Neonatal Dermatology – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion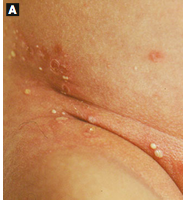
The name of the condition that develops in up to 5% of newborns with darkly pigmented skin with prominent pustules without erythema that rupture, leaving a collarette of scale and hyperpigmentation, located on forehead, chin, neck, back, shins, or widespread that may last several month? Smear of the pustule shows? Histology shows?

answer
Transient Neonatal Pustular Melanosis; PMN; subcorneal pustule with PMNS
question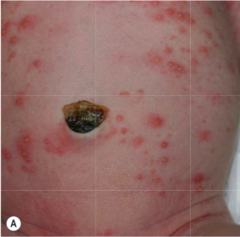
The name of the condition that develops within 24-48 hours after birth in 50% of full term infants on the face, trunk, limbs, buttocks (spares palms and soles) with blotchy erythematous macules, papules, pustules and wheals? Smear of pustule? History?

answer
Erythema Toxicum Neonatorum; eos; subcorneal pustule with eos (ass with pilosebaceous unit)
question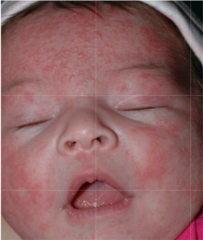
The name of the condition that occurs within the first 2-3 weeks of life as inflammatory non comedonal pustular eruption on cheeks mostly? Associated species in pathogenesis? Histology

answer
Neonatal Cephalic Pustulosis (neonatal acne) malassezia follicular pustules with PMNs
question
Form of panniculitis that occurs in severly ill premature infants within first week of life with diffuse cold, rigid, board like, woody hardening of skin sparing genitalia, palms, soles. What is the classic histology?
answer
Sclerema Neonatorum; needle shaped clefts in lipocyte with little inflammation
question
What three neonatal conditions are characterized histologically by formation of needle shaped clefts within lipocytes? Which type of crystal in each?
answer
Sclerema Neonatorum type A microsized crystal (normal but in excess with no associated inflammation); Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn post steroid panniculitis type B crystals (rosette arrangement with associated inflammation)
question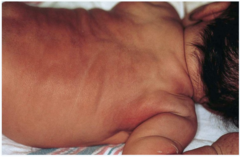
Form of panniculitis that occurs in full term neonates within the first few weeks of life with circumscribed, erythematous, indurated subcutaneous nodules favoring cheeks, shoulders, back, buttocks, thighs. Histologically with needle shaped clefts in fat necrosis and prominent inflammatory infiltrate. What is the main associated symptom that should be monitored until 1 month after full resolution?

answer
subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn hypercalcemia
question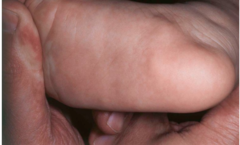
Soft, mostly non painful papules involving the heels. Common and infantile variant. What is the name of the condition and two diseases they are seen in?

answer
Pedal papules of infancy Ehlers Danlos Prader Willi
question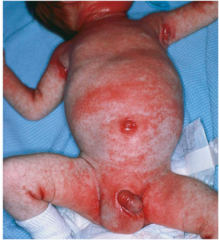
What is the name of the condition with ill defined erythematous patches with waxy scale over scalp, axillae, groin seen in infants typically 1 week after birth with resolution within 1 year? What are three etiologic links?

answer
Seborrheic Dermatitis active sebaceous glands abnormal sebum composition Malassezia Furfur
question
Name of condition that occurs in neonates less than 2 weeks of age, children and adults in hot climates who present with non pruritic clear fragile 1 mm vesicles on the face and trunk? Location of obstruction?

