MC: GABA-Sedatives – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What are the 2 types of *amino acids* that work as *neurotransmitters* & which is excitatory vs. inhibitory?
answer
1. GABA *INHIBITORY* 2. Glutamate *EXCITATORY*
question
How does *GABA* or * glutamate* elicit responses in the CNS?
answer
*GABA* or *glutamate* alter conductance of one or more ion channels causing hyper polarization, depolarization, etc.
question
What is *GABA* also know as?

answer
*gamma-Amino Butyric Acid*
question
What are the 3 *drug classes* considered *GABAa receptor modulators*?
answer
1. Barbiturates 2. Benzodiazepines 3. Benzodiazepine-Like drugs
question
What's the *problem* with *Barbiturates*
answer
*TOXICITY* limits their widespread use; they cause significant *CNS Depression, physical dependence ; tolerance*
question
List the *GABAa receptor modulators* from least safe to most safe according to Dr. Gupta:
answer
Barbiturates (LEAST SAFE) Benzodiazepines Benzodiazepine-Like Drugs (MOST SAFE)
question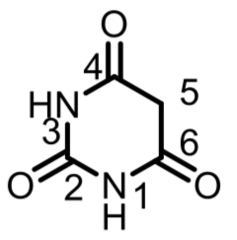
Clinically used *barbiturates* are mainly ________ ; what do they look like?

answer
*5,5-Disubstituted Barbituric Acids*
question
Depending on their structural features; What are 3 *therapeutic uses* of *barbiturates*?
answer
1. Sedatives/Hypnotics 2. Antiepileptics 3. Anesthetics
question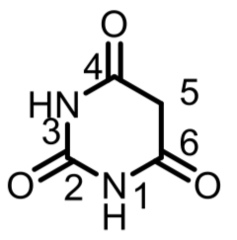
Are *barbiturates* acidic or basic?

answer
Weakly *ACIDIC*
question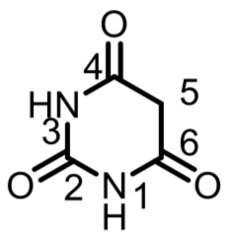
Which part of the *barbiturate* structure is important ; why?

answer
*5-Position* It will determine if a barbiturate has sedative/hypnotic action or not
question
What 2 substitution options must *5-position* barbiturates have?
answer
1. Dialkyl 2. ARYLalkyl
question
How many carbons on *each* substitution must *barbiturates* have?
answer
There are 2 substitutions: R1 and R2 on 5-position *EACH* must have *between 2-7 Carbons*
question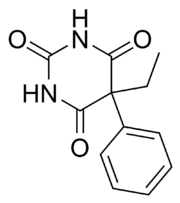
What happens when a *barbiturate* has a *PHENYL* group on its *5-position* ; what is the example?

answer
*PHENYL* group on 5-position indicates *ANTIEPILEPTIC ACTION* 1. Phenobarbital 2. Mephobarbital
question
What 2 things does *HIGH lipophilicity* in barbiturates lead to?
answer
HIGH lipophilicity 1. *RAPID onset of action* allowing rapid distribution into CNS 2. *SHORT duration of action* since compounds rapidly distribute into lipoid tissue
question
What 2 things does *.L.OW lipophilicity* in barbiturates lead to?
answer
1. *.L.*ong DOA: 4-12 hours 2. sl.*OW* onset of action LOW - L = *L*ong DOA OW = sl*OW* OOA
question
How many *carbons* do *LOW lipophilicity* barbiturates have ; what should be noted about *benzene rings*??
answer
LOW lipophilicity has ;5 Carbons *Smallest total number of carbon atoms* *BENZENE Ring*: equivalent to 3 to 4 carbons
question
What are the 4 *barbiturates* that have *LOW lipophilicity*?
answer
1. Barbital 2. Metharbital 3. Phenobarbital 4. Mephobarbital
question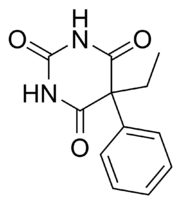
Which 2 *barbiturates* have the *benzene* ring in the *5-position*?

