Price Elasticity Of Demand Test Questions – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Demand Elasticity
answer
A measure of how quantity demanded will be affected by a change in price, income or related variables.
question
Elasticity
answer
Measures the extent to which demand will change given a change in price
question
Price Elasticity of Demand (PƐD)
answer
The responsiveness of changes in demand given a change in price.
question
PƐD Formula

answer
%△QD / %△P
question
%△ is always...
answer
(Difference / Original)x100
question
Price Elastic Demand
answer
Demand is price elastic if the value of elasticity is greater than -1 (PƐD>-1). If Demand for a good is price elastic then a %△ in P will bring about a large %△ in QD
question
Elastic Demand Revenue
answer
Increase In Price = Fall in Revenue (Drop in price to increase revenue)
question
Price Inelastic Demand
answer
Demand is price inelastic if the value of elasticity is between 0 and -1. (0<PƐD<-1). %△ in P is greater than %△ in QD
question
Inelastic Demand Revenue
answer
Increase in price = increase in revenue.
question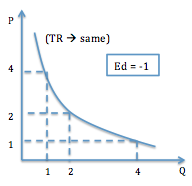
Unitary Elasticity

answer
PƐD = -1 Increase %△ in P = Decrease %△ in QD Rectangular hyperbola.
question
Perfectly Inelastic Demand Curve
answer
PƐD = 0 %△ in QD = 0% No change in demand regardless of price change (therefore increase in price increases revenue). EG: drugs.
question
Perfectly Elastic Demand Curve
answer
PƐD = - infinity Any change in price leads to demand falling to 0. (never a decrease in price because this decreases revenue). Hypothetical. Lots of perfect substitutes.
question
Factors Influencing Price Elasticity of Demand (PƐD)
answer
- If the product is an essential (e.g.: insulin = inelastic) - Availability of substitutes (more substitutes = elastic) - Width of market definition (wider market = less substitutes = more inelastic) - Number of complements (high number of complements = inelastic) - Strength of brand (stronger = more inelastic) - Level of addiction (change in price doesn't affect demand = inelastic) - Time (longer period of time = elastic) - % of Income (small% = inelastic).
question
Income Elasticity of Demand (YƐD)
answer
A measure of the responsiveness of demand to changes in income.
question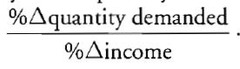
YƐD formula
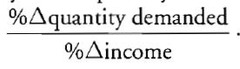
answer
%△QD / %△Y
question
YƐD values
answer
- When YƐD is positive the producer is a normal good (YƐD>0) - Normal Necessities (Income Inelastic) e.g. fruit/milk are between 0 and 1. (0<YƐD1) -Inferior goods have a negative YƐD. They are counter cyclical.
question
Cross Price Elasticity (XƐD)
answer
Measures responsiveness of demand for one good given a change in price of another.
question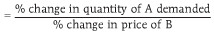
XƐD Formula
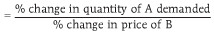
answer
%△QD of A / %△P of B
question
XƐD Values
answer
Complements are negative. The stronger the complementary nature the bigger negative number. Substitutes are positive. Unrelated goods are 0.
question
Price Elasticity of Supply (PƐS)
answer
A mesure of the responsiveness of supply to change in price.
question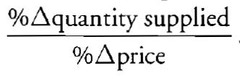
PƐS Formula
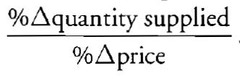
answer
%△QS / %△P
question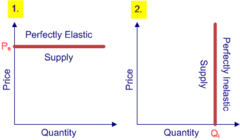
PƐS values

answer
Elastic > 1 eg: manufactured goods Inelastic < 1 eg: natural resources Perfectly Elastic = infinite Perfectly Inelastic = 0 Unitary Supply = 1
question
When will market supply be price elastic?
answer
When PES is greater than 1. Factors: - Supplier has spare capacity to increase output. - High stock levels are available - Short production time frame - Ease of substitution is high (resources can be reallocated.)



