Musculoskeletal, skin, connective tissue (USMLE First Aid) – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
anterior cruciate ligament origin/insertion
answer
lateral femoral condyle, anterior tibia
question
posterior cruciate ligament origin/insertion
answer
medial femoral condyle, posterior tibia
question
anterior drawer sign
answer
increased anterior tibial gliding due to ACL injury
question
What constitutes and abnormal passive knee abduction test?
answer
lateral/valgus force causes medial space widening, indicates MCL injury
question
What constitutes and abnormal passive knee adduction test?
answer
medial/varus force causes lateral space widening, indicates LCL injury
question
Greenstick fracture pathogenesis
answer
incomplete fx, extends part way through bone, follows bending stress
question
Torus fracture pathogenesis
answer
axial forced applied to immature bone, causes buckle fx of cortex
question
identify the fracture
answer
greenstick fx
question
identify the fracture
answer
torus fx
question
Unhappy triad pathogenesis
answer
lateral force applied to platned leg, damages ACL, MCL, medial meniscus
question
Prepatellar bursitis
answer
chronic trauma/pressure causes bursa inflammation
question
Baker cyst pathogenesis
answer
popliteal fluid collection in gastrocnemius-semimembranosus bursa
question
supraspinatus innervation
answer
suprascapular nerve
question
supraspinatus action
answer
arm abduction initiation
question
Infraspinatus innervation
answer
suprascapular nerve
question
Infraspinatus action
answer
arm lateral rotation
question
Supraspinatus typical injury mechanism
answer
trauma, degeneration, impingement
question
Infraspinatus typical injury mechanism
answer
pitching injury
question
Teres minor innervation
answer
axillary nerve
question
Teres minor action
answer
arm adduction, lateral rotation
question
Subscapularis innervation
answer
upper/lower subscapular nerves
question
Subscapularis action
answer
arm adduction, medial rotation
question
rotator cuff muscles primary spinal root innervation
answer
C5-C6
question
what is the primary muscle/nerve responsible for arm abduction? (0-15 degrees)
answer
supraspinatus, suprascapular nerve
question
what is the primary muscle/nerve responsible for arm abduction (150-100 degrees)
answer
Deltoid, axillary nerve
question
what is the primary muscle/nerve responsible for arm abduction (>90 degrees)
answer
Trapezius, CN XI
question
what is the primary muscle/nerve responsible for arm abduction (>100 degrees)
answer
Serratus anterior, long thoracic nerve
question
medial epicondylitis alternate name
answer
golfers elbow
question
medial epicondylitis pathogenesis
answer
repetitive flexion causes pain over medial epicondyle
question
lateral epicondylitis alternate name
answer
tennis elbow
question
lateral epicondylitis pathogenesis
answer
repetitive extensionc causes pain near lateral epicondyle
question
Scaphoid significant associated pathologies
answer
most commonly fx via FOSH, may cause osteonecrosis, nonunion
question
Lunate dislocation complications
answer
acute CTS
question
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) pathogenesis
answer
carpal tunnel compresses median nerve
question
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) clinical presentation
answer
paresthesia, pain, numbness in median nerve distribution, thenar atrophy
question
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) risk factors
answer
repetitive use, pregnancy, RA, hypothyroid, DM, acromegaly, dialysis related amyloidosis
question
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) diagnostic signs
answer
Tinel sign, phalen test
question
Guyon canal syndrome pathogenesis
answer
ulnar nerve compression at wrist/hand
question
Guyon canal syndrome risk factors
answer
cycling due to handlebar pressure
question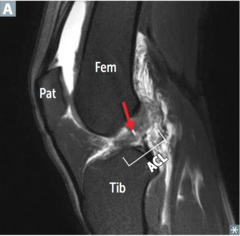
identify the pathology

answer
ACL tear
question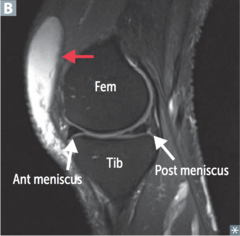
identify the pathology

answer
prepatellar bursitis
question
identify the pathology
answer
baker cyst
question
identify the pathology
answer
supraspinatus tear
question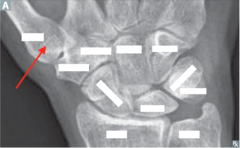
identify the bone

answer
1st metacarpal
question
identify the bone
answer
capitate
question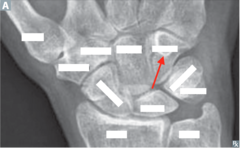
identify the bone

answer
Hamate
question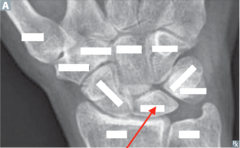
identify the bone

answer
Lunate
question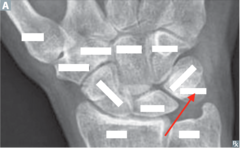
identify the bone

answer
Pisiform
question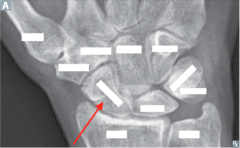
identify the bone

answer
Scaphoid
question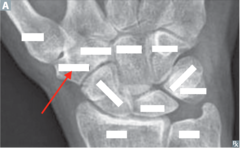
identify the bone

answer
trapezium
question
identify the bone
answer
trapezoid
question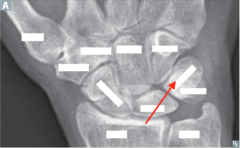
identify the bone

answer
triquetrum
question
Axillary nerve spinal roots
answer
C5-6
question
Axillary nerve most common mechanism of injury
answer
humerus surgical neck fx, anterior dislocation
question
Axillary nerve injury clinical presentation
answer
flattened deltoid, no arm abduction >15 degrees, deltoid/lateral arm anesthesia
question
Musculocutaneous nerve spinal roots
answer
C5-7
question
Musculocutaneous nerve most common mechanism of injury
answer
upper trunk compression
question
Musculocutaneous nerve injury clinical presentation
answer
no forearm flexion, supination, lateral forearm anesthesia
question
Radial nerve spinal roots
answer
C5-T1
question
Radial nerve most common mechanism of injury
answer
midshaft humeral fx, axillary compression
question
Radial nerve injury clinical presentation
answer
no elbow, wrist, finger extension, decreased grip strength, posterior arm, forearm, dorsal hand anesthesia
question
Median nerve spinal roots
answer
C5-T1
question
Median nerve most common mechanism of injury
answer
supracondylar humeral fx, CTS, wrist laceration
question
Median nerve injury clinical presentation
answer
ape hand, no wrist, lateral finger flexion, thumb opposition, dorsal/palmar hand anesthesia
question
Median nerve injury clinical presentation
answer
no wrist flexion medial finger flexion, abduction/adduction, medial 1.5 fingers, hypothenar anesthesia
question
recurrent branch of median nerve spinal roots
answer
C5-T1
question
recurrent branch of median nerve most common injury mechanism
answer
superficial palm laceration
question
recurrent branch of median nerve injury clinical presentation
answer
ape hand, loss of thenar muscle group
question
Erb palsy alternate name
answer
Waiter's tip
question
Erb palsy pathogenesis
answer
traction/tear of upper brachial plexus trunks, C5-6 roots
question
Erb palsy injury mechanism (infants)
answer
lateral neck traction during delivery
question
Erb palsy injury mechanism (adults)
answer
trauma
question
Erb palsy muscles affected
answer
deltoid, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, biceps brachii
question
Erb palsy functional deficits
answer
loss of arm abduction, lateral rotation, forearm flexion, supination
question
Klumpke palsy: pathogenesis
answer
traction/tear of brachial plexus lower trunk, C8-T1
question
Klumpke palsy: injury mechanism (infants)
answer
upward force on arm during delivery
question
Klumpke palsy: injury mechanism (adults)
answer
trauma (grabbing branch to break fall)
question
Klumpke palsy: muscles affected
answer
intrinsic hand muscles: lumbricals, interossei, thenar, hypothenar
question
Klumpke palsy: functional deficits
answer
total claw hand
question
Thoracic outlet syndrome pathogenesis
answer
compression of brachial plexus lower trunk, subclavian vessels
question
Thoracic outlet syndrome mechanism of injury
answer
cervical rib, pancost tumor
question
Thoracic outlet syndrome muscles affected
answer
intrinsic hand muscles: lumbricals, interossei, thenar, hypothenar
question
Thoracic outlet syndrome: functional deficits
answer
intrinsic hand muscle atrophy, ischemia, pain, edema
question
Winged Scapula pathogenesis
answer
long thoracic nerve lesion
question
Winged Scapula mechanism of injury
answer
axillary node dissection after mastectomy, stab wounds
question
Winged Scapula muscles affected
answer
serratus anterior
question
Winged Scapula functional deficits
answer
iniability to anchor scapula to thoracic cage, loss of end arm abduction
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
Waiters tip deformity, Erb palsy
question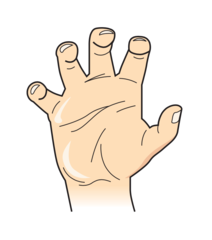
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology

