Nursing 137 Diabetes – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Diabetes is a heterogeneous group of chronic disorders characterized by ____________
answer
Hyperglycemia
question
Alterations in metabolism of fats, carbs, and proteins are caused by
answer
Insufficient insulin supply and/or action
question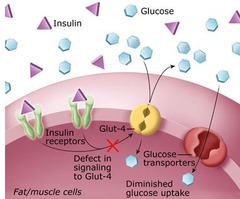
Fats and proteins are metabolized for energy if _______

answer
No insulin is available or given
question
Transport and metabolism of glucose for use as energy is the job of _______
answer
Insulin
question
Insulin stimulates storage of glucose in the _____________ & ____________ as glycogen
answer
Liver and muscles
question
What is polyuria
answer
Excessive urination
question
Polyuria leads to diuresis (severe water loss) and excretion of
answer
Sodium, chloride, and potassium
question
What is polydipsia
answer
Excessive thirst
question
Polydipsia and polyuria are caused by excessive sugar in the blood, causing your kidneys to work harder by _______
answer
Excreting excess sugar into the urine dragging fluids along, causing frequent urination and subsequent thirst
question
In order to move glucose into most body systems you need
answer
Insulin
question
What causes polyphagia
answer
Cells are starved for glucose causing excessive appetite
question
What is polyphagia
answer
Excessive eating
question
What are the three types of diabetes
answer
Type I and II and gestational ( pregnancy induced)
question
Type 1 is caused by ___________________ causing insulin deficiency, onset is ___
answer
beta cell destruction Juvenile ( <30 yrs)
question
Type 2 is caused by a lack of _______ or resistance to the action. Onset is _______
answer
Insulin, adult onset
question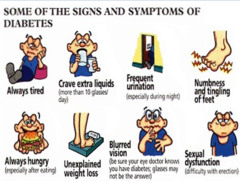
What are some signs and symptoms of type 1 diabetes

answer
Fatigue, weakness, vision changes, numbness/tingling in hands and feet, dry skin, wounds slow to heal, recurrent infections and sudden weight loss may occur.
question
What are some signs and symptoms of type 2 diabetes
answer
Fatigue, weakness, vision changes, numbness/tingling in hands and feet, sexual dysfunctions, dry skin, wounds slow to heal, recurrent infections, weight loss, vaginal infections.
question
Objective assessment symptoms include
answer
Weight loss ( type 1 ) Obesity ( type 2) Elevated fasting serum glucose Glycosuria Peripheral, neuro, and sensory changes
question
Ketones/ketones bodies are produced by
answer
Abnormal breakdown of fatty acids or fat
question
Excess acids caused by lack of insulin increase hydrogen and carbon dioxide causing
answer
Acidosis
question
What are Kussmaul respirations
answer
Deep gasping hyperventilation associated with severe diabetic acidosis
question
What other assessment of breathing would lead you to believe a case of diabetic acidosis
answer
Fruity breath odor
question
What blood test is used for long term glucose control
answer
Hemoglobin A1c/ glycosylated hemoglobin
question
How does exercise help

answer
Lowers blood sugar, aids in weight loss, lowers risk for cardiovascular problems
question
what glucose related problem can occur because of exercise
answer
Post work out hypoglycemia
question
Moderate exercise can _____________blood sugar Strenuous exercise can temporarily _____________blood sugar
answer
Lower, Raise
question
What are some of the risks associated with diabetes mellitus
answer
Macrovascular ( large blood vessels) Microvascular ( small blood vessels) Diabetic ketoacidosis ( DKA) HHS ( hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state- high glucose levels over 400)
question
What is Hypoglycemia
answer
Low blood glucose levels
question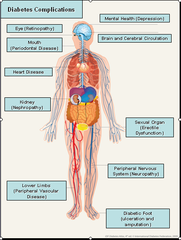
Macrovascular complications of diabetes can include:

answer
Macro: stroke, heart disease, hypertension, PVD, foot problems.
