Radiation Protection Final – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
which of the following would absorb the most x-rays? muscle air-filled lungs bone soft tissue
answer
bone
question
the decrese in exposure rate of radiation caused by absorption through the material is known as?
answer
attenuation
question
the probability of photoelectric effect increases with? incresing Kvp incresing atomic # of the absorber decresing Kvp
answer
incresing atomic # of the absorber AND decreasing Kvp
question
the compton effect is characterized by?
answer
partial transfer of energy upon collision
question
almost all of the scattered radiation that is produced during a diagnostic x-ray examination is produced by?
answer
compton effect
question
which type of interaction between matter and radiation does not occur in the normal diagnostic energy range?
answer
pair production
question
a recoil electron is synonymous with?
answer
compton electron
question
the photoelectric effect takes place when a?
answer
x-ray photon ejects an inner shell electron and is completly absorbed
question
with pair production occuring the oncoming photon must have an energy level of at least?
answer
1.02 MEV
question
when an incoming photon splits to form a positron and a negitron we have?
answer
pair production
question
the radiation that occurs when an electron moves from an outter orbit to fill a vacancy in an inner orbit during the photoelectric effect is?
answer
characteristic radiation/ secondary
question
image fog in diagnostic imaging is caused by?
answer
compton scatter
question
x-rays transmitted without interaction contribute to?
answer
the radiographic image
question
when an x-ray passes through matter, it undergoes a process called?
answer
attenuation
question
which atomic shell possesses the highest binding energy?
answer
K shell
question
during photoelectric absorption, a/an_______ shell electron is ejected
answer
inner
question
during photoelectric absorption, the ejected electron is called a/an_____
answer
photoelectron
question
the electron dislodged during compton scattering is called the?
answer
recoil electron
question
what is it called when a primary photon changes direction but not energy?
answer
classical coherent scattering
question
biological changes caused by x-rays are the result of what?
answer
ionization
question
which of the following has the greatest effect on radiographic contrast? compton scattering classical scattering pair production photoelectric effect
answer
photoelectric effect
question
which effect is most responsible for occupational exposure?
answer
compton effect
question
differential absorption is dependent on the ? kvp of the exposure atomic # of the absorber mass density of the absorber
answer
kvp of the exposure, atomic # of the absorber, and mass density of the absorber
question
coherent scattering occurs with _______ energy x-rays
answer
low
question
a photoelectric interaction cannot occur unless the incident x-ray has energy_______ than the electron-binding energy.
answer
equal to or greater
question
of the following three things that may occur when x-rays pass through tissue, which is not desirable for producing diagnostic images? absorption penetration scatter
answer
scatter
question
as the energy loevel increases beyond a moderate level, the probabilty of compton occuring?
answer
decreases
question
what is the effect called when an incedent x-ray photon interacts with an atom and produces a scattered secondary x-ray with the same energy but in a different direction?
answer
classical scattering
question
when the x-ray photon reaches some material, which interaction may occur? the energy may be totally absorbed the energy may be momentarily absorbed there may be no interaction at all The energy may be partially absorbed
answer
ALL OF THE ABOVE (the energy may be totally absorbed the energy may be momentarily absorbed there may be no interaction at all The energy may be partially absorbed)
question
photoelectric effect
answer
photoelectric effect
question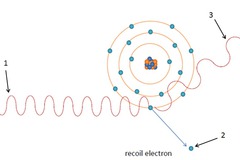
compton scatter

answer
compton scatter
question
what describes the wavelengths of a diagnostic x-ray beam?
answer
heterogeneous
question
x-rays are classified as what type of radiation?
answer
electromagnetic
question
anatomic structures that readily transmit x-rays are?
answer
radiolucent
question
the photoelectric effect is principally associated with which of the following? absorption of an xray bremsstrahling xray production characteristic xray production electron excitation scattering of an xray
answer
absorption of an xray
question
what happens to the energy of the xray photon when photodisintergration happens?
answer
absorbed by nucleus
question
how much energy does an xray need for photodisintergration to occur?
answer
10 Mev
question
what is the basic functional unit of all plants and animals?