answer
Claw hand, Klumpke palsy
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
cervical rib, thoracic outlet syndrome
question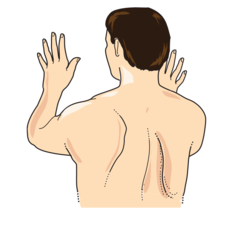
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology

answer
winged scapula, long thoracic nerve injury
question
Clawing of hands anatomical mechanism
answer
extrinsic digital flexors exaggerate lumbrical loss: MCP extension, DIP, PIP flexion
question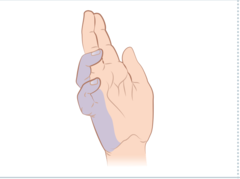
identify the clinical finding and the associated pathology (patient was asked to extend fingers)

answer
ulnar claw, distal ulnar nerve lesion
question
identify the clinical finding and the associated pathology (patient was asked to make a fist)
answer
pope's blessing, proximal median nerve lesion
question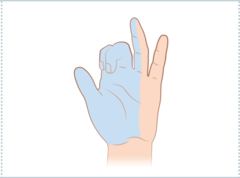
identify the clinical finding and the associated pathology (patient was asked to extend fingers)

answer
median claw, distal median nerve lesion
question
identify the clinical finding and the associated pathology (patient was asked to make a fist)
answer
OK gesture, proximal ulnar nerve lesion
question
name thanar muscles
answer
opponens, pollicis, abductor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis
question
name the hypothenar muscles
answer
opponens digiti minimi, abductor digiti minimi, flexor digiti minimi brevis
question
name the intrinsic hand muscles (not including thenar/hypothenar groups)
answer
dorsal/palmar interossei, lumbricals
question
Dorsal interossei muscles action
answer
finger abduction
question
Palmar interossei muscles action
answer
finger adduction
question
Lumbricals muscles action
answer
MCP flexion, PIP/DIP extension
question
Acetaminophen MOA
answer
reversibly inhibits COX in CNS, (inactivated peripherally)
question
Acetaminophen physiologic effects
answer
antipyretic, analgesic, not anti-inflammatory
question
Acetaminophen clinical uses
answer
fever, pain, use instead of ASA to avoid Reye syndrome
question
Acetaminophen adverse effects
answer
hepatic necrosis
question
Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity pathophysiology
answer
metabolite depletes glutathione, forms toxic byproducts, causes necrosis
question
Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity treatment
answer
N-acetylcysteine, regenerates glutathione
question
Aspirin MOA
answer
irreversibly inhibits COX 1/2, decreases prostaglandin, TXA2 synthesis
question
Aspirin effect on coagulation labs
answer
prolonged bleeding time, normal PT, PTT, lasts until new platelets produced
question
low dose aspirin clinical uses
answer
platelet aggregation inhibition (anticoagulation)
question
intermediate dose aspirin clinical uses
answer
antipyretic, analgesic
question
high dose aspirin clinical uses
answer
antiinflammatory
question
Aspirin adverse effects
answer
gastric ulcers, tinnitus, nephrotoxicity, reye syndrome
question
Aspirin toxicity pathophysiology
answer
initial respiratory alkalosis, transitions to compensated metabolic acidosis
question
Aspirin adverse effects: renal
answer
acute renal failure, interstitial nephritis
question
Celecoxib MOA
answer
selectively inhibits COX2
question
COX-2 function
answer
found in inflammatory cells, vascular endothelium, mediates inflammation, pain
question
Celecoxib beneficial effects
answer
anti-inflammatory w/o GI irritation, spares platelet function
question
Celecoxib clinical uses
answer
RA, osteoarthritis
question
Celecoxib adverse effects
answer
increased thrombosis risk, sulfa allergy
question
Ibuprofen drug class
answer
NSAID
question
Naproxen drug class
answer
NSAID
question
Indomethacin drug class
answer
NSAID
question
Ketorolac drug class
answer
NSAID
question
Diclofenac drug class
answer
NSAID
question
Piroxicam drug class
answer
NSAID
question
NSAIDs (Ibuprofen) MOA
answer
reversibly inhibits COX 1/2, prostaglandin synthesis
question
NSAIDs (Ibuprofen) clinical uses
answer
antipyretic, analgesic, anti-intlammatory
question
Indomethacin unique clinical uses
answer
close PDA in neonate
question
NSAIDs (Ibuprofen) adverse effects
answer
PUD, aplastic anemia, interstitial nephritis, renal ischemia
question
Leflunomide MOA
answer
reversibly inhibits dihydroorotate dehydrogenase, inhibits pyrimidine synthesis, T cell proliferation
question
Leflunomide clnical uses
answer
RA, psoriatic arthritis
question
Leflunomide adverse effects
answer
diarrhea, HTN, hepatotoxicity, teratogen
question
"-dronate" drug class
answer
bisphosphonate
question
Alendronate drug class
answer
bisphosphonate
question
Ibandronate drug class
answer
bisphosphonate
question
Zoledronate drug class
answer
bisphosphonate
question
Bisphosphonates (Alendronate) MOA
answer
pyrophosphate analog, binds bone hydroxyapatite, inhibits osteoclasts
question
Bisphosphonates (Alendronate) clincial uses
answer
osteoporosis, hypercalcemia, Pagets disease, bone metastasis, osteogenesis imperfecta
question
Bisphosphonates (Alendronate) adverse effects
answer
esophagitis, jaw osteonecrosis, atypical stress fx
question
Bisphosphonates (Alendronate) administration instructions
answer
take w/ H2O, remain upright for 30 minutes
question
Teriparatide MOA
answer
recombinant PTH analog, increases osteoblast activity
question
Teriparatide absorption
answer
SQ
question
Teriparatide clinical uses
answer
osteoporosis, causes increased bone growth
question
Teriparatide adverse effects
answer
osteosarcoma risk, transient hypercalcemia
question
Teriparatide contraindications
answer
hx of cancer, radiation therapy
question
Allopurinol drug class
answer
xanthine oxidase inhibitor
question
Febuxostat drug class
answer
xanthine oxidase inhibitor
question
Xanthine oxidase inhibitors (Allopurinol) MOA
answer
inhibits conversion of xanthine to urate
question
Xanthine oxidase inhibitors (Allopurinol) clinical uses
answer
chronic gout, leukemia/lymphoma tumor lysis syndrome
question
Pegloticase MOA
answer
recombinant uricase, converts urate to allantoin
question
Pegloticase clinical uses
answer
chronic gout
question
Probenecid MOA
answer
inhibits PCT urate reabsorption
question
Probenecid adverse effects
answer
uric acid calculi
question
Colchicine MOA
answer
stabilizes tubulin, inhibits microtubule polymerization, inhibits neutrophil chemotaxis, degranulation
question
Colchicine clinical uses
answer
acute/prophylactic gout
question
Colchicine adverse effects
answer
GI effects
question
Drugs used for acute gout attacks
answer
NSAIDS, steroids, colchicine
question
TNF-alpha inhibitors adverse effects
answer
infection risk, latent TB reactivation
question
Etanercept drug class
answer
TNF-alpha inhibitor
question
Etanercept MOA
answer
soluble TNF receptor + IgG Fc, binds TNF
question
Etanercept clinical uses
answer
RA, psoriasis, ankylosing spondylitis
question
Infliximab drug class
answer
TNF-alpha inhibitor
question
Adalimumab drug class
answer
