OMM Management of Knee problems – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What are considerations to take before doing OMM on the knee
answer
Imptortant to determine if somatic dysfxn in knee is orthopedically stable before doing OMT - need to rule out gross asymmetry - TART dx can be present w/ligament tear and tissue disruption = *restriction motion is a good sign of somatic dysfxn (while excessive motion is an actual orthopedic injury) --> "Too loose" ("empty" end-feel) = orthopedic "Too tight" (a barrier) = need to know --> "Too tight everywhere" (matched direction capsular pattern) =rheumatologic/pathology --> "Tight-free" barrier pattern = somatic dysfunction "Just right" *
question
What type of joint is the Knee and what type of motion does it have
answer
- Knee is largest joint of body, a hinge joint *(Knee is 3 joints: medial/lateral femur condyles, medial/lateral surface of tibial plateau, and proximal tibial-fibular jxn)* - Minimal rotation (torsional), translation, abduction, and adduction - Fully extended will see slight extension of tibia on the femur (tibia glides post., externally rotates on femur, injury prone) -->This position is most suscept. to injury
question
What position is most susceptible to injury in the knee and how do the bones around the knee move during this action?
answer
- Fully extended will see slight extension of tibia on the femur (tibia glides post., externally rotates on femur, injury prone) - This position is most suscept. to injury
question
Why is the knee a good target for injury?
answer
Frequent muscle imbalance between strong anterior (quadriceps) and relatively weak posterior (hamstrings) muscles combined with Extreme mobility required (primarily flexion/extension but minor motions also VERY important) make for a GOOD TARGET FOR INJURY
question
When do knee injuries commonly occur
answer
In sports, the knee is the most frequently injured structure - *Makes up ~ 50-60% of sports injuries* - Ankle is #2
question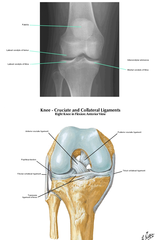
Describe the anatomy of knee

answer
Knee joint - Femur-Tibial Other articulations include: - Patellofemoral - Fibular-tibial
question
What is the function of Menisci
answer
Absorb shock; transmit loading forces; Act as joint filler, provide stability; Prevent synovial/capsular impingement with flexion and extension - unfortunately doesn't have good blood supply (so takes long to heal/doesn't heal well) - If it tears, it does NOT bleed
question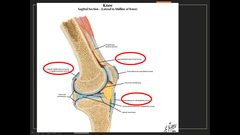
What are the bursae of the knee

answer
- lateral subtendinous bursa of gastrocnemius muscle - Suprapatellar (synovial) bursa - Subcutaneous infrapatellar bursa
question
Knee pain is due to
answer
? An intraarticular process such as a meniscal or ligamentous injury (internal derangement) or fracture ? Patellar malalignment or dysfunction ? Cartilage loss due to osteoarthritis or synovitis ? Periarticular bursitis or tendinopathy ? Referred pain from the hip, femur, or spine ? Inflammatory arthritides (synovitis)
question
What are some common knee pathologies
answer
- Ligament tear (ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL) - Meniscus tear - ITBS - Patellofemoral Syndrome (Runner's Knee) - Patellar Tendonitis (Jumper's Knee) - Osteoarthritis of knee
question
What is the presentation of the different Ligament tears in the knee?
answer
ACL: non-contact injury, most common, cutting injury PCL: Hyperflexion, posterior force on a planted leg, rare (car accident dashboard injury) MCL: valgus force from a blow on a planted leg (football, soccer) LCL: rare, devastating injury, associated with multiple pathology and neurovascular injury
question
How do you treat and diagnose the different ligamental tears in the knee
answer
Dx: MRI Special Tests: Anterior and Posterior Drawer, Lachman's, Valgus and Varus Stress Tx: Conservative (especially MCL), or Arthroscopic Reconstructive Surgery
question
Describe the presentation and cause of Meniscus Tear
answer
- Joint line knee pain. - Meniscus tears are from cutting maneuvers that cause tibial rotation on a flexed and fixed knee (football, soccer).
question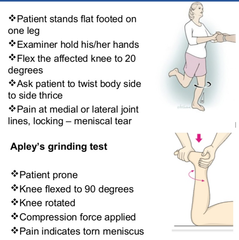
How do you diagnose meniscual tears

answer
Dx: MRI Special Tests: McMurray's, Thessaly, Apley's Grind
question
What is the Thessaly Test?