answer
cell
question
the human body is composed of about 80% ____.
answer
water
question
the ___________ in the body provide furl for cell metabolism.
answer
carbohydrates
question
the ____ in the cell are nucleic acids.
answer
DNA and RNA
question
the most radiosensitive target molecule in the human cell is the ____.
answer
DNA
question
DNA is located in the _____ of the cell.
answer
Nucleus
question
the metabolic process of building large molecules from smaller ones is called _____.
answer
anabolism
question
all the hereditary information about an individual is contained in the ____ cells.
answer
germ
question
the two major parts of the cell are the nucleus and the _____.
answer
cytoplasm
question
the cell "engines" are the ____.
answer
mitochondria
question
the ______ have the function of cleaning contaminants from the cell
answer
lysosomes
question
ribonucleic acid is located primarily in the ?
answer
cytoplasm
question
meiosis is the process of cell division for ____ cells
answer
genetic
question
a cell is in ______ when it is not undergoing mitosis or meiosis.
answer
interphase
question
any chromosome damage induced by radiation could be seen during the?
answer
metaphase
question
during the ___ phase of cell life each DNA molecule is replicated into two identical daughter DNA molecules.
answer
S phase
question
the process of cell meiosis results in cells with ______ chromosomes each
answer
23
question
before cells mature they are called _______ cells.
answer
stem, precursor, or undifferentiated
question
humans are most radiosensitive during?
answer
fetal stages
question
the most radiosensitive macromolecule is?
answer
DNA
question
DNA is contained in the ____ of the cell nucleus
answer
chromosomes
question
radiation damage to DNA can result in? cell death malignant disease genetic changes
answer
all of the above (cell death malignant disease genetic changes)
question
human cells are most radiosensitive during the ____ phase of the cell cycle
answer
synthesis
question
the genetic female cells sre the?
answer
Oogonium
question
what is the process of reduction cell division?
answer
meiosis
question
to make a base pair, the purine adenine must be bonded to the pyrimidine _______?
answer
thymine
question
the process of cell dicision results in ?
answer
two daughter cells
question
if a cell has 12 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will each of its daughter cells have after mitosis?
answer
12
question
the phase of mitosis during which the chromosomes become visible and centrioles seperate from one another is?
answer
prophase
question
which of the following is not a phase of mitosis? anaphase metaphase telophase prophase interphase
answer
interphase
question
in the cell cycle, the period between cell division is called?
answer
interphase
question
carbohydrates may also be referred to as?
answer
saccharides
question
the nucleolus contains which of the following? centrosomes RNA ribosomes lysosomes
answer
RNA
question
lipids are referred to as ?
answer
fats
question
the primary energy source for the cell is?
answer
glucose
question
cytosine bonds only with which of the following nitrogenous organic bases? adenine guanine thymine uracil
answer
guanine
question
the process of locating and identifying the genes in the human genome is called?
answer
mapping
question
the S phase of mitosis is the?
answer
actual DNA synthesis period
question
compounds that do not contain carbon are called?
answer
inorganic
question
messenger RNA (mRNA) transferes its genetic code to another kind of RNA molecule called transfer RNA (tRNA) T or F?
answer
TRUE
question
catabolism is the process of breaking down organic materials to produce energy for the cell T or F ?
answer
TRUE
question
the large, double-membrane, oval, or bean shaped, structures that function as the powerhouses of the cell are called?
answer
mitochondria
question
the protoplasm outside the cells nucleus is called what?
answer
cytoplasm
question
tissues that are ______ with a ______ metabolic rate are more radiosensitive. ? immature,low immature,high mature,low mature,high
answer
immature, high
question
as LET ______, the RBE_______ ? increases,remains the same decreases,remains the same increases,increases increases,decreases
answer
increases,increases
question
the protracted dose of radiation is given?
answer
over a long period of time
question
a dose of 1000 rads is given to a patient in 5 doe=es of 200 rads per day is a ____ dose
answer
fractionated
question
the LET of diagnostic xrays is _____ Kev/um
answer
3.0 Kev/um
question
tissue is _______ radiosensitive under high oxygen conditions and _______ radiosensitive under hypoxic conditions? less,equally less,more more,less more,equally
answer
more,less
question
fractionation and protraction are used for radiation therapy because they allow the patient to _____. recover between doses have higher total doses repair damaged tissues
answer
all of the above (recover between doses have higher total doses repair damaged tissues)
question
humans are most radiosensitive during?
