Macroeconomics – Pearson Etext Terms (Chap 1-4) – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Rewards or penalties for engaging in a particular activity.
answer
Incentives
question
The study of how people allocate their limited resources to satisfy their unlimited wants.
answer
Economics
question
Things used to produce goods and services to satisfy people's wants.

answer
Resources
question
What people would buy if their incomes were unlimited.
answer
Wants
question
The study of decision making undertaken by individuals or households and by firms.
answer
Microeconomics
question
The study of the behavior of the economy as a whole, including such economywide phenomena as changes in unemployment, the general price level, and national income.
answer
Macroeconomics
question
Total amounts or quantities. Aggregate demand, for example, is total planned expenditures throughout a nation.
answer
Aggregates
question
A society's institutional mechanism for determining the way in which scarce resources are uses to satisfy human desires.
answer
Economic system
question
The assumption that people do not intentionally make decisions that would leave them worse off.
answer
Rationality assumption
question
Economic system that is controlled by a central authority - a queen, dictator, a central government, or some other central authority. For instance, a government might decide that particular types of automobiles ought to be produced in certain numbers. They might issues specific rules for how to marshal resources to produce these vehicles or may establish ownership over those resources so that it can make all decisions directly.
answer
Centralized Command and Control
question
Under a pure price system, individuals and families own all of the scarce resources used in production. Choices about how to produce items are left to private parties.
answer
The Price System
question
The assumption that nothing changes except the factor or factors being studied.
answer
Ceteris paribus assumption
question
Relying on real-world data in evaluating the usefulness of a model.
answer
Empirical
question
An approach to the study of a consumer behavior that emphasizes psychological limitations and complications that potentially interfere with rational decision making.
answer
Behavioral economics
question
The hypothesis that people are nearly, but not fully, rational, so that they cannot examine every possible choice available to them but instead use simple rules of thumb to sort among the alternatives that happen to occur to them.
answer
Bounded rationality
question
Analysis that strictly limited to make either purely descriptive statements or scientific predictions. For example, "If A, then B." A statement of what is.
answer
Positive economics
question
Analysis involving value added judgments about economic policies; relates to whether outcomes are good or bad. A statement of what ought to be.
answer
Normative economics
question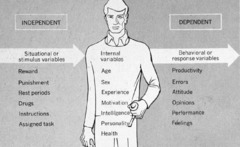
A variable whose value is determined independently of, or outside, the equation under study/

answer
Independent variable
question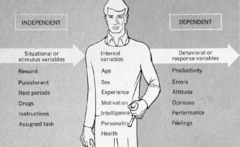
A variable whose value changes according to changes in the value of one or more independent variables.

answer
Dependent variable
question
A relationship between two variables that is positive, meaning that an increase in one variable is associated with an increase in the other and a decrease in one variable is associated with a decrease in the other.
answer
Direct relationship
question
A relationship between two variables that is negative, meaning that an increase in one variable is associated with a decrease in the other and a decrease in one variable is associated with an increase in the other.
answer
Inverse relationship
question
A line that can be divided into segments of equal length, each associated with a number.
answer
Number line
question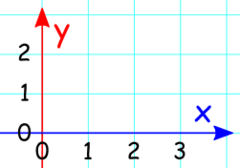
The vertical axis in a graph

answer
y axis
question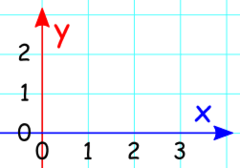
The horizontal axis in a graph

answer
x axis
question
The intersection of the y axis and the x axis in a graph
answer
Origin
question
The change in the y value divided by the corresponding change in the x value of a curve; the "incline" of the curve.
answer
Slope
question
A situation in which the ingredients for producing the things that people desire are insufficient to satisfy all wants at a zero price.
answer
Scarcity
question
Any activity that results in the conversion of resources into products that can be used in consumption.

answer
Production
question
The natural resources that are available from nature. Land as a resource includes location, original fertility and mineral deposits, topography, climate, water, and vegetation.
answer
Land
question
Productive contributions of humans who work.
answer
Labor
question
All manufactured resources, including building, equipment, machines, and improvements to land that are used for production.
answer
Physical capital
question
The accumulated training and education of workers.
answer
Human capital
question
The component of human resources that performs the functions of raising capital, organizing, managing, and assembling other factors of productions, making basic business policy decisions and taking risks.
answer
Enterpreneurship
question
All things from which individuals derive satisfaction or happiness.
answer
Goods
question
Goods that are scarce, for which the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied at a zero price.
answer
Economic goods
question
Mental or physical labor or assistance purchased by consumers. Examples are the assistance of physicians, lawyers, dentists, repair personnel. house cleaners, educators, retailers, and wholesalers; items purchased or used by consumers that do not have physical characteristics.
answer
Services
question
The highest-value, next-best alternative that must be sacrificed to obtain something or to satisfy a want.
answer
Opportunity cost
question
A curve representing all possible combinations of maximum outputs that could be produced, assuming a fixed amount of productive resources of a given quality.
answer
Production possibilities curve
question
The total pool of applied knowledge concerning how goods and services can be produced.
answer
Technology
question
The case in which a given level of inputs is used to produce the maximum output possible. Alternatively, the situation in which a given output is produced at minimum cost.
answer
Effciency
question
Any point below the production possibilities curve, at which the use of resources is not generating the maximum possible output.
answer
Inefficient point
question
The fact that the opportunity cost of additional units of a good generally increases as people attempt to produce more of that good. This accounts for the bowed-out shape of production possibilities curve.
answer
Law of increasing additional cost
question
The use of goods and services for personal satisfaction.
answer
Consupmtion
question
The organization of economic activity so that what each person (or region) consumes is not identical to what that person (or region) produces. An individual may specialize, for example, in law or medicine. A nation may specialize in the production of coffee, e-book readers, or digital cameras.
answer
Specialization
question
The ability to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost compared to other producers.
answer
Comparative advantage
question
The ability to produce more unites of a good or service using a given quantity of labor or resource inputs. Equivalently, the ability to produce the same quantity of a good or a service using fewer units of labor or resource inputs.
answer
Absolute advantage
question
The segregation of resources into different specific tasks. For instance, one automobile worker puts on bumper, another doors, and so on.
answer
Division of labor
question
All of the arrangements that individuals have for exchanging with one another. thus, for example, we can speak of the labor market, the automobile market, and the credit market.
answer
Market
question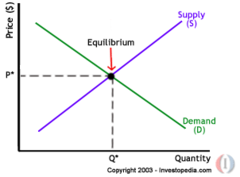
A schedule showing how much of a good or service people will purchase at any price during a specified time period, other things being constant.

