Massage therapy quiz 2 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Afferent nerves (AF-fer-ent)
answer
Sensory nerves that link sensory receptors with the central nervous system and transmit sensory information.
question
Autonomic nervous system (aw-toe-NOM-ik)
answer
A division of the peripheral nervous system composed of nerves that connect the central nervous system to the glands, heart, and smooth muscles to maintain the internal body environment.
question
Cranial nerves
answer
Twelve pairs of nerves that originate from the olfactory bulbs, thalamus, visual cortex, and brainstem. They transmit information to and from the sensory organs of the face and the muscles of the face, neck, and upper shoulders, as well as organs of the thorax and abdomen.
question
Dermatome (DER-mah-tohm)
answer
A cutaneous (skin) section supplied by a single spinal nerve. Efferent nerves (EF-fer-ent) Motor nerves that transmit motor impulses; they link the central nervous system to the effectors outside it.
question
Enteric nervous system (ENS)
answer
A subdivision of the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which directly controls the gastrointestinal system.
question
Free nerve endings
answer
Sensory receptors that detect itch and tickle sensations.
question
Kinesthesia (kin-uhs-THEE-zhuh)
answer
Sense of movement of body parts.
question
Mechanical receptors
answer
Sensory receptors that detect changes in pressure, movement, temperature, or other mechanical forces.
question
Mixed nerves
answer
Nerves that contain sensory and motor axons.
question
Myasthenia gravis (my-uhs-THEE-nee-uh)
answer
A disease that usually affects muscles in the face, lips, tongue, neck, and throat but can affect any muscle group.
question
Myotome (MY-o-tohm)
answer
A skeletal muscle or group of skeletal muscles that receives motor axons from a particular spinal nerve.
question
Neurovascular bundle
answer
A spinal nerve, artery, deep vein, and deep lymphatic vessel bound together by connective tissue, traveling the same pathway in the body.
question
Nerve
answer
A bundle of axons, dendrites, or both.
question
Nociceptors (no-se-SEP-tors)
answer
Sensory receptors that detect painful or intense stimuli. Parasympathetic nervous system The energy conservation and restorative system associated with what commonly is called the relaxation response.
question
Peripheral nervous system (pe-RIF-er-al)
answer
The system of somatic and autonomic neurons outside the central nervous system. The peripheral nervous system comprises the afferent (sensory) division and the efferent (motor) division.
question
Plexus (PLEK-sus)
answer
A network of intertwining nerves that innervates a particular region of the body.
question
Polio
answer
A viral infection, first of the intestines and then (for about 1% of exposed persons) of the anterior horn cells of the spinal cord.
question
Proprioceptors (pro-pree-o-SEP-tors)
answer
Sensory receptors that provide the body with information about position, movement, muscle tension, joint activity, and equilibrium.
question
Reflex
answer
An automatic, involuntary reaction to a stimulus.
question
Somatic nervous system (so-MA-tik)
answer
A system of nerves that keeps the body in balance with its external environment by transmitting impulses among the central nervous system, skeletal muscles, and skin.
question
Spinal nerves
answer
Thirty-one pairs of mixed nerves, originating in the spinal cord and emerging from the vertebral column; they are part of the peripheral nervous system.
question
Sympathetic nervous system
answer
The part of the autonomic nervous system that provides for most of the active function of the body; when the body is under stress, the sympathetic nervous system predominates with fight-or-flight responses.
question
Thermal receptors
answer
Sensory receptors that detect changes in temperature.
question
Epineurium connective tissue
answer
Surrounds the entire nerve•
question
Perineurium connective tissue
answer
Surrounds each fasciculus• Endoneurium : Surrounds and holds each nerve fiber
question
Endoneurium connective tissue
answer
Surrounds and holds each nerve fiber
question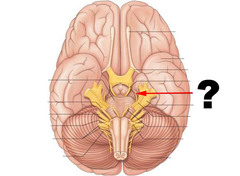
trochlear nerve

answer
IV are composed mainly of motor nerves, which begin in the midbrain. They innervate the superior oblique eye muscles. The few sensory neurons provide proprioceptive information about eye movement.
question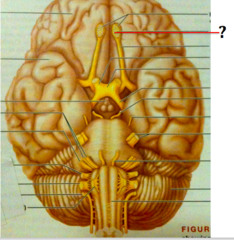
olfactory nerve

answer
I are sensory and transmit information about taste and smell from the nasal cavity to the cerebrum (into the olfactory bulb of the forem
question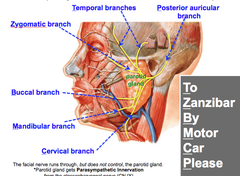
facial nerve

answer
VII have motor fibers that arise in the pons and innervate the muscles that produce facial expression and the glands that release tears and saliva. The sensory fibers carry information about taste to the cerebral cortex. Some of the fibers also relay proprioceptive information about the face and scalp.
question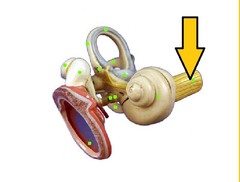
Vestibulocochlear nerve

answer
VIII are sensory and are divided into two branches. The vestibular branch begins in the semicircular canals of the ear and carries signals for equilibrium to the pons, medulla, and cerebellum. The cochlear branch arises in the organ of Corti and carries impulses for hearing to the pons and medulla.
question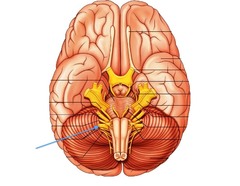
Vagus nerve