answer
fetal stages
question
the possible beneficial effect of a small amount of radiation is called ?
answer
hormesis
question
the type of dose-responce curve used to predict GENETIC effects is the ?
answer
linear, nonthreshold
question
the theory of radiation hormesis suggests that radiation doses below 10 rads are?
answer
beneficial
question
which statement is true concerning the effects of radiation exposure? no effects occur at low rad levels damage is not passed of to offspring the body can repair most damage mutation only occurs at high exposure
answer
the body can repair most damage
question
xrays cuase biological damage to tissue by a process known as>
answer
ionization
question
what does an nonthreshold dose look like on a graph?
answer
can be any line (straight or curved) originating on the Y axis
question
what does a non-linear dose-responce graphy look like?
answer
any curved line coming off either the X or Y axis
question
before cells mature they are called what?
answer
stem, precursor, or undifferentiated
question
in 1906 bergonie and tribondeau established a lawl which states that cells are more radiosensitive if they? have a low proliferation rate are stem cells are young
answer
are stem cells, and if they are young
question
______ is a measure of the rate of energy that is transferred from ionizing radiation to soft tissue.
answer
LET
question
the RBE of diagnostic xrays is equal to ___
answer
1
question
cataractogenosis does not occur at low levels of radiation exposure. therefore it is best expressed by what dose-responce relationship?
answer
A threshold dose-responce relationship
question
what does responce curve is the basic principle of radiation protection in medical radiography?
answer
linear,nonthreashold
question
cells are more radiosensitive when oxygenated. T or F ?
answer
TRUE
question
the amount of energy deposited by radiation per unit length of tissue being traversed is?
answer
linear energy trandfer (LET)
question
what does a linear non-threashold curve look like?
answer
a straight line that makes contact with the Y axis
question
what does a non linear threashold curve look like?
answer
any curved line that makes contact with the X axis
question
what does a linear threshold curve look like?
answer
any straight line that makes contact with the X axis
question
what are graphs called that show the relationship between dose of radiation recieved and incidence of effects?
answer
dose responce curves
question
what dose-responce relationship manes there is no safe level of radiation, and the responce to the radiation is not directly proportional to the dose recieved?
answer
nonlinear-nonthreashold effect
question
which of the following has the highest LET?
answer
alpha particles
question
LET is measured in which of the following? gray Kev/rad Kev/um rad rad/um
answer
Kev/um
question
LET is best defined as? a method of expressing radiation quality a measure of the rate at which radiation energy is transfered to soft tissue absorption of polyenergetic radiation
answer
all of the above (a method of expressing radiation quality a measure of the rate at which radiation energy is transfered to soft tissue absorption of polyenergetic radiation)
question
the skin responce to radiation exposure that appears as hair loss is known as?
answer
epilation
question
biologic material is least sensitive to irradiation under which of the following conditions? anoxic hypoxic oxygenated deoxygenated
answer
anoxic
question
diagnostic x-radiation may be correctly described as? low energy, low LET low energy, high LET high energy, low LET high energy, high LET
answer
low energy, Low LET
question
is a macromolecule has a _________ , it will break down into smaller molecules
answer
main-chain scission
question
molecular lesions of DNA are called?
answer
point mutations
question
two OH* free radicals can join to form _________ molecules
answer
hydrogen peroxide
question
OH-
answer
hydroxyl ion
question
OH*
answer
hydroxyl free radical
question
e-
answer
electron
question
H2O
answer
water molecule
question
H+
answer
hydrogen ion
question
H*
answer
hydrogen free radical
question
HOH+
answer
positive water molecule
question
HOH-
answer
negitive water molecule
question
main-chain scission _____ the size of the macromolecule and _______ the viscosity of the solution.
answer
decreases, decreases
question
irradation outside of the body is called?
answer
invitro
question
irradiation within the body is called?