TNF-alpha inhibitor
question
Certolizumab drug class
answer
TNF-alpha inhibitor
question
Golimumab drug class
answer
TNF-alpha inhibitor
question
TNF-alpha inhibitor monoclonal antibodies (Infliximab) clinical uses
answer
IBD, RA, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriasis
question
Iliohypogastric nerve spinal cord roots
answer
T12-L1
question
Genitofemoral nerve spinal cord roots
answer
L1-L2
question
Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve spinal cord roots
answer
L2-L3
question
Obturator nerve spinal cord roots
answer
L2-L4
question
Femoral nerve spinal cord roots
answer
L2-L4
question
Sciatic nerve spinal cord roots
answer
L4-S3
question
Common peroneal nerve spinal cord roots
answer
L4-S2
question
Tibial nerve spinal cord roots
answer
L4-S3
question
Iliohypogastric nerve sensory innervation
answer
suprapubic
question
genitofemoral nerve sensory innervation
answer
scrotum/labia majora, medial thigh
question
Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve sensory innervation
answer
anterior, lateral thigh
question
Obturator nerve sensory innervation
answer
medial thigh
question
Femoral nerve sensory innervation
answer
anterior thigh, medial leg
question
Sciatic nerve sensory innervation
answer
Posterior thigh
question
common peroneal nerve sensory innervation
answer
dorsum of foot
question
Tibial nerve sensory innervation
answer
sole of foot
question
Iliohypogastric nerve motor innervation
answer
transversus abdominis, internal oblique
question
Genitofemoral nerve motor innervation
answer
cremaster
question
Obturator nerve motor innervation
answer
obturator externus, adductor longus/brevis/magnus, gracilis, pectineus,
question
Femoral nerve motor innervation
answer
quadriceps, iliopsoas, pectineus, sartorius
question
Sciatic nerve motor innervation
answer
hamstrings, adductor magnus
question
Common peroneal nerve motor innervation
answer
biceps femoris, tibialis anterior, foot extensors
question
Tibial nerve motor innervation
answer
triceps surae, plantaris, popliteus, foot flexors
question
Iliohypogastric nerve most common cause of injury
answer
abd surgery
question
Genitofemoral most common cause of injury
answer
laparoscopic surgery
question
Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve most common cause of injury
answer
tight clothing, obesity, pregnancy
question
Obturator nerve most common cause of injury
answer
Pelvic surgery
question
Femoral nerve most common cause of injury
answer
pelvic fx
question
Sciatic nerve most common cause of injury
answer
herniated disc
question
Common peroneal nerve most common cause of injury
answer
Trauma, compress of lateral leg, fibular neck fx
question
Tibial nerve most common cause of injury
answer
knee trauma, baker cyst, tarsal tunnel syndrome
question
Iliohypogastric nerve injury clinical presentation
answer
burning/tingling in incision site, radiates to inguinal, suprapubic region
question
Genitofemoral nerve injury clinical presentation
answer
decreased anterior thigh sensation beneath inguinal ligament, absent cremaster reflex
question
Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve injury clinical presentation
answer
decreased thigh sensation
question
Obturator nerve injury clinical presentation
answer
decreased thigh sensation, adduction
question
Femoral nerve injury clinical presentation
answer
decreased thigh flexion, leg extension
question
Common peroneal nerve injury clinical presentation
answer
decreased dorsal foot sensation, foot drop
question
Tibial nerve injury clinical presentation
answer
decreased plantar foot sensation, foot inversion, plantarflexion
question
Superior gluteal nerve motor innervation
answer
gluteus medius/minimus, TFL
question
Inferior gluteal nerve motor innervation
answer
gluteus maximus
question
Pudendal nerve sensory innervation
answer
perineum
question
Pudendal nerve motor innervation
answer
external urethral/anal sphincter
question
Superior gluteal nerve spinal cord roots
answer
L4-S1
question
inferior gluteal nerve spinal cord roots
answer
L5-S2
question
Pudendal nerve spinal cord roots
answer
S2-S4
question
Superior gluteal nerve most common cause of injury
answer
Iatrogenic via intramuscular injection
question
Inferior gluteal nerve most common cause of injury
answer
posterior hip dislocation
question
Pudendal nerve most common cause of injury
answer
Stretch injury during childbirth
question
Superior gluteal nerve injury clinical presentation
answer
trendelenburg gait/sign, drop is c/l to lesion
question
Inferior gluteal nerve injury clinical presentation
answer
decreased hip extension, difficulty climbing stairs, rising from seated,
question
Pudendal nerve injury clinical presentation
answer
saddle anesthesia, incontinence
question
gluteus medius action (at hip)
answer
abduction, internal rotation
question
gluteus minimus action (at hip)
answer
abduction, internal rotation
question
Adductor magnus/longus/brevis action (at hip)
answer
adduction
question
Gluteus maximus action (at hip)
answer
extension, external rotation
question
semitendinosus action (at hip)
answer
extension
question
semimembranosus action (at hip)
answer
extension
question
Iliopsoas action (at hip)
answer
flexion, external rotation
question
Rectus femoris action (at hip)
answer
flexion
question
Tensor fascia lata action (at hip)
answer
flexion, internal rotation
question
piriformis action (at hip)
answer
external rotation
question
Obturator internus/externus action (at hip)
answer
external rotation
question
what direction to intervertebral discs typically herniate?
answer
posterolateral
question
if the L3-L4 intervertebral disc herniates, what clinical findings would be expected?
answer
weak knee extension, decreased patellar reflex
question
if the L4-L5 intervertebral disc herniates, what clinical findings would be expected?
answer
weak dorsiflexion, difficulty heel walking
question
if the L5-S1 intervertebral disc herniates, what clinical findings would be expected?
answer
weak plantar flexion, difficulty toe walking, decreased calcaneal reflex
question
what nerve/artery (respectively) is associated with the axilla/lateral thorax?
answer
long thoracic N, lateral thoracic A
question
what nerve/artery (respectively) is associated with the surgical neck of humerus?
answer
axillary N, posterior circumflex A
question
what nerve/artery (respectively) is associated with the midshaft humerus?
answer
radial N, deep brachial A
question
what nerve/artery (respectively) is associated with the distal humerus/cubital fossa?
answer
median N, brachial A
question
what nerve/artery (respectively) is associated with the popliteal fossa?
answer
tibial N, popliteal A
question
what nerve/artery (respectively) is associated with the posterior medial malleolus?
answer
tibial N, posterior tibial A
question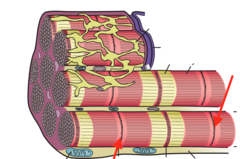

