Physics Subject Test: Atomic Physics 3 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What is an *atom*?
answer
The smallest unit of an element that displays the properties of that element.
question
What is a *subatomic particle*?
answer
A particle that makes up part of an atom; a smaller part of an atom.
question
What is a *proton*?
answer
A subatomic particle that is positively charged.
question
What is an *electron*?
answer
A subatomic particle that is negatively charged.
question
What is a *neutron*?
answer
A subatomic particle that is neutrally charged.
question
What is a *nucleus*?
answer
The central, dense part of an atom that contains most of the mass.
question
Which subatomic particles make up the nucleus?
answer
Protons and/or neutrons.
question
Which subatomic particle determines the *identity* of an element?
answer
Protons.
question
Which subatomic particle determines the *isotope* of an element?
answer
Neutrons.
question
Which subatomic particle determines the *ion* of an element?
answer
Electrons.
question
Who discovered the electron and came up with the "plum pudding" model of the atom?
answer
Thomson.
question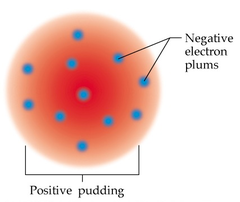
What is the "plum pudding" model of the atom?

answer
Positive charge is distributed throughout (like pudding) and negative charges are embedded within (like plums). You can also think of this as a spherical chocolate chip cookie: cookie = positive charge, chocolate chips = negative charges (electrons)
question
What is an *alpha particle*?
answer
A helium nucleus, made of 2 protons and 2 neutrons.
question
Who came up with the idea of a nucleus and the "planetary" model of the atom?
answer
Rutherford.
question
What did Rutherford do in his famous experiment?
answer
He shot a alpha particles at thin, gold foil.
question
What did Rutherford observe in his experiment?
answer
That most of the alpha particles passed through the gold foil undeflected, but that a few bounced off.
question
What did Rutherford conclude from his observation that *most of the alpha particles passed through the gold foil undeflected*?
answer
That an atom is mostly made of empty space.
question
What did Rutherford conclude from his observation that *a few of the alpha particles bounced off the gold foil*?
answer
That an atom has a dense, positively charged part. He called this part the nucleus.
question
What was the significance of Rutherford's gold foil (alpha scattering) experiment?
answer
Led to the idea of the nucleus around which electrons travel.
question
What is *planetary model* of the atom?
answer
Electrons orbit the nucleus.
question
What is one major thing that Rutherford's planetary model didn't explain?
answer
The electrons should collapse into the nucleus, but they don't. The electrons should collapse because opposite charges attract and because the electrons are losing energy as they travel around the nucleus.
question
How is Bohr's model of the atom different from Rutherford's?
answer
The orbits in Bohr's model are quantized - electrons travel in specific orbits that are set distances away from the nucleus. They don't travel at any random distance.
question
What did Bohr observe in his experiments that led to the idea of quantized orbits?
answer
He saw that hydrogen gas gave off line spectra instead of continuous spectra.
question
What did Bohr think the lines in the spectrum he observed represented?
answer
Each line represented the energy that was given off when electrons changed from a higher energy orbit to a lower energy orbit.
question
What is the *ground state*?
answer
When an electron occupies the lowest energy level (the orbit closest to the nucleus).
question
What is the *excited state*?
answer
When an electron occupies any energy level above the first level (the ground state).
question
When an electron jumps from *a higher to a lower* energy level, does it absorb or emit energy?
answer
Emit.
question
When an electron jumps from *a lower to a higher* energy level, does it absorb or emit energy?
answer
Absorb.
question
What happens when an electron absorbs more energy than required to jump to the highest energy level in the atom?
answer
The electron can escape the atom. Any excess energy is converted to kinetic energy.
question
Can an electron jump across more than one energy level at a time?
answer
Yes.
question
What is one major thing that Bohr's orbital model didn't explain?
answer
Electrons in the same energy level aren't always the same distance away from the nucleus.
question
What is the currently accepted model of the atom?
answer
The quantum mechanical model (electron cloud model).
question
How are electron "orbits" pictured in the quantum mechanical model?
answer
The "orbits" are not well-defined. Instead they're more like fuzzy clouds.
question
What do the varying densities of an electron cloud represent?
answer
Higher density areas represent higher probabilities of finding an electron at that location.



