operations management pearson – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
what is operations?
answer
the part of a business organization that is responsible for producing goods or services
question
operations management
answer
the management of systems or processes that create goods and or provide services
question
goods
answer
physical items that include raw materials, parts, subassembles, and final products
question
services
answer
activities that provide some combination of time, location, form or phsychological value
question
supply chain
answer
a sequence of activities and organizations involved in producing and delivering a good or service
question
supply chain:
answer
suppliers' suppliers -; direct suppliers-; producer-;distributor-; final customers
question
basic functions of the business organization
answer
marketing, operations, finance
question
Manufactoring vs Service
answer
1.degree of customer contact 2.uniformity of input 3.labor content of jobs 4.uniformity of output 5.measurement of productivity 6. production and delivery 7. quality assurance 8. amount of inventory 9. evaluation of work 10. ability to patent design
question
challenges in managing services
answer
1. jobs are less structured 2. contact with customers is higher 3. worker skills are typically low 4. many new workers 5. employee turnover is high, in low skilled jobs 6. input variability tends to be higher in many service environments 7. outside factors can affect the service performance
question
role of the operations manager
answer
the operations function consists of all activities directly related to producing goods or providing services a primary function of the operations manager is to guide the system by decision making -system design decision -system operation decisions
question
system design
answer
-capacity -facility location -facility layout -product and service planning -acquisition and placement of equipment strategic decisions: usually require long-term commitment of resources determine parameters of system operation
question
system operation decisions
answer
these are generally tactical and operational decisions -management of personnel -inventory management and control -scheduling -project management -quality assurance operations managers spend more time on system operation decisions than any other decision area -they still have a vital stake in system design
question
why study om?
answer
every aspect of business affects or is affected by operations many service jobs are closely related to operations -financial services -marketing services -accounting services -info services there is a significant amount of interaction and collaboration amongst the functional areas it provides an excellent vehicle for understanding the world in which we live
question
decision making
answer
what: what resources are needed? when: when will each resource be needed where: where will the work be done how: how will the product or service be designed who: who will do the work
question
model
answer
an abstraction of reality; a simplification of something features: they are simplification of real life phenomena they omit unimportant details of the real-life systems they mimic so that attention can be focused on the most important aspects of the real-life system
question
types of models
answer
physical model schematic model mathematical models
question
quantitative methods
answer
a decision making approach that frequently seeks to obtain a mathematically optimal solution
question
system
answer
a set of interrelated parts that must work together -marketing subsystem -operations subsystem -finance subsystem
question
the systems approach
answer
interrelationships among subsystems main theme is that the whole is greater than the sum of its parts the output and objectives of the organization take precendence over those of any other subsystem
question
industrial revolution
answer
pre industrial: craft production- system in which highly skilled workers use simple flexible tools to produce small quantities of customized goods key elements: began in england in 1770s division of labor application of the "rotative" steam engine cotton gin and interchangeble parts
question
scientific management
answer
frederick winslow taylor based on observation, measurement, analysis and improvement of work methods and economic incentives emphasis on max outputt
question
contributors of scientific management
answer
frank gilbreth- father of motion henry gantt harrington emerson- applied taylors ideas to organization structure henry ford- employed scientific management techniques to his factories moving assembly line
question
human relations movement
answer
importance of the human element in job design lillian gilbreth elton mayo- hawthorn studies on worker motivation abraham maslow- motivation theory 1940s; hierarchy of needs frederick hertzberg- two factor theory douglas mcgregor- theory x and theory Y william ouchi- theory Z 1981
question
Decision models and management science
answer
f.w. harris- mathematical model for inventory management 1915 dodge romig and shewart- stat procedures for sampling and quality control tippett- statistical sampling theory 1935 OR groups george dantzig- linear programming
question
key issues for operations managers today
answer
economic conditions innovating quality problems risk management competing in a global economy
question
sustainability
answer
using resources in ways that do not harm ecological systems that support human existence areas of business affected: product and service design, consumer education programs, disaster preparation and response, supply chain waste management, outsourcing decisions
question
ethical issues in operations
answer
financial statements worker safety product safety quality the environment the community hiring and firing closing facilities workers rights
question
supply chain issues
answer
-the need to improve -increasing levels of outsourcing -increasing transportation costs -competitive pressures -increasing globalization -increasing importance of e-business -the complexity of supply chains -the need to manage inventories
question
elements of supply chain management
answer
Customers - what products/services do customers want Forecasting - predicting timing and volume of customer demand Design - incorporating customer wants, manufacturability, and time to market Capacity planning - matching supply and demand Processing - controlling quality, scheduling work Inventory - meeting demand requirements while managing costs Purchasing - evaluating potential suppliers, supporting the needs of operations on purchased goods and services Suppliers - monitoring supplier quality, on-time delivery, and flexibility; maintaining supplier relations Location - determining the location of facilities logistics- deciding how to best move info
question
competitiveness
answer
how effectively an organization meets the wants and needs of customers relative to others that offer similar goods or services
question
business compete using operations
answer
Product and service design Cost Location Quality Quick response Flexibility Inventory management Supply chain management Service Managers and workers
question
mission
answer
the reason for an organizations existence -states purpose "what business are we in?"