answer
M line
question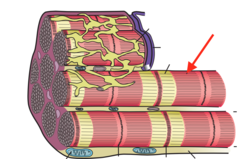

answer
myosin
question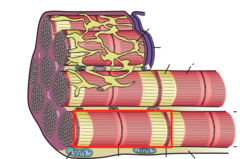

answer
sarcomere
question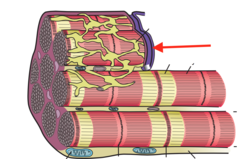

answer
T tubule
question
skeletal muscle triad
answer
T tubule + 2 terminal cisternae
question
cardiac muscle dyad
answer
T tubule + 1 terminal cisterna
question
type 1 muscle fiber characteristics
answer
slow twitch, red, aerobic, high mitochondria, Mb
question
type 2 muscle fiber characteristics
answer
fast twitch, white, anerobic, low mitochondria, Mb
question
if the myosin light chain kinase is active, does this cause smooth muscle to contract or relax?
answer
contract
question
if the myosin light chain phosphorylase is active, does this cause smooth muscle to contract or relax?
answer
relax
question
which bones undergo endochondral ossification
answer
axial/appendicualr skeleton, base of sull
question
which bones undergo membranous ossification?
answer
calvarium, facial bones, clavicle
question
endochondrial ossification mechanism
answer
cartilage replaced with woven bone, later replaced with lamellar bone
question
membranous ossification mechanism
answer
woven bone formed directly w/o cartilage, remodeled to lamellar bone
question
Osteoblast function
answer
builds bone via secreting collagen, catalyzing mineralization, produces ALP
question
Osteoblast cell of origin
answer
mesenchymal stem cells in periosteum
question
what lab tests are used to measure osteoblast activity?
answer
ALP, osteocalcin, type I procollagen propeptides
question
Osteoclast function
answer
secretes H+, collagenases to dissolve bone
question
Osteoclast cell of origin
answer
fusion of monocyte/macrophage precursors
question
PTH function (low concentration)
answer
anabolic effects on osteoblasts/osteoclasts, induces bone building
question
PTH function (high concentration)
answer
catabolic effects: osteitis fibrosa cystica
question
Estrogen effect on bone
answer
inhibits osteoblast apoptosis, induces osteoclast apoptosis, causes epiphyseal plate closure during puberty
question
Achondroplasia pathogenesis
answer
defective endochondral ossification, longitudinal bone growth causes short limbs, membranous ossification affected
question
Achondroplasia clinical presentation
answer
large head relative to limbs
question
Achondroplasia molecular pathogenesis
answer
constitutive activation of FGFR3, inhibits chondrocyte proliferation
question
Achondroplasia inheritance
answer
AD, full penetrance, homozygous is lethal
question
Osteoporosis pathogenesis
answer
trabecular/spongy bone loses mass, interconnections, due to increased bone resorption, decreased estrogen
question
Osteoporosis treatment
answer
eight bearing exercise, adequate Ca2+, vitamin D, bisphosphonates, teriparatide, SERMs, calcitonin
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
vertebral compression fx, osteoporosis
question
Osteopetrosis pathogenesis
answer
defective osteoclasts cause abnormal bone resorption, leads to thickened dense bones, prone to fx
question
Osteopetrosis complications
answer
fx, thikened bone causes decreased marrow, pancytopenia, cranial nerve impingement
question
Osteopetrosis treatment
answer
bone marrow transplant
question
Osteomalacia/rickets pathogenesis
answer
defective osteoid/growth plate mineralization
question
Osteomalacia/rickets most common etiology
answer
vitamin D deficiency
question
Osteomalacia clinical presentation
answer
osteopenia, pseudofractures
question
rickets clinical presentation
answer
epiphyseal widening, metaphyseal cupping, genu varum, bead-like costochondral junctions, craniotabes
question
Osteomalacia/rickets lab findings
answer
decreased vitamin D, Ca2+, PO4, increased PTH, ALP
question
Paget disease of bone (osteitis deformans) pathogenesis
answer
increased osteoclast activity followed by disorganized osteoblast activity, forms poor quality bone
question
Paget disease of bone (osteitis deformans) laboratory findings
answer
increased Ca2+, PO4, PTH, ALP
question
Paget disease of bone (osteitis deformans) clinical presentation
answer
mosaic pattern of woven/lamellar bone, long bone chalk stick fx
question
Paget disease of bone (osteitis deformans) complications
answer
high output CHF due to AV shunts, osteogenic sarcoma
question
lytic phase of Paget disease of bone (osteitis deformans)
answer
osteoclast activity
question
mixed phase of Paget disease of bone (osteitis deformans)
answer
osteoclast/osteoblast activity
question
Sclerotic phase of Paget disease of bone (osteitis deformans)
answer
osteoblast activity
question
Quiescent phase of Paget disease of bone (osteitis deformans)
answer
minimal osteoblast/osteoclast activity
question
Paget disease of bone (osteitis deformans) treatment
answer
bisphosphonates
question
Osteonecrosis (avascular necrosis) pathogenesis
answer
bone/marrow infarction via ischemia
question
Osteonecrosis (avascular necrosis) etiology
answer
steroids, alcoholism, sickle cell, trauma, the bends, LCP/SCFE, Gaucher disease
question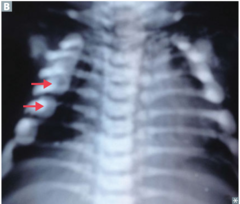
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology

answer
bead-like costochondral junctions, rickets
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
genu varum, rickets
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
skull thickening, paget disease of bone
question
identify the pathology
answer
osteonecrosis
question
osteoporosis lab findings
answer
normal electrolytes/hormones, decreased bone lab
question
Osteopetrosis lab findings
answer
normal/decreased CA2+ if severe
question
Paget disease of bone lab findings
answer
increased ALP
question
Osteitis fibrosa cystica (primary hyperparathyroidism) lab findings
answer
increased Ca2+, AlP, PTH, decreased PO4
question
secondary hyperparathryoidism lab findings
answer
increased PO4, ALP, PTH, decreased Ca2+
question
Osteomalacia/rickets lab findings
answer
increased ALP, PTH, decreased Ca2+, PO4
question
Hypervitaminosis D lab findings
answer
increased Ca2+, PO4, decreased PTH
question
Osteitis fibrosa cystica clinical presentation
answer
brown tumors, subperiosteal thinning
question
Osteitis fibrosa cystica etiology
answer
idiopathic, parathyroid hyperplasia/adenoma/carcinoma
question
hypervitaminosis D etiology
answer
oversupplementation, granulomatous disease
question
Osteochondroma characteristics
answer
bony exostosis with cartilagenous cap
question
Osteochondroma complications
answer
fx, arely transforms to chondrosarcoma
question
Giant cell tumor of bone most common location of origin
answer
long bone epiphysis, especially distal femur, proximal tibia
question
Giant cell tumor of bone typical behavior
answer
locally aggressive, benign
question
Giant cell tumor of bone radiographic morphology
answer
soap bubble
question
Giant cell tumor of bone histologic morphology
answer
giant cells, express RANKL
question
Osteosarcoma risk factors
answer
paget disease, bone infarcts, radiation, familal retinoblastoma, Li-fraumeni syndrome
question
Osteosarcoma most common site of origin
answer
metaphysis of long bones
question
Osteosarcoma radiographic morphology
answer
Codman triangle, sunburst pattern
question
Osteosarcoma typical behavior
answer
aggressive
question
Ewing sarcoma risk factors
answer
children <15
question
Ewing sarcoma typical location of origin
answer
long bone diaphysis, pelvis, scapula, ribs
question
Ewing sarcoma histologic morphology
answer
anaplastic, small round blue cells
question
Ewing sarcoma typical vehavior
answer
extremely aggressive, early mets, responsive to chemo
question
Ewing sarcoma molecular pathogenesis
answer
t11:22 causes EWS-FLI1 fusion protein
question
identify the pathology

answer
osteochondroma
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
soap bubble, giant cell tumor
question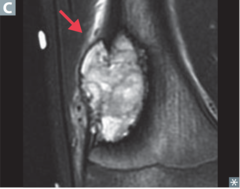
identify the pathology

answer
osteosarcoma
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
anaplastic small blue cells, ewing sarcoma
question
what type of bone lesion typically forms here?
answer
ewing sarcoma, myeloma
question
what type of bone lesion typically forms here?
answer
fibrous dysplasia
question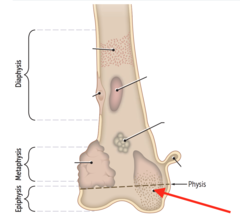
what type of bone lesion typically forms here?

answer
giant cell tumor
question
what type of bone lesion typically forms here?

answer
osteochondroma
question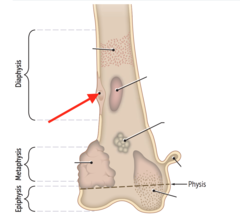
what type of bone lesion typically forms here?

answer
osteoid osteoma
question
what type of bone lesion typically forms here?

answer
osteosarcoma
question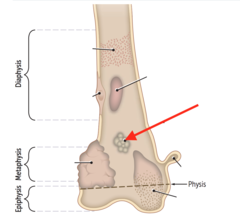
what type of bone lesion typically forms here?