question
Microvascular complications of diabetes can include:
answer
Diabetic eye disease (retinopathy and cataracts) Renal disease Neuropathy Foot problems
question
What additional factors increase risk for macrovascular complications
answer
Smoking, physical inactivity, increased body weight, hypertension, hyperlipidemia
question
Knowing that gluconeogenesis helps to maintain blood levels, a nurse should A Document weight changes because of fatty acid mobilization B Evaluate the patient's sensitivity to low room temperatures because of decreased adipose tissue insulation C Protect the patient from sources of infection because of decreased cellular protein deposits D Do all of the above
answer
D Do all of the above
question
Clinical manifestations associated with a diagnosis of type 1 DM include all of the following except: A Hypoglycemia B Hyponatremia C Ketonuria D Polyphagia
answer
A Hypoglycemia
question
The lowest fasting plasma glucose level suggestive of a diagnosis of DM is A 90mg/dl B 115mg/dl C 126mg/dl D 180mg/dl
answer
C 126mg/dl
question
Rotation sites for insulin injection should be separated from one another by 2.5 cm (1 inch) and should be used only every: A Third day B Week C 2-3 weeks D 2-4 weeks
answer
C 2-3 weeks To prevent lipodystrophy
question
A clinical feature that distinguishes a hypoglycemic reaction from a ketoacidosis reaction is: A Blurred vision B Diaphoresis C Nausea D Weakness
answer
B Diaphoresis
question
Clinical nursing assessment for a patient with microangiopathy who has manifested impaired peripheral arterial circulation includes all of the following except: A Integumentary inspection for the presence of brown spots on the lower extremities B Observation for paleness of the lower extremities C Observation for blanching of the feet after the legs are elevated for 60 seconds D Palpation for increased pulse volume in the arteries of the lower extremities
answer
D Palpation for increased pulse volume in the arteries of the lower extremities
question
The nurse expects that a type 1 diabetic may receive ____ of his or her morning dose of insulin preoperatively: A 10-20% B 25-40% C 50-60% D 85-90%
answer
C 50-60%
question
Albert, a 35-year-old insulin dependent diabetic, is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of pneumonia. He has been febrile since admission. His daily insulin requirement is 24 units of NPH. Every morning Albert is given NPH insulin at 0730. Meals are served at 0830, 1230, and 1830. The nurse expects that the NPH insulin will reach its maximum effect (peak) between the hours of: A 1130 and 1330 B 1330 and 1930 C 1530 and 2130 D 1730 and 2330
answer
B 1330 and 1930
question
A bedtime snack is provided for Albert. This is based on the knowledge that intermediate-acting insulins are effective for an approximate duration of: A 6-8 hours B 10-14 hours C 16-20 hours D 24-28 hours
answer
C 16-20 hours
question
Albert refuses his bedtime snack. This should alert the nurse to assess for: A Elevated serum bicarbonate and a decreased blood pH. B Signs of hypoglycemia earlier than expected. C Symptoms of hyperglycemia during the peak time of NPH insulin. D Sugar in the urine
answer
B Signs of hypoglycemia earlier than expected
question
A client is taking NPH insulin daily every morning. The nurse instructs the client that the most likely time for a hypoglycemic reaction to occur is: A 2-4 hours after administration B 6-14 hours after administration C 16-18 hours after administration D 18-24 hours after administration
answer
B 6-14 hours after administration NPH is intermediate acting insulin. The onset of action is 1-2 hours, it peaks in 6-14 hours, and it's duration of action is 24 hours. Hypoglycemic reactions most likely occur during peak time.
question
An external insulin pump is prescribed for a client with DM. The client asks the nurse about the functioning of the pump. The nurse bases the response on the information that the pump: A Gives small continuous dose of regular insulin subcutaneously, and the client can self-administer a bolus with an additional dosage from the pump before each meal. B Is timed to release programmed doses of regular or NPH insulin into the bloodstream at specific intervals. C Is surgically attached to the pancreas and infuses regular insulin into the pancreas, which in turn releases the insulin into the bloodstream. D Continuously infuses small amounts of NPH insulin into the bloodstream while regularly monitoring blood glucose levels
answer
A Gives small continuous dose of regular insulin subcutaneously, and the client can self-administer a bolus with an additional dosage from the pump before each meal. An insulin pump provides a small continuous dose of regular insulin subcutaneously throughout the day and night, and the client can self-administer a bolus with additional dosage from the pump before each meal as neede4. Regular insulin is used in an insulin pump. An external pump is not attached surgically to the pancreas.