answer
invivo
question
irradiation in vivo demonstrates that macromolecules are considerably ____ radiosensitive in this enviornment.
answer
more
question
name 3 principal abservable effects of DNA irradiation?
answer
main-chain scission cross-linking point lesions
question
which type of chemical can be produced by free hydroxyl radicals? water sulfahydryls hydrogen perioxide oxygen
answer
hydrogen peroxide
question
which of the following macromolecules is considered to be the most radiosensitive? proteins lipids DNA RNA
answer
DNA
question
which of the following contains all the hereditary information for a cell? pyridmidines nucleotides deoxyribonucleic acid ribonucleic acis
answer
deoxyribonucleic acid
question
irradiation of water molecules within the body, and their resulting breakdown is called?
answer
radiolysis
question
the probabilty of a hit is increased with ______ oxygen and ______ LET radiation.
answer
high, high
question
the principle radiation interaction within the human body is with ______.
answer
water
question
according to target theory, the target molecule of a cell is?
answer
the DNA in the nucleus
question
an indirect effect from ionizing radiation occurs on a __________ molecule.
answer
water
question
a hit to a target molecule can occur from a(n)_______ effect.
answer
indirect or direct
question
the principle radiation interactions within the human body are assumed to be _________ effects.
answer
indirect effects
question
the lethal effects of cell irradiation are measured by cell_______.
answer
survival
question
A ________ is an unstable molecule that loses one of its electrons and therefore becomes unbalanced and highly reative.
answer
free radical
question
free radicals are more easily produced in the presence of oxygen. T or F ?
answer
TRUE
question
when does radiolysis of water occur?
answer
when water is ionized
question
a negativley charged water molecule splits into what two components?
answer
hydrogen radical and hydroxyl ion
question
how do hydrogen and and hydroxyl radicals cause biological damage? they can destroy chemical bonds hydroxyl radical s can bond to form hydrogen peroxide hyrdogen radical can interact with molecular oxygen, forming a hydroperoxyl radical
answer
all of the above (they can destroy chemical bonds hydroxyl radical s can bond to form hydrogen peroxide hyrdogen radical can interact with molecular oxygen, forming a hydroperoxyl radical)
question
what first happens when an xray interacts with and ionizes a molecule of water?
answer
an electron is dislodged, creating an ion pair
question
what effect is responciple for producing free radicals?
answer
indirect effect
question
most of the damage to a cell occurs as a result of?
answer
indirect effect
question
cells are more readiosensitive when? fully oxygenated deoxygenated slowly dividing near the skin
answer
fully oxygenated
question
what is the name for changes in genetic code passed on to the next generation?
answer
mutations
question
what effect occurs when the target molecule is ionized?
answer
direcet effect
question
what states that each cell has a master molecule that direct all cellular activities and that, if inactivated, will result in cellular death?
answer
target theory
question
lab experiments have shown that damage caused by irradiation of macromolecules is not reversible through intracellular repair and recovery. T or F?
answer
FALSE the cell can repair and recover damage even in macromolecules
question
which type of irradiation of macromolecules have small, spur-like side structures that extend off the main chain?
answer
cross linking
question
___________ is the breaking down of nutrients into smaller molecules wiht an accompanying release of energy.
answer
catabolism
question
___________ is the production os large molecules for form and function for metabolism in the cell
answer
anabolism
question
proteins are less radiodensitive than nucleic acids. T or F?
answer
TRUE
question
most human cells that are in a normal state of proliferation have generation times of how many hours?
answer
24 hours
question
irradiation of mammalian cells with high-LET radiation follows which model? single-target, single-hit multitarget, single-hit
answer
single-target, single-hit
question
human cells are ________ radiosensitive in M phase and ______ radio resistant in late S phase of the cell cycle.
answer
most , most
question
a free radical is an uncharged molecule that contains a single unpaired electron in the outer shell. T or F?
answer
TRUE
question
according to the _________, cell death will occur only if the target molecule is inactivated.
answer
target theory
question
the form of ARS that results when the central nervous system and the cardiovascular system recieve ionizing radiation doses of 50 Gy (5000 rads) or more?
