Jarvis Ch. 17 Breasts & Lymphatics – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
breasts are located where anatomically?
answer
between 2nd and 6th ribs from sternum to midaxillary line
question
montgomery glands
answer
sebaceous glands that line areola that secrete protective lipids during lactation
question
breasts are made up of what?
answer
glandular tissue fibrous tissue (suspensatory ligaments) adipose tissue (makes up most of the breasts)
question
glandular tissue
answer
contains 15-20 lobules that contain alveoli clusters which produce milk & empty into lactiferous duct
question
coopers ligaments
answer
suspensatory ligaments that support breasts
question
axillary tail of Spence
answer
cone-shaped breast tissue that projects up into the axilla, close to pectoral group of axillary lymph nodes
question
location of most breast tumors
answer
upper outer quadrant
question
most breast lymphatics drain where?
answer
into the ipsilateral (same side) axillary nodes
question
4 groups of axillary nodes
answer
-central axillary nodes (receive lymph from other three groups) -pectoral -subscapular -lateral (see p. 387)
question
supernumerary nipple
answer
extra nipple
question
breasts at birth
answer
only structures present are lactiferous ducts & nipples, no alveoli
question
breasts in adolescence
answer
estrogen stimulates changes (enlargement with fat deposits, duct system) b/t 8-10 years; accompanied by temporary asymmetry, tenderness Note: slight asymmetry is normal in adulthood & left breast usually slightly larger
question
5 stages of breast development; Tanner stages
answer
p. 388 1. Preadolescent stage: only small elevated nipple 2. Breast bud stage: small mound of breast and nipple develops; areola widens 3. Breast & areola enlarge; nipple flush with breast surface 4. Areola & nipple form secondary mound over breast 5. Mature breast: only nipple protrudes, areola flush with breast contour but may continue as secondary mound in some women
question
breast changes during pregnancy
answer
-beginning 2nd month, a common early sign of pregnancy -expansion of ductal system & supporting fatty tissue & development of true secretory alveoli -breasts enlarge & feel more nodular, nipples enlarge & darken & become erect -areola become darker brown as pregnancy progresses (brown color fades after lactation but normal color never returns :( ) -prominent veins visible -colostrum - month 4 (thick, yellow fluid=milk precursor; rich in antibodies; produced 1st few days after delivery)
question
breast changes in older adult
answer
-after menopause ovarian secretion of estrogen & progesterone decreases --> glandular tissue atrophy & fibrous connective tissue growth; drooping, flattening; atrophy makes lumps & structures more palpable & granular; nipple feels firm & stringy & may be retracted or pulled outward -thickening of inframammary ridge at lower breast normal -at greater risk for developing breast cancer b/c of age --> annual CBE important
question
male breasts
answer
-disk of undeveloped tissue underlying nipple -temporary gynechomastia during adolescence is normal & may reappear during older adulthood with decrease in testosterone
question
Breast cancer
answer
we all have BRCA 1 & 2 genes, but mutations to these genes greatly increases risk of breast & ovarian cancer
question
Mastalgia
answer
occurs with trauma, inflammation, infection, benign breast disease
question
Galactorrhea
answer
some medications may cause clear nipple discharge (oral contraceptives, diuretics, steroids, etc.)
question
Eczema on breast
answer
usually starts at areola & moves to nipple unless breast-feeding related
question
Advantages of breastfeeding for 6 months
answer
provides perfect food & antibodies for baby, decreases risk of ear infections, promotes bonding, provides relaxation, protective against breast cancer
question
Breast cancer risk factors
answer
Age Biopsy confirmed hyperplasia BRCA1/2 mutations (genetically inherited) lobular carcinoma in situ mammographically dense breasts hx early onset (<40 years) breast cancer 2 x 1st degree relatives with breast cancer etc. on p. 393
