Modern Chemistry Chapter 3 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
law of conservation of mass
answer
States that matter can be neither destroyed nor created during ordinary chemical reactions or physical changes
question
law of definite proportions
answer
The fact that a chemical compounds contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample or source of the compound
question
law of multiple proportions
answer
if two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers
question
atom
answer
the smallest particle of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element
question
nucleus
answer
very small region located near the center of an atom. made of protons and neutrons
question
Proton
answer
positively charged particle
question
neutron
answer
neutral particle
question
electron
answer
negatively charged particle
question
atomic number
answer
the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of an element
question
isotope
answer
atom of the same element with a different mass
question
mass number
answer
total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an isotope
question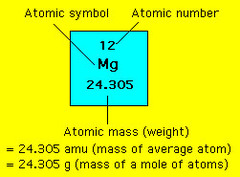
atomic mass unit

answer
exactly 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom
question
average atomic mass
answer
the weighted average of the atomic masses of naturally occurring isotopes of an element
question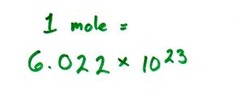
Avogadro's number
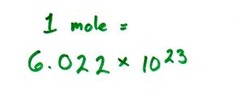
answer
6.022 x 10^23 The number of particles in exactly one mole of a pure substance
question
molar mass
answer
the mass of one mole of a pure substance
question
Dalton
answer
Early 1800's, chemist who was a pioneer in discovery of the atom. Thought atoms were indivisible.
question
Thompson
answer
English physicist accredited with the discovery and identification of the electron and isotopes.
question
Rutherford
answer
New Zealander physicist known as the Father of Nuclear Physics. Discovered the nucleus and radioactive substances.
question
Cathode Ray Tube Experiment
answer
This was JJ Thomson's experiment that led to the discovery of the electron and the development of the plum pudding model of the atom. showed cathode rays were composed of negatively charged particles.
question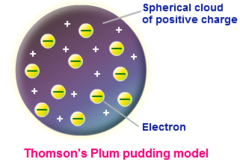
Plum Pudding Model

answer
model which Thomson thought electrons were randomly distributed within a positively charged cloud
question
Gold Foil Experiment
answer
This was Ernest Rutherford's experiment that led to the discovery of the nucleus as the small, dense, positively charged center of the atom and the development of the nuclear theory of the atom.
question
Nucleus
answer
contains the protons and neutrons of the atom
question
Milikan
answer
Used the oil drop experiment to determine the charge of an electron4red
question
Chadwick
answer
Discovered the neutron
question
alpha particle
answer
positively charged particles
question
ion
answer
A charged atom that has unequal numbers of electrons and protons
question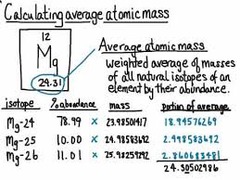
percent abundance

answer
the naturally occurring amount of a certain isotope of an element, out a of a 100
question
Avogadro
answer
scientist who worked with and determined the proportion of particles in 1 mole
question
relative abundance

answer
the naturally occurring amount of a certain isotope of an element, out a of 1.00
question
mol
answer
abbreviation for moles
question
Dalton's Atomic Theory
answer
All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged.
question
Modern Atomic Theory
answer
All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. A given element can have atoms with different masses; atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties. Atoms can be subdivided, but Law of Conservation of Mass holds. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged.
question
nuclear forces
answer
The short-range proton-neutron, proton- proton, and neutron-neutron forces that hold the nuclear particles together
question
Atomic Number
answer
the number of protons of each atom of that element.
question
Neutral atom
answer
# protons = # electrons Therefore, the atomic number is also equal to the number of electrons in a neutral atom.
question
Isotopes
answer
atoms of the same element that have different masses. all have the same number of protons and electrons, but different number of neutrons
question
Nuclide
answer
a general term for a specific isotope of an element.
question
The mass number
answer
is the total number of protons and neutrons that make up the nucleus of an isotope. A = #protons + #neutrons (under symbol)
question
Hyphen notation:
answer
The mass number is written with a hyphen after the name of the element. uranium-235
question
Average Atomic Mass
answer
is the weighted average of the atomic masses of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element. What is the atomic mass of chlorine if a naturally occurring sample contains 75.5% 35Cl and 24.5% 37Cl? 35 x (0.755) + 37 x (0.245) = 35.5 amu