answer
central nervous system syndrome
question
radiation sickness that occurs in human begins after whole body reception of large doses of ionizing radiation (1 Gy) (100 rads) or more delivered in a short time.
answer
Acute radiation syndrome
question
during the latent period the radiation victim experiences?
answer
well being
question
the LD 50/60 is the dose of radiation to the whole body that will result in death within ___ days to ___ % of the population
answer
60 days, 50% (percent always the numerator)
question
which of the following is noe a form of acute radiation syndrome? carcinogenic syndrome hematopoietic syndrome gastrointestinal syndrome central nervous system syndrome
answer
carcinogenic syndrome
question
a whole bosy dose equivalent of 3000 rem (30 msv) would probably cause death in 4-10 days by what mechanism?
answer
gastrointestinal death
question
three days after recieving a dose of 1000 rad, physiologic alterations in the small intedtine include all of the following except? crypt cell death diarrhea epilation leakage of proteins from the intestinal lumen loss of electrolytes and water
answer
epilation
question
which of the following is not one of the stages of acute radiation syndrome? prodromal manifest latent prophase
answer
prophase
question
which of the following are symptoms associated with the prodromal stage of ARS? nausea lethargy diarrhea
answer
nasuea and diarrhea
question
a whole body dose equivlent of 1000 rads would probably cause death in 4-10 days by what mechanism?
answer
gastrointestinal death
question
the latent period is the time after exposure during which there is no sign of radiation sickness. T or F ?
answer
TRUE
question
what is the most radio resistant species?
answer
cockroach
question
a victim may experiance the manifest ilness stage, which consists of the following? hematologic gastrointestinal central nervous system
answer
all of the above (hematologic gastrointestinal central nervous system)
question
what is the mean survival time of the ccentral nervous system syndrome?
answer
0-3 days
question
which of the following populations have experianced an excessive incidence of lung cancer? radium dial watch painters uranium miners TB fluro patients atomic bomb survivors
answer
uranium miners
question
during which period of pregnancy will hihg irradiation of the embryo or fetus most likley result in congenital abnormailty?
answer
weeks 2-10
question
which population has experienced an excessive incidence of breast cancer?
answer
TB fluro patients
question
when radiation effects are termed deterministic?
answer
the severity of the responce is dose-related
question
approximately what is the threashold dose after an acute xray exposure necessary to produce cataracts?
answer
200 rad
question
what population has experianced an excessive incidence of bone cancer?
answer
radium watch dial painters
question
radiation induced cataracts appear?
answer
on the posterior pole of the lens
question
which of the following is considered a late radiotion responce? cataracts moist desquamation lymphocytic depression epilation
answer
cataracts
question
human responces to radiation exposure that are late effects are called?
answer
stachastic
question
radiation induced leukemia is considered to have a letent period of ?
answer
4-7 years
question
which of the following is considered a late radiation responce? sterility lung cancer skin erythema hematological depression
answer
lung cancer
question
what population has experianced excessive incidence of liver cancer?
answer
thoratrast (contrast) patients
question
is a disease exceeds the number of cases of which it is expected, the difference between the observed cases and the expected number would be?
answer
excessive risk
question
the theory of radiation hormesis suggest that very high doses are beneficial. T or F?
answer
FASLE, LOW doses are beneficial
question
the dose of radiation that produces twice the frequency of genetic mutations as would have been observed without the radiation is?
answer
doubling dose
question
existing data on radiation-induced genetic effects in humans ?
answer
are still inconclusive
question
radiation protection guidelines are based on?
answer
late effects of radiation
question
an epidemiological study of the late effects of very low doses of radiation requires a population of ___ people
answer
millions
question
ankylosing spondylitis patients treated with radiation showed an increased incidence of?
answer
leukemia
question
peolpe who had radiation treatment to their thymus gland as children later showed excess risk for ?
answer
thyroid cancers
question
relative risk is written as?
answer
observed cases/expected cases
question
our information on the genetic effects of radiation has come from studies on?
answer
mice and fruit flies
question
the type of dose-responce curve used to predict genetic effects is the?