question
A client with a diagnosis of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is being treated in the ER. Which finding would a nurse expect to note as confirming this diagnosis? A Elevated blood glucose level and a low plasma bicarbonate B Decreased urine output C Increased respirations and an increase in pH D Comatose state
answer
A Elevated blood glucose level and a low plasma bicarbonate In diabetic acidiosis the arterial pH is less than 7.35. plasma bicarbonate is less than 15mEq/L, and the blood glucose level is higher than 250mg/dl and ketones are present in the blood and urine. The client would be experiencing polyuria, and Kussmauls respirations would be present. A comatose state may occur if DKA is not treated, but coma would not confirm the diagnosis
question
A client with DM demonstrates acute anxiety when first admitted for the treatment of hyperglycemia. The most appropriate intervention to decrease the client's anxiety would be to: A Administer a sedative B Make sure the client knows all the correct medical terms to understand what is happening C Ignore the signs and symptoms of anxiety so that they will soon disappear D Convey empathy, trust, and respect toward the client
answer
D Convey empathy, trust, and respect toward the client The most appropriate intervention is to address the client's feelings related to the anxiety. Administering a sedative is not the most appropriate intervention. The nurse should not ignore the client's anxious feelings. A client will not relate to medical terms, particularly when anxiety exists
question
A nurse is preparing a plan of care for a client with DM who has hyperglycemia. The priority nursing diagnosis would be: 1. High risk for d A High risk for deficient fluid volume B Deficient knowledge: disease process and treatment C Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements D Disabled family coping: compromised
answer
A High risk for deficient fluid volume Increased blood glucose will cause the kidneys to excrete the glucose on the urine. This glucose is accompanied by fluids and electrolytes, causing osmotic diuresis leading to dehydration. This fluid loss must be replaced when it becomes severe. Options B, C, and D are not related specifically to the issue of the question.
question
A nurse is caring for a client admitted to the ER with DKA. In the acute phase the priority nursing action is to prepare to: A Administer regular insulin intravenously B Administer 5% dextrose intravenously C Correct the acidosis D Apply an electrocardiogram monitor
answer
A Administer regular insulin intravenously lack (absolute or relative) of insulin is the primary cause of DK1. Treatment consists of insulin administration (regular insulin), IV fluid administration (normal saline initially), and potassium replacement, followed by correcting acidosis. Applying an electrocardiogram monitor is not a priority action.
question
A nurse performs a physical assessment on a client with type 2 DM. Findings include a fasting blood glucose of 120mg/dl, temperature of 101, pulse of 88, respirations of 22, and a bp of 140/84. Which finding would be of most concern of the nurse? A Pulse B BP C Respiration D Temperature
answer
D Temperature An elevated temperature may indicate infection. Infection is a leading cause of hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome or diabetic ketoacidosis
question
A client with type 1 DM calls the nurse to report recurrent episodes of hypoglycemia with exercise. Which statement by the client indicated an inadequate understanding of the peak action of NPH insulin and exercise? A "The best time for me to exercise is every afternoon." B "The best time for me to exercise is right after I eat." C "The best time for me to exercise is after breakfast." D "The best time for me to exercise is after my morning snack."
answer
A "The best time for me to exercise is every afternoon." A hypoglycemic reaction may occur in the response to increased exercise. Clients should avoid exercise during the peak time of insulin. NPH insulin peaks at 6-14 hours; therefore afternoon exercise will occur during the peak of the medication. Options B, C, and D do not address peak action times.
question
A client with diabetes mellitus visits a health care clinic. The client's diabetes previously had been well controlled with glyburide (Diabeta), 5 mg PO daily, but recently the fasting blood glucose has been running 180-200mg/dl. Which medication, if added to the clients regimen, may have contributed to the hyperglycemia? A Prednisone (Deltasone) B Atenolol (Tenormin) C Phenelzine (Nardil) D Allopurinol (Zyloprim)
answer
A Prednisone (Deltasone) Prednisone may decrease the effect of oral hypoglycemics, insulin, diuretics, and potassium supplements.
question
Glucose is an important molecule in a cell because this molecule is primarily used for: A Extraction of energy B Synthesis of protein C Building of genetic material D Formation of cell membranes
answer
A Extraction of energy Glucose catabolism is the main pathway for cellular energy production.
question
When a client is first admitted with hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome (HHNS), the nurse's priority is to provide: A Oxygen B Carbohydrates C Fluid replacement D Dietary instruction
answer
C Fluid replacement As a result of osmotic pressures created by increased serum glucose, the cells become dehydrated; the client must receive fluid and then insulin.