answer
1. Phenobarbital 2. Mephobarbital *Note:* Having the BENZENE ring gives them *antiepiliptic* indications
question
What 2 things does *INTERMEDIATE lipophilicity* in barbiturates lead to?
answer
1. *SHORT* DOA: 2-4hours 2. *INTERMEDIATE* Onset of Action
question
What are the 8 *barbiturates* that are *INTERMEDIATE Lipophilicity* ; what should be noted about their use?
answer
1. Pentobarbital 2. Butethal 3. Burabarbital 4. Amobarbital 5. Aprobarbital 6. Talbutal 7. Secobarbital 8. Hexobarbital *Not popular - have a lot of toxicity, physical dependence, etc.*
question
How many *carbons* do *INTERMEDIATE lipophilic* barbiturates have?
answer
INTERMEDIATE lipophilic barbiturates have 6 to 8 carbons at the 5-position
question
What 2 things do *barbiturates* that have *HIGH lipophilicity* lead to?
answer
1. *ULTRA SHORT DOA:* 1 hour 2. *RAPID* Onset of Action
question
What 2 features can *barbiturates* with *HIGH lipophilicity* have at the 5-position?
answer
All have *7-9 Carbons* ; Either *2-position Thiol* or *N-Methyl substitution*
question
What are the 3 *barbiturates* that are *HIGH lipophilicity*?
answer
1. Thiopental 2. Thiamylal 3. Methohexital *Note:* These are anesthetics
question
Which 2 *Phase 1* barbiturate metabolism pathways lead to *INACTIVE* metabolites ; which is MAJOR?
answer
1. Oxidation *MAJOR* 2. Ring Cleavage both lead to *INACTIVE* metabolites in Barbiturates
question
Which 2 *Phase 1* barbiturate metabolism pathways lead to *ACTIVE* metabolites?
answer
1. Desulfuration 2. N-demethylation lead to *ACTIVE* metabolites
question
What is the name of the *metabolite* that forms from *Desulfuration*?
answer
*Oxobarbiturates* form from *Desulfuration* ; is *ACTIVE*
question
What happens in *Phase 2* barbiturate metabolism?
answer
*Glucuronide conjugates*
question
What are the 2 classes of *benzodiazepines* ; what are the suffix of each?
answer
1. Class A *-AzePAM* 2. Class B *-AzoLAM*
question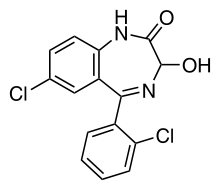
What is the general structure of Class A/*-Azepam*?

answer
Note - This is a picture of *lorazepam*
question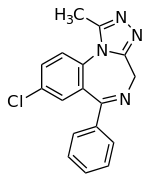
What is the general structure of Class B/*-Azolam* & what should be noted?