answer
simple bone cyst
question
osteoarthritis pathogenesis
answer
mechanical damage destroys articular cartilage, infalmmation w/ inadequate repair, chondrocytes mediate degradation
question
osteoarthritis risk factors
answer
age, female, obesity, joint trauma
question
osteoarthritis clinical presentation
answer
asymmetric pain in weight bearing joints, worse after use, better with rest
question
osteoarthritis joint findings
answer
osteophytes, joint space narrowing, subchondral sclerosis/cysts, noninflammatory fluid, involves DIP, PIP, 1st CMC joints, no MCP
question
osteoarthritis treatment
answer
acetaminophen, NSAIds, glucocorticoids
question
Rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis
answer
autoimmune: inflammation produces pannus, erodes articular cartilage/bone
question
Rheumatoid arthritis risk factors
answer
female, HLA DR4, smoking, silica exposure
question
Rheumatoid arthritis lab findings
answer
rheumatoid factor, anti-CCP antibody
question
Rheumatoid arthritis clinical presentation
answer
symmetric pain, swelling, morning stiffness, improves w/ use, extraarticular manifestations
question
Rheumatoid arthritis joint findings
answer
erosions, juxta-articular osteopenia, soft tissue swelling, subchondral cysts, joint space narrowing, involves MCP, PIP, wrist, not DIP, 2st CMC
question
Rheumatoid arthritis assocaited deformities
answer
cervical subluxation, ulnar finger deviation, swan neck/boutonniere deformity, i
question
Rheumatoid arthritis treatment
answer
NSAIDs, glucocorticoids, DMARDs
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
Pannus, RA
question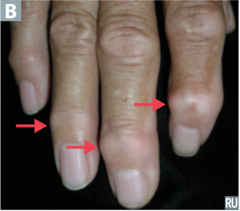
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology

answer
heberden nodes, OA
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
bouchard nodes, OA
question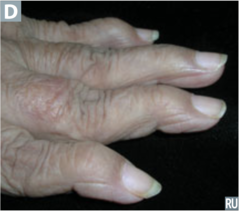
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology

answer
swan neck deformity, RA
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
boutonniere deformity, RA
question
Gout pathogenesis
answer
monosodium urate precipitation in joints cause inflammation, pain
question
what diseases can cause gout via underexcretion of uric acid?
answer
idiopathic, renal failure, certain meds (thiazides)
question
what diseases can cause gout via overproduction of uric acid?
answer
lesch-nyhan syndrome, PRPP excess, tumor lysis syndrome, von Gierke disease
question
Gout histologic morphology
answer
needl shaped cristals, negatively birefringent under polarized light
question
gout clinical presentation
answer
asymmetric joint swelling, redness, pain
question
acute gout treatment
answer
NSAIDs, glucocorticoids, colchicine
question
chronic gout treatment
answer
xanthine oxidase inhibitor
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
urate crystals, gout
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
urate crystals, gout
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
tophus, gout
question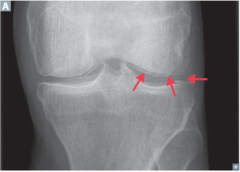
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology

answer
calcium pyrophosphate cyrstals in joint space, CPPD disease
question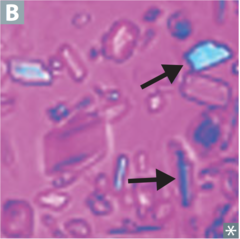
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology

answer
calcium pyrophosphate crystals, CPPD disease
question
Calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD disease) pathogenesis
answer
calcium pyrophosphate crystals deposit in joint space
question
Calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD disease) risk factors
answer
hemochromatosis, hyperparathyroidism, joint trauma
question
Calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD disease) most commonly affected joint
answer
knee
question
Calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD disease) radiographic findings
answer
chondrocalcinosis
question
Calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD disease) acute treatment
answer
NSAIDs, colchicine, glucocorticoids
question
Calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD disease) chronic/preventative treatment
answer
colchicine
question
Sjögren syndrome pathogenesis
answer
autoimmune destruction of exocrine glands, especially lacrimal, sailvary
question
Sjögren syndrome histologic morphology
answer
lymphocytic infiltrates
question
Sjögren syndrome clinical presentation
answer
inflammatory joint pain, keratoconjunctivitis sicca, xerostomia, b/l parotid enlargement
question
Sjögren syndrome lab findings
answer
ANA, rheumatoid factor, SS-A, SS-B
question
Sjögren syndrome complications
answer
dental caries, MALToma
question
most common causes of septic arthritis
answer
S. aureus, strep, N. gonorrhoeae
question
septic arthritis clinical presentation
answer
joint swelling, redness, pain
question
septic arthritis lab findings
answer
synovial WBCS >50,000
question
Gonococcal arthritis clinical presentation
answer
purulent arthritis or polyarthralgia, tenosynovitis, dermatitis
question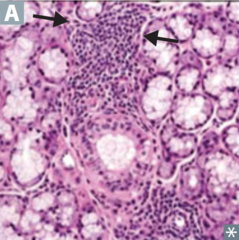
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology

answer
lymphocytic infiltrate, sjogren syndrome
question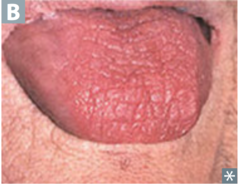
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology

answer
xerostomia, sjogren syndrome
question
identify the pathology
answer
septic arthritis
question
seronegative spondyloarthritis risk factors
answer
HLA B27
question
seronegative spondyloarthritis common clinical presentation
answer
inflammatory back pain, peripheral arthritis, enthesitis, dactylitis, uveitis
question
Psoriatic arthritis clinical presentation
answer
skin psoriasis, nail lesions, asymmetric patchy involvement, dactylitis, pencil in cup deformity
question
Ankylosing spondylitis clinical presentation
answer
symmetric spine/SI joint involvement, ankylosis, uveitis, aortic regurg
question
classic traid of reactive arthritis
answer
conjunctivitis, urethritis, arthritis
question
which pathogens are associated with reactive arthritis?
answer
shigella, salmonella, yersinia, chlamydia, campylobacter
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
dactylitis, psoriatic arthritis
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
pencil in cup deformity, psoriatic arthritis
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
bamboo spine, psoriatic arthritis
question
Ankylosing spondylitis copmlications
answer
restrictive lung disease
question
Systemic lupus erythematosus clinical presentation (classic)
answer
rash, joint, pain, fever
question
Libman-Sacks endocarditis (SLE complications)
answer
nonbacterial verrucous thrombi on mitral/aortic valve
question
Systemic lupus erythematosus complications
answer
Libman-Sacks endocarditis, nephritis, CV disease, infections
question
Systemic lupus erythematosus clinical presentation
answer
rash, arthritis, serositis, hematologic/renal/neurologic disorders, photosensitivity
question
Systemic lupus erythematosus lab findings
answer
ANA, anti-dsDNA, anti-Smith, antiphospholipid, decreased C3, C4, CH50
question
What does the presence of anti-dsDnA antibodies indicate? (SLE)
answer
poor prognosis due to renal disease
question
What does the presence of anti-histone antibodies indicate? (SLE)
answer
sensitive for drug induced SLE
question
Antiphospholipid syndrome pathogenesis
answer
anticardiolipin antibodes cause increased thrombosis, spontaneous abortion, false positive VDRL/RPR
question
Antiphospholipid syndrome laboratory findings
answer
lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin, anti-beta 2 glycoprotein antibdoesi
question
Antiphospholipid syndrome treatment
answer
anticoagulation
question
mixed connective tissue disease characteristics
answer
features of SLE, systemic sclerosis, polymyositis
question
mixed connective tissue disease lab findings
answer
anti-U1 RNP antibodies
question
Sarcoidosis pathogenesis
answer
immune mediated noncaseating granulomas
question
Sarcoidosis lab findings
answer
increased ACE, CD4/CD8 ratio in bronchoalveolar fluid
question
Sarcoidosis radiographic findings
answer
XR: b/l adenopathy, coarse reticular opacities, CT: extensive hilar/mediastinal adenopathy
question
Sarcoidosis complications
answer
restrictive lung disease, erythema nodosum, lupus pernio, bell's palsy, epithelioid granulomas, uveitis, hypercalcemia
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
malar rash, SLE
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
discoid rash, SLE
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
noncaseating granulomas, sarcoidosis
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
coarse reticular opacities, sarcoidosis
question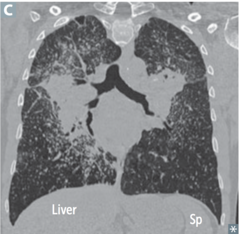
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology

answer
hilar/mediastinal adenopathy, sarcoidosis
question
polymyalgia rheumatica clinical presentation
answer
pain/stiffness in shoulders/hips, fever, malaise, weight loss, no weakness
question
polymyalgia rheumatica disease associations
answer
giant cell arteritis
question
polymyalgia rheumatica lab findings
answer
increased ESR, CRP, normal CK
question
polymyositis/dermatomyositis lab findings
answer
increased CK, + ANA, anti-Jo-1, anti-SRP, anti-Mi-2 antibodies
question
polymyositis/dermatomyositis treatment
answer
steroids, long term immunosuppression
question
Polymyositis clinical presentation
answer
progressive symmetric proximal muscle weakness, commonly involves shoulders
question
Polymyositis histologic morphology
answer
endomysial inflammation w/ CD8 T cells
question
Dermatomyositis clinical presentation
answer
polymyositis + malar rash, grotton papules, heliotrope rash
question
Dermatomyositis complications
answer
occult malignant
question
Dermatomyositis histologic morphology
answer
perimysial inflammation, atrophy w/ CD4 T cells
question
Myasthenia gravis pathogenesis
answer
autoantibodies to postsynaptic Ach receptor
question
Myasthenia gravis clincial presentation
answer
ptosis, diplopia, weakness, worse with use, better with edrophonium
question
Myasthenia gravis disease associations
answer
thymoma, thymic hyperplasia
question
Myasthenia gravis interaction with AchE inhibitor
answer
improves sx
question
Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic syndrome pathogenesis
answer
autoantibodies to presynaptic Ca2+ channel, decreases Ach release
question
Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic syndrome clinical presentation
answer
proximal muscle weakness, autonomic sx, improves with muscle use
question
Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic syndrome disease associations
answer
small cell lung cancer
question
Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic syndrome interaction with AchE inhibitors
answer
minimal effect
question
Raynaud phenomenon pathophysiology
answer
arteriolar vasospasm in response to cold/stress causes decreased skin blood flow, color change
question
difference between raynaud disease and raynaud syndrome
answer
disease=primary, syndrome=secondary
question
Raynaud syndrome (secondary) complciations
answer
digital ulceration
question
Raynaud disease/syndrome treatment
answer
calcium channel blocker
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
grotton's papules, dermatomyositis
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
heliotrope rash, dermatomyositis
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
shawl/face rash, dermatomyositis
question
identify the pathology
answer
Raynaud phenomenon
question
Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis) pathogenesis
answer
autoimmun, noninflammatory vasculopathy, collagen deposition with fibrosis
question
Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis) clinical presentation
answer
skin sclerosis causes puffy taut skin, fingertip pitting
question
Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis) complications
answer
renal, pulmonary, CV, GI sclerosis causes death
question
Diffuse scleroderma disease severity
answer
widespread skin involvement, rapid progression, early visceral involvement
question
Limited scleroderma disease severity
answer
limited skin involvement, confined tin fingers, face
question
Diffuse scleroderma lab findings
answer
anti-Scl-70/DNA topoisomerase I antibody
question
CREST syndrome (acronym)
answer
calcinosis, Raynaud phenoemon, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, telangiectasia
question
limited scleroderma/CREST syndrome lab findings
answer
anti-centromere antibody
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
puffy, taut skin, scleroderma
question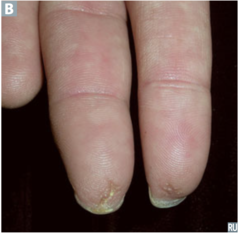
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology

answer
fingertip pitting, scleroderma
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
calcinosis, scleroderma/CREST syndrome
question
identify the layer indicated by C
answer
stratum corneum
question
identify the layer indicated by L
answer
stratum lucidum
question
identify the layer indicated by G
answer
stratum granulosum
question
identify the layer indicated by S
answer
stratum spinosum
question
identify the layer indicated by B
answer
stratum basale
question
tight junctions function
answer
prevents paracellular solute movement
question
tight junctions structural components
answer
claudins, occludins
question
Adherens junctions function
answer
forms belt that connects actin cytoskeletons of adjacent cells
question
Adherens junctions structural components
answer
Cadherins
question
Desmosomes function
answer
structural support
question
Desmosomes structural components
answer
intermediate filaments
question
Gap junctions function
answer
channel proteins that permit intercellular electrical/chemical communication
question
Gap junctions structural components
answer
connexons
question
Hemidesmosomes function
answer
connect keratin to basement membrane
question
Integrins function
answer
membrane proteins that bind collagen, laminin, maintain integrity of basement membrane
question
if autoantibodies target desmosomes, what disease does this cause?
answer
pemphigus vulgaris
question
if autoantibodies target hemidesmosomes, what disease does this cause?
answer
bullous pemphigoid
question
describe the lesion
answer
macule
question
describe the lesion
answer
patch
question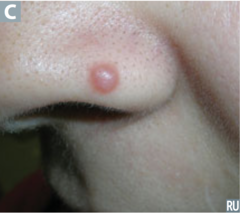
describe the lesion

answer
papule
question
describe the lesion
answer
plaque
question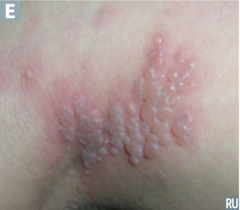
describe the lesion

answer
vesicle
question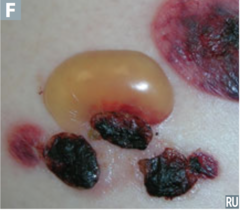
describe the lesion

answer
bulla
question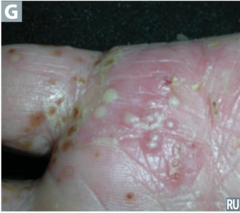
describe the lesion

answer
pustule
question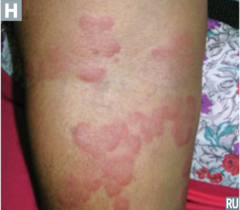
describe the lesion

answer
wheal
question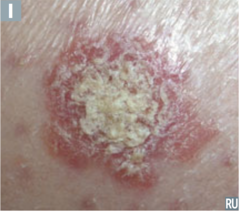
describe the lesion

answer
scale
question
describe the lesion
answer
crust
question
identify the pathology
answer
labial macule
question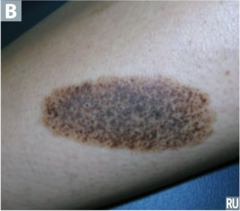
identify the pathology

answer
congenital nevus
question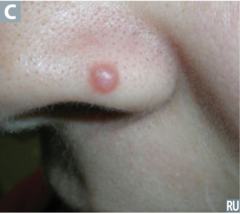
identify the pathology

answer
nevus
question
identify the pathology
answer
Psoriasis
question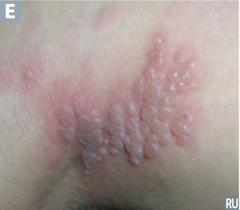
identify the pathology

answer
shingles
question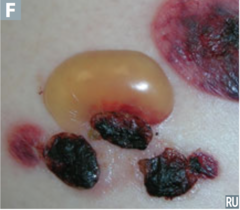
identify the pathology

answer
bullous pemphigoid
question
identify the pathology
answer
pustular psoriasis
question
identify the pathology
answer
urticaria
question
identify the pathology
answer
squamous cell carcinoma
question
identify the pathology
answer
impetigo
question
Hyperkeratosis definition (dermatology)
answer
increased thickness of stratum corneum
question
parakeratosis definition (dermatology)
answer
hyperkeratosis w/ retention of nuclei in stratum corneum
question
Hypergranulosis definition (dermatology)
answer
increased stratum granulosum thickness
question
Spongiosis definition (dermatology)
answer
epidermal accumulation of edematous fluid in intercellular spaces
question
Acantholysis definition (dermatology)
answer
epidermal cell separation
question
Acanthosis definition (dermatology)
answer
epidermal hyperplasia, increased stratum spinosum thickness
question
What diseases involve hyperkeratotic lesions? (dermatology)
answer
psoriasis, calluses
question
What diseases involve parakeratotic lesions? (dermatology)
answer
psoriasis
question
What diseases involve hypergranulolitic lesions? (dermatology)
answer
lichen planus
question
What diseases involve spongiotic lesions? (dermatology)
answer
eczematous dermatitis
question
What diseases involve acantholytic lesions? (dermatology)
answer
pempigus vulgaris
question
What diseases involve acanthotic lesions? (dermatology)
answer
acanthosis nigricans
question
Albinism pathogenesis
answer
tyrosinase deficiency causes decreased melanin production, normal number of melanocytes
question
Albinism complications
answer
skin cancer
question
Melasma (cholasma) pathogenesis
answer
hyperpigmentation associated with pregnancy, OCPs
question
Vitiligo pathogenesis
answer
autoimmune melanocyte destruction causes irregular areas of complete depigmentation
question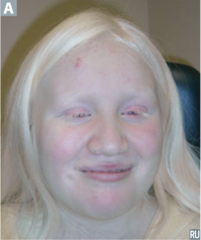
identify the pathology