question
goals
answer
provide detail and the scope of the mission -goals can be viewed as organizational destinations
question
strategy
answer
a plan for achieving organizational goals -serves as a roadmap for reaching the organizational destinations
question
tactics
answer
the methods and actions taken to accomplish strategies the "how to" part of the process
question
operations
answer
the actual "doing" part of the process
question
core competencies
answer
the special attributes or abilities that give an organization a competitive edge
question
strategy formulation
answer
takes into account: core competencies, environmental scanning, SWOT successful strategy fomulation takes into account: order qualifiers, order winners
question
order qualifiers
answer
characteristics that customer perceive as minimum standards of acceptability for a product or service to be considered as potential for purchase
question
order winners
answer
characteristics of an organization's goods or services that cause it to be perceived as better than the competition
question
environmental scanning
answer
identifies: internal factors -strengths and weaknesses external factors: opportunities and threats
question
key external factors
answer
1. economic conditions 2. political conditions 3. legal environment 4. technology 5. competition 6. markets
question
key internal factors
answer
Human Resources Facilities and equipment Financial resources Customers Products and services Technology Suppliers Other
question
operations strategy
answer
the approach consistent with organization strategy, that is used to guide the operations function
question
quality based strategy
answer
strategy that focuses on quality in all phases of an organization -pursuit of such a strategy is rooted in number of factors: *trying to overcome a poor quality reputation *desire to maintain a quality image *a desire to catch up with the competition *a part of a cost reduction strategy
question
time based strategies
answer
strategies that focus on the reduction of time needed to accomplish tasks
question
agile operations
answer
a strategic approach for competitive advantage that emphasizes the use of flexibility to adapt and prosper in an environment of change
question
productivity
answer
a measure of the effective use of resources, usually expressed as the ratio of output to input useful when: tracking an operating units performance over time judging the performance of an entire industry or country
question
why productivity matters
answer
High productivity is linked to higher standards of living Higher productivity relative to the competition leads to competitive advantage in the marketplace For an industry, high relative productivity makes it less likely it will be supplanted by foreign industry
question
measures
answer
productivity= output/input partial meausures: output/single input output/labor output/capital multifactor measures: output/multiple inputs output/labor+machines output/labor+capital+energy total measure: goods or services produced / all inputs used to produce them
question
productivity growth
answer
current productivity-previous productivity/ previous productivity x100%
question
forecast
answer
forecast a statement about the future value of a variable of interest
question
improving productivity
answer
Develop productivity measures for all operations Determine critical (bottleneck) operations Develop methods for productivity improvements Establish reasonable goals Make it clear that management supports and encourages productivity improvement Measure and publicize improvements Don't confuse productivity with efficiency
question
two important aspects of forecasts
answer
expected level of demand accuracy
question
common features of all forecasts
answer
Techniques assume some underlying causal system that existed in the past will persist into the future Forecasts are not perfect Forecasts for groups of items are more accurate than those for individual items Forecast accuracy decreases as the forecasting horizon increases
question
elements of a good forecast
answer
should be timely accurate reliable expressed in meaningful units should be in writing should be simple to undrstand and use should be const effective
question
steps in forecasting process
answer
determine the purpose of the forecast establish a time horizon obtain clean and analyze appropriate data select a forecasting technique make the forecast monitor the forecast
question
forecast accuracy
answer
error= actual-forecast if errors fall beyond acceptaale bounds, corrective action may be necessary
question
MAD
answer
sigma |actual-forecast|/n
question
MSE
answer
sigma(actual-forecast)squared / n-1
question
qualitative forecasting
answer
soft information: human factors personal opinions hunches
question
quantitative forecasting
answer
projection of historical data or the development of associative methods that attempt to use causal variables to make a forecast
question
time series:
answer
a time ordered sequence of observations taken at regular time intervals
question
judgemental
answer
uses subjective inputs
question
time series
answer
uses historical data assuming the future will be like the past
question
associative models
answer
uses explanatory variable to predict the future
question
regression
answer
a technique for fitting a line to a set of data points
question
simple linear regression
answer
the simplest form of regression that involves a linear relationship between two variables
question
SLR assumptions
answer
variations around the line are random deviations around the average value should be normally distributed predictions are made only within the range of observed values
question
standard error of estimate
answer
a measure of the scatter of points around a regression line small error, the prediction is more accurate
question
correlation
answer
a measure of the strength and direction of relationship between two variables ranges between -1.00 and +1.00
question
square of correlation coefficient
answer
a measure of the percentage of variability in the values of the y that is "explained" by the independent variable ranges between 0 and 1
question
naive forecast
answer
uses a single previous value of a time series as the basis for a forecast can be used with a stable time, seasonal variations, trend
question
averaging forecasting
answer
moving average weighted moving average exponential smoothing
question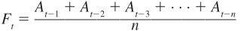
moving average:
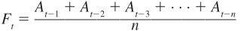
answer
fewer data poins-more responsive
question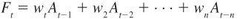
weighted moving average
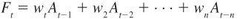
answer
the most recent are given more weight
question
exponential smoothing

answer
a weighted averaging method based on previous forecast plus a percentage of the forecast error
question
reactive approach
answer
view forecasts as a probable future demand react to meet that demand
question
proactive approach
answer
seeks to actively influence demand
question
strategic alliance- an agreement among firms that take up 3 forms
answer
-collaborative effort -joint venture -technology licensing