answer
Test for Meniscus tear:
question
What is the Apley's Grind

answer
Test for Meniscal tear - Compression tests for meniscal injury: rotate lower leg internally and externally - Distract. tests for collateral ligament sprain - Lower leg lifted w/femus stabilited and rotate lower leg int., ext.
question
What is included in the Initial Evaluation of Knee Problems
answer
Must determine: 1) Trauma or Disease ? 2) Treat or Refer ?
question
What part of the leg is more prone to reflex inihbition
answer
the Quads
question
The knee has more susceptibility of injury the future from what?
answer
nociception in knee pain
question
Why are short tight hammies common
answer
Hamstrings = ex. of a *tonic muscle, *why short tight hammies are common
question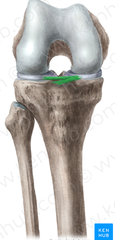
What is the transverse ligament of the knee

answer
Transverse ligament of knee can be thought of as annular ligament, surrounds knee circularly
question
What happens when the meniscus tears
answer
- unfortunately doesn't have good blood supply (so takes long to heal/doesn't heal well) - If it tears, it does NOT bleed - Gets transudate effusion, causes pain, even though the menisci is not as well innervated as the joint capsule
question
What is the Ts for a meniscal tear
answer
- Gets transudate effusion, causes pain, even though the menisci is not as well innervated as the joint capsule - Tx of choice: remove or burn menisci off - Stops transudate effusion from --> capsular distension or swelling
question
What is the most innervated joint in the knee
answer
The capsule: most innervated joint
question
What are the different types of meniscal tears
answer
- Bucket-handle tear can act as a flap, cause joint restriction and mechanical sx like a joint that is locked in 1 position - Almost surgical prob, needs repair to pull tibia away from femur, make space, make flap fall back into place
question
When is the patellar-femur joint loaded
answer
Patellar-femur joint is loaded when knee is flexed and pt is sitting
question
What is the cinemark sign:
answer
Look for Cinemark sign: pain when standing up from a sitting position
question
What is the STEPWISE CLINICAL APPROACH to knee conditions
answer
1) Traumatic versus nontraumatic a) High Energy "macro " vs Low Energy "Micro" b) Mechanism of injury ; Age; Comorbitites 2) Extrinsic versus intrinsic - pain is a referred symptom caused by pathology outside the knee (extrinsic) or intrinsic to the knee joint 3) Intra-articular versus Periarticular source of pain lies within the knee joint or directly adjacent to the knee 4) Structural (meniscal, ligamentous) or by inflammatory processes (OA, gout, septic arthritis, infection)
question
What are conditions associated with knee pain to consider before performing OMM
answer
*Septic Arthritis* - Lyme Disease - Erythema, fever, chills, effusion --> CBC, ESR, Joint aspiration *Deep vein thrombosis* - Edema, calf tenderness, Homan's sign --> Duplex Doppler study *Arterial Insufficiency* - Claudication, diminished or absent pulses --> Arterial Doppler and pressure measurements *Neoplasm* - Pain at rest, night pain, weight loss, cachexia --> X-ray
question
What Suggest the presence of a joint effusion
answer
various descriptions of generalized swelling and the mechanical consequence of the effusion, impaired bending.
question
What symptoms Reflect a Change in Overall Knee function
answer
loss of muscular or ligamentous support (weakness, giving out, collapsing), loss of smooth movement (catching, "something is wrong inside"), and difficulty with ambulation (limping, fatigue, favoring).
question
What are important considerations in the History
answer
Age as predictor - Birth to 12 years (open growth plate @ knees, if at proximal tibia, think Osgood-Schlatter ) - 12 to 18 years (sport injuries) - 18 to 30 years (sport injuries) - 45 years upward (degenerative meniscal problems)
question
What should you consider with pt in: Birth to 12 years of Age
answer
Discoid Meniscus - Cyst, since birth - Lateral aspect, behind meniscus Recurrent Synovitis - Synovium torn - Slight bleeding in joint --> Knee improves with rest, symptoms disappear, patient returns to activity, symptoms return
question
What should you consider with pt in: 12 to 18 Years of Age
answer
Osteochondritis dissecans - May affect other joints, but most common in knee - Diminished blood supply --> Cartilaginous separation may cause knee lock-up Osgood-Schlatter's Disease - Tibial Tuberosity pain secondary to epiphysitis/tendinitis Chondromalacia Patellae
question
What is Osgood-Schlatter's Disease
answer
Osgood-Schlatter disease is a common cause of knee pain in growing adolescents (12-18y/o). It is an inflammation of the area just below the knee where the tendon from the kneecap (patellar tendon) attaches to the shinbone (tibia).
question
What should you consider with pt in: 18 to 55 Years of Age
answer
- 18 to 30- Meniscal tears and Chondromalacia patellae - 30 to 50- Rheumatoid arthritis - 40 to 55- Degenerative meniscal lesions (generally in patients who were active athletically for years) - 45 upward- Osteoarthritis
question
What is Chondromalacia patellae
answer
Chondromalacia patellae (also known as CMP) is inflammation of the underside of the patella and softening of the cartilage. - also called runner's knee seen in pt 18-30 y/o
question
If a pt has a history of instability what should you consider
answer
1) Chronic Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) insufficiency 2) Knee Buckling Disorder
question
Describe the presentation of Chronic Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) insufficiency
answer
Patient may report *painless* giving-away of knee/leg or: Pain that follows the sensation of instability - This is usually associated with articular or meniscal injury --> Patients with a stable knee and chondromalacia may experience giving-away (preceded by pain)
question
What is Knee Buckling disorder
answer
Knee Buckling Disorder: Weakness and tender points of vastus medialis oblique (VMO) will cause reflex inhibition - Knee is only unstable when weight is on it and it cant react fast enough - Exam of knee is normal though
question
***A report of pivoting or twisting followed by pain and swelling. Dx?
answer
Ligamentous or cartilaginous injury
question
Repetitive micro-trauma are caused by?
answer
Running or bicycling Usually less severe and not associated with an event
question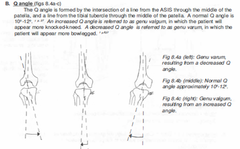
Describe inspection of the knee