question
The nurse is admitting a client with hypoglycemia. Identify the signs and symptoms the nurse should expect. Select all that apply. A Thirst B Palpitations C Diaphoresis D Slurred speech E Hyperventilation
answer
B- Palpitations C- Diaphoresis D- Slurred speech Palpitations, an adrenergic symptom, occur as the glucose levels fall; the sympathetic nervous system is activated and epinephrine and norepinephrine are secreted causing this response. Diaphoresis is a sympathetic nervous system response that occurs as epinephrine and norepinephrine are released. Slurred speech is a neuroglycopenic symptom; as the brain receives insufficient glucose, the activity of the CNS becomes depressed.
question
When a client is in diabetic ketoacidosis, the insulin that would be administered is: A Human NPH insulin B Human regular insulin C Insulin lispro injection D Insulin glargine injection
answer
B Human regular insulin Regular insulin (Humulin R) is a short-acting insulin and is administered via IV with an initial dose of 0.3 units/kg, followed by 0.2 units/kg 1 hour later, followed by 0.2 units/kg every 2 hours until blood glucose becomes ;13.9 mmol/L (;250 mg/dL). At this point, insulin dose should be decreased by half, to 0.1 units/kg every 2 hours, until the resolution of DKA.
question
The nurse recognizes that additional teaching is necessary when the client who is learning alternative site testing (AST) for glucose monitoring says: A "I need to rub my forearm vigorously until warm before testing at this site." B "The fingertip is preferred for glucose monitoring if hyperglycemia is suspected." C "I have to make sure that my current glucose monitor can be used at an alternate site." D "Alternate site testing is unsafe if I am experiencing a rapid change in glucose levels."
answer
B The fingertip is preferred for glucose monitoring if hyperglycemia is suspected. The fingertip is preferred for glucose monitoring if hypoglycemia, not hyperglycemia, is suspected
question
Which adaptations should the nurse caring for a client with diabetic ketoacidosis expect the client to exhibit? Select all that apply: A Sweating B Low PCO2 C Retinopathy D Acetone breath E Elevated serum bicarbonate
answer
B- Low PCO2 C- Retinopathy Metabolic acidosis initiates respiratory compensation in the form of Kussmaul respirations to counteract the effects of ketone buildup, resulting in a lowered PCO2. A fruity odor to the breath (acetone breath) occurs when the ketone level is elevated in ketoacidosis.
question
A client's blood gases reflect diabetic acidosis. The nurse should expect: A Increased pH B Decreased PO2 C Increased PCO2 D Decreased HCO3
answer
D Decreased HCO3 The bicarbonate-carbonic acid buffer system helps maintain the pH of the body fluids; in metabolic acidosis there is a decrease in bicarbonate because of an increase of metabolic acids.
question
The nurse knows that glucagon may be given in the treatment of hypoglycemia because it: A Inhibits gluconeogenesis B Stimulates the release of insulin C Increases blood glucose levels D Provides more storage of glucose
answer
C Increases blood glucose levels Glucagon, an insulin antagonist produced by the alpha cells in the islets of langerhans, leads to the conversion of glycogen to glucose in the liver.
question
A client with type 1 DM has a fingerstick glucose level of 258mg/dl at bedtime. An order for sliding scale insulin exists. The nurse should: A Call the physician B Encourage the intake of fluids C Administer the insulin as ordered D Give the client ½ c. of orange juice
answer
C Administer the insulin as ordered A value of 258mg/dl is above the expected range of 70-105 mg/dl; the nurse should administer the insulin as ordered.
question
The physician orders 36 units of NPH and 12 units of regular insulin. The nurse plans to administer these drugs in 1 syringe. Identify the steps in this procedure by listing them in priority order. 1. Inject air equal to NPH dose into NPH vial 2. Invert regular insulin bottle and withdraw regular insulin dose 3. Inject air equal to regular dose into regular dose 4. Invert NPH vial and withdraw NPH dose. A 1, 2, 3, 4. B 1, 4, 3, 2. C 1, 4, 2, 3, D 1, 3, 2, 4
answer
D 1, 3, 2, 4.
question
The insulin that has the most rapid onset of action would be: A Lente B Lispro C Ultralente D Humulin N
answer
B Lispro Lispro has an immediate onset, a peak of 30-90 minutes, and duration of 2-4 hours
question
A client with DM states, "I cannot eat big meals; I prefer to snack throughout the day." The nurse should carefully explain that the: A Regulated food intake is basic to control B Salt and sugar restriction is the main concern C Small, frequent meals are better for digestion D Large meals can contribute to a weight problem
answer
A Regulated food intake is basic to control An understanding of the diet is imperative for compliance. A balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats usually apportioned over three main meals and two-between meals snacks needs to be tailored to the client's specific needs, with due regard for activity, diet, and therapy.