answer
Miliaria crystallina stratum corneum (obstruction of eccrine ducts)
question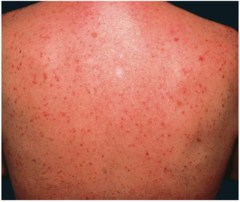
Name of condition that occurs in neonates 1-3 weeks of age, children and adults in hot climates with non follicular pruritic erythematous 1-3 mm papules, pustules on the neck and upper trunk? Location of obstruction

answer
Miliaria rubra mid epidermis (eccrine ducts)
question
Name of condition that occurs in adults in hot climates with non pruritic white 1-3 mm papules on the trunk and proximal extremities? Hx of multiple bouts of ___? Location of obstruction?
answer
Miliaria Profunda Rubra DEJ (eccrine ducts)
question
The hair collar sign can be seen in infants born with aplasia cutis congenita and consists of a ring of dark long hair encircling lesions. This may be a marker of what?
answer
neural tube defect
question
The name of syndrome with ACC of lower extremities + EBDD
answer
Bart
question
The name of syndrome with ACC on scalp with skull ossification defect + extensive CMTC (cutis marmorata telangiectatic congenita) + limb defects (reductions, syndactylyl) + cardiac
answer
Adams Oliver
question
The name of syndrome with Bilateral temporal ACC + abnormal eyelashes + leonine faces + upward slanting eyebrows
answer
Seitles
question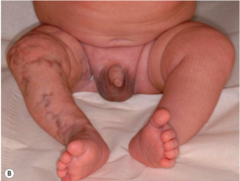
The name of condition present at birth with dark purple to red reticular pattern on trunk/extremities with segmental distribution that persists upon warming the affected infant. 50% of time associated with anomalies -- which are the two most common?

answer
CMTC hypoplasia vascular malformations
question
The name of condition seen at birth in 1 in 250 new borns with intact bullae, erosion, callus or superficial ulceration on a non inflamed base?
answer
Sucking blister
question
Which three congenital infections of the newborn have "blueberry muffin lesions" (i.e. red blue papules nodules)
answer
CMV Rubella Toxoplasmosis
question
Blueberry muffin lesions are seen in congenital infections of the newborn as red blue papules and nodules. What do they represent?
answer
Extramedullary erythropoiesis in dermis
question
Which congenital infection of the newborn is the leading cause of deafness and mental retardation in the US? Which leads to 50% change of deafness?
answer
CMV Rubella
question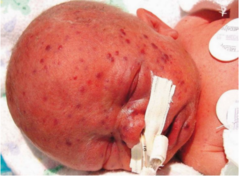
Which TORCH syndrome has histology with enlarged endothelial cells with intranuclear inclusions?

answer
CMV
question
Which TORCH syndrome has hemorrhagic and necrotic papules that favor the trunk (?blueberry muffin) and in 10-30% have chorioretinitis that leads to visual loss and 20% with neurologic manifestations?
answer
Toxoplasmosis
question
What does TORCHs stand for?
answer
Toxoplasmosis other (varicella) rubella CMV HSV syphilis
question
In toxoplasmosis the risk of transmission is greatest if mom is infected in third trimester but a more severe disease if contracted early on. In Rubella, severe birth defects are seen if infected in the first ____ weeks? For varicella the risk is within the first ____ weeks?
answer
16 20
question
What is the mortality rate of HSV congenital infection if left untreated?
answer
50-75
question
In which TORCHs syndrome do you see rhagades (radial periorificial mouth nose eyes anus scars from previous fissures), papulosquamous macules papules (like secondary syphillius) plus bullous lesions (symphilitic phemphigus) and erosive lesions; snuffles; LAD?
answer
Early syphillis
question
What is the hutchinson's triad seen in late syphilis?
answer
Interstitial keratitis hutchinsons teeth (peg shaped notced permanent incisors) neural deafness
question
What is the name of multiple rounded rudimentary cusps on permanent first molars that are seen in late congenital syphilis?
answer
Mulberry molars
question
What is Higoumenakis sign? Seen in which type of congenital syphilis?
answer
thickening of clavicle late
question
Neurosyphilis is classically a manifestation of tertiary syphilis but can occur at any stage of the disease and can be seen in early congentital syphilis. Tabes dorsalis affects up to a third of patients with neurosyphilis with loss of posterior column (vibratory and position) Argyll roberston pupils and occurs in ____ congential syphilis
answer
late
question
Which diaper dermatitis includes scrotum? which spares the inguinal folds? includes inguinal creases?
answer
Candida irritant psoriasis