answer
1) Gait Limp, antalgic gait, pronated or flat feet, bowed achilles, genu varus/valgus, 2) Swelling 3) Atrophy? a) Palpate - Check strength with resistance against quadriceps and/or hamstrings b) Measure - Within two weeks of a severe injury --> 1/2" atrophy of quadriceps
question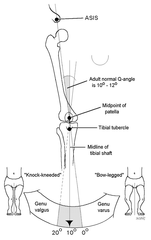
What is the Q angle?

answer
Normally 10-12o (0-20o) (use goniometer) Genu valgus (knock-kneed); ; 20o Not built for running! Chondromalacia patellae Pronation - coxa vara Genu varus (bow legged) ; 0
question
How do you look at swelling in the knee to help with your diagnosis
answer
Immediate- hemarthrosis - ACL tear, acute patellar dislocation, fracture Gradual- synovial - Inflammatory, secondary to meniscus tear Patellar outline obliterated! - Swelling above suprapatellar pouch? --> Extra-articular? --> Infection, Tumor, Massive Injury
question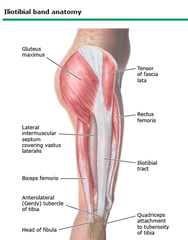
When palpating the knee what are you looking for?

answer
1) Temperature - Increased: Inflammation 2) Anterior Knee - Quadriceps; Patella; Patellar Tendon; Tibial Tuberosity 3) Medial Joint line: - Anterior horn of medial meniscus - Medial collateral ligament (origin and insertion are respectfully superior and inferior to the joint line) - Posterior horn of medial meniscus - Distal portion of medial hamstring (Semitendinosus ; Semimembranosus ) 4) Medial to patellar tendon ; below medial tibial plateau - insertion of semitendonosus, sartorius, gracilis form common pes anserine tendon/bursae 5) Lateral Joint Line - Iliotibial Band courses over the lateral femoral condyle to the anterolateral aspect of the proximal tibia - Distal portion of biceps femoris muscle and tendon (crosses joint line) - Lateral Collateral Ligament (origin and insertion are respectfully superior and inferior to the joint line) - Anterior horn of lateral meniscus - Posterior horn of lateral meniscus - Fibular head and tibiofibular syndesmosis 6) Posterior Knee - Fossa = space between medial ; lateral hamstring tendons - Pulse of popliteal artery
question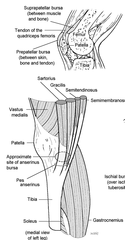
What muscles attached to the medial portion of the knee

answer
insertion of semitendonosus, sartorius, gracilis form common pes anserine tendon/bursae
question
What are the different types of pain in the knee?
answer
Location! 1) Medial or lateral joint lines a) Medial (tibial) collateral ligament - Stable or lax - Superficial or deep injury? b) Lateral (fibular) collateral - More posterior than its medial counterpart - *Less defined by joint line and area of pain is greater* 2) Postero-Lateral a) Biceps femoris strain/tendinitis b) Popliteus strain/tendinitis 3) Posterior a) Baker's Cyst or Popliteal Cyst 4) Lateral a) Iliotibial band 5) Tibial tuberosity a) Osgood-Schlatter's disease 6) Superior (cephalad) to tibial tubercle a) Patellar tendinitis ("jumper's knee") 7) Medial to tibial tuberosity a) Pes anserine tendinitis/bursitis
question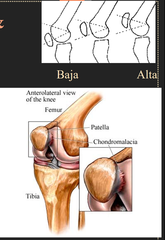
What are the different Patellar Positions ; Tests