answer
linear nonthreashold
question
A ____________ effect increases with incidence but not severity as the dose increases
answer
stochastic
question
BEIR stands for?
answer
biological effects of ionizing radiation
question
stochastic somatic effects are also called ?
answer
probabilistic effects
question
nonstochastic somatic effects are called?
answer
deterministic effects
question
what population has experianced an excessive incidence of leukemia?
answer
atomic bomb survivors
question
chataracts do not occur at low levels of radiation exposure. therefore it is best expressed by what dose-responce relationship?
answer
threashold
question
radiation effects that show up in the next generation are called?
answer
genetic
question
the best estimate for radiation induced life span shortening is?
answer
10 days for every rad
question
what situation will cause the greates harm from radiation exposure?
answer
large dose over a short period of time
question
what would be the most likley result of repeatedly subjecting the hands to radiation or to treatment for conditions such as ringworm and acne with high doses of low energy xrays?
answer
skin cancer
question
what dose responce curve is the basic principle of radiation protection in medical radiography based on?
answer
linear, nonthreashold
question
uranium miners in the colorado plateau who developed lung cancer years after exposure provide an extra example of what?
answer
late stochastic somatic effects
question
when a prediction is made that the number of excess cancers in a given population will increase as the natural incidence of cancer increases in that population with age, the risk is described by what term?
answer
relative
question
studies of postpartum patients treated with ionizing radiation for relief of mastitis indicate that in this group of individuals, radiation exposure to healthy breast tissue?
answer
can cause breast cancer
question
it is difficult to link cancer to radiation because it occurs ____ in the population
answer
in high proportion
question
a realtive risk of 2:1 means
answer
twice as many cases of disease as expected
question
the leakage radiatioin limit for an xray tube is less than _______ at 1 meter from the tube housing
answer
100 mR/hr
question
the xray control pannel must show?
answer
mAs used
question
the collimator light must be accurate to within ____% of the SID
answer
2%
question
the minimum requirement for filtratioin on xray equipment operating above 70 Kvp is ?
answer
2.5 mm Al equivalent
question
the output intensities of reproduced exposures should not vary more than _____ % from each other.
answer
5%
question
measuring the relationship between the output intensities of adjacent mA stations is a test of ?
answer
linearity
question
the source to skin distance must be no less than _____ cm on stationary fluroscopes.
answer
38 cm
question
the _____ is the primary protective barrier for the fluroscopic xray tube.
answer
image intensifier
question
the fluroscopic exposure control switch is always a(n) ______ type.
answer
deadman
question
the bucky slot opening in the side of the table must be automatically covered with _____ mm Pb during fluroscopy
answer
0.25 mm Pb
question
a cumulative timer is designed to ____ of fluroscopy beam on time.
answer
make the radiologist aware
question
primary radiation is ?
answer
the useful beam
question
the intensity of scatter radiation 1 meter from the patient is approximately _______ of the intensity of the incident beam at the patient.
answer
0.1%
question
at the level of the tabletop, the intesity of the fluroscopic beam should not exceed ______ for each mA of operation at 80 kVp
answer
2.1 R/min
question
a controlled area is one primarily occupied by ?
answer
radiology personnel and patients
question
a quantity that reflects both dose and volume of tissue irradiated is the ?
answer
dose area product
question
the design of an uncontrolled area in radiology is based on the NCRP recommended limit of _____ mrem/yr for the public.
answer
100 mrem/yr
question
gas-filled radiation detectors are based on the?
answer
ionization of gas
question
a geiger-muller counter is a(n) ________.
answer
gas filled detector
question
tha advantages of using thermoluminescent dosimeters are?
answer
small size and tissue equivalent responce
question
when preforming a mobile fluroscopic procedure, to reduce the radiation exposure to the patient, the radiographer must use minimal source-skin distance of _____ cm ( ___inches)
answer
30 cm (12 inches)
question
during fluroscopic examination a resettable cumulative timing device times the xray beam-on time and sounds an audible alarm of temporarily interrupts the exposure after the fluroscope has been activated for what length of time?
answer
5 minutes
question
the control pannel, where technical exposure factors are selected and seen on indicators by the equipment operator, must be located?