answer
Demand
question
The observation that there is a negative, or inverse, relationship between the price of any good or service and the quantity of demanded, holding other factors constant.
answer
Law of demand
question
The money price of one commodity divided by the money price of another commodity, the number of units of one commodity that must be sacrifices to purchase one unit of another commodity.
answer
Relative price
question
The price expressed in today's dollars, also called the absolute or nominal price.
answer
Money price
question
A graphical representation of the demand schedule. It is a negatively sloped line showing the inverse relationship between the price and the quantity demanded (other things being equal).
answer
Demand curve
question
The demand of all consumers in the marketplace for a particular good or service. The summation at each price of the quantity demanded by each individual.
answer
Market demand
question
Determines of the relationship between price and quantity that are unchanged along a curve. Changes in these factors cause the curve to shift.
answer
Ceteris paribus conditions
question
Goods for which demand rises as income rises. Most goods are normal goods.
answer
Normal goods
question
Goods for which demand falls as income rises.
answer
Inferior goods
question
Two goods are complements when a change in the price of one causes an opposite shift in the demand for the other.
answer
Complements
question
A schedule showing the relationship between price and quantity suppolioe
answer
Supply
question
The observation that the higher the price of a good, the more of that good sellers will make available over a specified time period, other things being equal.
answer
Law of supply
question
The graphical representation of the supply schedule, a line (curve) showing the supply schedule, which generally slopes upward (has a positive slope), other things being equal.
answer
Supply curve
question
A negative tax - a payment to a producer from the government usually in the form of a cash grant per unit.
answer
Subsidy
question
The price that clears the market, at which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied; the price where the demand curve intersects the supply curve.
answer
Market clearing, or equilibrium price
question
The situation when quantity supplied equals quantity demanded at a particular price.
answer
Equilibrium
question
A situation in which quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied at a price below the market clearing price.
answer
Shortage
question
A situation in which quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded at a price above the market cleaning price.
answer
Surplus
question
An economic system in which relative prices are constantly changing to reflect changes in supply and demand for different commodities. The prices of those commodities are signals to everyone within the system as to what is relatively scarce and what is relatively abundant.
answer
Price system
question
An act of trading, done on an elective basis, in which both parties to the trade expect to be better off after the exchange.
answer
Voluntary exchange
question
All of the costs associated with exchange, including the informational costs of finding out the price and quality, service record, and durability of a product, plus the cost of contracting and enforcing that contract.

answer
Transaction costs
question
Government-mandated minimum or maximum prices that may be charged for goods and services.
answer
Price controls
question
A legal maximum price that may be charged for a particular good or service.
answer
Price ceiling
question
A legal minimum price below which a good or service may not be sold. Legal minimum wages are an example.
answer
Price floor
question
All methods used to ration scarce goods that are price-controlled. Whenever the price system is not allowed to work, non-price rationing devices will evolve to ration the affected goods and services.
answer
Nonprice rationing devices
question
A market in which goods are traded at prices above their legal maximum prices in which illegal goods are sold.

answer
Black market
question
Price ceilings on rents.
answer
Rent control
question
A wage floor, legislated by government, setting the lowest hourly rate that firms may legally pay workers.
answer
Minimum wage
question
A physical supply restriction on imports of a particular good, such as sugar. Foreign exporters are unable to sell in the United States more than the quantity specified in the import quota.
answer
Import quota
question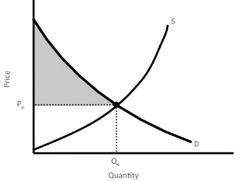
The difference between the total amount that consumers would have been willing to pay for an item and the total amount that they actually pay.

answer
Consumer surplus
question
The difference between the total amount that producers actually receive for an item and the total amount that they would have to be willing to accept for supplying that item.
answer
Producer surplus
question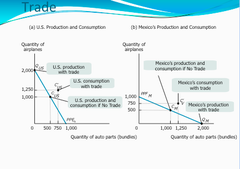
The sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus.

answer
Gains from trade