answer
1) Patient seated: both knees flexed over the end of table - Patella alta: Superior position - Patella baja: Inferior position - Lateral displacement 2) Track with F-E motion - *"Apprehension test" * when add lateral pressure as flex (Unstable pt will get anxious fearing re-displacement of patella) 3) *Patellar grind test for* chondromalacia patellae - Also Pain / "Apprehension" Test
question
What is crepitiance a sign of

answer
damage to articular surfaces: With palm of hand over the patella, place thumb and index finger along medial and lateral joint lines, respectively Then, flex and extend the knee If crepitus present, think damaged articular surfaces Watch the patellar tracking
question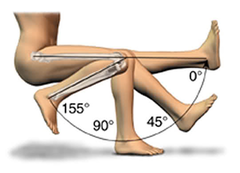
Range of motion of the Knee

answer
Flexion - ~140-155 degrees - Minor motion = posterior glide Extension - 0-10 degrees - Minor motion = anterior glide Internal/ External - Rotation - 10 degrees - Minor motions = posterolateral/anteromedial glides respectively
question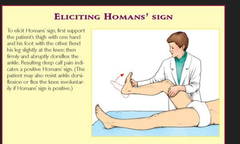
homan's sign

answer
sign for DVT
question
What do you look for with arterial deficiency to the knee
answer
look for deep myotonal pain, claudication, absent pulses (gastrocnemius is most common)
question
What are signs of Neoplasms
answer
Neoplasm: night pain, wt loss, cachexia
question
Joint insecurity should be considered due to what until proven otherwise
answer
torn meniscus
question
****medial meniscus tear is associated with what structures*
answer
MCL and medial meniscus are anatomically assoc. w/one another, slim chance of damaging just one of them - Also, if med. meniscus is torn, invariable so is the joint capsule
question
Tx for Lock knees
answer
- Can get locking of knee, poss need surgery but rest, traction, OMT, relaxants can unlock
question
A pertinent negative of no effusion menas what
answer
If no effusion, means joint is not within the capsule, lesion is extra-articular
question
Medial meniscal injury is generally more common when
answer
in sports = 75-90% of them - Usually along w/ligamentous insult
question
- Meniscal injury in wrestlers tend to involve what part of the knee
answer
= tend to involve lateral collateral (~45%) - With internal rotation in take down moves - Shearing forces in varus position
question
Why do you need to bend the knees when testing MCL and LCL
answer
- Valgus/MCL and Varus/LCL stress test - Cruciate ligaments are in same place so need to bend knee 15-20 deg first
question
Which side do you test first when checking MCL and LCL
answer
- Check uninjured side first, then injured
question
What is the postive test for Mac Murray's. Describe the test.
answer
: need pain from joint line and meniscal click from joint line for positive test - Pt supine, hip fully flexed, knee flexed to 90deg. And external rotate (click w/pain is medical meniscus tear) and internal rotate (click with pain is lateral meniscus tear) - Pain with deep flexion is prob. A posterior meniscus, and pain closer to full extension is prob. An anterior meniscus
question
Describe presentation of SD in the knee
answer
Somatic dysfxn will present with decreased ROM and an orthopedic injury while orthopedic injury will have more ROM
question
What are the symptoms and presentation of Anterior tibial/post. femoral problem
answer
- Symptoms: decreased extension with anterior pain/stiffness - Find: pain over anterior joint margin bilat., prominence of antero-medial/lat. Tibial plateaus, motion quality poor on posterior drawer, motion free on anterior drawer
question
What are the symptoms and presentation of - Posterior tibial/anterior femoral problem
answer
- Sx: less flexion with posterior pain/stiff. - Find pain over posterior joint margin bilaterally, motion is poor on anterior drawer but motion FREE on posterior drawer - Tx: pull it forward
question
what are the symptoms and presentation of - Anterior fibular (proximal)
answer
- Sx: pain @ posterior-lateral knee margin, may radiate to lateral lower leg - Find: fibular head moves forward easy, but resists posterior movement
question
What are the symptoms and presentation of - Posterior fibular (proximal)
answer
- Sx: Same as anterior fibular - Find: fibular head moves post. easy but resistant to forward movement
question
What are the symptoms and presentation of - Anterior medial meniscal protrusion or bulge
answer
- Sx: pain/fullness @ antero-medial joint margin and decreased extension - Find: click of MacMurray test, small painful and beadlike swelling at antero- medial joint margin, less extension
question
LCL injuries also include what structure
answer
- Fibular head, LCL are directly connected so LCL injury will = fibular head disconnection - Medial meniscus is continuous w/MCL
question
How does hamstring tension affect diagnosis
answer
- Hamstring tension: makes anterior drawer less likely to show acute injury (try MFR to lower tension, makes the test more useful)
question
What does threshold laxing have to do with knee OMT
answer
- Most important for OMT: NO threshold laxing! If it is laxing, needs PT or surg!