answer
albinism
question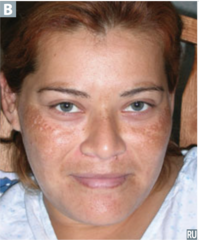
identify the pathology

answer
melasma
question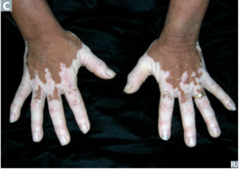
identify the pathology

answer
vitiligo
question
Acne vulgaris pathogenesis
answer
increased sebum, androgens causes abnormal keratinocyte desquamation, infection causes inflammation
question
Atopic dermatitis clinical presentation
answer
pruritic eruption, typically on flexor creases, face in infancy
question
Atopic dermatitis lab findings
answer
increased IgE
question
Atopic dermatitis disease associations
answer
asthma, allergies
question
Allergic contact dermatitis pathogenesis
answer
type IV hypersensitivity, occurs at site of contact
question
Melanocytic nevus alternate name
answer
mole
question
Melanocytic nevus pathogenesis
answer
benign melanocyte tumor, can transform to atypical mole, melanoma
question
Psoriasis clinical presentation
answer
papules/plaques with silver scale, common on knees, elbows, Auspitz sign
question
Psoriasis histologic morphology
answer
acanthosis w/ parakeratotic scaling, munro microabscesses, large stratum spinosum, small stratum granulosum
question
Psoriasis disease associations
answer
nail pitting, psoriatic arthritis
question
Rosacea pathogenesis
answer
inflammation facial skin disorder
question
Rosacea clinical presentation
answer
erythematous papules/pustules, no comedones, possible facial flushing with external stimuli
question
Seborrheic keratosis pathogenesis
answer
flat greasy pigmented squamous epithelial proliferation, keratin filled cysts, benign neoplasm
question
Leser-Trelat sign
answer
sudden appearance of multiple seborrheic keratoses, indicates underlying malignancy
question
Verrucae pathogenesis
answer
warts due to HPV
question
Verrucae clinical presentation
answer
soft, tan, cauliflower liek papules
question
Verrucae histologic morphology
answer
epidermal hyperplasia, hyperkeratosis, koilocytosis
question
Urticaria pathogenesis
answer
pruritic wheals due to mast cell degranulation
question
Urticaria histologic morphology
answer
superficial dermal edema, lymphatic channel dilation
question
identify the pathology
answer
Acne vulgaris
question
identify the pathology
answer
atopic dermatitis
question
identify the pathology
answer
atopic dermatitis
question
identify the pathology
answer
allergic contact dermatitis
question
identify the pathology
answer
allergic contact dermatitis
question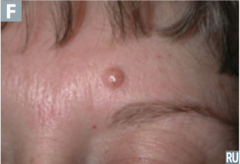
identify the pathology

answer
papular intradermal nevus
question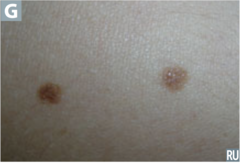
identify the pathology

answer
junctional nevus
question
Identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
papules/plaques w/ silver scale, psoriasis
question
Identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
auspitz sign, psoriasis
question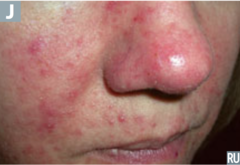
identiy the pathology

answer
rosacea
question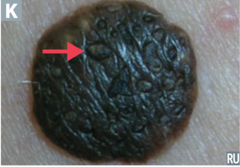
Identify the clinical finding and associated pathology

answer
horn cyst, seborrheic keratosis
question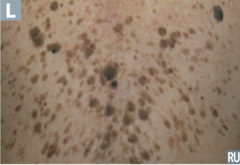
identify the pathology

answer
leser-trelat sign
question
identify the pathology
answer
verrucae
question
Identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
condyloma acuminatum, HPV
question
identify he pathology
answer
urticaria
question
identify the pathology
answer
bacillary angiomatosis
question
identify the pathology
answer
cherry angioma
question
identify the pathology
answer
cystic hygroma
question
identify the pathology
answer
glomus tumur
question
identify the pathology
answer
pyogenic granuloma
question
identify the pathology
answer
strawberry hemangioma
question
Angiosarcoma typical distribution
answer
head, neck, breast
question
Angiosarcoma risk factors
answer
elderly, sun exposure, radaiation, chronic postmastectomy lymphedema
question
Hepatic Angiosarcoma risk factors
answer
vinyl chloride, aresenic
question
Angiosarcoma typical behavior
answer
very aggressive, difficult to resect
question
Bacillary angiomatosis clinical presentation
answer
benign capillary skin papules
question
Bacillary angiomatosis causative agent
answer
B. henselae, only in AIDS
question
Bacillary angiomatosis histologic morphology
answer
neutrophilic infiltrate
question
Cherry hemangioma pathogenesis
answer
benign capillary hemangioma, does not regress
question
cystic hygroma pathogenesis
answer
cavernous lymphangioma of neck
question
cystic hygroma disease associations
answer
turner syndrome
question
glomus tumor clinical presentation
answer
benign painful, red blue tumor, commonly under fingernails
question
glomus tumor pathogenesis
answer
tumor of modified SMCs of thermoregulatory glomus body
question
Kaposi sarcoma causative agent
answer
HHV8 in HIV+ patients
question
Kaposi sarcoma pathogenesis
answer
endothelial malignancy of skin, mouth, GI, respiratory tract
question
Kaposi sarcoma histologic morphology
answer
lymphocytic infiltrate
question
Pyogenic granuloma pathogenesis
answer
polypoid lobulated capillary hemangioma, can ulcerate/bleed
question
Pyogenic granuloma risk factors
answer
trauma, pregnancy
question
Strawberry hemangioma pathogenesis
answer
benign capillary hemangioma of infancy
question
Strawberry hemangioma clinical course/behavior
answer
appears in first few weeks of life, grows rapidly, regresses spontaneously
question
Impetigo pathogenesis
answer
strep/staph superficial skin infection, highly contageous
question
Impetigo clinical presentation
answer
honey colored crust
question
Bullous impetigo characteristics
answer
similar to Impetigo + bullae, due to S. aureus
question
Erysipelas pathogenesis
answer
upper dermal/superficial lymphatics infection due to S. pyogenes
question
Erysipelas clinical presentation
answer
well defined demarcation between infected/normal skin
question
Cellulitis pathogenesis
answer
acute painful spreading infection of deeper dermis/SQ, due to strep/staph
question
Cellulitis risk factors
answer
skin break/trauma
question
Abscess pathogenesis
answer
collectin of walled of infection/pus within deeper skin layers
question
Abscess most common causative agent
answer
S. aureus
question
Necrotizing fasciitis pathogenesis
answer
deeper tissue injury causes S. pyogenes/anaerobic infection, produces bullae, purple color
question
Necrotizing fasciitis clinical presentation
answer
pain out of proportion to exam, crepitus due to gas production
question
Hairy leukoplakia clinical presentation
answer
irregular white painless plaques on lateral tongue, cannot be scraped off
question
Hairy leukoplakia pathogenesis
answer
EBV mediated in immunosuppressed patients
question
identify the pathology
answer
impetigo
question
identify the pathology
answer
bullous impetigo
question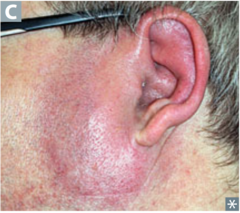
identify the pathology

answer
erysipelas
question
identify the pathology
answer
cellulitis
question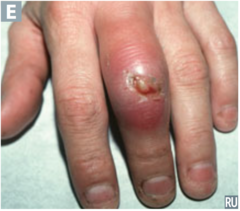
identify the pathology