answer
X contain sensory and motor neurons. The motor fibers originate in the medulla and carry signals that control the muscles involved in swallowing and speaking. Other motor fibers terminate in the muscles of the digestive and respiratory tracts and in the heart. The sensory fibers arise from the same structures that the motor fibers innervate and carry information about sensations and proprioception of these organs.
question
Accessory nerve
answer
XII arise in the medulla and are primarily motor neurons for speaking, turning the head, and moving the shoulders. The few sensory neurons relay proprioceptive information from these muscles.
question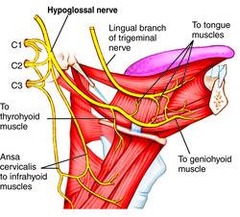
Hypoglossal nerve

answer
XII originate in the medulla and contain mostly motor neurons, which innervate the tongue and throat. A few sensory neurons carry proprioceptive information from the tongue.
question
Glossopharygeal nerve
answer
IX contain sensory and motor neurons. The sensory fibers extend to the medulla from the pharynx and the tongue; they are concerned primarily with taste. Another sensory fiber extends from the carotid sinus in the internal carotid artery and aids in the control of respiration and blood pressure. The motor neurons arise in the medulla and affect saliva production, swallowing, and the gag reflex.
question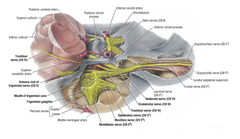
Trigeminal nerve

answer
V arise in the pons. The motor neurons innervate the muscles involved in chewing. The sensory neurons carry information about sensations and proprioception for the head, face, skin of the face, mucosal linings, eyelids, and tongue. The trigeminal nerves are the largest of the cranial nerves.
question
Optic nerve

answer
II are sensory and transmit information about clarity and field of vision from the retina to the midbrain of the cerebrum by way of the thalamus
question
Oculomotor nerve
answer
III are sensory and motor. The sensory portion transmits information about eye movement The motor portion originates in the midbrain and controls all external eye muscles (except the superior oblique and lateral rectus muscles) and pupil contraction and relaxation.
question
The abducens nerves
answer
VI arise in the pons. The motor neurons innervate the lateral rectus eye muscle (an eye abductor). The sensory neurons provide proprioceptive information about eye movement.
question
Brachial Plexus
answer
formed from nerves C5 to T1, is organized into three divisions: the superior, middle, and inferior trunks. These divisions supply the skin and muscles of the upper limbs
question
Lumbar Plexus
answer
The lumbar plexus is composed of nerves L1 to L4.
question
Sacral Plexus
answer
The sacral plexus is created from nerves L5 to S3.
question
neuroma,
answer
a nerve scar called a
question
Hyperesthesia
answer
(excessive sensation)
question
• Hypoesthesia
answer
(decreased sensation)
question
Paresthesia
answer
(numbness, tingling, burning sensation)
question
Anesthesia
answer
(loss of sensation)
question
Ansa cervicalis
answer
Hyoid muscles
question
Lesser occipital
answer
Skin behind and above the earGreater auricularSkin in front of, below, and over the ear and parotid glands
question
Transverse cervical
answer
Skin on the anterior portion of the neck
question
PhrenicDiaphragmSupraclavicular
answer
Skin on the shoulders and upper portion of the chest
question
Segmental branches
answer
Deep neck muscles, midscalenes, and levator scapula muscle
question
Dorsoscapular
answer
Superficial muscles of the scapulaL
question
Long thoracic
answer
Serratus anterior muscle
question
Subclavian
answer
Subclavius muscle
question
Suprascapular
answer
Infraspinatus and supraspinatus muscles
question
Musculocutaneous
answer
Biceps, brachialis, and coracobrachialis muscles; skin
question
Subscapular
answer
Subscapularis and teres major muscles
question
Median
answer
Forearm flexors and palmar surface of the skin of the thumb, index, and middle fingers
question
Thoracodorsal
answer
Latissimus dorsi muscle
question
Pectorals
answer
Pectoralis major and minor muscles
question
Axillary
answer
Deltoid and teres minor muscles and skin
question
Radial
answer
Triceps and forearm extensors, skin of the forearm and hand, and dorsal surface of the thumb, index, and middle fingers
question
Medial cutaneous
answer
Skin of the arm
question
Ulnar
answer
Muscles of the hand and skin of the ring and pinkie finger
question
Iliohypogastric
answer
Abdominal muscles and skin of the abdomen and buttocks
question
Ilioinguinal
answer
Abdominal muscles and skin of the external genitalia
question
Genitofemoral
answer
Skin of the external genitalia and inguinal region
question
Lateral femoral
answer
Skin of the thigh (except the medial cutaneous portion)
question
Femoral
answer
Hip flexors and extensors and skin of the medial and anterior thigh and medial leg and foot
question
Obturator
answer
Adductor muscles and skin of the medial thigh
question
Sacral plexus
answer
Created from nerves L5 to S3
question
Sciatic
answer
Leg and foot muscles; the skin of the foot, which divides into the tibial and peroneal nerves at the popliteal fossa
question
Gluteal
answer
Buttocks and tensor fasciae latae muscle
question
Nerves to hip
answer
Piriformis, quadratus femoris, rotators, obturator internus, and superior and inferior gemellus
question
Posterior femoral
answer
Skin of the buttocks, perineum, back, cutaneous of the thigh, and leg
question
Pudendal
answer
Muscles and skin of the perineum (may be considered in the coccygeal plexus)



