (GTP)
question
Oncogenic Ras
answer
has point mutations in codons 12, 13 or 61; inhibits GTPase activity locking the Ras into active configuration (Ras-GTP)
question
Ras mutations found in ____% of human cancer cells
answer
30
question
Ras mutations found in ____% of pancreatic cancer cells
answer
90
question
Other ways of deregulating the Ras-Raf-MAPK pathway in cancer
answer
(1) autocrine production of growth factors (2) constitutive activation of growth factor receptor mutation (3) over-expression of growth factor receptor though gene amplification
question
Autocrine
answer
term for hormones that act on same cells that secrete them
question
Constitutive activation
answer
an appreciable level of activation existing even when no receptor ligand is present;
question
Constitutive activation of GF receptor mutation is found in what cancer
answer
found in EGFR in some lung cancers
question
Over-expression of GF receptor through gene amplification is found in what cancer
answer
found in HER2 (EGFR family) in a subset of breast cancers
question
Herceptin
answer
monoclonal antibody to HER2; used to target some breast cancers
question
EGFR
answer
epidermal growth factor receptor
question
First cell cycle checkpoint
answer
prevent cells from entering S phase with damaged DNA
question
Second cell cycle checkpoint
answer
prevent cells with incomplete or damaged DNA from entering mitosis
question
Third cell cycle checkpoint
answer
prevent cells in metaphase from entering anaphase before all the chromosomes are attached to the mitotic spindle
question
Tumour suppressor p53
answer
involved in first and second cell cycle checkpoint
question
Activation of tumour suppressor p53
answer
(1) p53 is phosphorylated following DNA damage (2) activate p53 induces transcription of p21
question
p21
answer
inhibits activation of cyclin dependent kinase (Cdk) by cyclin and prevents entry into S-phase or M-phase
question
Some transcriptional targets of p53
answer
trigger apoptosis
question
Mutated p53
answer
Will increase the likelihood of cancer because damaged DNA can go through the cell cycle
question
Unattached kinetochores
answer
generates a signal that prevents entry into anaphase
question
Mad2 (for e.g.)
answer
product of genes essential for proper chromosome segregation
question
Role of Mad2 precursor genes
answer
prevent anaphase onset; are displaced when spindle attachment occurs
question
Spindle assembly checkpoint
answer
defective in some cancers, leading to chromosome instability; causes non-disjunction
question
Deregulation of the cell cycle in cancer depends on
answer
(1) gain of function mutations in genes regulating growth factor signalling pathways to generate oncogenes (2) loss of function mutations in genes whose products repress the cell cycle
question
Mutations in certain genes, e.g. _____, results in a gain of function in GF signalling pathways > oncogenes
answer
Ras
question
Mutations in certain genes, e.g. _____ and _____, results in a loss of function > failure to repress the cell cycle
answer
Rb and p53
question
Incidence of cancer increased rapidly with _____
answer
age
question
Rate of increases suggests _______, ______ genes must be mutated, typically
answer
multiple, independent
question
Minimum number of gene mutations required to cause cancer
answer
5-7
question
Properties that must be acquired by a mutated cell to cause cancer (6 items)
answer
(1) loss of growth factor dependence (2) immortality (3) resistance to apoptosis (4) angiogenesis (5) tissue-invasion (6) metastasis
question
Angiogenesis
answer
the process through which the tumor supports its growth by creating its own blood supply
question
Systolic pressure
answer
occurs when the ventricles contract; the highest pressure against the walls of an artery
question
Diastolic pressure
answer
occurs when the ventricles are relaxed; the lowest pressure against the walls of an artery
question
Mean pressure is the highest in which blood vessel
answer
aorta
question
Mean pressure (mmHg) is the lowest in which blood vessel
answer
vena cava
question
Lumen diameter of the aorta
answer
25 mm
question
Lumen diameter of the arteries
answer
4 mm
question
Lumen diameter of arterioles
answer
20 micro meters
question
Lumen diameter of capillaries
answer
5 micro meters
question
Lumen diameter of venules
answer
20 micro meters
question
Lumen diameter of veins
answer
5 mm
question
Lumen diameter of vena cava
answer
30 mm
question
Wall thickness of aorta
answer
2 mm
question
Wall thickness of arteries
answer
15 micro meters
question
Wall thickness of capillaries
answer
1 micro meter
question
Wall thickness of venules
answer
2 micro meter
question
Wall thickness of veins
answer
0.5 mm
question
Wall thickness of vena cava
answer
1.5 mm
question
Blood pressure across blood vessels (highest to lowest)
answer
aorta (systolic level) > arteries > arterioles (diastolic level) > capillaries > venules > veins > vena cava
question
Arterial system
answer
carries blood away from the heart
question
Venous system
answer
carries blood towards the heart
question
Lymphatic system
answer
composed of a network of vessels, ducts, nodes, and organs; provides defence against infection.