answer
behind a suitable protective barrier that has a radiation-absorbent window that permits observation of the patient during any procedure
question
what is another term for use factor (U)?
answer
beam direction factor
question
what is the term for the proportional amount of time during which the xray beam is energized or directed toward a particular barrier?
answer
use factor
question
________ is the radiation output weighted time the unit is actually delivering radiation during the week.
answer
workload
question
secondary radiation includes ____ radiation
answer
leakage and scatter
question
who should determine the exact shielding requirments for a particular imaging facility?
answer
medical physicist
question
the goal of the alliance for radiation saftey in pediatric imaging is to ?
answer
increase the awareness of the need to reduce patient dose for pediatric patients
question
what do film badges, optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) dosimeters, pocket ionization chambers, and TLD's have in common?
answer
these devices are all use for personnel monitoring
question
what device contains an aluminium oxide detector?
answer
OSL dosimeter
question
Which of the following is not a basic component of the film badge dosimeter? radiographic film packet durable plastic film holder charged electrodes assortment of metal filters
answer
charged electrodes
question
what should be given to a radiation worker on termination of employment?
answer
a summary of an occupational exposure report
question
the OSL dosimeter is read out by using
answer
a lazer light at selected frequencies
question
health physics is concerned with minimizing radiation to ?
answer
radiation physicists, radiation workers, and public
question
exposure is measured by multiplying ______ by ____
answer
exposure rate, exposure time
question
a tenth value layer is equal to _____ half value layers.
answer
3.3
question
the dose limit for the general public is ____ the dose limit for occupational exposure.
answer
1/10
question
the use factor is based on?
answer
what percentage of time the primary xray beam will be striking a barrier
question
types of secondary barriers include?
answer
control booth walls, and mobile xray barriers
question
a controlled area is defiened as one?
answer
that is occupied by people trained in radiation saftey, and that is occupied by people who wear radiation monitors
question
any wall that the useful beam can be directed towards is called a ?
answer
primary barrier
question
which of the following locations in a hospital should have the highest occupancy? lab elevator corridor restroom waiting room
answer
lab
question
what contributes to the exposure of radiologic technologists?
answer
scatter radiation
question
in thermoluminescence dosimetery, a plot of output intensitiy versus tempurature is called?
answer
a glow curve
question
when using mobile radiographic equipmet, where should the radiographer stand in realetion to the patient and primary beam?
answer
at right angles to the xray beam scattering object (patient) line
question
how can radiographers minimixe their risk orf radiation exposure during fluroscopy?
answer
using a protective drap, bucky slot cover, and rotating personnel through the fluro department on a reguar basis
question
when considering the occupancy of rooms and areas, what does the general public refer to?
answer
patients, visitiors, and personnel that do not work with radiographic equipment
question
what are the primary protective barriers designed to protect against?
answer
primary or useful beam radiation
question
in determining barrier thickness, what does the use factor or beam direction factor represent?
answer
the fractional amount of time the primary beam is energized and directed at a barrier
question
in terms of the occupancy factor in radiation protection, parking lots, elevators, and stairways are considered to be what?
answer
uncontrolled areas
question
what is the best location for the control pannel exposure switch?
answer
either stationary onthe control pannel or on a short cord so it can be used only from within the control pannel
question
the cord on a moblie radiographic unti should allow the radiographic technologist to stand at least how far from the unit?
answer
6 feet
question
what are primary protective berriers?
answer
those at which the primary beam is directed
question
in determining barrier thickness, the amount of time an xray unit operates is referred to as what?
answer
workload factor
question
when are bucky slot covers and protective curtains used?
answer
during fluro procedures
question
how thick must lead be in the primary barrier of a radiographic room?
answer
1/16 "
question
what is the best protection from radiation?
answer
distance
question
the level of radiation activity in a room each week is called _______ and is measured in mAmin/wk
answer
workload
question
which of the following methods is used to determine if an xray tube has adequate filtration?
answer
half-value layer (HVL) measurement
question
if 2mm Al is added to an xray bean that has a HVL of 2 mm Al, how much will the exposure be reduced?