answer
Note the top right *additional ring* Gives *-Azolam* HIGH AFFINITY FOR RECEPTOR
question
In the *additional ring* for Class B/*-Azolam's* what are the 2 different types of rings they can have?
answer
1. Triazole 2. Imidazole
question
Do *benzodiazepines* have a high or low *Log-P* & what does that do for their *physicochemical properties*?
answer
*HIGH* Log-P it will lead to BZD's being *COMPLETELY ABSORBED* after oral administration & *RAPIDLY DISTRIBUTED* to the brain & other highly perfused organs
question
What are the 5 *metabolism processes* that *benzodiazepines* are able to do?
answer
1. 3-Hydroxylation 2. N-Dealkylation 3. 3-OH Hydroxylation 4. Decarboxylation 5. Glucoronide Conjugation
question
What is the ONLY *metabolism process* with *benzodiazepines* that leads to *INACTIVE metabolites*?
answer
*Glucoronide Conjugation* leads to an *INACTIVE* Oxazepam glucuronide metabolite
question
slide 24 ****
answer
******
question
Does *TriazoLAM* have a longer or shorter half-life & what does this mean for the therapeutic uses?
answer
TriazoLAM has *SHORTER* half-life So it can *Reduce Hangover Problem* & can be used as *Sleep Inducer*
question
What are the 3 *benzodiazepines* that have a *3-OH*?
answer
1. Oxazepam 2. Temazepam 3. Lorazepam
question
What does having a *3-OH* lead to for *duration of action* & why?
answer
3-OH for BZD's leads to *SHORT* Duration of Action because; its only metabolite will be the INACTIVE glucuronide
question
If a *benzodiazepine* has a *3-OH* with a SHORT duration of action; what happens with insomnia patients?
answer
Can lead to *Rebound Insomnia* *Note:* Oxazepam, Temazepam & Lorazepam have 3-OH therefore can all cause rebound insomnia
question
What are the 3 *benzodiazepines* that have *N-Alkyl group WITHOUT 3-OH*?
answer
1. Flurazepam 2. Diazepam 3. Halazepam
question
What does having an *N-Alkyl group WITHOUT 3-OH* lead to & why?
answer
N-Alkyl group WITHOUT 3-OH leads to LONG half-lives because- they have ACTIVE metabolites
question
Because of the *N-Alkyl group WITHOUT 3-OH* what happens to patients with *insomnia*?
answer
they will NOT get rebound insomnia on withdrawal *Note:* Flurazepam, Diazepam & Halazepam
question
What are the 3 *BZD-Like* Drugs?
answer
1. Zaleplon 2. Eszopiclone 3. Zolpidem
question
Are *BZD-Like* drugs lipophilic or hydrophilic & how does that help with their therapeutic effects?
answer
*VERY LIPOPHILIC* Helps to facilitate *RAPID absorption* - so FASTER onset of action
question
Do *BZD-Like* drugs have slow or fast *elimination* & how does that help with their therapeutic effects?
answer
*RAPID Elimination* so patients experience *LESS* residual side effects
question
Is *zaleplon* a sleep maintainer or inducer?
answer
Zaleplon is a Sleep *INDUCER*
question
Is *eszopiclone* a sleep maintainer or inducer?
answer
Eszopiclone is a Sleep *MAINTAINER*
question
Is *zolpidem* a sleep maintainer or inducer?
answer
Zolpidem is a Sleep *MAINTAINER*
question
What are the 2 different *Melatonin receptors* & how do each work in sleep processes?
answer
1. MT1 *Induces Sleep* 2. MT2 *Maintains Sleep/wake cycle Regulation of circadian Rhythms*
question
What are the 2 *Melatonin Receptor Agonists* & which receptor are they more selective for?
answer
1. Ramelteon *MT1* 2. Tasimelteon *MT2*
question
How does *ramelteon* work?
answer
Ramelteon Effective in *INITIATING SLEEP* does NOT maintain sleep *Note:* Ramelteon is a MT1
question
How does *tasimelteon* work?
answer
Tasimelteon Treats non-24 hour sleep wake disorder in BLIND patients *Note:* Tasimelteon isa MT2
question
What are 3 things to note about *Melatonin Receptor Agonists*?
answer
1. *NOT* GABAergic 2. Not Controlled substance 3. NO Abuse potential *Ramelteon & Tasimelteon*
question
What is the *new agent* just approved last year & what kind of drug is it?
answer
*Suvorexant* Orexin Receptor Antagonist
question
What does *suvorexant* help with?
answer
Helps treat difficulty in falling & staying asleep
question
What is the *mechanism of action* with *suvorexant*?
answer
Blocks the binding of wake-promoting neuropeptides orexin A or orexin B to receptors OX1R & OX2R