question
sudden unilateral increase in breast size indicates
answer
inflammation or new growth
question
breast abnormals
answer
hyperpigmentation redness/heat with inflammation unilateral dilated superficial veins in nonpregnant women edema
question
nipple abnormals
answer
deviation in pointing recent nipple retraction signifies acquired disease discharge may be abnormal supernumerary nipple (extra nipple)
question
how to screen for retraction
answer
-have woman lift arms slowly over head -->normal both breasts move up symmetrically; abnormal lag in movement of one breasts (caused by fibrosis/neoplasm) indicating retraction -have woman put hands on hips and push palms together --> normal slight lifting; abnormal dimpling or pucker which indicates retraction -have woman with large breasts lean forward to note symmetric free forward movement of breasts; abnormal fixation to chest wall indicates retraction
question
axillae abnormals
answer
nodes that are palpable (normally they're not) indicate local infection of breast, arm, hand or wrist or breast cancer metastasis
question
BREAST acronym
answer
lists physical signs associated with more advanced cancer: -breast mass -retraction -edema -axillary mass -scaly nipple -tender breast
question
BSE technique
answer
lie down, press 3 fingers in circular motion using 3 levels of pressure, follow up and down pattern; then sit up, examine underarm with arm raised; then inspect for surface changes with hands pushed on hips, shoulders hunched *for male, inspect & palpate for lumps & swelling (Should feel even with no nodules)
question
Best time to do BSE
answer
right after menstrual period; if postmenopausal, anytime that's easy to remember
question
male breast cancer
answer
rare (1% of breast cancers); presents with painless, firm, retroareolar lump; nipple discharge rare but strongly associated with cancer, also rarely but notable nipple discharge, ulceration, retraction, axillary lymphadenopathy
question
gynechomasia
answer
benign growth of male breast tissue when estrogen > testosterone; feels like smooth, firm, movable disk; normally occurs in 50% of 13-14 year old boys; occurs with use of anabolic steroids, some medication, cirrhosis, Cushing's/hyperthyroid, etc. (that is abnormal); may also occur in older men
question
normal neonate breasts
answer
may be enlarged & visible from maternal estrogen & secrete clear white fluid (witch's milk) - resolves in days-weeks
question
normal child breasts
answer
nipples symmetric, just lateral to midclavicular line b/t 4th & 5th ribs; nipple flat, areola darker
question
premature thelarche
answer
early breast development with no other hormone dependent signs (pubic hair, menses)
question
normal adolescent breasts
answer
breast development begins 8-10 years old; expect asymmetry during growth; growth begins earlier in hispanic & african american girls; with maturing adolescents you assess the same way you would with an adult by palpating; can be difficult to differentiate adipose tissue from breasts esp. if BMI higher
question
precocious puberty
answer
puberty before 8 years old; normal but aso occurs with thyroid dysfunction, stilbestrol ingestion, ovarian or adrenal tumor
question
delayed development
answer
occurs with hormone failure, anorexia nervosa, severe malnutrition
question
breast masses in adolescents
answer
almost always benign fibroadenoma
question
lactating woman
answer
colostrum changes to milk production on 3rd postpartum day; at this time, breasts become engorged, enlarged, red, shiny, warm, hard - must breastfeed to drain & stimulate milk production; nipple soreness = normal around 20th nursing & disappears rapidly
question
one section of breast surface that appears red & tender in breastfeeding woman indicates what?
answer
plugged duct
question
Dimpling
answer
shallow dimple that is a sign of skin retraction; cancer causes fibrosis --> contracts suspensatory ligaments --> dimple
question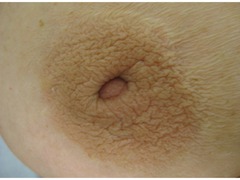
nipple retraction