answer
abscess
question
identify the pathology
answer
necrotizing fasciitis
question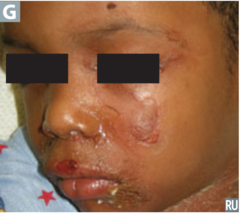
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology

answer
Nikolsky sign, staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
herpetic whitlow, HSV
question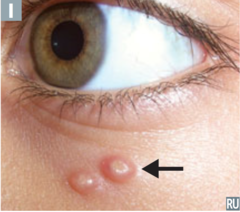
identify the pathology

answer
molluscum contagiosum
question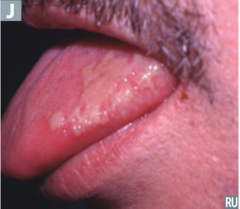
identify the pathology

answer
hairy leukoplakia
question
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome pathogenesis
answer
S. aureus exotoxin destroys keratinocyte attachment, causes skin sloughing
question
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome clinical presentation
answer
fever, generalized erythematous rash, upper epidermal sloughing, no scarring, + nikolsky sign
question
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome risk factors
answer
neonates, children, renal insufficiency
question
Pemphigus vulgaris pathogenesis
answer
type II hypersensitivity: anti-desmoglein IgG destroys intracellular desmosomes, acantholysis
question
Pemphigus vulgaris
answer
flaccid intraepidermal bullae, + nikolsky sign, may involve oral mucosa
question
Nikolsky sign
answer
epidermis separates upon manual skin stroking
question
Pemphigus vulgaris immunofluorescence findings
answer
antibodies around epidermal cells in reticular pattern
question
Bullous pemphigoid pathogenesis
answer
type II hypersensitivity: anti-hemidesmosome IgG detaches epidermis from basement membrane
question
Bullous pemphigoid clinical presentation
answer
tense blisters w/ eosinphils, spares oral mucosa
question
Bullous pemphigoid immunosluorescence findings
answer
linear pattern of antibodies at epidermal-dermal junction
question
dermatitis herpetiformis clinical presentation
answer
pruritic papules, vesicles, bullae
question
dermatitis herpetiformis disease associations
answer
celiac disease
question
dermatitis herpetiformis immunofluorescence findings
answer
IgA deposits at tips of dermal papillae
question
dermatitis herpetiformis treatment
answer
dapsone, gluten free diet
question
Erythema multiforme disease associations
answer
infections, (M. pneumoniae, HSV) drugs (sulfa, beta lactam, phenytoin), cancer, autoimmunity
question
Erythema multiforme clinical presentation
answer
multiple types of lesions
question
Stevens-Johnson syndrome clinical presentation (early)
answer
fever, bullae formation, necrosis, skin sloughing, involves >2 mucous membranes
question
Stevens-Johnson syndrome clinical presentation (late)
answer
targetoid skin lesions
question
Stevens-Johnson syndrome typical etiology
answer
drug adverse effect
question
toxic epidermal necrolysis
answer
more severe form of SJS
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
flaccid bullae, pemphigus vulgaris
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
reticular pattern, pemphigus vulgaris
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
tense blisters, bullous pemphigoid
question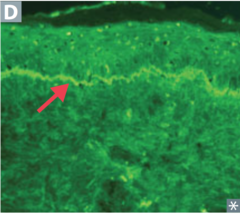
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology

answer
linear pattern, bullous pemphigoid
question
identify the pathology
answer
dermatitis herpetiformis
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
targetoid lesions, erythema multiforme
question
identify the pathology
answer
SJS involving mucous membranes
question
identify the pathology
answer
SJS involving mucous membranes
question
identify the pathology
answer
toxic epidermal necrolysis/SJS
question
identify the pathology
answer
toxic epidermal necrolysis/SJS
question
acanthosis nigricans pathogenesis
answer
epidermal hyperplasia causes symmetric skin thickening w/ hyperpigmentation
question
acanthosis nigricans typical distribution
answer
axilla, neck
question
acanthosis nigricans disease associations
answer
insulin resistance, visceral malignancy
question
Actinic keratosis pathogenesis
answer
premalignant lesions due to sun exposure
question
Actinic keratosis clinical presentation
answer
small rough erythematous/brown papules/plaques
question
Actinic keratosis complications
answer
squamous cell carcinoma risk
question
Erythema nodosum pathogenesis
answer
painful raised inflammatory lesions of SQ fat
question
Erythema nodosum disease associations
answer
Sarcoidosis, Cocci, histoplasma, TB, strep, leprosy, IBD
question
Lichen planus clinical presentation
answer
pruritic, purple, polygonal, planar papules
question
Lichen planus histologic morphology
answer
sawtooth lymphcytic infiltrate at dermal-epidermal junction
question
Lichen planus disease associations
answer
HCV
question
Pityriasis rosea clinical presentation
answer
herald patch followed by other scaly erythematous plaques, christmas tree distribution
question
Pityriasis rosea typical distrubiont
answer
trunk
question
Pityriasis rosea clinical course
answer
resolves in 6-8 weeks spontaneously
question
Sunburn pathogenesis
answer
acute cutaneous inflammatory reaction due to excess UV light
question
Sunburn complications
answer
skin cancer, impetigo
question
identify the pathology
answer
acanthosis nigricans
question
identify the pathology
answer
acanthosis nigricans
question
identify the pathology
answer
actinic keratosis
question
identify the pathology
answer
actinic keratosis
question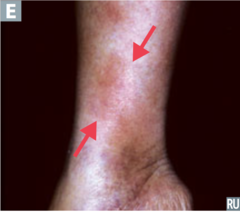
identify the pathology

answer
erythema nodosum
question
identify the pathology

answer
erythema nodosum
question
identify the pathology
answer
lichen planus
question
identify the pathology
answer
lichen planus
question
identify the pathology
answer
pityriasis rosacea
question
identify the pathology
answer
pityriasis rosacea
question
basal cell carcinoma typical distribution
answer
sun exposed areas, esp. face
question
basal cell carcinoma typical behavior
answer
locally invasive, rarely metastasizes
question
basal cell carcinoma clinical presentation
answer
waxy pink pearly nodules with telangiectasias, rolled borders, central crust/ulceration
question
basal cell carcinoma histologic morphology
answer
palisading nuclei
question
Squamous cell carcinoma risk factors
answer
excessive sunlight exposure, immunosuppression, chronicaly draining sinuses, arsenic exposure
question
Squamous cell carcinoma typical distribution
answer
face, lower lip, ears, hands
question
Squamous cell carcinoma typical behavior
answer
locally invasive, may spread to lymph nodes, rarely metastasizes
question
Squamous cell carcinoma clinical presentation
answer
ulcerative red lesions w/ scale
question
Squamous cell carcinoma histologic morphology
answer
keratin pearls
question
Keratoacanthoma characteristics
answer
squamous cell carcinoma variant, grows rapidly, then regresses spontaneously
question
Melanoma immunostaining characteristics
answer
S100
question
Melanoma risk factors
answer
sunlight, dysplastic nevi, light skin
question
Melanoma molecular pathogenesis
answer
BRAF mutation
question
Melanoma treatment
answer
excision, BRAF kinase inhibitors (vemurafenib)
question
identify the pathology
answer
basal cell carcinoma
question
identify the pathology
answer
ulcerated basal cell carcinoma
question
identify the pathology
answer
superficial BCC
question
identify the pathology
answer
BCC
question
identify the pathology
answer
squamous cell carcinoma
question
identify the pathology
answer
squamous cell carcinoma
question
identify the clinical finding and associated pathology
answer
squamous pearl, squamous cell carcinoma
question
identify the pathology
answer
keratoacanthoma
question
identify the pathology
answer
superficial spreading melanoma
question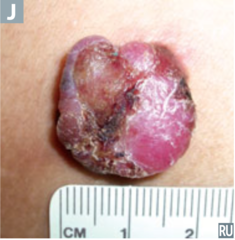
identify the pathology

answer
nodular melanoma
question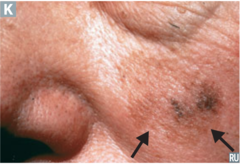
identify the pathology

answer
lentigo maligna (melanoma)
question
identify the pathology
answer
acral lentiginous melanoma



