Oceanography 11 – Ocean currents – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Oceanic circulation is determined by...
answer
wind and density/gravity (sun) Shallow = wind, Deep = Thermohaline circulation
question
Surface Currents
answer
top 10% (400m) of oceans = wind driven 3% of wind speed. Easterlies at equator + Westerlies
question
Gyres
answer
generated by tradewinds. —surface currents that flow in a circle around the periphery of an ocean basin due to Coriolis effect. Without Coriolis, water moves in same direction.
question
Ekman spirals
answer
Water deep can flow in the opposite direction of the wind but NET transport of water to be 90 degrees from the wind direction. (Ekman transport)
question
Ekman transport
answer
causes water to gather at center of the gyres. Balance between ekman spiral and gravity (try to flat it out).
question
Geostrophic Currents
answer
Currents of gyros.
question
western boundary currents
answer
The fastest, deepest and warmest geostrophic currents are found at the western boundaries of ocean basins. Gulf Stream (2 m/s, 70 km wide, 450 m deep) = largest (55 million m3/s
question
Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities
answer
formed from turbulence generated by shear at an interface between two moving fluids (western boundary currents)
question
Eastern boundary currents
answer
broad (<1000 km), • shallow • slow • cold • flow toward the equator.
question
Transverse currents
answer
flow eastward or westward, linking boundary currents together in the gyres.
question
Why are western boundary currents concentrated and fast and eastern boundary currents diffuse and slow?
answer
western turn faster to the right cause away from equator. Eastern moves towards the equator so much slower and less Coriolis. Thus the hill of water is more western than center
question
Western/Eastern boundary currents also transports different temp water...
answer
warm water western boundary currents to north. Cold water eastern boundary currents to south.
question
Upwelling...
answer
Upwelling has effect on climate and organic productivity. Upwelling occur at equator and some Coastal.
question
Downwelling...
answer
usually at poles
question
Equatorial upwelling
answer
made possible by ekman transport/surface wind. Water moves out to enable new space.
question
Coastal upwelling
answer
west side of continents
question
Langmuir circulation
answer
Caused by slow, steady winds that form windrows (sea foam)
question
El Nino
answer
trades weaken or reverse, upwelling is surpressed, and warm water spreads over most of the Pacific, including offshore of Central and South America (areas where water is typically cold).
question
La Nina
answer
years are essentially strong normal years
question
Three ways the atmosphere (and ultimately the Sun) forces the ocean patterns:
answer
Winds, Heating/Cooling, Evaporation/Precipitation
question
Thermohaline circulation
answer
whole-ocean circulation driven by density imbalances related to variations in water temperature ("thermo-"), and also salt content ("-haline"). Entire ocean; it is sometimes referred to as the "global conveyor belt". Currents are slow and deep.
question
brinicles
answer
Formed when the very cold and salty sea water downwells and freezes near-by water.
question
caballing (aka cabbeling)
answer
the mixing of two water masses (A,B) with different temperatures and salinities, which generates a third mass that is more dense (C) and consequently sinks beneath the parent water masses.
question
Antarctic Bottom Water (AABW)
answer
extremely dense (the densest water in ocean) due to its extreme cold and salty nature. Formed from southern Hemisphere sea ice formation.
question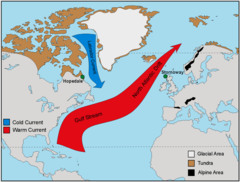
North Atlantic Deep Water (NADW).

answer
warm, salty North Atlantic Ocean cools as cold winds from Northern Canada sweep over it. It drops from 10° to 2°C in the process, and sinks to depth.
question
Antarctic Intermediate Water, North Atlantic Intermediate Water
answer
generated by caballing
question
Mediterranean Deep Water
answer
generated by very salty (3.8%), very warm water emanating from the Mediterranean Sea. Below atlantic ocean.
question
The downwelling at poles are countered by upwelling from...
answer
(1) Wind driven upwelling, and (2) turbulent mixing acrossthe thermocline (mixed-layer + abyssal layer) Water remain down there for Pacific is the oldest in the ocean—about 1200 years on average. Water in the Atlantic and Arctic oceans is younger, about 200-600 years old
question
Water mass
answer
Body of water in the ocean with distinct physical and chemical properties (temp, salinity, nutrients, gases, etc) obtained at the sea surface.