answer
flatter & broader like an underlying crater; recent retraction suggests cancer, which causes fibrosis & duct system pulls nipple inward
question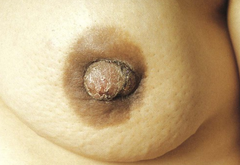
edema (peau d'orange)

answer
lymphatic obstruction --> edema, thickened skin & exaggerated hair follicles/pigskin/orange peel look
question
fixation of breast
answer
asymmetry, distortion or decreased mobility with elevated arm maneuver. As cancer becomes invasive, the fibrosis fixes the breast to the underlying pectoral muscles. The fixated breast is held against the chest wall. p. 407
question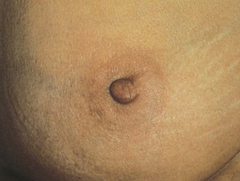
deviation in nipple pointing

answer
underlying cancer that causes fibrosis in mammary ducts, which pulls nipple angle towards it; nipple tilts laterally
question
benign (fibrocystic) breast disease
answer
-multiple benign tender masses that occur with numerous symptoms & physical findings: -swelling, tenderness (cyclic discomfort) -mastalgia (severe pain, both cyclic & noncyclic) - may or may not have pain -bilateral nodularity (nodules are firm, regular, mobile, well demarcated, rubbery) -dominant lumps -nipple discharge -infections & inflammations -no skin retraction -mobile (see chart p. 409)
question
cancer
answer
-solitary, unilateral, nontender mass -firm to stony hard, fixed to underlying tissues or skin as cancer becomes more invasive -irregular, poorly defined borders, star-shaped -most commonly found in upper outer quadrant & usually with skin retraction -occurs in 30-80 year olds, risk increases after 50 years -nonmobile/fixed (see chart p. 409)
question
fibroadenoma
answer
-benign tumor, most commonly self-detected in late adolescence -solitary nontender mass that is solid, firm, rubbery, elastic -round, oval, or lobulated -very mobile, slippery -diagnose by triple test (palpate, ultrasound, biopsy) -no skin retraction (see chart p. 409)
question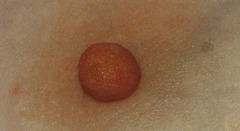
mammary duct ectasia

answer
pastelke matter in subareolar ducts produces sticky, purulent discharge that may be white, gray, brown, green, bloody. Caused by stagnation of cellular debris & secretions in the ducts leading to obstruction, inflammation, infection. Occurs in menopause. Itching, pain around nipple. Ducts are palpable as rubbery, twisted tubules under areola. Not malignant but pt will need biopsy.
question
intraductal papilloma
answer
discrete benign tumors tahtarise in single or multiple papillary ducts; may have srous or serousanguineous discharge. Often there's a palpable nodule underlying duct. Occurs in women 40-60. Most are benign. Requires biopsy. (photo on p. 408 - looks like black streak coming off of nipple)
question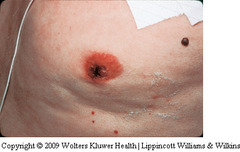
carcinoma nipple

answer
unilateral bloody nipple discharge from a single duct, but no palpable lump associated with discharge; must do imaging to see if there's a mass.
question
paget disease (intraductal carcinoma)
answer
early lesion has unilateral clear, yellow discharge with dry scaling crusts, friable nipple apex. spreads outward to areola with erythematous halo on areola & crusted eczematous, retracted nipple (photo p. 410)
question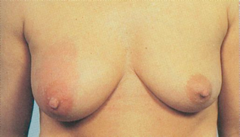
mastitis

answer
uncommon, inflammatory mass (red, swollen, very hot, hard) before abscess formation; usually in a single quadrant. Accompanied by headache, fever, chills, sweating, increased pulse, flulike symptoms. May occur 1st 4 months of lactation from infection from stasis of plugged duct. Treat with antibiotics, rest, frequent nursing to keep breast as empty as possible. Usually resolves 2-3 days.
question
breast abscess
answer
rare complication of generalized infection (i.e. mastitis) if untreated. a pocket of pus that feels hard, looks, red & is quite tender (p. 410 photo). Pt may continue to nurse. Needs antibiotics, drainage.
question
plugged duct
answer
occurs when milk not removed completely because of poor latching, ineffective suckling, infrequent nursing, or switching to second breast too soon. There is a tender red, warm lump. No infection. Must keep nursing to keep breast as empty as possible. Usually resolves in a day or so.