answer
50%
question
patient dose is estimated by conducting simulated xray examinations with ?
answer
human phantoms and test objects
question
the frequency of xray examinations being prefoemed is increasing inall age groups. T or F ?
answer
TRUE
question
patient dose from diagnostic xrays is most often reported in?
answer
entrance skin exposure
question
how is ESE calculated?
answer
output intensity (mR/mAs) X mAs = mR
question
acute skin effects from radiation exposure have been reported following?
answer
angiointerventional exams
question
for the average fluro exam the ESE is?
answer
4 R/min
question
an estimation of patient dose is reported as?
answer
ESE, bone marrow dose, and gonadal dose
question
bone marrow dose is measured ?
answer
as an estimate from ESE
question
the simpliest way to measure patient dose is to measure the ?
answer
ESE
question
the approximate bone marrow dose to the population of the US is?
answer
100 mR/yr
question
the genetically siginificant dose for the general public is important because of the risk of ?
answer
effects on the gene pool
question
CT is considered a low dose procedure. T or F?
answer
FALSE, it is considered a high dose procedure
question
the period of major organogenesis is during the _____ of pregnancy
answer
2-10 week
question
preforming routine xray exams without indication is acceptable?
answer
never
question
what exam does NOT have the highest repeat rates?
answer
chest xray
question
breast dose for a scoliosis exam can be minimized by using the _______.
answer
PA projection, and lead shielding
question
for diagnostic xray personnel, the highest occupational exposure occurs during _____ exams.
answer
fluro and mobile
question
personnel working in interventional radiography should be provided with?
answer
extremity monitoring
question
the lens of the eye should never recieve more than _____ per year.
answer
150 mSv (15 Rem)
question
dose limits are described as ?
answer
effective dose
question
the tissue weighting factor has a higher value for tissues with more?
answer
radiosensitivity
question
for nursing personnel present during mobile xray imaging, a personnel monitoring device is required?
answer
not at all
question
the dose limit for extermities is?
answer
500mSv/yr (50rem/yr)
question
the lowest occupational exposure of diagnostic xray personnel occurs during?
answer
CT and mammography
question
the dose limit to the general public is?
answer
1mSv/yr (100mrem/yr)
question
techs working in fluro should use the radiologist as shielding whenever possible in addition to the apron and curtains. T or F ?
answer
TRUE
question
occupational radiation monitoring is required if the individual may get ______ of the recomended dose limit.
answer
10%
question
OSL monitors are superior to thermoluminescent dosimeters in that they are ____.
answer
more sensitive to low exposure
question
during fluro the exposure to the collar is _____ times greater than exposure to the trunk of the body under the protective apron
answer
20
question
the minimum required thickness of a lead apron is?
answer
0.25 mm lead equivalent
question
the dose limit for the tech during pregnancy is?
answer
0.5mSv/mo (50 mrem/mo)
question
every radiation department should provide a radiation saftey program that includes?
answer
training new employees, periodic in-services for all employees, counseling during pregnancy
question
there are no circumstances under which a tech should be given an involuntary leave of absence due to preganacy T or F ?
answer
TRUE
question
a traditional unit of measurement for radiation exposure in air is?
answer
roentgen
question
what traditional unit of measurement is used to describe exposure recorded on a film badge?
answer
rem
question
for rad protection perposes...
answer
1 R=1rem=1rad
question
which traditional unit of radiation measurement describes patient dose?
answer
rad
question
what is the annual whole body effective dose for a technologist?
answer
5 rem (50mSv)
question
in 1994, the NRC changed the term describing maximum dosage for techs, the new correct term is?
answer
dose-limiting recommendations
question
the cumulative dose limit for an occupationally exposed worker is ?
answer
10 mSv x age
question
what is the minimum thickness of a gonadal shield for primary beam shielding in the 50-100 kvp range?
answer
1 mm lead equivalent
question
when correctly placed, gonadal shielding will reduce dose by ____ if gonads are in the primary xray field
answer
50%-90%
question
which of the protection devices must be in place before a fluroscopic procedure?
answer
bucky slot shield
question
what are SI units?
answer
coulomb per kg, Gray, Sievert