question
A client with DM has an above-knee amputation because of severe peripheral vascular disease, Two days following surgery, when preparing the client for dinner, it is the nurse's primary responsibility to: A Check the client's serum glucose level B Assist the client out of bed to the chair C Place the client in a high-fowlers position D Ensure that the client's residual limb is elevated
answer
A Check the client's serum glucose level Because the client has diabetes, it is essential that the blood glucose level be determined before meals to evaluate the success of control of diabetes and the possible need for insulin coverage.
question
Which of the following nursing interventions should be taken for a client who complains of nausea and vomits one hour after taking his glyburide (DiaBeta)? A Give subcutaneous insulin and monitor blood glucose B Monitor blood glucose closely, and look for signs of hypoglycemia D Monitor blood glucose, and assess for signs of hyperglycemia
answer
B Monitor blood glucose closely, and look for signs of hypoglycemia When a client who has taken an oral antidiabetic agent vomits, the nurse would monitor glucose and assess him frequently for signs of hypoglycemic. Most of the medication has probably been absorbed. Therefore, repeating the dose would further lower glucose levels later in the day. Giving insulin would also lower the glucose levels, causing hypoglycemic. The client wouldn't have hyperglycemia if the glyburide was absorbed.
question
Which of the following chronic complications is associated with diabetes? A Dizziness, dyspnea on exertion, and coronary artery disease B Retinopathy, neuropathy, and coronary artery disease C Leg ulcers, cerebral ischemic events, and pulmonary infarcts D Fatigue, nausea, vomiting, muscle weakness, and cardiac arrhythmia's
answer
B Retinopathy, neuropathy, and coronary artery disease These are all chronic complications of diabetes. Dizziness, dyspnea on exertion, and coronary artery disease are symptoms of aortic valve stenosis. Fatigue, nausea, vomiting, muscle weakness, and cardiac arrhythmias are symptoms of hyperparathyroidism. Leg ulcers, cerebral ischemic events, and pulmonary infarcts are complications of sickle cell anemia
question
Rotating injection sites when administering insulin prevents which of the following complications? A Insulin edema B Insulin lipodystrophy C Insulin resistance D Systemic allergic reactions
answer
B Insulin lipodystrophy Insulin lipodystrophy produces fatty masses at the injection sites, causing unpredictable absorption of insulin injected into these sites.
question
Which of the following methods of insulin administration would be used in the initial treatment of hyperglycemia in a client with diabetic ketoacidosis? A Subcutaneous B Intramuscular C IV bolus only D IV bolus, followed by continuous infusion
answer
D IV bolus, followed by continuous infusion An IV bolus of insulin is given initially to control the hyperglycemia; followed by a continuous infusion, titrated to control blood glucose. After the client is stabilized, subcutaneous insulin is given. Insulin is never given intramuscularly.
question
Insulin forces which of the following electrolytes out of the plasma and into the cells? A Calcium B Magnesium C Phosphorus D Potassium
answer
D Potassium Insulin forces potassium out of the plasma, back into the cells, causing hypokalemia. Potassium is needed to help transport glucose and insulin into the cells. Calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus aren't affected by insulin
question
Which of the following causes of HHNS is most common? A Insulin overdose B Removal of the adrenal gland C Undiagnosed, untreated hyperpituitarism D Undiagnosed, untreated diabetes mellitus
answer
D Undiagnosed, untreated diabetes mellitus Undiagnosed, untreated DM is one of the most common causes of HHNS.
question
A client is in DKA, secondary to infection. As the condition progresses, which of the following symptoms might the nurse see? A Kussmaul's respirations and a fruity odor on the breath B Shallow respirations and severe abdominal pain C Decreased respirations and increased urine output D Cheyne-stokes respirations and foul-smelling urine
answer
A Kussmaul's respirations and a fruity odor on the breath Coma and severe acidosis are ushered in with Kussmaul's respirations (very deep but not labored respirations) and a fruity odor on the breath (acetone breath).
question
Clients with type 1 diabetes may require which of the following changes to their daily routine during periods of infection? A No changes B Less insulin C More insulin D Oral antidiabetic agents
answer
C More insulin During periods of infection or illness, diabetics may need even more insulin to compensate for increased blood glucose levels.
question
Hemoglobin A1c reflects blood glucose for the how many days prior to test
answer
100-120 days



